SPRUJC6A December 2024 – July 2025 AM2752-Q1 , AM2754-Q1
- 1
- Read This First
-
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Overview
- 1.2 Module Allocation and Instances within Device Domains
- 1.3 Functional Block Diagram
- 1.4
Device MAIN Domain
- 1.4.1 Audio Asynchronous Sample Rate Converter
- 1.4.2 Analog-to-Digital Converter
- 1.4.3 Audio Tracking Logic
- 1.4.4 DSP C7x
- 1.4.5 3-port Gigabit Ethernet Switch (CPSW3G)
- 1.4.6 Dual Clock Comparator
- 1.4.7 Data Movement Subsystem (DMSS)
- 1.4.8 Enhanced Capture Module (ECAP)
- 1.4.9 Enhanced Pulse-Width Modulation Module (EPWM)
- 1.4.10 Error Signaling Module (ESM)
- 1.4.11 Flash Subsystem (FSS) Peripheral
- 1.4.12 General Purpose Input/Output Interface (GPIO)
- 1.4.13 Inter-Integrated Circuit Interface (I2C)
- 1.4.14 Dual-Core Arm Cortex-R5F Processor (R5FSS)
- 1.4.15 Mailbox (MAILBOX)
- 1.4.16 Controller Area Network (MCAN)
- 1.4.17 Multi-Channel Audio Serial Port
- 1.4.18 Cyclic Redundancy Check
- 1.4.19 Multi-Media Card/Secure Digital Interface (MMCSD)
- 1.4.20 Windowed Watchdog Timer/Real Time Interrupt
- 1.4.21 Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI)
- 1.4.22 Spinlock (SPINLOCK)
- 1.4.23 Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (UART)
- 1.4.24 Universal Serial Bus (USB) Subsystem 2.0
- 1.4.25 TIMER
- 1.5 Device Top Level Domain
- 1.6 Device WKUP Domain
- 1.7 Device Identification
- 2 Memory Map
- 3 Interconnect
-
4 Module Integration
- 4.1 Integration Overview
- 4.2 Processors and Accelerators
- 4.3 Device Configuration
- 4.4 Interprocessor Communication
- 4.5 Interrupts
- 4.6 Data Movement Architecture
- 4.7 Audio
- 4.8 General Connectivity
- 4.9 High-speed Serial Interfaces
- 4.10 Memory Interfaces
- 4.11 Industrial and Control Interfaces
- 4.12 Timer Modules
- 4.13 Internal Diagnostic Modules
- 4.14 On-Chip Debug
-
5 Initialization
- 5.1 Initialization Overview
- 5.2 Boot Process
- 5.3 BOOTMODE Pin Mapping
- 5.4 Boot Modes
- 5.5 PLL Configuration
- 5.6 Boot Parameter Tables
- 5.7 Boot Image Format
- 5.8 Boot Memory Maps
-
6 Device Configuration
- 6.1 Control Module (CTRLMMR)
- 6.2 Power
- 6.3
Reset
- 6.3.1 Overview
- 6.3.2 Reset Sources
- 6.3.3 Reset Status
- 6.3.4 Reset Controls
- 6.3.5 Reset Details
- 6.4 Clocking
- 6.5
PLLs
- 6.5.1 MAIN Domain PLLs Overview
- 6.5.2 Top Level Domain PLL Overview
- 6.5.3 PLL Reference Clocks
- 6.5.4 Generic PLL Overview
- 6.5.5 PLLs Device-Specific Information
- 6.5.6 PLL Controller (PLLCTRL)
- 6.5.7 PLL, PLLCTRL, and HSDIV Controllers Programming Guide
-
7 Processors and Accelerators
- 7.1
Dual-R5F MCU Subsystem
- 7.1.1 R5FSS Overview
- 7.1.2
R5FSS Functional Description
- 7.1.2.1 R5FSS Block Diagram
- 7.1.2.2 R5FSS Cortex-R5F Core
- 7.1.2.3 R5FSS Interfaces
- 7.1.2.4 R5FSS Power, Clocking and Reset
- 7.1.2.5 R5FSS Lockstep Error Detection Logic
- 7.1.2.6 R5FSS Vectored Interrupt Manager (VIM)
- 7.1.2.7 R5FSS Region Address Translation (RAT)
- 7.1.2.8 R5FSS ECC Support
- 7.1.2.9 R5FSS Memory View
- 7.1.2.10 R5FSS Interrupts
- 7.1.2.11 R5FSS Debug and Trace
- 7.1.2.12 R5FSS Boot Options
- 7.1.2.13 R5FSS Core Memory ECC Events
- 7.2
DSP Processing (C7x256v)
- 7.2.1 C7x Functional Description
- 7.1
Dual-R5F MCU Subsystem
-
8 Inter-processor Communication Scheme (IPC)
- 8.1 IPC Overview
- 8.2 Mailbox
- 8.3 Spinlock
- 8.4 Secure Proxy (SEC_PROXY)
- 9 Memory Controllers
- 10Interrupts
-
11Data Movement Architecture
- 11.1
Data Movement Architecture Overview
- 11.1.1
Overview
- 11.1.1.1 Ring Accelerator (RINGACC)
- 11.1.1.2 Secure Proxy (SEC_PROXY)
- 11.1.1.3 Interrupt Aggregator (INTAGGR)
- 11.1.1.4
Packet DMA (PKTDMA)
- 11.1.1.4.1
PKTDMA Submodule Descriptions
- 11.1.1.4.1.1 Bus Interface Unit
- 11.1.1.4.1.2 Config CR
- 11.1.1.4.1.3 Configuration Registers
- 11.1.1.4.1.4 Tx Packet DMA Unit
- 11.1.1.4.1.5 Tx Packet Coherency Unit
- 11.1.1.4.1.6 Tx Per Channel Buffers
- 11.1.1.4.1.7 Rx Per Channel Buffers
- 11.1.1.4.1.8 Rx Packet DMA Unit
- 11.1.1.4.1.9 Rx Packet Coherency Unit
- 11.1.1.4.1.10 Event Handler
- 11.1.1.4.2 Channel Classes
- 11.1.1.4.1
PKTDMA Submodule Descriptions
- 11.1.1.5
Block Copy DMA (BCDMA)
- 11.1.1.5.1
BCDMA Submodule Descriptions
- 11.1.1.5.1.1 Bus Interface Unit
- 11.1.1.5.1.2 Config CR
- 11.1.1.5.1.3 Configuration Registers
- 11.1.1.5.1.4 Read Unit(s)
- 11.1.1.5.1.5 TR Coherency Unit
- 11.1.1.5.1.6 Per-Copy-Channel Buffers
- 11.1.1.5.1.7 Tx Per-Split-Channel Buffers
- 11.1.1.5.1.8 Rx Per-Split-Channel Buffers
- 11.1.1.5.1.9 Write Unit(s)
- 11.1.1.5.1.10 Event Coherency Unit
- 11.1.1.5.1.11 Event Handler
- 11.1.1.5.2 Channel Classes
- 11.1.1.5.1
BCDMA Submodule Descriptions
- 11.1.2 Definition of Terms
- 11.1.3
DMSS Hardware/Software Interface
- 11.1.3.1 Data Buffers
- 11.1.3.2 Descriptors
- 11.1.3.3
Transfer Request Record
- 11.1.3.3.1 Overview
- 11.1.3.3.2 Addressing Algorithm
- 11.1.3.3.3 Transfer Request Formats
- 11.1.3.3.4 Flags Field Definition
- 11.1.3.3.5
TR Address and Size Attributes
- 11.1.3.3.5.1 ICNT0
- 11.1.3.3.5.2 ICNT1
- 11.1.3.3.5.3 ADDR
- 11.1.3.3.5.4 DIM1
- 11.1.3.3.5.5 ICNT2
- 11.1.3.3.5.6 ICNT3
- 11.1.3.3.5.7 DIM2
- 11.1.3.3.5.8 DIM3
- 11.1.3.3.5.9 DDIM1
- 11.1.3.3.5.10 DADDR
- 11.1.3.3.5.11 DDIM2
- 11.1.3.3.5.12 DDIM3
- 11.1.3.3.5.13 DICNT0
- 11.1.3.3.5.14 DICNT1
- 11.1.3.3.5.15 DICNT2
- 11.1.3.3.5.16 DICNT3
- 11.1.3.4 Transfer Response Record
- 11.1.3.5 Channels
- 11.1.3.6 Flows
- 11.1.3.7 Queues
- 11.1.4
Operational Description
- 11.1.4.1 Resource Allocation
- 11.1.4.2 PKTDMA/BCDMA - Ring Operation
- 11.1.4.3 PKTDMA/BCDMA - Output Event Generation
- 11.1.4.4 PKTDMA - Transmit Channel Setup
- 11.1.4.5 PKTDMA - Transmit Channel Pause
- 11.1.4.6 PKTDMA - Transmit Channel Teardown
- 11.1.4.7 PKTDMA - Transmit Operation
- 11.1.4.8 PKTDMA - Receive Free Descriptor / Buffer Queue Setup
- 11.1.4.9 PKTDMA - Receive Channel Setup
- 11.1.4.10 PKTDMA - Receive Channel Teardown
- 11.1.4.11 PKTDMA - Receive Channel Pause
- 11.1.4.12 PKTDMA - Receive Operation
- 11.1.4.13 BCDMA - Block Copy Channel Setup
- 11.1.4.14 BCDMA - Block Copy Channel Pause
- 11.1.4.15 BCDMA - Block Copy Channel Teardown
- 11.1.4.16 BCDMA - Block Copy Operation (TR Packet)
- 11.1.4.17 BCDMA - Block Copy Error/Exception Handling
- 11.1.4.18 BCDMA - Split Transmit Channel Setup
- 11.1.4.19 BCDMA - Split Transmit Operation Pause
- 11.1.4.20 BCDMA - Split Transmit Channel Teardown
- 11.1.4.21 BCDMA - Split Transmit Operation (TR Packet)
- 11.1.4.22 BCDMA - Split Transmit Error / Exception Handling
- 11.1.4.23 BCDMA - Split Receive Channel Setup
- 11.1.4.24 BCDMA - Split Receive Channel Pause
- 11.1.4.25 BCDMA - Split Receive Channel Teardown
- 11.1.4.26 BCDMA - Split Receive Operation (TR Packet)
- 11.1.4.27 BCDMA - Split Receive Error / Exception Handling
- 11.1.1
Overview
- 11.2
Data Movement
Subsystem (DMSS)
- 11.2.1 Data Movement Subsystem (DMSS)
- 11.2.2
Ring Accelerator (RINGACC)
- 11.2.2.1 RINGACC Overview
- 11.2.2.2
RINGACC Functional Description
- 11.2.2.2.1
Block Diagram
- 11.2.2.2.1.1 Configuration Registers
- 11.2.2.2.1.2 Source Command FIFO
- 11.2.2.2.1.3 Source Write Data FIFO
- 11.2.2.2.1.4 Source Read Data FIFO
- 11.2.2.2.1.5 Source Write Status FIFO
- 11.2.2.2.1.6 Main State Machine
- 11.2.2.2.1.7 Destination Command FIFO
- 11.2.2.2.1.8 Destination Write Data FIFO
- 11.2.2.2.1.9 Destination Read Data FIFO
- 11.2.2.2.1.10 Destination Write Status FIFO
- 11.2.2.2.2
RINGACC Functional Operation
- 11.2.2.2.2.1 Queue Modes
- 11.2.2.2.2.2 VBUSM Target Ring Operations
- 11.2.2.2.2.3 VBUSM Initiator Interface Command ID Selection
- 11.2.2.2.2.4 Ring Push Operation (VBUSM Write to Source Interface)
- 11.2.2.2.2.5 Ring Pop Operation (VBUSM Read from Source Interface)
- 11.2.2.2.2.6 Host Doorbell Access
- 11.2.2.2.2.7 Queue Push Operation (VBUSM Write to Source Interface)
- 11.2.2.2.2.8 Queue Pop Operation (VBUSM Read from Source Interface)
- 11.2.2.2.2.9 Mismatched Element Size Handling
- 11.2.2.2.3 Events
- 11.2.2.2.4 Bus Error Handling
- 11.2.2.2.5 Monitors
- 11.2.2.2.1
Block Diagram
- 11.2.3
Secure
Proxy (SEC_PROXY)
- 11.2.3.1 Secure Proxy Overview
- 11.2.3.2
Secure Proxy Functional Description
- 11.2.3.2.1 Targets
- 11.2.3.2.2 Buffers
- 11.2.3.2.3 Proxy Thread Sizes
- 11.2.3.2.4 Proxy Thread Interleaving
- 11.2.3.2.5 Proxy States
- 11.2.3.2.6 Proxy Host Access
- 11.2.3.2.7 Permission Inheritance
- 11.2.3.2.8 Resource Association
- 11.2.3.2.9 Direction
- 11.2.3.2.10 Threshold Events
- 11.2.3.2.11 Error Events
- 11.2.3.2.12 Bus Error and Credits
- 11.2.3.2.13 Debug
- 11.2.4 Interrupt Aggregator (INTAGGR)
- 11.2.5 Packet Streaming Interface Link (PSI-L)
- 11.3
Peripheral DMA (PDMA)
- 11.3.1
PDMA Controller
- 11.3.1.1 PDMA Overview
- 849
- 11.3.1.2
Functional Description - SPI
- 11.3.1.2.1 Compliance to Standards
- 11.3.1.2.2
Functional Operation
- 11.3.1.2.2.1 Submodule Descriptions
- 11.3.1.2.2.2 General Functionality (Applicable to All Functions/Modes)
- 11.3.1.2.2.3 Events and Flow Control
- 11.3.1.2.2.4
Transmit Operation
- 11.3.1.2.2.4.1 Destination (Tx) Channel Allocation
- 11.3.1.2.2.4.2 Destination (Tx) Channel Out of Band Signals
- 11.3.1.2.2.4.3 Destination Channel Initialization
- 11.3.1.2.2.4.4 Data Transfer
- 11.3.1.2.2.4.5 Transmit PSI-L Interface Transactions
- 11.3.1.2.2.4.6 Tx Pause
- 11.3.1.2.2.4.7 Tx Teardown
- 11.3.1.2.2.4.8 Tx Channel Reset
- 11.3.1.2.2.4.9 Tx Debug/State Register
- 11.3.1.2.2.5 Receive Operation
- 11.3.1.3
Functional Description - UART
- 11.3.1.3.1 Compliance to Standards
- 11.3.1.3.2
Functional Operation
- 11.3.1.3.2.1 Submodule Descriptions
- 11.3.1.3.2.2 General Functionality (Applicable to All Functions/Modes)
- 11.3.1.3.2.3 Events and Flow Control
- 11.3.1.3.2.4
Transmit Operation
- 11.3.1.3.2.4.1 Destination (Tx) Channel Allocation
- 11.3.1.3.2.4.2 Destination (Tx) Channel Out of Band Signals
- 11.3.1.3.2.4.3 Destination Channel Initialization
- 11.3.1.3.2.4.4 Data Transfer
- 11.3.1.3.2.4.5 Transmit PSI-L Interface Transactions
- 11.3.1.3.2.4.6 Tx Pause
- 11.3.1.3.2.4.7 Tx Teardown
- 11.3.1.3.2.4.8 Tx Channel Reset
- 11.3.1.3.2.4.9 Tx Debug/State Register
- 11.3.1.3.2.5
Receive Operation
- 11.3.1.3.2.5.1 Source (Rx) Channel Allocation
- 11.3.1.3.2.5.2 Source Channel Initialization
- 11.3.1.3.2.5.3 Data Transfer
- 11.3.1.3.2.5.4 Receive PSI-L Interface Transactions
- 11.3.1.3.2.5.5 Rx Pause
- 11.3.1.3.2.5.6 Rx Teardown
- 11.3.1.3.2.5.7 Rx Channel Reset
- 11.3.1.3.2.5.8 Rx Debug/State Register
- 11.3.1.4
Functional Description - McASP
- 11.3.1.4.1 Compliance to Standards
- 11.3.1.4.2
Functional Operation
- 11.3.1.4.2.1 Submodule Descriptions
- 11.3.1.4.2.2 General Functionality (Applicable to All Functions/Modes)
- 11.3.1.4.2.3 Events and Flow Control
- 11.3.1.4.2.4
Transmit Operation
- 11.3.1.4.2.4.1 Destination (Tx) Channel Allocation
- 11.3.1.4.2.4.2 Destination (Tx) Channel Out of Band Signals
- 11.3.1.4.2.4.3 Destination Channel Initialization
- 11.3.1.4.2.4.4 Data Transfer
- 11.3.1.4.2.4.5 Transmit PSI-L Interface Transactions
- 11.3.1.4.2.4.6 Tx Pause
- 11.3.1.4.2.4.7 Tx Teardown
- 11.3.1.4.2.4.8 Tx Channel Reset
- 11.3.1.4.2.4.9 Tx Debug/State Register
- 11.3.1.4.2.5 Receive Operation
- 11.3.1.5
Functional Description - ADC
- 11.3.1.5.1 Compliance to Standards
- 11.3.1.5.2
Functional Operation
- 11.3.1.5.2.1 Submodule Descriptions
- 11.3.1.5.2.2 General Functionality (Applicable to All Functions/Modes)
- 11.3.1.5.2.3 Events and Flow Control
- 11.3.1.5.2.4
Transmit Operation
- 11.3.1.5.2.4.1 Destination (Tx) Channel Allocation
- 11.3.1.5.2.4.2 Destination (Tx) Channel Out of Band Signals
- 11.3.1.5.2.4.3 Destination Channel Initialization
- 11.3.1.5.2.4.4 Data Transfer
- 11.3.1.5.2.4.5 Transmit PSI-L Interface Transactions
- 11.3.1.5.2.4.6 Tx Pause
- 11.3.1.5.2.4.7 Tx Teardown
- 11.3.1.5.2.4.8 Tx Channel Reset
- 11.3.1.5.2.4.9 Tx Debug/State Register
- 11.3.1.5.2.5 Receive Operation
- 11.3.1.6
Functional Description - ASRC
- 11.3.1.6.1 Compliance to Standards
- 11.3.1.6.2
Functional Operation
- 11.3.1.6.2.1 Submodule Descriptions
- 11.3.1.6.2.2 General Functionality (Applicable to All Functions/Modes)
- 11.3.1.6.2.3 Events and Flow Control
- 11.3.1.6.2.4
Transmit Operation
- 11.3.1.6.2.4.1 Destination (Tx) Channel Allocation
- 11.3.1.6.2.4.2 Destination (Tx) Channel Out of Band Signals
- 11.3.1.6.2.4.3 Destination Channel Initialization
- 11.3.1.6.2.4.4 Data Transfer
- 11.3.1.6.2.4.5 Transmit PSI-L Interface Transactions
- 11.3.1.6.2.4.6 Tx Pause
- 11.3.1.6.2.4.7 Tx Teardown
- 11.3.1.6.2.4.8 Tx Channel Reset
- 11.3.1.6.2.4.9 Tx Debug/State Register
- 11.3.1.6.2.5 Receive Operation
- 11.3.1
PDMA Controller
- 11.1
Data Movement Architecture Overview
-
12Peripherals
- 12.1
Audio Peripherals
- 12.1.1
Audio Sample Rate Converter (ASRC)
- 12.1.1.1 ASRC Overview
- 12.1.1.2
ASRC Functional Description
- 12.1.1.2.1 ASRC Block Diagram and Implementation
- 12.1.1.2.2 ASRC Data Rate and Traffic Behavior
- 12.1.1.2.3 ASRC Data Interface and Formats
- 12.1.1.2.4 ASRC Clock Configuration
- 12.1.1.2.5 ASRC Reset Configuration
- 12.1.1.2.6 ASRC Power Management
- 12.1.1.2.7 ASRC Interrupts and Data Transfer Model
- 12.1.1.2.8 ASRC DMA Events and Data Transfer Model
- 12.1.1.2.9 ASRC Group Mode Configuration
- 12.1.1.2.10 ASRC Stream Mode Configuration
- 12.1.1.2.11 ASRC Programming Ranges and Restrictions
- 12.1.1.2.12 ASRC Registers Shadowing
- 12.1.2
Multichannel Audio Serial Port (MCASP)
- 12.1.2.1 MCASP Overview
- 12.1.2.2 MCASP Environment
- 12.1.2.3 Integration
- 12.1.2.4
MCASP Functional Description
- 12.1.2.4.1 MCASP Block Diagram
- 12.1.2.4.2 MCASP Clock and Frame-Sync Configurations
- 12.1.2.4.3 MCASP Serializers
- 12.1.2.4.4 MCASP Format Units
- 12.1.2.4.5 MCASP State-Machines
- 12.1.2.4.6 MCASP TDM Sequencers
- 12.1.2.4.7 MCASP Software Reset
- 12.1.2.4.8 MCASP Power Management
- 12.1.2.4.9 MCASP Transfer Modes
- 12.1.2.4.10 MCASP Data Transmission and Reception
- 12.1.2.4.11 MCASP Audio FIFO (AFIFO)
- 12.1.2.4.12 MCASP Events and Interrupt Requests
- 12.1.2.4.13 MCASP DMA Requests
- 12.1.2.4.14 MCASP Loopback Modes
- 12.1.2.4.15 MCASP Error Reporting
- 12.1.2.5
MCASP Programming Guide
- 12.1.2.5.1
MCASP Global Initialization
- 12.1.2.5.1.1 Surrounding Modules Global Initialization
- 12.1.2.5.1.2
MCASP Global Initialization
- 12.1.2.5.1.2.1
Main Sequence – MCASP Global Initialization for DIT-Transmission
- 12.1.2.5.1.2.1.1 Subsequence – Transmit Format Unit Configuration for DIT-Transmission
- 12.1.2.5.1.2.1.2 Subsequence – Transmit Frame Synchronization Generator Configuration for DIT-Transmission
- 12.1.2.5.1.2.1.3 Subsequence – Transmit Clock Generator Configuration for DIT-Transmission
- 12.1.2.5.1.2.1.4 Subsequence - MCASP Pins Functional Configuration
- 12.1.2.5.1.2.1.5 Subsequence – DIT-specific Subframe Fields Configuration
- 12.1.2.5.1.2.2
Main Sequence – MCASP Global Initialization for TDM-Reception
- 12.1.2.5.1.2.2.1 Subsequence – Receive Format Unit Configuration in TDM Mode
- 12.1.2.5.1.2.2.2 Subsequence – Receive Frame Synchronization Generator Configuration in TDM Mode
- 12.1.2.5.1.2.2.3 Subsequence – Receive Clock Generator Configuration
- 12.1.2.5.1.2.2.4 Subsequence—MCASP Receiver Pins Functional Configuration
- 12.1.2.5.1.2.3
Main Sequence – MCASP Global Initialization for TDM -Transmission
- 12.1.2.5.1.2.3.1 Subsequence – Transmit Format Unit Configuration in TDM Mode
- 12.1.2.5.1.2.3.2 Subsequence – Transmit Frame Synchronization Generator Configuration in TDM Mode
- 12.1.2.5.1.2.3.3 Subsequence – Transmit Clock Generator Configuration for TDM Cases
- 12.1.2.5.1.2.3.4 Subsequence—MCASP Transmit Pins Functional Configuration
- 12.1.2.5.1.2.1
Main Sequence – MCASP Global Initialization for DIT-Transmission
- 12.1.2.5.2 MCASP Operational Modes Configuration
- 12.1.2.5.1
MCASP Global Initialization
- 12.1.3 Audio Tracking Logic (ATL)
- 12.1.4
Media Local Bus Subsystem (MLBSS)
- 12.1.4.1 MLBSS Overview
- 12.1.4.2 MLBSS Environment
- 12.1.4.3 MLBSS Functional Description
- 12.1.4.4 MLBSS Programming Guide
- 12.1.1
Audio Sample Rate Converter (ASRC)
- 12.2
General Connectivity Peripherals
- 12.2.1
General-Purpose Interface (GPIO)
- 12.2.1.1 GPIO Overview
- 12.2.1.2 GPIO Environment
- 12.2.1.3 Integration
- 12.2.1.4 GPIO Functional Description
- 12.2.1.5 GPIO Programming Guide
- 12.2.2
Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C) Interface
- 12.2.2.1 I2C Overview
- 12.2.2.2
I2C Environment
- 12.2.2.2.1 I2C Typical Application
- 12.2.2.2.2
I2C Typical Connection Protocol and Data Format
- 12.2.2.2.2.1 I2C Serial Data Format
- 12.2.2.2.2.2 I2C Data Validity
- 12.2.2.2.2.3 I2C Start and Stop Conditions
- 12.2.2.2.2.4 I2C Addressing
- 12.2.2.2.2.5 I2C Controller Transmitter
- 12.2.2.2.2.6 I2C Controller Receiver
- 12.2.2.2.2.7 I2C Target Transmitter
- 12.2.2.2.2.8 I2C Target Receiver
- 12.2.2.2.2.9 I2C Bus Arbitration
- 12.2.2.2.2.10 I2C Clock Generation and Synchronization
- 12.2.2.3 I2C Functional Description
- 12.2.2.4 I2C Programming Guide
- 12.2.3
Multichannel Serial Peripheral Interface (MCSPI)
- 12.2.3.1 MCSPI Overview
- 12.2.3.2 MCSPI Environment
- 12.2.3.3 Integration
- 12.2.3.4
MCSPI Functional Description
- 12.2.3.4.1 MCSPI Block Diagram
- 12.2.3.4.2 MCSPI Reset
- 12.2.3.4.3
MCSPI Controller Mode
- 12.2.3.4.3.1 Controller Mode Features
- 12.2.3.4.3.2 Controller Transmit-and-Receive Mode (Full Duplex)
- 12.2.3.4.3.3 Controller Transmit-Only Mode (Half Duplex)
- 12.2.3.4.3.4 Controller Receive-Only Mode (Half Duplex)
- 12.2.3.4.3.5 Single-Channel Controller Mode
- 12.2.3.4.3.6 Start-Bit Mode
- 12.2.3.4.3.7 Chip-Select Timing Control
- 12.2.3.4.3.8 Programmable MCSPI Clock (SPICLK)
- 12.2.3.4.4 MCSPI Peripheral Mode
- 12.2.3.4.5 MCSPI 3-Pin or 4-Pin Mode
- 12.2.3.4.6 MCSPI FIFO Buffer Management
- 12.2.3.4.7 MCSPI Interrupts
- 12.2.3.4.8 MCSPI DMA Requests
- 12.2.3.4.9 MCSPI Power Saving Management
- 12.2.3.5
MCSPI Programming Guide
- 12.2.3.5.1 MCSPI Global Initialization
- 12.2.3.5.2
MCSPI Operational Mode Configuration
- 12.2.3.5.2.1
MCSPI Operational Modes
- 12.2.3.5.2.1.1 Common Transfer Sequence
- 12.2.3.5.2.1.2 End of Transfer Sequences
- 12.2.3.5.2.1.3 Transmit-and-Receive (Controller and Peripheral)
- 12.2.3.5.2.1.4 Transmit-Only (Controller and Peripheral)
- 12.2.3.5.2.1.5 Controller Normal Receive-Only
- 12.2.3.5.2.1.6 Controller Turbo Receive-Only
- 12.2.3.5.2.1.7 Peripheral Receive-Only
- 12.2.3.5.2.1.8
Transfer Procedures With FIFO
- 12.2.3.5.2.1.8.1 Common Transfer Sequence in FIFO Mode
- 12.2.3.5.2.1.8.2 End of Transfer Sequences in FIFO Mode
- 12.2.3.5.2.1.8.3 Transmit-and-Receive With Word Count
- 12.2.3.5.2.1.8.4 Transmit-and-Receive Without Word Count
- 12.2.3.5.2.1.8.5 Transmit-Only
- 12.2.3.5.2.1.8.6 Receive-Only With Word Count
- 12.2.3.5.2.1.8.7 Receive-Only Without Word Count
- 12.2.3.5.2.1.9 Common Transfer Procedures Without FIFO – Polling Method
- 12.2.3.5.2.1
MCSPI Operational Modes
- 12.2.3.5.3 Common Transfer Procedures Without FIFO – Polling Method
- 12.2.4
Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (UART)
- 12.2.4.1 UART Overview
- 12.2.4.2
UART Environment
- 12.2.4.2.1 UART Functional Interfaces
- 12.2.4.2.2 RS-485 Functional Interfaces
- 12.2.4.2.3 IrDA Functional Interfaces
- 12.2.4.2.4 CIR Functional Interfaces
- 12.2.4.3 Integration
- 12.2.4.4
UART Functional Description
- 12.2.4.4.1 UART Block Diagram
- 12.2.4.4.2 UART Clock Configuration
- 12.2.4.4.3 UART Software Reset
- 12.2.4.4.4 UART Power Management
- 12.2.4.4.5 UART Interrupt Requests
- 12.2.4.4.6 UART FIFO Management
- 12.2.4.4.7 UART Mode Selection
- 12.2.4.4.8
UART Protocol Formatting
- 12.2.4.4.8.1
UART Mode
- 12.2.4.4.8.1.1 UART Clock Generation: Baud Rate Generation
- 12.2.4.4.8.1.2 Choosing the Appropriate Divisor Value
- 12.2.4.4.8.1.3 UART Data Formatting
- 12.2.4.4.8.2 RS-485 Mode
- 12.2.4.4.8.3
IrDA Mode
- 12.2.4.4.8.3.1 IrDA Clock Generation: Baud Generator
- 12.2.4.4.8.3.2 Choosing the Appropriate Divisor Value
- 12.2.4.4.8.3.3
IrDA Data Formatting
- 12.2.4.4.8.3.3.1 IR RX Polarity Control
- 12.2.4.4.8.3.3.2 IrDA Reception Control
- 12.2.4.4.8.3.3.3 IR Address Checking
- 12.2.4.4.8.3.3.4 Frame Closing
- 12.2.4.4.8.3.3.5 Store and Controlled Transmission
- 12.2.4.4.8.3.3.6 Error Detection
- 12.2.4.4.8.3.3.7 Underrun During Transmission
- 12.2.4.4.8.3.3.8 Overrun During Receive
- 12.2.4.4.8.3.3.9 Status FIFO
- 12.2.4.4.8.3.3.10 Multi-drop Parity Mode with Address Match
- 12.2.4.4.8.3.3.11 Time-guard
- 12.2.4.4.8.3.4 SIR Mode Data Formatting
- 12.2.4.4.8.3.5 MIR and FIR Mode Data Formatting
- 12.2.4.4.8.4 CIR Mode
- 12.2.4.4.8.1
UART Mode
- 12.2.4.5
UART Programming Guide
- 12.2.4.5.1 UART Global Initialization
- 12.2.4.5.2 UART Mode selection
- 12.2.4.5.3 UART Submode selection
- 12.2.4.5.4 UART Load FIFO trigger and DMA mode settings
- 12.2.4.5.5 UART Protocol, Baud rate and interrupt settings
- 12.2.4.5.6 UART Hardware and Software Flow Control Configuration
- 12.2.4.5.7 IrDA Programming Model
- 12.2.1
General-Purpose Interface (GPIO)
- 12.3
High-Speed Serial Interfaces
- 12.3.1
Gigabit Ethernet Switch
(CPSW3G)
- 12.3.1.1 CPSW0 Overview
- 12.3.1.2 CPSW0 Environment
- 12.3.1.3 Integration
- 12.3.1.4
CPSW0 Functional Description
- 12.3.1.4.1 Functional Block Diagram
- 12.3.1.4.2 CPSW Ports
- 12.3.1.4.3 Clocking
- 12.3.1.4.4 Software IDLE
- 12.3.1.4.5 Interrupt Functionality
- 12.3.1.4.6
CPSW_3G
- 12.3.1.4.6.1
Address Lookup Engine (ALE)
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.1 Error Handling
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.2 Bypass Operations
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.3 OUI Deny or Accept
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.4 Statistics Counting
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.5 Automotive Security Features
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.6 CPSW Switching Solutions
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.7 VLAN Routing and OAM Operations
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.8 Supervisory packets
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.9
Address Table Entry
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.9.1 Multicast Address Table Entry
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.9.2 OUI Unicast Address Table Entry
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.9.3 Unicast Address Table Entry (Bit 40 == 0)
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.9.4 Multicast Address Table Entry (Bit 40==1)
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.9.5 VLAN/Unicast Address Table Entry (Bit 40 == 0)
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.9.6 VLAN/Multicast Address Table Entry (Bit 40==1)
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.9.7 Inner VLAN Table Entry
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.9.8 Outer VLAN Table Entry
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.9.9 EtherType Table Entry
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.9.10 IPv4 Table Entry
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.9.11 IPv6 Table Entry High
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.9.12 IPv6 Table Entry Low
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.10 Multicast Address
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.11 Aging and Auto Aging
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.12 ALE Policing and Classification
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.13 Mirroring
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.14 Trunking
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.15 DSCP
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.16 Packet Forwarding Processes
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.17 VLAN Aware Mode
- 12.3.1.4.6.1.18 VLAN Unaware Mode
- 12.3.1.4.6.2 Packet Priority Handling
- 12.3.1.4.6.3 CPPI Port Ingress
- 12.3.1.4.6.4 Packet CRC Handling
- 12.3.1.4.6.5 FIFO Memory Control
- 12.3.1.4.6.6 FIFO Transmit Queue Control
- 12.3.1.4.6.7 Intersperced Express Traffic (IET – P802.3br/D2.0)
- 12.3.1.4.6.8
Enhanced Scheduled Traffic (EST – P802.1Qbv/D2.2)
- 12.3.1.4.6.8.1 Enhanced Scheduled Traffic Overview
- 12.3.1.4.6.8.2 Enhanced Scheduled Traffic Fetch RAM
- 12.3.1.4.6.8.3 Enhanced Scheduled Traffic Time Interval
- 12.3.1.4.6.8.4 Enhanced Scheduled Traffic Fetch Values
- 12.3.1.4.6.8.5 Enhanced Scheduled Traffic Packet Fill
- 12.3.1.4.6.8.6 Enhanced Scheduled Traffic Time Stamp
- 12.3.1.4.6.8.7 Enhanced Scheduled Traffic Packets Per Priority
- 12.3.1.4.6.9 Audio Video Bridging
- 12.3.1.4.6.10
Ethernet MAC Sliver
- 12.3.1.4.6.10.1
Ethernet MAC Sliver
Overview
- 12.3.1.4.6.10.1.1 CRC Insertion
- 12.3.1.4.6.10.1.2 MTXER
- 12.3.1.4.6.10.1.3 Adaptive Performance Optimization (APO)
- 12.3.1.4.6.10.1.4 Inter-Packet-Gap Enforcement
- 12.3.1.4.6.10.1.5 Back Off
- 12.3.1.4.6.10.1.6 Programmable Transmit Inter-Packet Gap
- 12.3.1.4.6.10.1.7 Speed, Duplex and Pause Frame Support Negotiation
- 12.3.1.4.6.10.2 RMII Interface
- 12.3.1.4.6.10.3 RGMII Interface
- 12.3.1.4.6.10.4 Frame Classification
- 12.3.1.4.6.10.5 Receive FIFO Architecture
- 12.3.1.4.6.10.1
Ethernet MAC Sliver
Overview
- 12.3.1.4.6.11 Embedded Memories
- 12.3.1.4.6.12 Memory Error Detection and Correction
- 12.3.1.4.6.13 Ethernet Port Flow Control
- 12.3.1.4.6.14 Energy Efficient Ethernet Support (802.3az)
- 12.3.1.4.6.15 Ethernet Switch Latency
- 12.3.1.4.6.16 MAC Emulation Control
- 12.3.1.4.6.17 MAC Command IDLE
- 12.3.1.4.6.18
CPSW Network Statistics
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.1
Rx-only Statistics Descriptions
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.1.1 Good Rx Frames (Offset = 3A000h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.1.2 Broadcast Rx Frames (Offset = 3A004h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.1.3 Multicast Rx Frames (Offset = 3A008h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.1.4 Pause Rx Frames (Offset = 3A00Ch)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.1.5 Rx CRC Errors (Offset = 3A010h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.1.6 Rx Align/Code Errors (Offset = 3A014h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.1.7 Oversize Rx Frames (Offset = 3A018h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.1.8 Rx Jabbers (Offset = 3A01Ch)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.1.9 Undersize (Short) Rx Frames (Offset = 3A020h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.1.10 Rx Fragments (Offset = 3A024h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.1.11 RX IPG Error (Offset = 3A05Ch)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.1.12 ALE Drop (Offset = 3A028h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.1.13 ALE Overrun Drop (Offset = 3A02Ch)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.1.14 Rx Octets (Offset = 3A030h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.1.15 Rx Bottom of FIFO Drop (Offset = 3A084h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.1.16 Portmask Drop (Offset = 3A088h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.1.17 Rx Top of FIFO Drop (Offset = 3A08Ch)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.1.18 ALE Rate Limit Drop (Offset = 3A090h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.1.19
ALE VLAN Ingress Check Drop (Offset = 3A094h)
- 3.1.4.6.18.1.19.1 ALE DA=SA Drop (Offset = 3A098h)
- 3.1.4.6.18.1.19.2 Block Address Drop (Offset = 3A09Ch)
- 3.1.4.6.18.1.19.3 ALE Secure Drop (Offset = 3A0A0h)
- 3.1.4.6.18.1.19.4 ALE Authentication Drop (Offset = 3A0A4h)
- 3.1.4.6.18.1.19.5 ALE Unknown Unicast (Offset = 3A0A8h)
- 3.1.4.6.18.1.19.6 ALE Unknown Unicast Bytecount (Offset = 3A0ACh)
- 3.1.4.6.18.1.19.7 ALE Unknown Multicast (Offset = 3A0B0h)
- 3.1.4.6.18.1.19.8 ALE Unknown Multicast Bytecount (Offset = 3A0B4h)
- 3.1.4.6.18.1.19.9 ALE Unknown Broadcast (Offset = 3A0B8h)
- 3.1.4.6.18.1.19.10 ALE Unknown Broadcast Bytecount (Offset = 3A0BCh)
- 3.1.4.6.18.1.19.11 ALE Policer/Classifier Match (Offset = 3A0C0h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.2 ALE Policer Match Red (Offset = 3A0C4h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.3 ALE Policer Match Yellow (Offset = 3A0C8h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.4 IET Receive Assembly Error (Offset = 3A140h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.5 IET Receive Assembly OK (Offset = 3A144h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.6 IET Receive SMD Error (Offset = 3A148h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.7 IET Receive Merge Fragment Count (Offset = 3A14Ch)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.8 Rx Cut Thru with No Delay
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.9 Rx Cut Thru with Delay
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.10 Rx Cut Thru Store-and-Forward
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.11
Tx-only Statistics Descriptions
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.11.1 Good Tx Frames (Offset = 3A034h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.11.2 Broadcast Tx Frames (Offset = 3A038h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.11.3 Multicast Tx Frames (Offset = 3A03Ch)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.11.4 Pause Tx Frames (Offset = 3A040h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.11.5 Deferred Tx Frames (Offset = 3A044h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.11.6 Collisions (Offset = 3A048h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.11.7 Single Collision Tx Frames (Offset = 3A04Ch)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.11.8 Multiple Collision Tx Frames (Offset = 3A050h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.11.9 Excessive Collisions (Offset = 3A054h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.11.10 Late Collisions (Offset = 3A058h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.11.11 Carrier Sense Errors (Offset = 3A060h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.11.12 Tx Octets (Offset = 3A064h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.11.13 Transmit Priority 0-7 (Offset = 3A180h to 3A1A8h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.11.14 Transmit Priority 0-7 Drop (Offset = 3A1C0h to 3A1E8)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.11.15 Tx Memory Protect Errors (Offset = 3A17Ch)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.11.16 IET Transmit Merge Hold Count (Offset = 3A150h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.11.17 IET Transmit Merge Fragment Count (Offset = 3A14Ch)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.11.18 Tx CRC Errors
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.11.19 Tx Cut Thru
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.11.20 Tx Cut Thru Store-and-Forward
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.12
Rx- and Tx (Shared) Statistics Descriptions
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.12.1 Rx + Tx 64 Octet Frames (Offset = 3A068h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.12.2 Rx + Tx 65–127 Octet Frames (Offset = 3A06Ch)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.12.3 Rx + Tx 128–255 Octet Frames (Offset = 3A070h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.12.4 Rx + Tx 256–511 Octet Frames (Offset = 3A074h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.12.5 Rx + Tx 512–1023 Octet Frames (Offset = 3A078h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.12.6 Rx + Tx 1024_Up Octet Frames (Offset = 3A07Ch)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.12.7 Net Octets (Offset = 3A080h)
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.13 1884
- 12.3.1.4.6.18.1
Rx-only Statistics Descriptions
- 12.3.1.4.6.1
Address Lookup Engine (ALE)
- 12.3.1.4.7
Common Platform Time Sync (CPTS)
- 12.3.1.4.7.1 CPSW0 CPTS Integration
- 12.3.1.4.7.2 CPTS Architecture
- 12.3.1.4.7.3 CPTS Initialization
- 12.3.1.4.7.4 32-bit Time Stamp Value
- 12.3.1.4.7.5 64-bit Time Stamp Value
- 12.3.1.4.7.6 64-Bit Timestamp Nudge
- 12.3.1.4.7.7 64-bit Timestamp PPM
- 12.3.1.4.7.8 Event FIFO
- 12.3.1.4.7.9 Timestamp Compare Output
- 12.3.1.4.7.10 Timestamp Sync Output
- 12.3.1.4.7.11 Timestamp GENFn Output
- 12.3.1.4.7.12 Timestamp ESTFn
- 12.3.1.4.7.13 Time Sync Events
- 12.3.1.4.7.14 Timestamp Compare Event
- 12.3.1.4.7.15 Host Transmit Event
- 12.3.1.4.7.16 CPTS Interrupt Handling
- 12.3.1.4.8
CPPI Streaming Packet Interface
- 12.3.1.4.8.1 Port 0 CPPI Transmit Packet Streaming Interface (CPSW_3G Egress)
- 12.3.1.4.8.2 Port 0 CPPI Receive Packet Streaming Interface (CPSW_3G Ingress)
- 12.3.1.4.8.3 Cut-Thru
- 12.3.1.4.8.4 Port Speed
- 12.3.1.4.8.5 CPPI Checksum Offload
- 12.3.1.4.8.6 CPPI Receive Checksum Offload
- 12.3.1.4.8.7 Egress Packet Operations
- 12.3.1.4.9 MII Management Interface (MDIO)
- 12.3.1.5 CPSW0 Programming Guide
- 12.3.2 Universal Serial Bus Subsystem (USBSS)
- 12.3.1
Gigabit Ethernet Switch
(CPSW3G)
- 12.4
Memory Interfaces
- 12.4.1 Flash Subsystem (FSS)
- 12.4.2
Octal Serial Peripheral Interface (OSPI)
- 12.4.2.1 OSPI Overview
- 12.4.2.2 OSPI Environment
- 12.4.2.3
OSPI Functional Description
- 12.4.2.3.1 OSPI Block Diagram
- 12.4.2.3.2 OSPI Modes
- 12.4.2.3.3 OSPI Power Management
- 12.4.2.3.4 Auto HW Polling
- 12.4.2.3.5 Flash Reset
- 12.4.2.3.6 OSPI Memory Regions
- 12.4.2.3.7 OSPI Interrupt Requests
- 12.4.2.3.8 OSPI Data Interface
- 12.4.2.3.9 OSPI Direct Access Controller (DAC)
- 12.4.2.3.10 OSPI Indirect Access Controller (INDAC)
- 12.4.2.3.11 OSPI Software-Triggered Instruction Generator (STIG)
- 12.4.2.3.12 OSPI Arbitration Between Direct / Indirect Access Controller and STIG
- 12.4.2.3.13
OSPI Programming Guide
- 12.4.2.3.13.1 Configuring the OSPI Controller for Use After Reset
- 12.4.2.3.13.2 Configuring the OSPI Controller for Optimal Use
- 12.4.2.3.13.3 Using the Flash Command Control Register (STIG Operation)
- 12.4.2.3.13.4 Using SPI Legacy Mode
- 12.4.2.3.13.5 Entering XIP Mode from POR
- 12.4.2.3.13.6 Entering XIP Mode Otherwise
- 12.4.2.3.13.7 Exiting XIP Mode
- 12.4.3 HyperBus
- 12.4.4
OptiFlash Submodules
- 12.4.4.1
Regional L2-Cache (RL2)
- 12.4.4.1.1 RL2 Overview
- 12.4.4.1.2 Environment
- 12.4.4.1.3
Functional Description
- 12.4.4.1.3.1
Block Diagram
- 12.4.4.1.3.1.1 C and R FIFO Blocks
- 12.4.4.1.3.1.2 Correction and Copying Block
- 12.4.4.1.3.1.3 Address Translation Block
- 12.4.4.1.3.1.4 Tag LRU RAM Block
- 12.4.4.1.3.1.5 DEC Block
- 12.4.4.1.3.1.6 Regs Block
- 12.4.4.1.3.1.7 Way Tag Compare Block
- 12.4.4.1.3.1.8 Mux Block
- 12.4.4.1.3.1.9 Tracking and Control Block
- 12.4.4.1.3.2 Privilege Passing and Manipulation
- 12.4.4.1.3.3 Error Handling and Flushing
- 12.4.4.1.3.4 Tightly Coupled RL2 Tag Memory
- 12.4.4.1.3.5 Remote Cache Data Storage Memory
- 12.4.4.1.3.6 RL2 Cache Allocation
- 12.4.4.1.3.7 Dual Mode
- 12.4.4.1.3.8 Emulation Debug
- 12.4.4.1.3.9 ASIL-D/SIL-3 Safety
- 12.4.4.1.3.10 Latencies
- 12.4.4.1.3.11 Critical Word First (CWF)
- 12.4.4.1.3.1
Block Diagram
- 12.4.4.2 Fast Local Copy (FLC)
- 12.4.4.1
Regional L2-Cache (RL2)
- 12.4.5
Multi-Media Card Secure Digital (MMCSD) Interface
- 12.4.5.1 MMCSD Overview
- 12.4.5.2 MMCSD Environment
- 12.4.5.3 Integration
- 12.4.5.4 MMCSD Functional Description
- 12.4.5.5
MMCSD Programming Guide
- 12.4.5.5.1
Sequences
- 12.4.5.5.1.1 SD Card Detection
- 12.4.5.5.1.2 SD Clock Control
- 12.4.5.5.1.3 SD Bus Power Control
- 12.4.5.5.1.4 Changing Bus Width
- 12.4.5.5.1.5 Timeout Setting on DAT Line
- 12.4.5.5.1.6 Card Initialization and Identification (for SD I/F)
- 12.4.5.5.1.7 SD Transaction Generation
- 12.4.5.5.1.8 Abort Transaction
- 12.4.5.5.1.9 Changing Bus Speed Mode
- 12.4.5.5.1.10 Error Recovery
- 12.4.5.5.1.11 Wakeup Control (Optional)
- 12.4.5.5.1.12 Suspend/Resume (Optional, Not Supported from Version 4.00)
- 12.4.5.5.2 Driver Flow Sequence
- 12.4.5.5.1
Sequences
- 12.5
Industrial and Control Interfaces
- 12.5.1
Modular Controller Area Network (MCAN)
- 12.5.1.1 MCAN Overview
- 12.5.1.2 MCAN Environment
- 12.5.1.3 Integration
- 12.5.1.4
MCAN Functional Description
- 12.5.1.4.1 Module Clocking Requirements
- 12.5.1.4.2 Interrupt and DMA Requests
- 12.5.1.4.3
Operating Modes
- 12.5.1.4.3.1 Software Initialization
- 12.5.1.4.3.2 Normal Operation
- 12.5.1.4.3.3 CAN FD Operation
- 12.5.1.4.3.4 Transmitter Delay Compensation
- 12.5.1.4.3.5 Restricted Operation Mode
- 12.5.1.4.3.6 Bus Monitoring Mode
- 12.5.1.4.3.7 Disabled Automatic Retransmission (DAR) Mode
- 12.5.1.4.3.8 Power Down (Sleep Mode)
- 12.5.1.4.3.9 Test Modes
- 12.5.1.4.4 Timestamp Generation
- 12.5.1.4.5 Timeout Counter
- 12.5.1.4.6 ECC Support
- 12.5.1.4.7 Rx Handling
- 12.5.1.4.8 Tx Handling
- 12.5.1.4.9 FIFO Acknowledge Handling
- 12.5.1.4.10 Message RAM
- 12.5.2
Enhanced Capture (ECAP) Module
- 12.5.2.1 ECAP Overview
- 12.5.2.2 ECAP Environment
- 12.5.2.3 Integration
- 12.5.2.4
ECAP Functional Description
- 12.5.2.4.1
Capture and APWM Operating Modes
- 12.5.2.4.1.1
ECAP Capture Mode Description
- 12.5.2.4.1.1.1 ECAP Event Prescaler
- 12.5.2.4.1.1.2 ECAP Edge Polarity Select and Qualifier
- 12.5.2.4.1.1.3 ECAP Continuous/One-Shot Control
- 12.5.2.4.1.1.4 ECAP 32-Bit Counter and Phase Control
- 12.5.2.4.1.1.5 CAP1-CAP4 Registers
- 12.5.2.4.1.1.6 ECAP Interrupt Control
- 12.5.2.4.1.1.7 ECAP Shadow Load and Lockout Control
- 12.5.2.4.1.2 ECAP APWM Mode Operation
- 12.5.2.4.1.1
ECAP Capture Mode Description
- 12.5.2.4.2 Summary of ECAP Functional Registers
- 12.5.2.4.1
Capture and APWM Operating Modes
- 12.5.2.5
ECAP Use Cases
- 12.5.2.5.1 Absolute Time-Stamp Operation Rising Edge Trigger Example
- 12.5.2.5.2 Absolute Time-Stamp Operation Rising and Falling Edge Trigger Example
- 12.5.2.5.3 Time Difference (Delta) Operation Rising Edge Trigger Example
- 12.5.2.5.4 Time Difference (Delta) Operation Rising and Falling Edge Trigger Example
- 12.5.2.5.5 Application of the APWM Mode
- 12.5.3
Enhanced Pulse Width Modulation (EPWM) Module
- 12.5.3.1 EPWM Overview
- 12.5.3.2 EPWM Environment
- 12.5.3.3 Integration
- 12.5.3.4
EPWM Functional Description
- 12.5.3.4.1 EPWM Submodule Features
- 12.5.3.4.2 EPWM Time-Base (TB) Submodule
- 12.5.3.4.3 EPWM Counter-Compare (CC) Submodule
- 12.5.3.4.4 EPWM Action-Qualifier (AQ) Submodule
- 12.5.3.4.5 EPWM Dead-Band Generator (DB) Submodule
- 12.5.3.4.6 EPWM-Chopper (PC) Submodule
- 12.5.3.4.7 EPWM Trip-Zone (TZ) Submodule
- 12.5.3.4.8 EPWM Event-Trigger (ET) Submodule
- 12.5.3.4.9 EPWM Functional Register Groups
- 12.5.3.4.10 Proper EPWM Interrupt Initialization Procedure
- 12.5.4
Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC)
- 12.5.4.1 ADC Overview
- 12.5.4.2 ADC Environment
- 12.5.4.3
ADC Functional Description
- 12.5.4.3.1 ADC FSM Sequencer Functional Description
- 12.5.4.3.2 ADC AFE Functional Description
- 12.5.4.3.3 ADC FIFOs and DMA
- 12.5.4.3.4 ADC Error Correcting Code (ECC)
- 12.5.4.3.5 ADC Functional Debug Mode
- 12.5.4.4 ADC Programming Guide
- 12.5.1
Modular Controller Area Network (MCAN)
- 12.6
Timer Modules
- 12.6.1 Global Timebase Counter (GTC)
- 12.6.2 RTI-Windowed Watchdog Timer (WWDT)
- 12.6.3 Real-Time Clock (RTC)
- 12.6.4
Timers
- 12.6.4.1 Timers Overview
- 12.6.4.2 Timers Environment
- 12.6.4.3 Integration
- 12.6.4.4
Timers Functional Description
- 12.6.4.4.1 Timer Block Diagram
- 12.6.4.4.2 Timer Power Management
- 12.6.4.4.3 Timer Software Reset
- 12.6.4.4.4 Timer Interrupts
- 12.6.4.4.5 Timer Mode Functionality
- 12.6.4.4.6 Timer Capture Mode Functionality
- 12.6.4.4.7 Timer Compare Mode Functionality
- 12.6.4.4.8 Timer Prescaler Functionality
- 12.6.4.4.9 Timer Pulse-Width Modulation
- 12.6.4.4.10 Timer Counting Rate
- 12.6.4.4.11 Timer Under Emulation
- 12.6.4.4.12 Accessing Timer Registers
- 12.6.4.4.13 Timer Posted Mode Selection
- 12.6.4.5 Timers Low-Level Programming Models
- 12.7
Internal Diagnostics Modules
- 12.7.1
Dual Clock Comparator (DCC)
- 12.7.1.1 DCC Overview
- 12.7.1.2
DCC Functional Description
- 12.7.1.2.1 DCC Counter Operation
- 12.7.1.2.2 DCC Low Power Mode Operation
- 12.7.1.2.3 DCC Suspend Mode Behavior
- 12.7.1.2.4 DCC Single-Shot Mode
- 12.7.1.2.5 DCC Continuous mode
- 12.7.1.2.6 DCC Control and count hand-off across clock domains
- 12.7.1.2.7 DCC Error Trajectory record
- 12.7.1.2.8 DCC Count read registers
- 12.7.2
Error Signaling Module (ESM)
- 12.7.2.1 ESM Overview
- 12.7.2.2 ESM Environment
- 12.7.2.3 Integration
- 12.7.2.4
ESM Functional Description
- 12.7.2.4.1 ESM Interrupt Requests
- 12.7.2.4.2 ESM Error Event Inputs
- 12.7.2.4.3 ESM Error Pin Output
- 12.7.2.4.4 PWM Mode
- 12.7.2.4.5 ESM Minimum Time Interval
- 12.7.2.4.6 ESM Protection for Registers
- 12.7.2.4.7 ESM Clock Stop
- 12.7.3
Memory Cyclic Redundancy Check (MCRC) Controller
- 12.7.3.1 MCRC Overview
- 12.7.3.2
MCRC Functional Description
- 12.7.3.2.1 MCRC Block Diagram
- 12.7.3.2.2 MCRC General Operation
- 12.7.3.2.3 MCRC Modes of Operation
- 12.7.3.2.4 PSA Signature Register
- 12.7.3.2.5 PSA Sector Signature Register
- 12.7.3.2.6 CRC Value Register
- 12.7.3.2.7 Raw Data Register
- 12.7.3.2.8 Example DMA Controller Setup
- 12.7.3.2.9 Pattern Count Register
- 12.7.3.2.10 Sector Count Register/Current Sector Register
- 12.7.3.2.11 Interrupts
- 12.7.3.2.12 Power Down Mode
- 12.7.3.2.13 Emulation
- 12.7.3.3 MCRC Programming Examples
- 12.7.4 ECC Aggregator
- 12.7.5 Interconnect ECC Aggregators
- 12.7.1
Dual Clock Comparator (DCC)
- 12.1
Audio Peripherals
-
13On-Chip Debug
- 13.1 On-Chip Debug Overview
- 13.2 On-Chip Debugs Features
- 13.3
On-Chip Debug Functional Description
- 13.3.1 Block Diagram
- 13.3.2 Device Interfaces
- 13.3.3 Debug and Boundary Scan Access and Control
- 13.3.4 Debug Boot Modes and Boundary Scan Compliance
- 13.3.5 Power, Reset, Clock Management
- 13.3.6 Debug Cross Triggering
- 13.3.7 MAIN_R5F and WKUP_R5F Debug
- 13.3.8 SMS0_HSM Debug
- 13.3.9 C7XSS0 and C7XSS1 Debug
- 13.3.10 SoC Debug and Trace
- 13.3.11 Trace Traffic
-
14Registers
- 14.1
System Interconnect Registers
- 14.1.1
CBASS
- 14.1.1.1 CBASS Summaries
- 14.1.1.2
CBASS Registers
- 14.1.1.2.1 CBASS_ERR_PID Register
- 14.1.1.2.2 CBASS_ERR_DESTINATION_ID Register
- 14.1.1.2.3 CBASS_ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.4 CBASS_ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.5 CBASS_ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.6 CBASS_ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.7 CBASS_ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.8 CBASS_ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA3 Register
- 14.1.1.2.9 CBASS_ERR_ERR_INTR_RAW_STAT Register
- 14.1.1.2.10 CBASS_ERR_ERR_INTR_ENABLED_STAT Register
- 14.1.1.2.11 CBASS_ERR_ERR_INTR_ENABLE_SET Register
- 14.1.1.2.12 CBASS_ERR_ERR_INTR_ENABLE_CLR Register
- 14.1.1.2.13 CBASS_ERR_EOI Register
- 14.1.1.2.14 CBASS_FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.15 CBASS_FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.16 CBASS_FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.17 CBASS_FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.18 CBASS_FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.19 CBASS_FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.20 CBASS_FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.21 CBASS_FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.22 CBASS_FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_1_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.23 CBASS_FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.24 CBASS_FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.25 CBASS_FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.26 CBASS_FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.27 CBASS_FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.28 CBASS_FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.29 CBASS_FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.30 CBASS_FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_2_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.31 CBASS_FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.32 CBASS_FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.33 CBASS_FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.34 CBASS_FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.35 CBASS_FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.36 CBASS_FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.37 CBASS_FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.38 CBASS_FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_3_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.39 CBASS_FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.40 CBASS_FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.41 CBASS_FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.42 CBASS_FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.43 CBASS_FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.44 CBASS_FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.45 CBASS_FW_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_SLV_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.46 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.47 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.48 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.49 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.50 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.51 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.52 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.53 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.54 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_1_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.55 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.56 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.57 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.58 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.59 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.60 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.61 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.62 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_2_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.63 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.64 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.65 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.66 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.67 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.68 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.69 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.70 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_3_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.71 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.72 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.73 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.74 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.75 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.76 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.77 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.78 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_4_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.79 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.80 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.81 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.82 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_4_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.83 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_4_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.84 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_4_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.85 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_4_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.86 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_5_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.87 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.88 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.89 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.90 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_5_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.91 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_5_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.92 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_5_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.93 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_5_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.94 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_6_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.95 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.96 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.97 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.98 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_6_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.99 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_6_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.100 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_6_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.101 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_6_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.102 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_7_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.103 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.104 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.105 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.106 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_7_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.107 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_7_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.108 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_7_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.109 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_7_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.110 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_8_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.111 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_8_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.112 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_8_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.113 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_8_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.114 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_8_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.115 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_8_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.116 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_8_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.117 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_8_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.118 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_9_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.119 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_9_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.120 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_9_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.121 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_9_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.122 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_9_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.123 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_9_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.124 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_9_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.125 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_9_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.126 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_10_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.127 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_10_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.128 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_10_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.129 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_10_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.130 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_10_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.131 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_10_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.132 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_10_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.133 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_10_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.134 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_11_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.135 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_11_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.136 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_11_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.137 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_11_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.138 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_11_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.139 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_11_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.140 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_11_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.141 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_11_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.142 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_12_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.143 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_12_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.144 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_12_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.145 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_12_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.146 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_12_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.147 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_12_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.148 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_12_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.149 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_12_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.150 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_13_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.151 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_13_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.152 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_13_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.153 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_13_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.154 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_13_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.155 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_13_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.156 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_13_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.157 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_13_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.158 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_14_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.159 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_14_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.160 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_14_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.161 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_14_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.162 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_14_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.163 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_14_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.164 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_14_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.165 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_14_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.166 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_15_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.167 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_15_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.168 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_15_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.169 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_15_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.170 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_15_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.171 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_15_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.172 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_15_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.173 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_MAIN_INFRA_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_15_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.174 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.175 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.176 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.177 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.178 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.179 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.180 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.181 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.182 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_1_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.183 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.184 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.185 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.186 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.187 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.188 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.189 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.190 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_2_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.191 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.192 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.193 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.194 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.195 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.196 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.197 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.198 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_3_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.199 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.200 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.201 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.202 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.203 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.204 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.205 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.206 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_4_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.207 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.208 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.209 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.210 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_4_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.211 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_4_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.212 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_4_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.213 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_4_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.214 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_5_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.215 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.216 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.217 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.218 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_5_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.219 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_5_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.220 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_5_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.221 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_5_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.222 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_6_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.223 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.224 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.225 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.226 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_6_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.227 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_6_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.228 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_6_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.229 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_6_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.230 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_7_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.231 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.232 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.233 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.234 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_7_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.235 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_7_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.236 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_7_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.237 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_7_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.238 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_8_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.239 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_8_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.240 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_8_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.241 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_8_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.242 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_8_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.243 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_8_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.244 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_8_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.245 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_8_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.246 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_9_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.247 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_9_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.248 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_9_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.249 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_9_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.250 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_9_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.251 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_9_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.252 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_9_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.253 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_9_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.254 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_10_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.255 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_10_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.256 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_10_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.257 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_10_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.258 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_10_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.259 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_10_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.260 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_10_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.261 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_10_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.262 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_11_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.263 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_11_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.264 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_11_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.265 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_11_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.266 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_11_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.267 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_11_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.268 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_11_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.269 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_11_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.270 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_12_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.271 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_12_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.272 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_12_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.273 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_12_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.274 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_12_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.275 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_12_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.276 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_12_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.277 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_12_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.278 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_13_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.279 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_13_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.280 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_13_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.281 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_13_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.282 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_13_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.283 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_13_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.284 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_13_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.285 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_13_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.286 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_14_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.287 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_14_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.288 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_14_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.289 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_14_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.290 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_14_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.291 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_14_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.292 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_14_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.293 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_14_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.294 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_15_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.295 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_15_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.296 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_15_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.297 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_15_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.298 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_15_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.299 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_15_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.300 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_15_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.301 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_15_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.302 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_16_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.303 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_16_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.304 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_16_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.305 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_16_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.306 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_16_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.307 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_16_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.308 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_16_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.309 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_16_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.310 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_17_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.311 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_17_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.312 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_17_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.313 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_17_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.314 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_17_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.315 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_17_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.316 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_17_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.317 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_17_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.318 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_18_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.319 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_18_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.320 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_18_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.321 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_18_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.322 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_18_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.323 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_18_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.324 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_18_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.325 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_18_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.326 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_19_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.327 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_19_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.328 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_19_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.329 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_19_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.330 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_19_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.331 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_19_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.332 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_19_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.333 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_19_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.334 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_20_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.335 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_20_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.336 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_20_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.337 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_20_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.338 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_20_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.339 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_20_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.340 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_20_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.341 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_20_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.342 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_21_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.343 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_21_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.344 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_21_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.345 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_21_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.346 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_21_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.347 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_21_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.348 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_21_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.349 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_21_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.350 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_22_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.351 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_22_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.352 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_22_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.353 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_22_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.354 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_22_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.355 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_22_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.356 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_22_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.357 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_22_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.358 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_23_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.359 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_23_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.360 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_23_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.361 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_23_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.362 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_23_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.363 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_23_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.364 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_23_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.365 CBASS_FW_BR_SCRM_64_DM_CLK1_TO_SCRP_32_DM_CLK4_L0_FW_REGION_23_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.366 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.367 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.368 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.369 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.370 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.371 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.372 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.373 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.374 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_1_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.375 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.376 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.377 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.378 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.379 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.380 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.381 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.382 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_2_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.383 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.384 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.385 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.386 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.387 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.388 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.389 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.390 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_3_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.391 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.392 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.393 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.394 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.395 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.396 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.397 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.398 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_4_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.399 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.400 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.401 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.402 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_4_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.403 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_4_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.404 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_4_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.405 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_4_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.406 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_5_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.407 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.408 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.409 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.410 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_5_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.411 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_5_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.412 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_5_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.413 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_5_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.414 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_6_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.415 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.416 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.417 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.418 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_6_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.419 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_6_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.420 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_6_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.421 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_6_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.422 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_7_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.423 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.424 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.425 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.426 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_7_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.427 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_7_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.428 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_7_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.429 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_7_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.430 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_8_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.431 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_8_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.432 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_8_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.433 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_8_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.434 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_8_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.435 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_8_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.436 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_8_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.437 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_8_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.438 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_9_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.439 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_9_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.440 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_9_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.441 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_9_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.442 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_9_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.443 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_9_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.444 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_9_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.445 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_9_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.446 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_10_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.447 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_10_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.448 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_10_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.449 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_10_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.450 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_10_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.451 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_10_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.452 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_10_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.453 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_10_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.454 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_11_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.455 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_11_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.456 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_11_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.457 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_11_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.458 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_11_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.459 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_11_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.460 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_11_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.461 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_11_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.462 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_12_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.463 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_12_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.464 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_12_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.465 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_12_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.466 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_12_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.467 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_12_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.468 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_12_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.469 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_12_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.470 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_13_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.471 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_13_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.472 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_13_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.473 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_13_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.474 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_13_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.475 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_13_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.476 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_13_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.477 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_13_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.478 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_14_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.479 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_14_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.480 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_14_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.481 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_14_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.482 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_14_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.483 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_14_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.484 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_14_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.485 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_14_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.486 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_15_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.487 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_15_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.488 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_15_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.489 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_15_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.490 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_15_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.491 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_15_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.492 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_15_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.493 CBASS_FW_EXPORT_AM275_WKUP_DM_CBASS_TO_AM275_WKUP_SAFE_CBASS_DATA_L0_FW_REGION_15_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.494 CBASS_FW_IDMTIMER_DMC1MS_WKUP_0_TIMER_CFG_VBP_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.495 CBASS_FW_IDMTIMER_DMC1MS_WKUP_0_TIMER_CFG_VBP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.496 CBASS_FW_IDMTIMER_DMC1MS_WKUP_0_TIMER_CFG_VBP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.497 CBASS_FW_IDMTIMER_DMC1MS_WKUP_0_TIMER_CFG_VBP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.498 CBASS_FW_IDMTIMER_DMC1MS_WKUP_0_TIMER_CFG_VBP_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.499 CBASS_FW_IDMTIMER_DMC1MS_WKUP_0_TIMER_CFG_VBP_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.500 CBASS_FW_IDMTIMER_DMC1MS_WKUP_0_TIMER_CFG_VBP_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.501 CBASS_FW_IDMTIMER_DMC1MS_WKUP_0_TIMER_CFG_VBP_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.502 CBASS_FW_IDMTIMER_DMC1MS_WKUP_1_TIMER_CFG_VBP_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.503 CBASS_FW_IDMTIMER_DMC1MS_WKUP_1_TIMER_CFG_VBP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.504 CBASS_FW_IDMTIMER_DMC1MS_WKUP_1_TIMER_CFG_VBP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.505 CBASS_FW_IDMTIMER_DMC1MS_WKUP_1_TIMER_CFG_VBP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.506 CBASS_FW_IDMTIMER_DMC1MS_WKUP_1_TIMER_CFG_VBP_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.507 CBASS_FW_IDMTIMER_DMC1MS_WKUP_1_TIMER_CFG_VBP_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.508 CBASS_FW_IDMTIMER_DMC1MS_WKUP_1_TIMER_CFG_VBP_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.509 CBASS_FW_IDMTIMER_DMC1MS_WKUP_1_TIMER_CFG_VBP_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.510 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.511 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.512 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.513 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.514 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.515 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_1_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.516 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.517 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.518 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.519 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.520 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_2_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.521 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.522 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.523 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.524 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.525 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_3_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.526 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.527 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.528 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.529 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.530 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_DEF_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.531 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_RMST_ISC_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.532 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_RMST_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.533 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_RMST_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.534 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_RMST_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.535 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_RMST_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.536 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_RMST_ISC_REGION_1_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.537 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_RMST_ISC_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.538 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_RMST_ISC_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.539 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_RMST_ISC_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.540 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_RMST_ISC_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.541 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_RMST_ISC_REGION_2_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.542 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_RMST_ISC_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.543 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_RMST_ISC_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.544 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_RMST_ISC_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.545 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_RMST_ISC_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.546 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_RMST_ISC_REGION_3_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.547 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_RMST_ISC_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.548 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_RMST_ISC_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.549 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_RMST_ISC_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.550 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_RMST_ISC_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.551 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_RMST_ISC_REGION_DEF_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.552 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_WMST_ISC_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.553 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_WMST_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.554 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_WMST_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.555 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_WMST_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.556 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_WMST_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.557 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_WMST_ISC_REGION_1_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.558 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_WMST_ISC_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.559 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_WMST_ISC_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.560 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_WMST_ISC_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.561 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_WMST_ISC_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.562 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_WMST_ISC_REGION_2_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.563 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_WMST_ISC_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.564 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_WMST_ISC_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.565 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_WMST_ISC_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.566 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_WMST_ISC_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.567 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_WMST_ISC_REGION_3_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.568 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_WMST_ISC_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.569 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_WMST_ISC_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.570 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_WMST_ISC_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.1.2.571 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_WMST_ISC_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.1.2.572 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_WMST_ISC_REGION_DEF_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.573 CBASS_GLB_PID Register
- 14.1.1.2.574 CBASS_GLB_DESTINATION_ID Register
- 14.1.1.2.575 CBASS_GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.1.2.576 CBASS_GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.577 CBASS_GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.578 CBASS_GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.579 CBASS_GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA1 Register
- 14.1.1.2.580 CBASS_GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA2 Register
- 14.1.1.2.581 CBASS_GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA3 Register
- 14.1.1.2.582 CBASS_GLB_EXCEPTION_PEND_SET Register
- 14.1.1.2.583 CBASS_GLB_EXCEPTION_PEND_CLEAR Register
- 14.1.1.2.584 CBASS_QOS_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_PMST_MAP0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.585 CBASS_QOS_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_RMST_MAP0 Register
- 14.1.1.2.586 CBASS_QOS_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_WMST_MAP0 Register
- 14.1.2
CBASS_DBG
- 14.1.2.1 CBASS_DBG Summaries
- 14.1.2.2
CBASS_DBG Registers
- 14.1.2.2.1 CBASS_ERR_PID Register
- 14.1.2.2.2 CBASS_ERR_DESTINATION_ID Register
- 14.1.2.2.3 CBASS_ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER0 Register
- 14.1.2.2.4 CBASS_ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER1 Register
- 14.1.2.2.5 CBASS_ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA0 Register
- 14.1.2.2.6 CBASS_ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA1 Register
- 14.1.2.2.7 CBASS_ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA2 Register
- 14.1.2.2.8 CBASS_ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA3 Register
- 14.1.2.2.9 CBASS_ERR_ERR_INTR_RAW_STAT Register
- 14.1.2.2.10 CBASS_ERR_ERR_INTR_ENABLED_STAT Register
- 14.1.2.2.11 CBASS_ERR_ERR_INTR_ENABLE_SET Register
- 14.1.2.2.12 CBASS_ERR_ERR_INTR_ENABLE_CLR Register
- 14.1.2.2.13 CBASS_ERR_EOI Register
- 14.1.3
CBASS_INFRA
- 14.1.3.1 CBASS_INFRA Summaries
- 14.1.3.2
CBASS_INFRA Registers
- 14.1.3.2.1 CBASS_ERR_PID Register
- 14.1.3.2.2 CBASS_ERR_DESTINATION_ID Register
- 14.1.3.2.3 CBASS_ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER0 Register
- 14.1.3.2.4 CBASS_ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER1 Register
- 14.1.3.2.5 CBASS_ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA0 Register
- 14.1.3.2.6 CBASS_ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA1 Register
- 14.1.3.2.7 CBASS_ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA2 Register
- 14.1.3.2.8 CBASS_ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA3 Register
- 14.1.3.2.9 CBASS_ERR_ERR_INTR_RAW_STAT Register
- 14.1.3.2.10 CBASS_ERR_ERR_INTR_ENABLED_STAT Register
- 14.1.3.2.11 CBASS_ERR_ERR_INTR_ENABLE_SET Register
- 14.1.3.2.12 CBASS_ERR_ERR_INTR_ENABLE_CLR Register
- 14.1.3.2.13 CBASS_ERR_EOI Register
- 14.1.3.2.14 CBASS_FW_IAM275_MAIN_PSC_WRAP_MAIN_0_VBUS_FWCH_REGION_0_CH_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.3.2.15 CBASS_FW_IAM275_MAIN_PSC_WRAP_MAIN_0_VBUS_FWCH_REGION_0_CH_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.3.2.16 CBASS_FW_IAM275_MAIN_PSC_WRAP_MAIN_0_VBUS_FWCH_REGION_0_CH_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.3.2.17 CBASS_FW_IAM275_MAIN_PSC_WRAP_MAIN_0_VBUS_FWCH_REGION_0_CH_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.3.2.18 CBASS_FW_IAM275_MAIN_PSC_WRAP_MAIN_0_VBUS_FWCH_REGION_1_CH_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.3.2.19 CBASS_FW_IAM275_MAIN_PSC_WRAP_MAIN_0_VBUS_FWCH_REGION_1_CH_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.3.2.20 CBASS_FW_IAM275_MAIN_PSC_WRAP_MAIN_0_VBUS_FWCH_REGION_1_CH_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.3.2.21 CBASS_FW_IAM275_MAIN_PSC_WRAP_MAIN_0_VBUS_FWCH_REGION_1_CH_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.3.2.22 CBASS_FW_IAM275_MAIN_PSC_WRAP_MAIN_0_VBUS_FWCH_REGION_2_CH_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.3.2.23 CBASS_FW_IAM275_MAIN_PSC_WRAP_MAIN_0_VBUS_FWCH_REGION_2_CH_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.3.2.24 CBASS_FW_IAM275_MAIN_PSC_WRAP_MAIN_0_VBUS_FWCH_REGION_2_CH_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.3.2.25 CBASS_FW_IAM275_MAIN_PSC_WRAP_MAIN_0_VBUS_FWCH_REGION_2_CH_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.3.2.26 CBASS_FW_IAM275_MAIN_PSC_WRAP_MAIN_0_VBUS_FWCH_REGION_3_CH_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.3.2.27 CBASS_FW_IAM275_MAIN_PSC_WRAP_MAIN_0_VBUS_FWCH_REGION_3_CH_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.3.2.28 CBASS_FW_IAM275_MAIN_PSC_WRAP_MAIN_0_VBUS_FWCH_REGION_3_CH_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.3.2.29 CBASS_FW_IAM275_MAIN_PSC_WRAP_MAIN_0_VBUS_FWCH_REGION_3_CH_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.3.2.30 CBASS_FW_IAM275_MAIN_PSC_WRAP_MAIN_0_VBUS_FWCH_REGION_4_CH_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.3.2.31 CBASS_FW_IAM275_MAIN_PSC_WRAP_MAIN_0_VBUS_FWCH_REGION_4_CH_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.3.2.32 CBASS_FW_IAM275_MAIN_PSC_WRAP_MAIN_0_VBUS_FWCH_REGION_4_CH_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.3.2.33 CBASS_FW_IAM275_MAIN_PSC_WRAP_MAIN_0_VBUS_FWCH_REGION_4_CH_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.3.2.34 CBASS_GLB_PID Register
- 14.1.3.2.35 CBASS_GLB_DESTINATION_ID Register
- 14.1.3.2.36 CBASS_GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.3.2.37 CBASS_GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER0 Register
- 14.1.3.2.38 CBASS_GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER1 Register
- 14.1.3.2.39 CBASS_GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA0 Register
- 14.1.3.2.40 CBASS_GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA1 Register
- 14.1.3.2.41 CBASS_GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA2 Register
- 14.1.3.2.42 CBASS_GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA3 Register
- 14.1.3.2.43 CBASS_GLB_EXCEPTION_PEND_SET Register
- 14.1.3.2.44 CBASS_GLB_EXCEPTION_PEND_CLEAR Register
- 14.1.4
CBASS_MCASP
- 14.1.4.1 CBASS_MCASP Summaries
- 14.1.4.2
CBASS_MCASP Registers
- 14.1.4.2.1 CBASS_ERR_PID Register
- 14.1.4.2.2 CBASS_ERR_DESTINATION_ID Register
- 14.1.4.2.3 CBASS_ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER0 Register
- 14.1.4.2.4 CBASS_ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER1 Register
- 14.1.4.2.5 CBASS_ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA0 Register
- 14.1.4.2.6 CBASS_ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA1 Register
- 14.1.4.2.7 CBASS_ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA2 Register
- 14.1.4.2.8 CBASS_ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA3 Register
- 14.1.4.2.9 CBASS_ERR_ERR_INTR_RAW_STAT Register
- 14.1.4.2.10 CBASS_ERR_ERR_INTR_ENABLED_STAT Register
- 14.1.4.2.11 CBASS_ERR_ERR_INTR_ENABLE_SET Register
- 14.1.4.2.12 CBASS_ERR_ERR_INTR_ENABLE_CLR Register
- 14.1.4.2.13 CBASS_ERR_EOI Register
- 14.1.5
CBASS_MEM
- 14.1.5.1 CBASS_MEM Summaries
- 14.1.5.2
CBASS_MEM Registers
- 14.1.5.2.1 CBASS_ERR_PID Register
- 14.1.5.2.2 CBASS_ERR_DESTINATION_ID Register
- 14.1.5.2.3 CBASS_ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.4 CBASS_ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.5 CBASS_ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.6 CBASS_ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.7 CBASS_ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.8 CBASS_ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA3 Register
- 14.1.5.2.9 CBASS_ERR_ERR_INTR_RAW_STAT Register
- 14.1.5.2.10 CBASS_ERR_ERR_INTR_ENABLED_STAT Register
- 14.1.5.2.11 CBASS_ERR_ERR_INTR_ENABLE_SET Register
- 14.1.5.2.12 CBASS_ERR_ERR_INTR_ENABLE_CLR Register
- 14.1.5.2.13 CBASS_ERR_EOI Register
- 14.1.5.2.14 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.15 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.16 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.17 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.18 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.19 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.20 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.21 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.22 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_1_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.23 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.24 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.25 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.26 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.27 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.28 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.29 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.30 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_2_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.31 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.32 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.33 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.34 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.35 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.36 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.37 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.38 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_3_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.39 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.40 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.41 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.42 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.43 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.44 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.45 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.46 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_4_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.47 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.48 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.49 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.50 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_4_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.51 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_4_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.52 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_4_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.53 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_4_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.54 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_5_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.55 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.56 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.57 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.58 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_5_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.59 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_5_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.60 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_5_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.61 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_5_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.62 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_6_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.63 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.64 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.65 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.66 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_6_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.67 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_6_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.68 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_6_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.69 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_6_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.70 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_7_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.71 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.72 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.73 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.74 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_7_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.75 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_7_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.76 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_7_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.77 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_7_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.78 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.79 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.80 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.81 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.82 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.83 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.84 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.85 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.86 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_1_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.87 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.88 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.89 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.90 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.91 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.92 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.93 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.94 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_2_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.95 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.96 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.97 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.98 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.99 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.100 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.101 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.102 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_3_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.103 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.104 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.105 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.106 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.107 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.108 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.109 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.110 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_4_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.111 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.112 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.113 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.114 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_4_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.115 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_4_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.116 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_4_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.117 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_4_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.118 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_5_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.119 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.120 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.121 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.122 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_5_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.123 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_5_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.124 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_5_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.125 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_5_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.126 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_6_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.127 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.128 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.129 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.130 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_6_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.131 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_6_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.132 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_6_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.133 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_6_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.134 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_7_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.135 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.136 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.137 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.138 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_7_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.139 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_7_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.140 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_7_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.141 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_7_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.142 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.143 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.144 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.145 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.146 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.147 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.148 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.149 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.150 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_1_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.151 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.152 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.153 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.154 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.155 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.156 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.157 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.158 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_2_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.159 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.160 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.161 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.162 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.163 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.164 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.165 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.166 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_3_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.167 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.168 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.169 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.170 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.171 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.172 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.173 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.174 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_4_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.175 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.176 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.177 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.178 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_4_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.179 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_4_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.180 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_4_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.181 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_4_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.182 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_5_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.183 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.184 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.185 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.186 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_5_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.187 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_5_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.188 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_5_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.189 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_5_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.190 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_6_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.191 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.192 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.193 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.194 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_6_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.195 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_6_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.196 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_6_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.197 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_6_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.198 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_7_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.199 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.200 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.201 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.202 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_7_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.203 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_7_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.204 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_7_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.205 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_7_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.206 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.207 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.208 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.209 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.210 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.211 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.212 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.213 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.214 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_1_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.215 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.216 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.217 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.218 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.219 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.220 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.221 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.222 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_2_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.223 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.224 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.225 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.226 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.227 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.228 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.229 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.230 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_3_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.231 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.232 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.233 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.234 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.235 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.236 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.237 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.238 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_4_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.239 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.240 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.241 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.242 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_4_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.243 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_4_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.244 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_4_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.245 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_4_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.246 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_5_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.247 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.248 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.249 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.250 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_5_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.251 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_5_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.252 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_5_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.253 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_5_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.254 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_6_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.255 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.256 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.257 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.258 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_6_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.259 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_6_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.260 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_6_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.261 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_6_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.262 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_7_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.263 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.264 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.265 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.266 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_7_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.267 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_7_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.268 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_7_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.269 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_7_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.270 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.271 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.272 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.273 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.274 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.275 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.276 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.277 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.278 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_1_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.279 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.280 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.281 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.282 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.283 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.284 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.285 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.286 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_2_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.287 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.288 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.289 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.290 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.291 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.292 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.293 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.294 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_3_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.295 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.296 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.297 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.298 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.299 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.300 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.301 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.302 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_4_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.303 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.304 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.305 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.306 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_4_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.307 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_4_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.308 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_4_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.309 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_4_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.310 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_5_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.311 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.312 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.313 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.314 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_5_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.315 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_5_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.316 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_5_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.317 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_5_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.318 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_6_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.319 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.320 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.321 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.322 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_6_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.323 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_6_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.324 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_6_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.325 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_6_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.326 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_7_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.327 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.328 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.329 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.330 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_7_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.331 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_7_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.332 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_7_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.333 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_7_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.334 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.335 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.336 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.337 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.338 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.339 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.340 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.341 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.342 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_1_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.343 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.344 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.345 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.346 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.347 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.348 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.349 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.350 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_2_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.351 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.352 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.353 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.354 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.355 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.356 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.357 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.358 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_3_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.359 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.360 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.361 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.362 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.363 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.364 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.365 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.366 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_4_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.367 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.368 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.369 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.370 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_4_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.371 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_4_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.372 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_4_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.373 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_4_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.374 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_5_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.375 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.376 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.377 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.378 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_5_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.379 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_5_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.380 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_5_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.381 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_5_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.382 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_6_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.383 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.384 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.385 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.386 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_6_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.387 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_6_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.388 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_6_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.389 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_6_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.390 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_7_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.391 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.392 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.393 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.394 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_7_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.395 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_7_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.396 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_7_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.397 CBASS_FW_IMSRAM32KX256E_MAIN_5_SLV_FW_REGION_7_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.398 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.399 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.400 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.401 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.402 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.403 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.404 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.405 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.406 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_1_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.407 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.408 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.409 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.410 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.411 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.412 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.413 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.414 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_2_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.415 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.416 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.417 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.418 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.419 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.420 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.421 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.422 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_3_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.423 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.424 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.425 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.426 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.427 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.428 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.429 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.430 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_4_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.431 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.432 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.433 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.434 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_4_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.435 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_4_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.436 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_4_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.437 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_4_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.438 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_5_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.439 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.440 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.441 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.442 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_5_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.443 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_5_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.444 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_5_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.445 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_5_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.446 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_6_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.447 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.448 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.449 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.450 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_6_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.451 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_6_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.452 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_6_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.453 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_6_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.454 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_7_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.455 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.456 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.457 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.458 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_7_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.459 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_7_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.460 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_7_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.461 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_7_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.462 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.463 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.464 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.465 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.466 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.467 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.468 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.469 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.470 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_1_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.471 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.472 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.473 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.474 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.475 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.476 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.477 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.478 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_2_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.479 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.480 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.481 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.482 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.483 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.484 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.485 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.486 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_3_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.487 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.488 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.489 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.490 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.491 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.492 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.493 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.494 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_4_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.495 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.496 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.497 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.498 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_4_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.499 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_4_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.500 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_4_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.501 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_4_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.502 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_5_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.503 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.504 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.505 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.506 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_5_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.507 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_5_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.508 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_5_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.509 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_5_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.510 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_6_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.511 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.512 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.513 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.514 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_6_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.515 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_6_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.516 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_6_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.517 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_6_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.518 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_7_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.519 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.520 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.521 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.522 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_7_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.523 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_7_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.524 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_7_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.525 CBASS_FW_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_SOC_C7XV_FW_REGION_7_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.526 CBASS_ISC_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_C7XV_SOC_ISC_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.527 CBASS_ISC_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_C7XV_SOC_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.528 CBASS_ISC_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_C7XV_SOC_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.529 CBASS_ISC_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_C7XV_SOC_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.530 CBASS_ISC_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_C7XV_SOC_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.531 CBASS_ISC_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_C7XV_SOC_ISC_REGION_1_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.532 CBASS_ISC_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_C7XV_SOC_ISC_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.533 CBASS_ISC_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_C7XV_SOC_ISC_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.534 CBASS_ISC_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_C7XV_SOC_ISC_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.535 CBASS_ISC_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_C7XV_SOC_ISC_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.536 CBASS_ISC_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_C7XV_SOC_ISC_REGION_DEF_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.537 CBASS_ISC_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_C7XV_SOC_ISC_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.538 CBASS_ISC_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_C7XV_SOC_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.539 CBASS_ISC_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_C7XV_SOC_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.540 CBASS_ISC_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_C7XV_SOC_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.541 CBASS_ISC_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_C7XV_SOC_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.542 CBASS_ISC_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_C7XV_SOC_ISC_REGION_1_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.543 CBASS_ISC_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_C7XV_SOC_ISC_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.544 CBASS_ISC_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_C7XV_SOC_ISC_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.545 CBASS_ISC_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_C7XV_SOC_ISC_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.546 CBASS_ISC_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_C7XV_SOC_ISC_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.547 CBASS_ISC_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_C7XV_SOC_ISC_REGION_DEF_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.548 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_IIFR_ISC_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.549 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_IIFR_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.550 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_IIFR_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.551 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_IIFR_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.552 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_IIFR_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.553 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_IIFR_ISC_REGION_1_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.554 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_IIFR_ISC_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.555 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_IIFR_ISC_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.556 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_IIFR_ISC_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.557 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_IIFR_ISC_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.558 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_IIFR_ISC_REGION_2_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.559 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_IIFR_ISC_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.560 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_IIFR_ISC_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.561 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_IIFR_ISC_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.562 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_IIFR_ISC_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.563 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_IIFR_ISC_REGION_3_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.564 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_IIFR_ISC_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.565 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_IIFR_ISC_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.566 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_IIFR_ISC_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.567 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_IIFR_ISC_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.568 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_IIFR_ISC_REGION_DEF_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.569 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_IIFW_ISC_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.570 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_IIFW_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.571 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_IIFW_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.572 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_IIFW_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.573 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_IIFW_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.574 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_IIFW_ISC_REGION_1_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.575 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_IIFW_ISC_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.576 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_IIFW_ISC_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.577 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_IIFW_ISC_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.578 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_IIFW_ISC_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.579 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_IIFW_ISC_REGION_2_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.580 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_IIFW_ISC_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.581 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_IIFW_ISC_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.582 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_IIFW_ISC_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.583 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_IIFW_ISC_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.584 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_IIFW_ISC_REGION_3_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.585 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_IIFW_ISC_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.586 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_IIFW_ISC_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.587 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_IIFW_ISC_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.588 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_IIFW_ISC_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.589 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_IIFW_ISC_REGION_DEF_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.590 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_IIFR_ISC_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.591 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_IIFR_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.592 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_IIFR_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.593 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_IIFR_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.594 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_IIFR_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.595 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_IIFR_ISC_REGION_1_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.596 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_IIFR_ISC_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.597 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_IIFR_ISC_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.598 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_IIFR_ISC_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.599 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_IIFR_ISC_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.600 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_IIFR_ISC_REGION_2_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.601 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_IIFR_ISC_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.602 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_IIFR_ISC_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.603 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_IIFR_ISC_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.604 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_IIFR_ISC_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.605 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_IIFR_ISC_REGION_3_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.606 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_IIFR_ISC_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.607 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_IIFR_ISC_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.608 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_IIFR_ISC_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.609 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_IIFR_ISC_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.610 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_IIFR_ISC_REGION_DEF_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.611 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_IIFW_ISC_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.612 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_IIFW_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.613 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_IIFW_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.614 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_IIFW_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.615 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_IIFW_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.616 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_IIFW_ISC_REGION_1_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.617 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_IIFW_ISC_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.618 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_IIFW_ISC_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.619 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_IIFW_ISC_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.620 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_IIFW_ISC_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.621 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_IIFW_ISC_REGION_2_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.622 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_IIFW_ISC_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.623 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_IIFW_ISC_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.624 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_IIFW_ISC_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.625 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_IIFW_ISC_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.626 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_IIFW_ISC_REGION_3_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.627 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_IIFW_ISC_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.628 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_IIFW_ISC_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.629 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_IIFW_ISC_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.630 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_IIFW_ISC_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.631 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_IIFW_ISC_REGION_DEF_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.632 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_IIFR_ISC_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.633 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_IIFR_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.634 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_IIFR_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.635 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_IIFR_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.636 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_IIFR_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.637 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_IIFR_ISC_REGION_1_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.638 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_IIFR_ISC_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.639 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_IIFR_ISC_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.640 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_IIFR_ISC_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.641 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_IIFR_ISC_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.642 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_IIFR_ISC_REGION_2_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.643 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_IIFR_ISC_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.644 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_IIFR_ISC_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.645 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_IIFR_ISC_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.646 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_IIFR_ISC_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.647 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_IIFR_ISC_REGION_3_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.648 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_IIFR_ISC_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.649 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_IIFR_ISC_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.650 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_IIFR_ISC_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.651 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_IIFR_ISC_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.652 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_IIFR_ISC_REGION_DEF_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.653 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_IIFW_ISC_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.654 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_IIFW_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.655 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_IIFW_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.656 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_IIFW_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.657 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_IIFW_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.658 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_IIFW_ISC_REGION_1_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.659 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_IIFW_ISC_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.660 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_IIFW_ISC_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.661 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_IIFW_ISC_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.662 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_IIFW_ISC_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.663 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_IIFW_ISC_REGION_2_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.664 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_IIFW_ISC_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.665 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_IIFW_ISC_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.666 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_IIFW_ISC_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.667 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_IIFW_ISC_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.668 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_IIFW_ISC_REGION_3_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.669 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_IIFW_ISC_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.670 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_IIFW_ISC_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.671 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_IIFW_ISC_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.672 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_IIFW_ISC_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.673 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_IIFW_ISC_REGION_DEF_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.674 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_IIFR_ISC_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.675 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_IIFR_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.676 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_IIFR_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.677 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_IIFR_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.678 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_IIFR_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.679 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_IIFR_ISC_REGION_1_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.680 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_IIFR_ISC_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.681 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_IIFR_ISC_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.682 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_IIFR_ISC_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.683 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_IIFR_ISC_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.684 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_IIFR_ISC_REGION_2_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.685 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_IIFR_ISC_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.686 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_IIFR_ISC_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.687 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_IIFR_ISC_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.688 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_IIFR_ISC_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.689 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_IIFR_ISC_REGION_3_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.690 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_IIFR_ISC_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.691 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_IIFR_ISC_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.692 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_IIFR_ISC_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.693 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_IIFR_ISC_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.694 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_IIFR_ISC_REGION_DEF_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.695 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_IIFW_ISC_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.696 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_IIFW_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.697 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_IIFW_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.698 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_IIFW_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.699 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_IIFW_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.700 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_IIFW_ISC_REGION_1_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.701 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_IIFW_ISC_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.702 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_IIFW_ISC_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.703 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_IIFW_ISC_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.704 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_IIFW_ISC_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.705 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_IIFW_ISC_REGION_2_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.706 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_IIFW_ISC_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.707 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_IIFW_ISC_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.708 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_IIFW_ISC_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.709 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_IIFW_ISC_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.710 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_IIFW_ISC_REGION_3_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.711 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_IIFW_ISC_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.712 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_IIFW_ISC_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.713 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_IIFW_ISC_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.5.2.714 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_IIFW_ISC_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.5.2.715 CBASS_ISC_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_IIFW_ISC_REGION_DEF_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.716 CBASS_GLB_PID Register
- 14.1.5.2.717 CBASS_GLB_DESTINATION_ID Register
- 14.1.5.2.718 CBASS_GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.5.2.719 CBASS_GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.720 CBASS_GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.721 CBASS_GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.722 CBASS_GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.723 CBASS_GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA2 Register
- 14.1.5.2.724 CBASS_GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA3 Register
- 14.1.5.2.725 CBASS_GLB_EXCEPTION_PEND_SET Register
- 14.1.5.2.726 CBASS_GLB_EXCEPTION_PEND_CLEAR Register
- 14.1.5.2.727 CBASS_QOS_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_C7XV_SOC_MAP0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.728 CBASS_QOS_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_0_MAIN_0_C7XV_SOC_MAP1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.729 CBASS_QOS_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_C7XV_SOC_MAP0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.730 CBASS_QOS_IAM275_C7XV_WRAP_1_MAIN_0_C7XV_SOC_MAP1 Register
- 14.1.5.2.731 CBASS_QOS_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_IIFR_MAP0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.732 CBASS_QOS_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_IIFW_MAP0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.733 CBASS_QOS_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_IIFR_MAP0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.734 CBASS_QOS_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_IIFW_MAP0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.735 CBASS_QOS_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_IIFR_MAP0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.736 CBASS_QOS_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_IIFW_MAP0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.737 CBASS_QOS_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_IIFR_MAP0 Register
- 14.1.5.2.738 CBASS_QOS_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_IIFW_MAP0 Register
- 14.1.6
CBASS_MISC_PERI
- 14.1.6.1 CBASS_MISC_PERI Summaries
- 14.1.6.2
CBASS_MISC_PERI Registers
- 14.1.6.2.1 CBASS_ERR_PID Register
- 14.1.6.2.2 CBASS_ERR_DESTINATION_ID Register
- 14.1.6.2.3 CBASS_ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER0 Register
- 14.1.6.2.4 CBASS_ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER1 Register
- 14.1.6.2.5 CBASS_ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA0 Register
- 14.1.6.2.6 CBASS_ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA1 Register
- 14.1.6.2.7 CBASS_ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA2 Register
- 14.1.6.2.8 CBASS_ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA3 Register
- 14.1.6.2.9 CBASS_ERR_ERR_INTR_RAW_STAT Register
- 14.1.6.2.10 CBASS_ERR_ERR_INTR_ENABLED_STAT Register
- 14.1.6.2.11 CBASS_ERR_ERR_INTR_ENABLE_SET Register
- 14.1.6.2.12 CBASS_ERR_ERR_INTR_ENABLE_CLR Register
- 14.1.6.2.13 CBASS_ERR_EOI Register
- 14.1.6.2.14 CBASS_FW_IADC12FC_16FFC_MAIN_0_CBA0_CFG_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.15 CBASS_FW_IADC12FC_16FFC_MAIN_0_CBA0_CFG_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.6.2.16 CBASS_FW_IADC12FC_16FFC_MAIN_0_CBA0_CFG_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.6.2.17 CBASS_FW_IADC12FC_16FFC_MAIN_0_CBA0_CFG_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.6.2.18 CBASS_FW_IADC12FC_16FFC_MAIN_0_CBA0_CFG_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.19 CBASS_FW_IADC12FC_16FFC_MAIN_0_CBA0_CFG_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.20 CBASS_FW_IADC12FC_16FFC_MAIN_0_CBA0_CFG_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.21 CBASS_FW_IADC12FC_16FFC_MAIN_0_CBA0_CFG_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.22 CBASS_FW_IADC12FC_16FFC_MAIN_0_CBA1_DMA_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.23 CBASS_FW_IADC12FC_16FFC_MAIN_0_CBA1_DMA_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.6.2.24 CBASS_FW_IADC12FC_16FFC_MAIN_0_CBA1_DMA_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.6.2.25 CBASS_FW_IADC12FC_16FFC_MAIN_0_CBA1_DMA_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.6.2.26 CBASS_FW_IADC12FC_16FFC_MAIN_0_CBA1_DMA_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.27 CBASS_FW_IADC12FC_16FFC_MAIN_0_CBA1_DMA_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.28 CBASS_FW_IADC12FC_16FFC_MAIN_0_CBA1_DMA_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.29 CBASS_FW_IADC12FC_16FFC_MAIN_0_CBA1_DMA_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.30 CBASS_FW_IAM275_MAIN_MEM_CBASS_MAIN_0_CBASS_ERR_SLV_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.31 CBASS_FW_IAM275_MAIN_MEM_CBASS_MAIN_0_CBASS_ERR_SLV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.6.2.32 CBASS_FW_IAM275_MAIN_MEM_CBASS_MAIN_0_CBASS_ERR_SLV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.6.2.33 CBASS_FW_IAM275_MAIN_MEM_CBASS_MAIN_0_CBASS_ERR_SLV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.6.2.34 CBASS_FW_IAM275_MAIN_MEM_CBASS_MAIN_0_CBASS_ERR_SLV_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.35 CBASS_FW_IAM275_MAIN_MEM_CBASS_MAIN_0_CBASS_ERR_SLV_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.36 CBASS_FW_IAM275_MAIN_MEM_CBASS_MAIN_0_CBASS_ERR_SLV_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.37 CBASS_FW_IAM275_MAIN_MEM_CBASS_MAIN_0_CBASS_ERR_SLV_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.38 CBASS_FW_IECAP_MAIN_0_ECAP_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.39 CBASS_FW_IECAP_MAIN_0_ECAP_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.6.2.40 CBASS_FW_IECAP_MAIN_0_ECAP_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.6.2.41 CBASS_FW_IECAP_MAIN_0_ECAP_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.6.2.42 CBASS_FW_IECAP_MAIN_0_ECAP_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.43 CBASS_FW_IECAP_MAIN_0_ECAP_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.44 CBASS_FW_IECAP_MAIN_0_ECAP_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.45 CBASS_FW_IECAP_MAIN_0_ECAP_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.46 CBASS_FW_IECAP_MAIN_1_ECAP_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.47 CBASS_FW_IECAP_MAIN_1_ECAP_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.6.2.48 CBASS_FW_IECAP_MAIN_1_ECAP_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.6.2.49 CBASS_FW_IECAP_MAIN_1_ECAP_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.6.2.50 CBASS_FW_IECAP_MAIN_1_ECAP_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.51 CBASS_FW_IECAP_MAIN_1_ECAP_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.52 CBASS_FW_IECAP_MAIN_1_ECAP_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.53 CBASS_FW_IECAP_MAIN_1_ECAP_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.54 CBASS_FW_IECAP_MAIN_2_ECAP_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.55 CBASS_FW_IECAP_MAIN_2_ECAP_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.6.2.56 CBASS_FW_IECAP_MAIN_2_ECAP_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.6.2.57 CBASS_FW_IECAP_MAIN_2_ECAP_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.6.2.58 CBASS_FW_IECAP_MAIN_2_ECAP_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.59 CBASS_FW_IECAP_MAIN_2_ECAP_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.60 CBASS_FW_IECAP_MAIN_2_ECAP_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.61 CBASS_FW_IECAP_MAIN_2_ECAP_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.62 CBASS_FW_IECAP_MAIN_3_ECAP_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.63 CBASS_FW_IECAP_MAIN_3_ECAP_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.6.2.64 CBASS_FW_IECAP_MAIN_3_ECAP_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.6.2.65 CBASS_FW_IECAP_MAIN_3_ECAP_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.6.2.66 CBASS_FW_IECAP_MAIN_3_ECAP_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.67 CBASS_FW_IECAP_MAIN_3_ECAP_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.68 CBASS_FW_IECAP_MAIN_3_ECAP_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.69 CBASS_FW_IECAP_MAIN_3_ECAP_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.70 CBASS_FW_IECAP_MAIN_4_ECAP_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.71 CBASS_FW_IECAP_MAIN_4_ECAP_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.6.2.72 CBASS_FW_IECAP_MAIN_4_ECAP_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.6.2.73 CBASS_FW_IECAP_MAIN_4_ECAP_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.6.2.74 CBASS_FW_IECAP_MAIN_4_ECAP_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.75 CBASS_FW_IECAP_MAIN_4_ECAP_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.76 CBASS_FW_IECAP_MAIN_4_ECAP_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.77 CBASS_FW_IECAP_MAIN_4_ECAP_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.78 CBASS_FW_IECAP_MAIN_5_ECAP_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.79 CBASS_FW_IECAP_MAIN_5_ECAP_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.6.2.80 CBASS_FW_IECAP_MAIN_5_ECAP_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.6.2.81 CBASS_FW_IECAP_MAIN_5_ECAP_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.6.2.82 CBASS_FW_IECAP_MAIN_5_ECAP_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.83 CBASS_FW_IECAP_MAIN_5_ECAP_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.84 CBASS_FW_IECAP_MAIN_5_ECAP_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.85 CBASS_FW_IECAP_MAIN_5_ECAP_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.86 CBASS_FW_IK3_EPWM_MAIN_0_EPWM_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.87 CBASS_FW_IK3_EPWM_MAIN_0_EPWM_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.6.2.88 CBASS_FW_IK3_EPWM_MAIN_0_EPWM_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.6.2.89 CBASS_FW_IK3_EPWM_MAIN_0_EPWM_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.6.2.90 CBASS_FW_IK3_EPWM_MAIN_0_EPWM_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.91 CBASS_FW_IK3_EPWM_MAIN_0_EPWM_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.92 CBASS_FW_IK3_EPWM_MAIN_0_EPWM_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.93 CBASS_FW_IK3_EPWM_MAIN_0_EPWM_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.94 CBASS_FW_IK3_EPWM_MAIN_1_EPWM_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.95 CBASS_FW_IK3_EPWM_MAIN_1_EPWM_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.6.2.96 CBASS_FW_IK3_EPWM_MAIN_1_EPWM_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.6.2.97 CBASS_FW_IK3_EPWM_MAIN_1_EPWM_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.6.2.98 CBASS_FW_IK3_EPWM_MAIN_1_EPWM_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.99 CBASS_FW_IK3_EPWM_MAIN_1_EPWM_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.100 CBASS_FW_IK3_EPWM_MAIN_1_EPWM_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.101 CBASS_FW_IK3_EPWM_MAIN_1_EPWM_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.102 CBASS_FW_IK3_EPWM_MAIN_2_EPWM_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.103 CBASS_FW_IK3_EPWM_MAIN_2_EPWM_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.6.2.104 CBASS_FW_IK3_EPWM_MAIN_2_EPWM_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.6.2.105 CBASS_FW_IK3_EPWM_MAIN_2_EPWM_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.6.2.106 CBASS_FW_IK3_EPWM_MAIN_2_EPWM_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.107 CBASS_FW_IK3_EPWM_MAIN_2_EPWM_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.108 CBASS_FW_IK3_EPWM_MAIN_2_EPWM_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.109 CBASS_FW_IK3_EPWM_MAIN_2_EPWM_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.110 CBASS_FW_IMSHSI2C_MAIN_0_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.111 CBASS_FW_IMSHSI2C_MAIN_0_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.6.2.112 CBASS_FW_IMSHSI2C_MAIN_0_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.6.2.113 CBASS_FW_IMSHSI2C_MAIN_0_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.6.2.114 CBASS_FW_IMSHSI2C_MAIN_0_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.115 CBASS_FW_IMSHSI2C_MAIN_0_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.116 CBASS_FW_IMSHSI2C_MAIN_0_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.117 CBASS_FW_IMSHSI2C_MAIN_0_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.118 CBASS_FW_IMSHSI2C_MAIN_1_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.119 CBASS_FW_IMSHSI2C_MAIN_1_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.6.2.120 CBASS_FW_IMSHSI2C_MAIN_1_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.6.2.121 CBASS_FW_IMSHSI2C_MAIN_1_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.6.2.122 CBASS_FW_IMSHSI2C_MAIN_1_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.123 CBASS_FW_IMSHSI2C_MAIN_1_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.124 CBASS_FW_IMSHSI2C_MAIN_1_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.125 CBASS_FW_IMSHSI2C_MAIN_1_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.126 CBASS_FW_IMSHSI2C_MAIN_2_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.127 CBASS_FW_IMSHSI2C_MAIN_2_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.6.2.128 CBASS_FW_IMSHSI2C_MAIN_2_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.6.2.129 CBASS_FW_IMSHSI2C_MAIN_2_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.6.2.130 CBASS_FW_IMSHSI2C_MAIN_2_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.131 CBASS_FW_IMSHSI2C_MAIN_2_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.132 CBASS_FW_IMSHSI2C_MAIN_2_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.133 CBASS_FW_IMSHSI2C_MAIN_2_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.134 CBASS_FW_IMSHSI2C_MAIN_3_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.135 CBASS_FW_IMSHSI2C_MAIN_3_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.6.2.136 CBASS_FW_IMSHSI2C_MAIN_3_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.6.2.137 CBASS_FW_IMSHSI2C_MAIN_3_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.6.2.138 CBASS_FW_IMSHSI2C_MAIN_3_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.139 CBASS_FW_IMSHSI2C_MAIN_3_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.140 CBASS_FW_IMSHSI2C_MAIN_3_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.141 CBASS_FW_IMSHSI2C_MAIN_3_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.142 CBASS_FW_IMSHSI2C_MAIN_4_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.143 CBASS_FW_IMSHSI2C_MAIN_4_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.6.2.144 CBASS_FW_IMSHSI2C_MAIN_4_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.6.2.145 CBASS_FW_IMSHSI2C_MAIN_4_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.6.2.146 CBASS_FW_IMSHSI2C_MAIN_4_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.147 CBASS_FW_IMSHSI2C_MAIN_4_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.148 CBASS_FW_IMSHSI2C_MAIN_4_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.149 CBASS_FW_IMSHSI2C_MAIN_4_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.150 CBASS_FW_IMSHSI2C_MAIN_5_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.151 CBASS_FW_IMSHSI2C_MAIN_5_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.6.2.152 CBASS_FW_IMSHSI2C_MAIN_5_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.6.2.153 CBASS_FW_IMSHSI2C_MAIN_5_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.6.2.154 CBASS_FW_IMSHSI2C_MAIN_5_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.155 CBASS_FW_IMSHSI2C_MAIN_5_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.156 CBASS_FW_IMSHSI2C_MAIN_5_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.157 CBASS_FW_IMSHSI2C_MAIN_5_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.158 CBASS_FW_IMSHSI2C_MAIN_6_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.159 CBASS_FW_IMSHSI2C_MAIN_6_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.6.2.160 CBASS_FW_IMSHSI2C_MAIN_6_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.6.2.161 CBASS_FW_IMSHSI2C_MAIN_6_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.6.2.162 CBASS_FW_IMSHSI2C_MAIN_6_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.163 CBASS_FW_IMSHSI2C_MAIN_6_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.164 CBASS_FW_IMSHSI2C_MAIN_6_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.165 CBASS_FW_IMSHSI2C_MAIN_6_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.166 CBASS_FW_IMCANSS_MAIN_0_MCANSS_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.167 CBASS_FW_IMCANSS_MAIN_0_MCANSS_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.6.2.168 CBASS_FW_IMCANSS_MAIN_0_MCANSS_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.6.2.169 CBASS_FW_IMCANSS_MAIN_0_MCANSS_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.6.2.170 CBASS_FW_IMCANSS_MAIN_0_MCANSS_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.171 CBASS_FW_IMCANSS_MAIN_0_MCANSS_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.172 CBASS_FW_IMCANSS_MAIN_0_MCANSS_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.173 CBASS_FW_IMCANSS_MAIN_0_MCANSS_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.174 CBASS_FW_IMCANSS_MAIN_1_MCANSS_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.175 CBASS_FW_IMCANSS_MAIN_1_MCANSS_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.6.2.176 CBASS_FW_IMCANSS_MAIN_1_MCANSS_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.6.2.177 CBASS_FW_IMCANSS_MAIN_1_MCANSS_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.6.2.178 CBASS_FW_IMCANSS_MAIN_1_MCANSS_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.179 CBASS_FW_IMCANSS_MAIN_1_MCANSS_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.180 CBASS_FW_IMCANSS_MAIN_1_MCANSS_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.181 CBASS_FW_IMCANSS_MAIN_1_MCANSS_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.182 CBASS_FW_IMCANSS_MAIN_2_MCANSS_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.183 CBASS_FW_IMCANSS_MAIN_2_MCANSS_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.6.2.184 CBASS_FW_IMCANSS_MAIN_2_MCANSS_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.6.2.185 CBASS_FW_IMCANSS_MAIN_2_MCANSS_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.6.2.186 CBASS_FW_IMCANSS_MAIN_2_MCANSS_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.187 CBASS_FW_IMCANSS_MAIN_2_MCANSS_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.188 CBASS_FW_IMCANSS_MAIN_2_MCANSS_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.189 CBASS_FW_IMCANSS_MAIN_2_MCANSS_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.190 CBASS_FW_IMCANSS_MAIN_3_MCANSS_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.191 CBASS_FW_IMCANSS_MAIN_3_MCANSS_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.6.2.192 CBASS_FW_IMCANSS_MAIN_3_MCANSS_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.6.2.193 CBASS_FW_IMCANSS_MAIN_3_MCANSS_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.6.2.194 CBASS_FW_IMCANSS_MAIN_3_MCANSS_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.195 CBASS_FW_IMCANSS_MAIN_3_MCANSS_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.196 CBASS_FW_IMCANSS_MAIN_3_MCANSS_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.197 CBASS_FW_IMCANSS_MAIN_3_MCANSS_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.198 CBASS_FW_IMCANSS_MAIN_4_MCANSS_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.199 CBASS_FW_IMCANSS_MAIN_4_MCANSS_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.6.2.200 CBASS_FW_IMCANSS_MAIN_4_MCANSS_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.6.2.201 CBASS_FW_IMCANSS_MAIN_4_MCANSS_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.6.2.202 CBASS_FW_IMCANSS_MAIN_4_MCANSS_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.203 CBASS_FW_IMCANSS_MAIN_4_MCANSS_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.204 CBASS_FW_IMCANSS_MAIN_4_MCANSS_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.205 CBASS_FW_IMCANSS_MAIN_4_MCANSS_VBUSP_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.206 CBASS_FW_ISAM67_PDMA_SPI_MAIN_0_ECCAGGR_CFG_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.207 CBASS_FW_ISAM67_PDMA_SPI_MAIN_0_ECCAGGR_CFG_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.6.2.208 CBASS_FW_ISAM67_PDMA_SPI_MAIN_0_ECCAGGR_CFG_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.6.2.209 CBASS_FW_ISAM67_PDMA_SPI_MAIN_0_ECCAGGR_CFG_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.6.2.210 CBASS_FW_ISAM67_PDMA_SPI_MAIN_0_ECCAGGR_CFG_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.211 CBASS_FW_ISAM67_PDMA_SPI_MAIN_0_ECCAGGR_CFG_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.212 CBASS_FW_ISAM67_PDMA_SPI_MAIN_0_ECCAGGR_CFG_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.213 CBASS_FW_ISAM67_PDMA_SPI_MAIN_0_ECCAGGR_CFG_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.214 CBASS_FW_IAM275_PDMA_SPI1_MAIN_0_ECCAGGR_CFG_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.215 CBASS_FW_IAM275_PDMA_SPI1_MAIN_0_ECCAGGR_CFG_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.6.2.216 CBASS_FW_IAM275_PDMA_SPI1_MAIN_0_ECCAGGR_CFG_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.6.2.217 CBASS_FW_IAM275_PDMA_SPI1_MAIN_0_ECCAGGR_CFG_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.6.2.218 CBASS_FW_IAM275_PDMA_SPI1_MAIN_0_ECCAGGR_CFG_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.219 CBASS_FW_IAM275_PDMA_SPI1_MAIN_0_ECCAGGR_CFG_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.220 CBASS_FW_IAM275_PDMA_SPI1_MAIN_0_ECCAGGR_CFG_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.221 CBASS_FW_IAM275_PDMA_SPI1_MAIN_0_ECCAGGR_CFG_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.222 CBASS_FW_ISAM62_PDMA_UART_MAIN_0_ECCAGGR_CFG_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.223 CBASS_FW_ISAM62_PDMA_UART_MAIN_0_ECCAGGR_CFG_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.6.2.224 CBASS_FW_ISAM62_PDMA_UART_MAIN_0_ECCAGGR_CFG_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.6.2.225 CBASS_FW_ISAM62_PDMA_UART_MAIN_0_ECCAGGR_CFG_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.6.2.226 CBASS_FW_ISAM62_PDMA_UART_MAIN_0_ECCAGGR_CFG_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.227 CBASS_FW_ISAM62_PDMA_UART_MAIN_0_ECCAGGR_CFG_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.228 CBASS_FW_ISAM62_PDMA_UART_MAIN_0_ECCAGGR_CFG_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.229 CBASS_FW_ISAM62_PDMA_UART_MAIN_0_ECCAGGR_CFG_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.230 CBASS_FW_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_CFG_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.231 CBASS_FW_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_CFG_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.6.2.232 CBASS_FW_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_CFG_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.6.2.233 CBASS_FW_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_CFG_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.6.2.234 CBASS_FW_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_CFG_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.235 CBASS_FW_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_CFG_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.236 CBASS_FW_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_CFG_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.237 CBASS_FW_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_CFG_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.238 CBASS_FW_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_CFG_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.239 CBASS_FW_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_CFG_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.6.2.240 CBASS_FW_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_CFG_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.6.2.241 CBASS_FW_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_CFG_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.6.2.242 CBASS_FW_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_CFG_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.243 CBASS_FW_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_CFG_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.244 CBASS_FW_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_CFG_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.245 CBASS_FW_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_CFG_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.246 CBASS_FW_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_CFG_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.247 CBASS_FW_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_CFG_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.6.2.248 CBASS_FW_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_CFG_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.6.2.249 CBASS_FW_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_CFG_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.6.2.250 CBASS_FW_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_CFG_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.251 CBASS_FW_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_CFG_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.252 CBASS_FW_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_CFG_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.253 CBASS_FW_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_CFG_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.254 CBASS_FW_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_CFG_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.255 CBASS_FW_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_CFG_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.6.2.256 CBASS_FW_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_CFG_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.6.2.257 CBASS_FW_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_CFG_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.6.2.258 CBASS_FW_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_CFG_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.259 CBASS_FW_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_CFG_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.260 CBASS_FW_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_CFG_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.261 CBASS_FW_IRL2_OF_CBA4_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_CFG_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.262 CBASS_FW_IRTI_CFG1_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_SLV_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.263 CBASS_FW_IRTI_CFG1_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_SLV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.6.2.264 CBASS_FW_IRTI_CFG1_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_SLV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.6.2.265 CBASS_FW_IRTI_CFG1_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_SLV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.6.2.266 CBASS_FW_IRTI_CFG1_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_SLV_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.267 CBASS_FW_IRTI_CFG1_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_SLV_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.268 CBASS_FW_IRTI_CFG1_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_SLV_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.269 CBASS_FW_IRTI_CFG1_MAIN_R5_0_CORE0_SLV_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.270 CBASS_FW_IRTI_CFG1_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_SLV_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.271 CBASS_FW_IRTI_CFG1_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_SLV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.6.2.272 CBASS_FW_IRTI_CFG1_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_SLV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.6.2.273 CBASS_FW_IRTI_CFG1_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_SLV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.6.2.274 CBASS_FW_IRTI_CFG1_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_SLV_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.275 CBASS_FW_IRTI_CFG1_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_SLV_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.276 CBASS_FW_IRTI_CFG1_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_SLV_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.277 CBASS_FW_IRTI_CFG1_MAIN_R5_0_CORE1_SLV_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.278 CBASS_FW_IRTI_CFG1_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_SLV_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.279 CBASS_FW_IRTI_CFG1_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_SLV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.6.2.280 CBASS_FW_IRTI_CFG1_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_SLV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.6.2.281 CBASS_FW_IRTI_CFG1_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_SLV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.6.2.282 CBASS_FW_IRTI_CFG1_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_SLV_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.283 CBASS_FW_IRTI_CFG1_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_SLV_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.284 CBASS_FW_IRTI_CFG1_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_SLV_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.285 CBASS_FW_IRTI_CFG1_MAIN_R5_1_CORE0_SLV_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.286 CBASS_FW_IRTI_CFG1_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_SLV_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.287 CBASS_FW_IRTI_CFG1_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_SLV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.6.2.288 CBASS_FW_IRTI_CFG1_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_SLV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.6.2.289 CBASS_FW_IRTI_CFG1_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_SLV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.6.2.290 CBASS_FW_IRTI_CFG1_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_SLV_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.291 CBASS_FW_IRTI_CFG1_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_SLV_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.292 CBASS_FW_IRTI_CFG1_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_SLV_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.293 CBASS_FW_IRTI_CFG1_MAIN_R5_1_CORE1_SLV_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.294 CBASS_FW_ISPI_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.295 CBASS_FW_ISPI_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.6.2.296 CBASS_FW_ISPI_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.6.2.297 CBASS_FW_ISPI_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.6.2.298 CBASS_FW_ISPI_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.299 CBASS_FW_ISPI_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.300 CBASS_FW_ISPI_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.301 CBASS_FW_ISPI_MAIN_0_SLV_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.302 CBASS_FW_ISPI_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.303 CBASS_FW_ISPI_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.6.2.304 CBASS_FW_ISPI_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.6.2.305 CBASS_FW_ISPI_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.6.2.306 CBASS_FW_ISPI_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.307 CBASS_FW_ISPI_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.308 CBASS_FW_ISPI_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.309 CBASS_FW_ISPI_MAIN_1_SLV_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.310 CBASS_FW_ISPI_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.311 CBASS_FW_ISPI_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.6.2.312 CBASS_FW_ISPI_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.6.2.313 CBASS_FW_ISPI_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.6.2.314 CBASS_FW_ISPI_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.315 CBASS_FW_ISPI_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.316 CBASS_FW_ISPI_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.317 CBASS_FW_ISPI_MAIN_2_SLV_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.318 CBASS_FW_ISPI_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.319 CBASS_FW_ISPI_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.6.2.320 CBASS_FW_ISPI_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.6.2.321 CBASS_FW_ISPI_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.6.2.322 CBASS_FW_ISPI_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.323 CBASS_FW_ISPI_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.324 CBASS_FW_ISPI_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.325 CBASS_FW_ISPI_MAIN_3_SLV_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.326 CBASS_FW_ISPI_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.327 CBASS_FW_ISPI_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.6.2.328 CBASS_FW_ISPI_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.6.2.329 CBASS_FW_ISPI_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.6.2.330 CBASS_FW_ISPI_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.331 CBASS_FW_ISPI_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.332 CBASS_FW_ISPI_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.333 CBASS_FW_ISPI_MAIN_4_SLV_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.334 CBASS_FW_IUSART_MAIN_0_VBUSP_CBA_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.335 CBASS_FW_IUSART_MAIN_0_VBUSP_CBA_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.6.2.336 CBASS_FW_IUSART_MAIN_0_VBUSP_CBA_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.6.2.337 CBASS_FW_IUSART_MAIN_0_VBUSP_CBA_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.6.2.338 CBASS_FW_IUSART_MAIN_0_VBUSP_CBA_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.339 CBASS_FW_IUSART_MAIN_0_VBUSP_CBA_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.340 CBASS_FW_IUSART_MAIN_0_VBUSP_CBA_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.341 CBASS_FW_IUSART_MAIN_0_VBUSP_CBA_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.342 CBASS_FW_IUSART_MAIN_1_VBUSP_CBA_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.343 CBASS_FW_IUSART_MAIN_1_VBUSP_CBA_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.6.2.344 CBASS_FW_IUSART_MAIN_1_VBUSP_CBA_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.6.2.345 CBASS_FW_IUSART_MAIN_1_VBUSP_CBA_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.6.2.346 CBASS_FW_IUSART_MAIN_1_VBUSP_CBA_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.347 CBASS_FW_IUSART_MAIN_1_VBUSP_CBA_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.348 CBASS_FW_IUSART_MAIN_1_VBUSP_CBA_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.349 CBASS_FW_IUSART_MAIN_1_VBUSP_CBA_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.350 CBASS_FW_IUSART_MAIN_2_VBUSP_CBA_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.351 CBASS_FW_IUSART_MAIN_2_VBUSP_CBA_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.6.2.352 CBASS_FW_IUSART_MAIN_2_VBUSP_CBA_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.6.2.353 CBASS_FW_IUSART_MAIN_2_VBUSP_CBA_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.6.2.354 CBASS_FW_IUSART_MAIN_2_VBUSP_CBA_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.355 CBASS_FW_IUSART_MAIN_2_VBUSP_CBA_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.356 CBASS_FW_IUSART_MAIN_2_VBUSP_CBA_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.357 CBASS_FW_IUSART_MAIN_2_VBUSP_CBA_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.358 CBASS_FW_IUSART_MAIN_3_VBUSP_CBA_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.359 CBASS_FW_IUSART_MAIN_3_VBUSP_CBA_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.6.2.360 CBASS_FW_IUSART_MAIN_3_VBUSP_CBA_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.6.2.361 CBASS_FW_IUSART_MAIN_3_VBUSP_CBA_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.6.2.362 CBASS_FW_IUSART_MAIN_3_VBUSP_CBA_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.363 CBASS_FW_IUSART_MAIN_3_VBUSP_CBA_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.364 CBASS_FW_IUSART_MAIN_3_VBUSP_CBA_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.365 CBASS_FW_IUSART_MAIN_3_VBUSP_CBA_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.366 CBASS_FW_IUSART_MAIN_4_VBUSP_CBA_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.367 CBASS_FW_IUSART_MAIN_4_VBUSP_CBA_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.6.2.368 CBASS_FW_IUSART_MAIN_4_VBUSP_CBA_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.6.2.369 CBASS_FW_IUSART_MAIN_4_VBUSP_CBA_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.6.2.370 CBASS_FW_IUSART_MAIN_4_VBUSP_CBA_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.371 CBASS_FW_IUSART_MAIN_4_VBUSP_CBA_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.372 CBASS_FW_IUSART_MAIN_4_VBUSP_CBA_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.373 CBASS_FW_IUSART_MAIN_4_VBUSP_CBA_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.374 CBASS_FW_IUSART_MAIN_5_VBUSP_CBA_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.375 CBASS_FW_IUSART_MAIN_5_VBUSP_CBA_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.6.2.376 CBASS_FW_IUSART_MAIN_5_VBUSP_CBA_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.6.2.377 CBASS_FW_IUSART_MAIN_5_VBUSP_CBA_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.6.2.378 CBASS_FW_IUSART_MAIN_5_VBUSP_CBA_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.379 CBASS_FW_IUSART_MAIN_5_VBUSP_CBA_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.380 CBASS_FW_IUSART_MAIN_5_VBUSP_CBA_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.381 CBASS_FW_IUSART_MAIN_5_VBUSP_CBA_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.382 CBASS_FW_IUSART_MAIN_6_VBUSP_CBA_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.383 CBASS_FW_IUSART_MAIN_6_VBUSP_CBA_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.6.2.384 CBASS_FW_IUSART_MAIN_6_VBUSP_CBA_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.6.2.385 CBASS_FW_IUSART_MAIN_6_VBUSP_CBA_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.6.2.386 CBASS_FW_IUSART_MAIN_6_VBUSP_CBA_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.387 CBASS_FW_IUSART_MAIN_6_VBUSP_CBA_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.388 CBASS_FW_IUSART_MAIN_6_VBUSP_CBA_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.389 CBASS_FW_IUSART_MAIN_6_VBUSP_CBA_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.390 CBASS_FW_IAM275_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_MAIN_0_CBASS_ERR_SLV_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.391 CBASS_FW_IAM275_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_MAIN_0_CBASS_ERR_SLV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.6.2.392 CBASS_FW_IAM275_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_MAIN_0_CBASS_ERR_SLV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.6.2.393 CBASS_FW_IAM275_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_MAIN_0_CBASS_ERR_SLV_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.6.2.394 CBASS_FW_IAM275_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_MAIN_0_CBASS_ERR_SLV_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.395 CBASS_FW_IAM275_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_MAIN_0_CBASS_ERR_SLV_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.396 CBASS_FW_IAM275_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_MAIN_0_CBASS_ERR_SLV_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.397 CBASS_FW_IAM275_MAIN_MISC_PERI_CBASS_MAIN_0_CBASS_ERR_SLV_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.398 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.399 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.400 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.401 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.402 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.403 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_1_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.404 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.405 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.406 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.407 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.408 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_2_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.409 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.410 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.411 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.412 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.413 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_3_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.414 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.415 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.416 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.417 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.418 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_0_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_DEF_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.419 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_0_CPU1_PMST_ISC_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.420 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_0_CPU1_PMST_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.421 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_0_CPU1_PMST_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.422 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_0_CPU1_PMST_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.423 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_0_CPU1_PMST_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.424 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_0_CPU1_PMST_ISC_REGION_1_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.425 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_0_CPU1_PMST_ISC_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.426 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_0_CPU1_PMST_ISC_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.427 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_0_CPU1_PMST_ISC_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.428 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_0_CPU1_PMST_ISC_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.429 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_0_CPU1_PMST_ISC_REGION_2_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.430 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_0_CPU1_PMST_ISC_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.431 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_0_CPU1_PMST_ISC_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.432 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_0_CPU1_PMST_ISC_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.433 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_0_CPU1_PMST_ISC_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.434 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_0_CPU1_PMST_ISC_REGION_3_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.435 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_0_CPU1_PMST_ISC_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.436 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_0_CPU1_PMST_ISC_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.437 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_0_CPU1_PMST_ISC_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.438 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_0_CPU1_PMST_ISC_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.439 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_0_CPU1_PMST_ISC_REGION_DEF_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.440 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_1_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.441 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_1_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.442 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_1_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.443 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_1_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.444 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_1_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.445 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_1_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_1_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.446 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_1_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.447 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_1_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.448 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_1_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.449 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_1_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.450 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_1_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_2_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.451 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_1_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.452 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_1_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.453 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_1_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.454 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_1_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.455 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_1_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_3_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.456 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_1_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.457 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_1_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.458 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_1_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.459 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_1_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.460 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_1_CPU0_PMST_ISC_REGION_DEF_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.461 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_1_CPU1_PMST_ISC_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.462 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_1_CPU1_PMST_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.463 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_1_CPU1_PMST_ISC_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.464 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_1_CPU1_PMST_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.465 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_1_CPU1_PMST_ISC_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.466 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_1_CPU1_PMST_ISC_REGION_1_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.467 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_1_CPU1_PMST_ISC_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.468 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_1_CPU1_PMST_ISC_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.469 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_1_CPU1_PMST_ISC_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.470 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_1_CPU1_PMST_ISC_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.471 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_1_CPU1_PMST_ISC_REGION_2_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.472 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_1_CPU1_PMST_ISC_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.473 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_1_CPU1_PMST_ISC_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.474 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_1_CPU1_PMST_ISC_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.475 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_1_CPU1_PMST_ISC_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.476 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_1_CPU1_PMST_ISC_REGION_3_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.477 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_1_CPU1_PMST_ISC_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.478 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_1_CPU1_PMST_ISC_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.479 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_1_CPU1_PMST_ISC_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.6.2.480 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_1_CPU1_PMST_ISC_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.6.2.481 CBASS_ISC_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_1_CPU1_PMST_ISC_REGION_DEF_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.482 CBASS_GLB_PID Register
- 14.1.6.2.483 CBASS_GLB_DESTINATION_ID Register
- 14.1.6.2.484 CBASS_GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.6.2.485 CBASS_GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER0 Register
- 14.1.6.2.486 CBASS_GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER1 Register
- 14.1.6.2.487 CBASS_GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA0 Register
- 14.1.6.2.488 CBASS_GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA1 Register
- 14.1.6.2.489 CBASS_GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA2 Register
- 14.1.6.2.490 CBASS_GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA3 Register
- 14.1.6.2.491 CBASS_GLB_EXCEPTION_PEND_SET Register
- 14.1.6.2.492 CBASS_GLB_EXCEPTION_PEND_CLEAR Register
- 14.1.6.2.493 CBASS_QOS_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_0_CPU0_PMST_MAP0 Register
- 14.1.6.2.494 CBASS_QOS_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_0_CPU1_PMST_MAP0 Register
- 14.1.6.2.495 CBASS_QOS_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_1_CPU0_PMST_MAP0 Register
- 14.1.6.2.496 CBASS_QOS_IPULSAR_SL_MAIN_1_CPU1_PMST_MAP0 Register
- 14.1.7
CBASS_SAFE
- 14.1.7.1 CBASS_SAFE Summaries
- 14.1.7.2
CBASS_SAFE Registers
- 14.1.7.2.1 CBASS_ERR_PID Register
- 14.1.7.2.2 CBASS_ERR_DESTINATION_ID Register
- 14.1.7.2.3 CBASS_ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER0 Register
- 14.1.7.2.4 CBASS_ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER1 Register
- 14.1.7.2.5 CBASS_ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA0 Register
- 14.1.7.2.6 CBASS_ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA1 Register
- 14.1.7.2.7 CBASS_ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA2 Register
- 14.1.7.2.8 CBASS_ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA3 Register
- 14.1.7.2.9 CBASS_ERR_ERR_INTR_RAW_STAT Register
- 14.1.7.2.10 CBASS_ERR_ERR_INTR_ENABLED_STAT Register
- 14.1.7.2.11 CBASS_ERR_ERR_INTR_ENABLE_SET Register
- 14.1.7.2.12 CBASS_ERR_ERR_INTR_ENABLE_CLR Register
- 14.1.7.2.13 CBASS_ERR_EOI Register
- 14.1.8
am275_main_IPCSS_cbass
- 14.1.8.1 am275_main_IPCSS_cbass Summaries
- 14.1.8.2
am275_main_IPCSS_cbass Registers
- 14.1.8.2.1 CBASS_ERR_PID Register
- 14.1.8.2.2 CBASS_ERR_DESTINATION_ID Register
- 14.1.8.2.3 CBASS_ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER0 Register
- 14.1.8.2.4 CBASS_ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER1 Register
- 14.1.8.2.5 CBASS_ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA0 Register
- 14.1.8.2.6 CBASS_ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA1 Register
- 14.1.8.2.7 CBASS_ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA2 Register
- 14.1.8.2.8 CBASS_ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA3 Register
- 14.1.8.2.9 CBASS_ERR_ERR_INTR_RAW_STAT Register
- 14.1.8.2.10 CBASS_ERR_ERR_INTR_ENABLED_STAT Register
- 14.1.8.2.11 CBASS_ERR_ERR_INTR_ENABLE_SET Register
- 14.1.8.2.12 CBASS_ERR_ERR_INTR_ENABLE_CLR Register
- 14.1.8.2.13 CBASS_ERR_EOI Register
- 14.1.8.2.14 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.8.2.15 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.8.2.16 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.8.2.17 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.8.2.18 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.8.2.19 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.8.2.20 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.8.2.21 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.8.2.22 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_1_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.8.2.23 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.8.2.24 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.8.2.25 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.8.2.26 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.8.2.27 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.8.2.28 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.8.2.29 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.8.2.30 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_2_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.8.2.31 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.8.2.32 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.8.2.33 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.8.2.34 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.8.2.35 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.8.2.36 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.8.2.37 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.8.2.38 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_3_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.8.2.39 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.8.2.40 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.8.2.41 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.8.2.42 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.8.2.43 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.8.2.44 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.8.2.45 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.8.2.46 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_4_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.8.2.47 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.8.2.48 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.8.2.49 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.8.2.50 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_4_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.8.2.51 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_4_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.8.2.52 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_4_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.8.2.53 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_4_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.8.2.54 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_5_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.8.2.55 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.8.2.56 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.8.2.57 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.8.2.58 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_5_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.8.2.59 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_5_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.8.2.60 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_5_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.8.2.61 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_5_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.8.2.62 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_6_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.8.2.63 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.8.2.64 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.8.2.65 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.8.2.66 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_6_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.8.2.67 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_6_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.8.2.68 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_6_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.8.2.69 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_6_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.8.2.70 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_7_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.8.2.71 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.8.2.72 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.8.2.73 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.8.2.74 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_7_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.8.2.75 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_7_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.8.2.76 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_7_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.8.2.77 CBASS_FW_IDMSS_AM275_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_7_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.8.2.78 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_0_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.8.2.79 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.8.2.80 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.8.2.81 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_0_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.8.2.82 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.8.2.83 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_0_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.8.2.84 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.8.2.85 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_0_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.8.2.86 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_1_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.8.2.87 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.8.2.88 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.8.2.89 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_1_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.8.2.90 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.8.2.91 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_1_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.8.2.92 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.8.2.93 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_1_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.8.2.94 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_2_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.8.2.95 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.8.2.96 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.8.2.97 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_2_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.8.2.98 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.8.2.99 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_2_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.8.2.100 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.8.2.101 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_2_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.8.2.102 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_3_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.8.2.103 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.8.2.104 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.8.2.105 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_3_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.8.2.106 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.8.2.107 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_3_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.8.2.108 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.8.2.109 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_3_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.8.2.110 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_4_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.8.2.111 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.8.2.112 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.8.2.113 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_4_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.8.2.114 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_4_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.8.2.115 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_4_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.8.2.116 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_4_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.8.2.117 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_4_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.8.2.118 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_5_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.8.2.119 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.8.2.120 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.8.2.121 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_5_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.8.2.122 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_5_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.8.2.123 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_5_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.8.2.124 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_5_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.8.2.125 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_5_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.8.2.126 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_6_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.8.2.127 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.8.2.128 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.8.2.129 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_6_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.8.2.130 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_6_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.8.2.131 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_6_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.8.2.132 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_6_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.8.2.133 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_6_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.8.2.134 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_7_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.8.2.135 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_0 Register
- 14.1.8.2.136 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_1 Register
- 14.1.8.2.137 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_7_PERMISSION_2 Register
- 14.1.8.2.138 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_7_START_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.8.2.139 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_7_START_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.8.2.140 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_7_END_ADDRESS_L Register
- 14.1.8.2.141 CBASS_FW_ISA3SS_AM62A_MAIN_0_IPCSS_VBM_DST_FW_REGION_7_END_ADDRESS_H Register
- 14.1.8.2.142 CBASS_GLB_PID Register
- 14.1.8.2.143 CBASS_GLB_DESTINATION_ID Register
- 14.1.8.2.144 CBASS_GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_CONTROL Register
- 14.1.8.2.145 CBASS_GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER0 Register
- 14.1.8.2.146 CBASS_GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER1 Register
- 14.1.8.2.147 CBASS_GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA0 Register
- 14.1.8.2.148 CBASS_GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA1 Register
- 14.1.8.2.149 CBASS_GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA2 Register
- 14.1.8.2.150 CBASS_GLB_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA3 Register
- 14.1.8.2.151 CBASS_GLB_EXCEPTION_PEND_SET Register
- 14.1.8.2.152 CBASS_GLB_EXCEPTION_PEND_CLEAR Register
- 14.1.1
CBASS
- 14.2
Device Configuration Registers
- 14.2.1
Control Module (CTRL_MMR)
- 14.2.1.1
General Purpose Control Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1
MAIN_CTRL_MMR
- 14.2.1.1.1.1 MAIN_CTRL_MMR Summaries
- 14.2.1.1.1.2
MAIN_CTRL_MMR Registers
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.1 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PID Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.2 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MMR_CFG1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.3 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_IPC_SET_J Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.4 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_IPC_SET16 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.5 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_IPC_SET17 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.6 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_IPC_SET18 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.7 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_IPC_SET19 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.8 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_IPC_CLR_J Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.9 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_IPC_CLR16 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.10 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_IPC_CLR17 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.11 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_IPC_CLR18 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.12 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_IPC_CLR19 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.13 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK0_KICK0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.14 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK0_KICK1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.15 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_INTR_RAW_STATUS Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.16 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_INTR_ENABLED_STATUS_CLEAR Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.17 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_INTR_ENABLE Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.18 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_INTR_ENABLE_CLEAR Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.19 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_EOI Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.20 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FAULT_ADDRESS Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.21 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FAULT_TYPE_STATUS Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.22 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FAULT_ATTR_STATUS Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.23 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FAULT_CLEAR Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.24 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R0_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.25 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R2_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.26 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R3_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.27 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R6_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.28 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PID_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.29 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MMR_CFG1_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.30 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_IPC_SET_PROXY_J Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.31 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_IPC_SET16_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.32 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_IPC_SET17_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.33 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_IPC_SET18_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.34 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_IPC_SET19_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.35 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_IPC_CLR_PROXY_J Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.36 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_IPC_CLR16_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.37 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_IPC_CLR17_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.38 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_IPC_CLR18_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.39 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_IPC_CLR19_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.40 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK0_KICK0_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.41 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK0_KICK1_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.42 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_INTR_RAW_STATUS_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.43 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_INTR_ENABLED_STATUS_CLEAR_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.44 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_INTR_ENABLE_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.45 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_INTR_ENABLE_CLEAR_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.46 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_EOI_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.47 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FAULT_ADDRESS_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.48 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FAULT_TYPE_STATUS_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.49 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FAULT_ATTR_STATUS_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.50 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FAULT_CLEAR_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.51 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.52 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.53 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R2 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.54 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R3 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.55 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R4 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.56 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R5 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.57 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R6 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.58 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ENET1_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.59 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ENET2_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.60 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_EPWM_TB_CLKEN Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.61 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_EPWM0_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.62 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_EPWM1_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.63 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_EPWM2_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.64 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER0_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.65 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER1_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.66 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER2_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.67 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER3_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.68 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER4_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.69 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER5_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.70 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER6_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.71 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER7_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.72 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER8_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.73 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER9_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.74 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER10_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.75 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER11_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.76 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER12_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.77 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER13_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.78 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER14_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.79 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER15_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.80 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMERIO0_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.81 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMERIO1_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.82 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMERIO2_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.83 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMERIO3_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.84 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMERIO4_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.85 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMERIO5_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.86 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMERIO6_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.87 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMERIO7_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.88 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_C7XV_CTRL0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.89 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_C7XV_CTRL1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.90 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_EMMC0_STAT Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.91 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ADC0_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.92 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ADC0_CAL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.93 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FSS0_CTRL0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.94 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FSS0_CTRL1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.95 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FSS1_CTRL0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.96 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_DCC_STAT Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.97 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS0_CORE0_RL2_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.98 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS0_CORE1_RL2_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.99 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS1_CORE0_RL2_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.100 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS1_CORE1_RL2_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.101 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK1_KICK0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.102 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK1_KICK1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.103 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R0_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.104 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R2_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.105 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R3_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.106 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R4_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.107 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R6_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.108 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R8_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.109 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R9_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.110 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ENET1_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.111 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ENET2_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.112 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_EPWM_TB_CLKEN_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.113 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_EPWM0_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.114 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_EPWM1_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.115 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_EPWM2_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.116 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER0_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.117 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER1_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.118 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER2_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.119 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER3_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.120 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER4_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.121 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER5_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.122 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER6_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.123 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER7_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.124 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER8_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.125 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER9_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.126 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER10_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.127 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER11_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.128 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER12_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.129 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER13_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.130 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER14_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.131 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER15_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.132 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMERIO0_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.133 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMERIO1_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.134 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMERIO2_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.135 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMERIO3_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.136 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMERIO4_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.137 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMERIO5_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.138 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMERIO6_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.139 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMERIO7_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.140 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_C7XV_CTRL0_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.141 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_C7XV_CTRL1_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.142 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_EMMC0_STAT_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.143 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ADC0_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.144 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ADC0_CAL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.145 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FSS0_CTRL0_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.146 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FSS0_CTRL1_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.147 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FSS1_CTRL0_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.148 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_DCC_STAT_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.149 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS0_CORE0_RL2_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.150 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS0_CORE1_RL2_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.151 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS1_CORE0_RL2_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.152 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS1_CORE1_RL2_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.153 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK1_KICK0_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.154 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK1_KICK1_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.155 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.156 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.157 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R2 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.158 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R3 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.159 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R4 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.160 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R5 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.161 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R6 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.162 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R7 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.163 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R8 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.164 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R9 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.165 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R10 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.166 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R11 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.167 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R12 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.168 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R13 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.169 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R14 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.170 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_OBSCLK0_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.171 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLKOUT_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.172 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MAIN_PLL0_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.173 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MAIN_PLL1_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.174 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MAIN_PLL2_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.175 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MAIN_PLL4_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.176 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MAIN_PLL7_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.177 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MAIN_PLL14_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.178 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CPSW_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.179 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_EMMC0_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.180 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER0_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.181 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER1_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.182 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER2_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.183 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER3_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.184 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER4_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.185 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER5_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.186 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER6_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.187 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER7_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.188 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER8_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.189 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER9_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.190 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER10_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.191 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER11_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.192 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER12_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.193 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER13_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.194 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER14_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.195 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER15_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.196 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_SPI0_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.197 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_SPI1_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.198 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_SPI2_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.199 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_SPI3_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.200 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_SPI4_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.201 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USART0_CLK_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.202 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USART1_CLK_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.203 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USART2_CLK_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.204 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USART3_CLK_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.205 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USART4_CLK_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.206 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USART5_CLK_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.207 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USART6_CLK_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.208 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USART0_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.209 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USART1_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.210 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USART2_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.211 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USART3_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.212 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USART4_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.213 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USART5_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.214 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USART6_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.215 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ATL_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.216 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ATL_BWS0_SEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.217 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ATL_BWS1_SEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.218 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ATL_BWS2_SEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.219 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ATL_BWS3_SEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.220 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ATL_AWS0_SEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.221 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ATL_AWS1_SEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.222 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ATL_AWS2_SEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.223 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ATL_AWS3_SEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.224 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_AUDIO_REFCLK0_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.225 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_AUDIO_REFCLK1_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.226 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_AUDIO_REFCLK2_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.227 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC_SYNC_DIV_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.228 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP0_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.229 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP1_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.230 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP2_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.231 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP3_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.232 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP4_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.233 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP0_AHCLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.234 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP1_AHCLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.235 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP2_AHCLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.236 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP3_AHCLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.237 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP4_AHCLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.238 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_WWD0_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.239 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_WWD1_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.240 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_WWD2_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.241 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_WWD3_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.242 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_WWD4_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.243 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_WWD5_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.244 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP0_GF_CLK_SEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.245 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP1_GF_CLK_SEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.246 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP2_GF_CLK_SEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.247 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP3_GF_CLK_SEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.248 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP4_GF_CLK_SEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.249 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCAN0_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.250 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCAN1_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.251 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCAN2_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.252 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCAN3_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.253 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCAN4_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.254 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC0_RXSYNC0_SEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.255 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC0_RXSYNC1_SEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.256 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC0_RXSYNC2_SEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.257 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC0_RXSYNC3_SEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.258 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC1_RXSYNC0_SEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.259 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC1_RXSYNC1_SEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.260 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC1_RXSYNC2_SEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.261 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC1_RXSYNC3_SEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.262 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC0_TXSYNC0_SEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.263 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC0_TXSYNC1_SEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.264 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC0_TXSYNC2_SEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.265 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC0_TXSYNC3_SEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.266 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC1_TXSYNC0_SEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.267 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC1_TXSYNC1_SEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.268 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC1_TXSYNC2_SEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.269 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC1_TXSYNC3_SEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.270 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_OSPI0_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.271 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_OSPI1_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.272 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ADC0_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.273 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS0_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.274 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS1_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.275 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK2_KICK0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.276 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK2_KICK1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.277 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R0_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.278 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R1_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.279 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R2_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.280 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R3_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.281 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R4_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.282 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R5_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.283 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R6_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.284 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R7_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.285 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R9_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.286 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R10_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.287 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_OBSCLK0_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.288 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLKOUT_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.289 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MAIN_PLL0_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.290 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MAIN_PLL1_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.291 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MAIN_PLL2_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.292 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MAIN_PLL4_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.293 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MAIN_PLL7_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.294 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MAIN_PLL14_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.295 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CPSW_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.296 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_EMMC0_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.297 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER0_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.298 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER1_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.299 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER2_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.300 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER3_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.301 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER4_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.302 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER5_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.303 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER6_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.304 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER7_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.305 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER8_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.306 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER9_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.307 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER10_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.308 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER11_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.309 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER12_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.310 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER13_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.311 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER14_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.312 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER15_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.313 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_SPI0_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.314 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_SPI1_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.315 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_SPI2_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.316 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_SPI3_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.317 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_SPI4_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.318 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USART0_CLK_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.319 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USART1_CLK_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.320 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USART2_CLK_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.321 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USART3_CLK_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.322 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USART4_CLK_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.323 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USART5_CLK_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.324 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USART6_CLK_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.325 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USART0_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.326 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USART1_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.327 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USART2_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.328 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USART3_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.329 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USART4_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.330 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USART5_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.331 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USART6_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.332 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ATL_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.333 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ATL_BWS0_SEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.334 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ATL_BWS1_SEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.335 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ATL_BWS2_SEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.336 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ATL_BWS3_SEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.337 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ATL_AWS0_SEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.338 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ATL_AWS1_SEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.339 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ATL_AWS2_SEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.340 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ATL_AWS3_SEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.341 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_AUDIO_REFCLK0_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.342 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_AUDIO_REFCLK1_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.343 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_AUDIO_REFCLK2_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.344 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC_SYNC_DIV_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.345 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP0_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.346 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP1_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.347 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP2_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.348 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP3_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.349 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP4_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.350 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP0_AHCLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.351 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP1_AHCLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.352 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP2_AHCLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.353 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP3_AHCLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.354 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP4_AHCLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.355 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_WWD0_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.356 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_WWD1_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.357 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_WWD2_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.358 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_WWD3_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.359 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_WWD4_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.360 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_WWD5_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.361 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP0_GF_CLK_SEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.362 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP1_GF_CLK_SEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.363 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP2_GF_CLK_SEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.364 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP3_GF_CLK_SEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.365 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP4_GF_CLK_SEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.366 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCAN0_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.367 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCAN1_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.368 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCAN2_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.369 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCAN3_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.370 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCAN4_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.371 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC0_RXSYNC0_SEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.372 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC0_RXSYNC1_SEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.373 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC0_RXSYNC2_SEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.374 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC0_RXSYNC3_SEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.375 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC1_RXSYNC0_SEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.376 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC1_RXSYNC1_SEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.377 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC1_RXSYNC2_SEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.378 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC1_RXSYNC3_SEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.379 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC0_TXSYNC0_SEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.380 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC0_TXSYNC1_SEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.381 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC0_TXSYNC2_SEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.382 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC0_TXSYNC3_SEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.383 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC1_TXSYNC0_SEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.384 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC1_TXSYNC1_SEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.385 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC1_TXSYNC2_SEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.386 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC1_TXSYNC3_SEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.387 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_OSPI0_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.388 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_OSPI1_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.389 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ADC0_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.390 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS0_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.391 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS1_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.392 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK2_KICK0_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.393 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK2_KICK1_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.394 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.395 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.396 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R2 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.397 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R3 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.398 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R4 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.399 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R5 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.400 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R6 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.401 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R7 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.402 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R8 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.403 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R9 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.404 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R10 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.405 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R11 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.406 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS0_LBIST_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.407 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS0_LBIST_PATCOUNT Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.408 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS0_LBIST_SEED0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.409 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS0_LBIST_SEED1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.410 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS0_LBIST_SPARE0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.411 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS0_LBIST_SPARE1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.412 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS0_LBIST_STAT Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.413 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS0_LBIST_MISR Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.414 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS1_LBIST_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.415 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS1_LBIST_PATCOUNT Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.416 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS1_LBIST_SEED0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.417 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS1_LBIST_SEED1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.418 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS1_LBIST_SPARE0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.419 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS1_LBIST_SPARE1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.420 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS1_LBIST_STAT Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.421 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS1_LBIST_MISR Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.422 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS0_LBIST_SIG Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.423 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS1_LBIST_SIG Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.424 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK3_KICK0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.425 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK3_KICK1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.426 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P3_R0_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.427 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P3_R5_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.428 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS0_LBIST_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.429 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS0_LBIST_PATCOUNT_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.430 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS0_LBIST_SEED0_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.431 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS0_LBIST_SEED1_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.432 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS0_LBIST_SPARE0_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.433 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS0_LBIST_SPARE1_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.434 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS0_LBIST_STAT_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.435 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS0_LBIST_MISR_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.436 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS1_LBIST_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.437 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS1_LBIST_PATCOUNT_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.438 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS1_LBIST_SEED0_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.439 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS1_LBIST_SEED1_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.440 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS1_LBIST_SPARE0_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.441 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS1_LBIST_SPARE1_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.442 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS1_LBIST_STAT_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.443 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS1_LBIST_MISR_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.444 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS0_LBIST_SIG_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.445 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS1_LBIST_SIG_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.446 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK3_KICK0_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.447 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK3_KICK1_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.448 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P3_R0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.449 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P3_R1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.450 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P3_R2 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.451 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P3_R3 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.452 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P3_R4 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.453 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P3_R5 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.454 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R10_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.455 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R14_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.456 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.457 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.458 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R2 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.459 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R3 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.460 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R4 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.461 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R5 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.462 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R6 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.463 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R7 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.464 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R8 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.465 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R9 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.466 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R10 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.467 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R11 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.468 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R12 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.469 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R13 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.470 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R14 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.471 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.472 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.473 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R2 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.474 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R3 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.475 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R4 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.476 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R5 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.477 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R6 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.478 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R7 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1.2.479 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R8 Register
- 14.2.1.1.2 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PID Register
- 14.2.1.1.3 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MMR_CFG1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.4 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_IPC_SET_J Register
- 14.2.1.1.5 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_IPC_SET16 Register
- 14.2.1.1.6 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_IPC_SET17 Register
- 14.2.1.1.7 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_IPC_SET18 Register
- 14.2.1.1.8 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_IPC_SET19 Register
- 14.2.1.1.9 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_IPC_CLR_J Register
- 14.2.1.1.10 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_IPC_CLR16 Register
- 14.2.1.1.11 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_IPC_CLR17 Register
- 14.2.1.1.12 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_IPC_CLR18 Register
- 14.2.1.1.13 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_IPC_CLR19 Register
- 14.2.1.1.14 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK0_KICK0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.15 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK0_KICK1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.16 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_INTR_RAW_STATUS Register
- 14.2.1.1.17 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_INTR_ENABLED_STATUS_CLEAR Register
- 14.2.1.1.18 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_INTR_ENABLE Register
- 14.2.1.1.19 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_INTR_ENABLE_CLEAR Register
- 14.2.1.1.20 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_EOI Register
- 14.2.1.1.21 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FAULT_ADDRESS Register
- 14.2.1.1.22 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FAULT_TYPE_STATUS Register
- 14.2.1.1.23 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FAULT_ATTR_STATUS Register
- 14.2.1.1.24 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FAULT_CLEAR Register
- 14.2.1.1.25 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R0_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.26 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R2_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.27 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R3_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.28 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R6_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.29 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PID_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.30 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MMR_CFG1_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.31 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_IPC_SET_PROXY_J Register
- 14.2.1.1.32 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_IPC_SET16_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.33 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_IPC_SET17_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.34 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_IPC_SET18_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.35 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_IPC_SET19_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.36 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_IPC_CLR_PROXY_J Register
- 14.2.1.1.37 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_IPC_CLR16_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.38 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_IPC_CLR17_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.39 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_IPC_CLR18_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.40 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_IPC_CLR19_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.41 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK0_KICK0_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.42 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK0_KICK1_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.43 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_INTR_RAW_STATUS_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.44 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_INTR_ENABLED_STATUS_CLEAR_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.45 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_INTR_ENABLE_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.46 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_INTR_ENABLE_CLEAR_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.47 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_EOI_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.48 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FAULT_ADDRESS_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.49 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FAULT_TYPE_STATUS_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.50 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FAULT_ATTR_STATUS_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.51 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FAULT_CLEAR_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.52 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.53 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.54 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R2 Register
- 14.2.1.1.55 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R3 Register
- 14.2.1.1.56 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R4 Register
- 14.2.1.1.57 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R5 Register
- 14.2.1.1.58 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R6 Register
- 14.2.1.1.59 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ENET1_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.60 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ENET2_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.61 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_EPWM_TB_CLKEN Register
- 14.2.1.1.62 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_EPWM0_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.63 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_EPWM1_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.64 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_EPWM2_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.65 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER0_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.66 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER1_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.67 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER2_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.68 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER3_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.69 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER4_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.70 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER5_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.71 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER6_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.72 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER7_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.73 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER8_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.74 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER9_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.75 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER10_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.76 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER11_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.77 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER12_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.78 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER13_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.79 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER14_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.80 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER15_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.81 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMERIO0_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.82 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMERIO1_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.83 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMERIO2_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.84 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMERIO3_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.85 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMERIO4_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.86 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMERIO5_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.87 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMERIO6_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.88 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMERIO7_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.89 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_C7XV_CTRL0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.90 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_C7XV_CTRL1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.91 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_EMMC0_STAT Register
- 14.2.1.1.92 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ADC0_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.93 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ADC0_CAL Register
- 14.2.1.1.94 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FSS0_CTRL0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.95 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FSS0_CTRL1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.96 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FSS1_CTRL0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.97 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_DCC_STAT Register
- 14.2.1.1.98 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS0_CORE0_RL2_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.99 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS0_CORE1_RL2_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.100 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS1_CORE0_RL2_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.101 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS1_CORE1_RL2_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.102 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK1_KICK0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.103 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK1_KICK1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.104 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R0_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.105 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R2_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.106 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R3_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.107 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R4_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.108 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R6_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.109 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R8_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.110 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R9_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.111 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ENET1_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.112 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ENET2_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.113 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_EPWM_TB_CLKEN_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.114 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_EPWM0_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.115 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_EPWM1_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.116 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_EPWM2_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.117 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER0_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.118 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER1_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.119 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER2_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.120 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER3_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.121 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER4_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.122 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER5_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.123 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER6_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.124 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER7_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.125 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER8_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.126 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER9_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.127 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER10_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.128 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER11_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.129 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER12_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.130 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER13_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.131 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER14_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.132 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER15_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.133 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMERIO0_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.134 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMERIO1_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.135 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMERIO2_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.136 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMERIO3_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.137 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMERIO4_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.138 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMERIO5_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.139 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMERIO6_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.140 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMERIO7_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.141 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_C7XV_CTRL0_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.142 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_C7XV_CTRL1_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.143 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_EMMC0_STAT_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.144 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ADC0_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.145 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ADC0_CAL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.146 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FSS0_CTRL0_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.147 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FSS0_CTRL1_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.148 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FSS1_CTRL0_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.149 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_DCC_STAT_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.150 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS0_CORE0_RL2_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.151 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS0_CORE1_RL2_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.152 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS1_CORE0_RL2_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.153 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS1_CORE1_RL2_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.154 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK1_KICK0_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.155 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK1_KICK1_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.156 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.157 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.158 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R2 Register
- 14.2.1.1.159 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R3 Register
- 14.2.1.1.160 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R4 Register
- 14.2.1.1.161 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R5 Register
- 14.2.1.1.162 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R6 Register
- 14.2.1.1.163 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R7 Register
- 14.2.1.1.164 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R8 Register
- 14.2.1.1.165 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R9 Register
- 14.2.1.1.166 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R10 Register
- 14.2.1.1.167 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R11 Register
- 14.2.1.1.168 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R12 Register
- 14.2.1.1.169 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R13 Register
- 14.2.1.1.170 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R14 Register
- 14.2.1.1.171 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_OBSCLK0_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.172 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLKOUT_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.173 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MAIN_PLL0_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.174 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MAIN_PLL1_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.175 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MAIN_PLL2_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.176 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MAIN_PLL4_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.177 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MAIN_PLL7_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.178 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MAIN_PLL14_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.179 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CPSW_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.180 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_EMMC0_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.181 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER0_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.182 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER1_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.183 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER2_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.184 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER3_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.185 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER4_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.186 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER5_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.187 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER6_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.188 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER7_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.189 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER8_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.190 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER9_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.191 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER10_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.192 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER11_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.193 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER12_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.194 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER13_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.195 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER14_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.196 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER15_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.197 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_SPI0_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.198 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_SPI1_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.199 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_SPI2_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.200 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_SPI3_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.201 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_SPI4_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.202 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USART0_CLK_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.203 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USART1_CLK_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.204 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USART2_CLK_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.205 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USART3_CLK_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.206 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USART4_CLK_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.207 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USART5_CLK_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.208 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USART6_CLK_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.209 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USART0_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.210 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USART1_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.211 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USART2_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.212 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USART3_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.213 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USART4_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.214 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USART5_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.215 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USART6_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.216 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ATL_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.217 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ATL_BWS0_SEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.218 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ATL_BWS1_SEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.219 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ATL_BWS2_SEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.220 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ATL_BWS3_SEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.221 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ATL_AWS0_SEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.222 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ATL_AWS1_SEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.223 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ATL_AWS2_SEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.224 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ATL_AWS3_SEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.225 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_AUDIO_REFCLK0_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.226 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_AUDIO_REFCLK1_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.227 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_AUDIO_REFCLK2_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.228 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC_SYNC_DIV_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.229 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP0_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.230 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP1_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.231 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP2_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.232 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP3_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.233 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP4_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.234 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP0_AHCLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.235 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP1_AHCLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.236 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP2_AHCLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.237 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP3_AHCLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.238 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP4_AHCLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.239 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_WWD0_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.240 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_WWD1_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.241 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_WWD2_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.242 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_WWD3_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.243 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_WWD4_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.244 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_WWD5_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.245 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP0_GF_CLK_SEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.246 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP1_GF_CLK_SEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.247 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP2_GF_CLK_SEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.248 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP3_GF_CLK_SEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.249 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP4_GF_CLK_SEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.250 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCAN0_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.251 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCAN1_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.252 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCAN2_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.253 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCAN3_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.254 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCAN4_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.255 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC0_RXSYNC0_SEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.256 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC0_RXSYNC1_SEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.257 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC0_RXSYNC2_SEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.258 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC0_RXSYNC3_SEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.259 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC1_RXSYNC0_SEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.260 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC1_RXSYNC1_SEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.261 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC1_RXSYNC2_SEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.262 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC1_RXSYNC3_SEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.263 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC0_TXSYNC0_SEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.264 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC0_TXSYNC1_SEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.265 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC0_TXSYNC2_SEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.266 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC0_TXSYNC3_SEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.267 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC1_TXSYNC0_SEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.268 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC1_TXSYNC1_SEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.269 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC1_TXSYNC2_SEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.270 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC1_TXSYNC3_SEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.271 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_OSPI0_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.272 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_OSPI1_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.273 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ADC0_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.274 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS0_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.275 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS1_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.276 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK2_KICK0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.277 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK2_KICK1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.278 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R0_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.279 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R1_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.280 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R2_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.281 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R3_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.282 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R4_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.283 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R5_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.284 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R6_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.285 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R7_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.286 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R9_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.287 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R10_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.288 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_OBSCLK0_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.289 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLKOUT_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.290 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MAIN_PLL0_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.291 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MAIN_PLL1_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.292 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MAIN_PLL2_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.293 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MAIN_PLL4_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.294 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MAIN_PLL7_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.295 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MAIN_PLL14_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.296 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CPSW_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.297 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_EMMC0_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.298 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER0_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.299 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER1_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.300 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER2_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.301 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER3_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.302 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER4_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.303 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER5_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.304 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER6_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.305 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER7_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.306 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER8_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.307 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER9_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.308 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER10_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.309 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER11_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.310 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER12_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.311 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER13_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.312 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER14_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.313 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TIMER15_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.314 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_SPI0_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.315 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_SPI1_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.316 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_SPI2_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.317 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_SPI3_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.318 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_SPI4_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.319 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USART0_CLK_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.320 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USART1_CLK_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.321 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USART2_CLK_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.322 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USART3_CLK_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.323 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USART4_CLK_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.324 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USART5_CLK_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.325 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USART6_CLK_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.326 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USART0_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.327 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USART1_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.328 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USART2_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.329 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USART3_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.330 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USART4_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.331 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USART5_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.332 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USART6_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.333 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ATL_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.334 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ATL_BWS0_SEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.335 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ATL_BWS1_SEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.336 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ATL_BWS2_SEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.337 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ATL_BWS3_SEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.338 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ATL_AWS0_SEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.339 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ATL_AWS1_SEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.340 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ATL_AWS2_SEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.341 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ATL_AWS3_SEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.342 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_AUDIO_REFCLK0_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.343 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_AUDIO_REFCLK1_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.344 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_AUDIO_REFCLK2_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.345 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC_SYNC_DIV_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.346 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP0_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.347 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP1_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.348 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP2_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.349 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP3_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.350 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP4_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.351 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP0_AHCLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.352 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP1_AHCLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.353 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP2_AHCLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.354 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP3_AHCLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.355 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP4_AHCLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.356 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_WWD0_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.357 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_WWD1_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.358 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_WWD2_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.359 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_WWD3_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.360 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_WWD4_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.361 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_WWD5_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.362 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP0_GF_CLK_SEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.363 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP1_GF_CLK_SEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.364 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP2_GF_CLK_SEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.365 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP3_GF_CLK_SEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.366 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCASP4_GF_CLK_SEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.367 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCAN0_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.368 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCAN1_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.369 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCAN2_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.370 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCAN3_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.371 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCAN4_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.372 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC0_RXSYNC0_SEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.373 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC0_RXSYNC1_SEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.374 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC0_RXSYNC2_SEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.375 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC0_RXSYNC3_SEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.376 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC1_RXSYNC0_SEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.377 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC1_RXSYNC1_SEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.378 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC1_RXSYNC2_SEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.379 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC1_RXSYNC3_SEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.380 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC0_TXSYNC0_SEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.381 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC0_TXSYNC1_SEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.382 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC0_TXSYNC2_SEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.383 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC0_TXSYNC3_SEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.384 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC1_TXSYNC0_SEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.385 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC1_TXSYNC1_SEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.386 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC1_TXSYNC2_SEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.387 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ASRC1_TXSYNC3_SEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.388 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_OSPI0_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.389 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_OSPI1_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.390 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ADC0_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.391 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS0_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.392 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS1_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.393 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK2_KICK0_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.394 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK2_KICK1_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.395 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.396 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.397 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R2 Register
- 14.2.1.1.398 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R3 Register
- 14.2.1.1.399 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R4 Register
- 14.2.1.1.400 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R5 Register
- 14.2.1.1.401 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R6 Register
- 14.2.1.1.402 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R7 Register
- 14.2.1.1.403 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R8 Register
- 14.2.1.1.404 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R9 Register
- 14.2.1.1.405 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R10 Register
- 14.2.1.1.406 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R11 Register
- 14.2.1.1.407 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS0_LBIST_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.408 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS0_LBIST_PATCOUNT Register
- 14.2.1.1.409 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS0_LBIST_SEED0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.410 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS0_LBIST_SEED1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.411 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS0_LBIST_SPARE0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.412 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS0_LBIST_SPARE1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.413 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS0_LBIST_STAT Register
- 14.2.1.1.414 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS0_LBIST_MISR Register
- 14.2.1.1.415 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS1_LBIST_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.416 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS1_LBIST_PATCOUNT Register
- 14.2.1.1.417 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS1_LBIST_SEED0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.418 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS1_LBIST_SEED1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.419 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS1_LBIST_SPARE0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.420 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS1_LBIST_SPARE1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.421 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS1_LBIST_STAT Register
- 14.2.1.1.422 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS1_LBIST_MISR Register
- 14.2.1.1.423 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS0_LBIST_SIG Register
- 14.2.1.1.424 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS1_LBIST_SIG Register
- 14.2.1.1.425 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK3_KICK0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.426 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK3_KICK1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.427 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P3_R0_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.428 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P3_R5_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.429 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS0_LBIST_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.430 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS0_LBIST_PATCOUNT_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.431 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS0_LBIST_SEED0_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.432 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS0_LBIST_SEED1_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.433 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS0_LBIST_SPARE0_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.434 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS0_LBIST_SPARE1_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.435 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS0_LBIST_STAT_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.436 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS0_LBIST_MISR_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.437 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS1_LBIST_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.438 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS1_LBIST_PATCOUNT_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.439 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS1_LBIST_SEED0_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.440 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS1_LBIST_SEED1_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.441 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS1_LBIST_SPARE0_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.442 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS1_LBIST_SPARE1_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.443 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS1_LBIST_STAT_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.444 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS1_LBIST_MISR_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.445 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS0_LBIST_SIG_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.446 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_R5SS1_LBIST_SIG_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.447 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK3_KICK0_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.448 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK3_KICK1_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.449 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P3_R0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.450 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P3_R1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.451 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P3_R2 Register
- 14.2.1.1.452 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P3_R3 Register
- 14.2.1.1.453 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P3_R4 Register
- 14.2.1.1.454 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P3_R5 Register
- 14.2.1.1.455 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R10_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.456 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R14_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.457 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.458 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.459 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R2 Register
- 14.2.1.1.460 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R3 Register
- 14.2.1.1.461 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R4 Register
- 14.2.1.1.462 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R5 Register
- 14.2.1.1.463 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R6 Register
- 14.2.1.1.464 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R7 Register
- 14.2.1.1.465 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R8 Register
- 14.2.1.1.466 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R9 Register
- 14.2.1.1.467 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R10 Register
- 14.2.1.1.468 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R11 Register
- 14.2.1.1.469 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R12 Register
- 14.2.1.1.470 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R13 Register
- 14.2.1.1.471 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R14 Register
- 14.2.1.1.472 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.473 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.474 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R2 Register
- 14.2.1.1.475 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R3 Register
- 14.2.1.1.476 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R4 Register
- 14.2.1.1.477 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R5 Register
- 14.2.1.1.478 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R6 Register
- 14.2.1.1.479 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R7 Register
- 14.2.1.1.480 MAIN_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R8 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481
MCU_CTRL_MMR0
- 14.2.1.1.481.1 MCU_CTRL_MMR0 Summaries
- 14.2.1.1.481.2
MCU_CTRL_MMR0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.1 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PID Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.2 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MMR_CFG1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.3 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_IPC_SET0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.4 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_IPC_CLR0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.5 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CBA_ERR_STAT Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.6 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ACCESS_ERR_STAT Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.7 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK0_KICK0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.8 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK0_KICK1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.9 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_INTR_RAW_STATUS Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.10 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_INTR_ENABLED_STATUS_CLEAR Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.11 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_INTR_ENABLE Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.12 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_INTR_ENABLE_CLEAR Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.13 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_EOI Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.14 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FAULT_ADDRESS Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.15 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FAULT_TYPE_STATUS Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.16 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FAULT_ATTR_STATUS Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.17 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FAULT_CLEAR Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.18 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R0_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.19 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R2_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.20 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R3_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.21 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R4_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.22 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R5_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.23 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PID_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.24 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MMR_CFG1_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.25 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_IPC_SET0_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.26 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_IPC_CLR0_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.27 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CBA_ERR_STAT_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.28 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ACCESS_ERR_STAT_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.29 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK0_KICK0_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.30 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK0_KICK1_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.31 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_INTR_RAW_STATUS_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.32 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_INTR_ENABLED_STATUS_CLEAR_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.33 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_INTR_ENABLE_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.34 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_INTR_ENABLE_CLEAR_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.35 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_EOI_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.36 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FAULT_ADDRESS_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.37 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FAULT_TYPE_STATUS_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.38 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FAULT_ATTR_STATUS_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.39 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FAULT_CLEAR_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.40 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.41 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.42 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R2 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.43 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R3 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.44 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R4 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.45 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R5 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.46 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCU_GPIO_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.47 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_DBOUNCE_CFG1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.48 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_DBOUNCE_CFG2 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.49 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_DBOUNCE_CFG3 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.50 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_DBOUNCE_CFG4 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.51 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_DBOUNCE_CFG5 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.52 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_DBOUNCE_CFG6 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.53 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_IO_VOLTAGE_STAT Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.54 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_WKUP_MTOG_CTRL0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.55 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TOG_STAT Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.56 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK1_KICK0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.57 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK1_KICK1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.58 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R0_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.59 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R1_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.60 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R2_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.61 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCU_GPIO_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.62 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_DBOUNCE_CFG1_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.63 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_DBOUNCE_CFG2_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.64 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_DBOUNCE_CFG3_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.65 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_DBOUNCE_CFG4_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.66 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_DBOUNCE_CFG5_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.67 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_DBOUNCE_CFG6_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.68 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_IO_VOLTAGE_STAT_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.69 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_WKUP_MTOG_CTRL0_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.70 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_TOG_STAT_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.71 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK1_KICK0_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.72 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK1_KICK1_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.73 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.74 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.75 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R2 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.76 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R3 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.77 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R4 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.78 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R5 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.79 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R6 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.80 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R7 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.81 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R8 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.82 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R9 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.83 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R10 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.84 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R11 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.85 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R12 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.86 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCU_OBSCLK_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.87 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_HFOSC0_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.88 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_HFOSC1_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.89 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_HFOSC0_STAT Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.90 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_HFOSC0_CLKOUT_32K_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.91 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LFXOSC_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.92 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCU_PLL_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.93 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_DEVICE_CLKOUT_32K_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.94 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCU_GPIO_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.95 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK2_KICK0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.96 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK2_KICK1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.97 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R0_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.98 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCU_OBSCLK_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.99 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_HFOSC0_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.100 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_HFOSC1_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.101 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_HFOSC0_STAT_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.102 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_HFOSC0_CLKOUT_32K_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.103 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LFXOSC_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.104 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCU_PLL_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.105 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_DEVICE_CLKOUT_32K_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.106 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MCU_GPIO_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.107 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK2_KICK0_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.108 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK2_KICK1_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.109 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.110 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK4_KICK0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.111 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK4_KICK1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.112 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK4_KICK0_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.113 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK4_KICK1_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.114 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.115 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.116 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R2 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.117 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R3 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.118 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R4 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.119 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R5 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.120 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R6 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.121 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R7 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.122 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R8 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.123 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R9 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.124 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R10 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.125 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R11 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.126 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R12 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.127 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R13 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.128 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R14 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.129 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R15 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.130 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R16 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.131 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R17 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.132 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R18 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.133 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R19 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.134 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_POR_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.135 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_POR_STAT Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.136 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_POK_VDDA_MCU_UV_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.137 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_POK_VDDA_MCU_OV_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.138 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_POK_VDD_CORE_UV_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.139 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_POK_VDD_CORE_OV_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.140 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_POK_VDDR_CORE_UV_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.141 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_POK_VDDR_CORE_OV_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.142 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_POK_VMON_CAP_MCU_GENERAL_UV_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.143 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_POK_VMON_CAP_MCU_GENERAL_OV_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.144 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_POK_VDDSHV_MAIN_1P8_UV_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.145 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_POK_VDDSHV_MAIN_1P8_OV_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.146 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_POK_VDDSHV_MAIN_3P3_UV_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.147 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_POK_VDDSHV_MAIN_3P3_OV_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.148 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_POK_VDDA_PMIC_IN_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.149 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_RST_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.150 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_RST_STAT Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.151 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_RST_SRC Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.152 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_VDD_CORE_GLDTC_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.153 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_VDD_CORE_GLDTC_STAT Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.154 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PRG_PP_0_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.155 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PRG_PP_1_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.156 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLKGATE_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.157 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK6_KICK0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.158 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK6_KICK1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.159 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R0_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.160 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R2_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.161 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R3_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.162 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R4_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.163 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R5_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.164 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_POR_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.165 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_POR_STAT_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.166 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_POK_VDDA_MCU_UV_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.167 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_POK_VDDA_MCU_OV_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.168 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_POK_VDD_CORE_UV_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.169 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_POK_VDD_CORE_OV_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.170 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_POK_VDDR_CORE_UV_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.171 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_POK_VDDR_CORE_OV_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.172 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_POK_VMON_CAP_MCU_GENERAL_UV_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.173 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_POK_VMON_CAP_MCU_GENERAL_OV_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.174 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_POK_VDDSHV_MAIN_1P8_UV_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.175 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_POK_VDDSHV_MAIN_1P8_OV_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.176 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_POK_VDDSHV_MAIN_3P3_UV_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.177 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_POK_VDDSHV_MAIN_3P3_OV_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.178 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_POK_VDDA_PMIC_IN_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.179 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_RST_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.180 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_RST_STAT_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.181 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_RST_SRC_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.182 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_VDD_CORE_GLDTC_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.183 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_VDD_CORE_GLDTC_STAT_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.184 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PRG_PP_0_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.185 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PRG_PP_1_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.186 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLKGATE_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.187 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK6_KICK0_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.188 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK6_KICK1_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.189 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.190 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.191 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R2 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.192 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R3 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.193 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R4 Register
- 14.2.1.1.481.2.194 MCU_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R5 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482
WKUP_CTRL_MMR0
- 14.2.1.1.482.1 WKUP_CTRL_MMR0 Summaries
- 14.2.1.1.482.2
WKUP_CTRL_MMR0 Registers
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.1 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PID Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.2 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MMR_CFG1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.3 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_BOOT_PROGRESS Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.4 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_DEVICE_FEATURE0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.5 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_DEVICE_FEATURE1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.6 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_DEVICE_FEATURE2 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.7 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_DEVICE_FEATURE3 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.8 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_DEVICE_FEATURE5 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.9 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_DEVICE_FEATURE6 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.10 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MAC_ID0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.11 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MAC_ID1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.12 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USB_DEVICE_ID0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.13 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_GP_SW0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.14 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_GP_SW1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.15 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_GP_SW2 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.16 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_GP_SW3 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.17 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CBA_ERR_STAT Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.18 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ACCESS_ERR_STAT Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.19 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK0_KICK0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.20 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK0_KICK1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.21 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_INTR_RAW_STATUS Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.22 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_INTR_ENABLED_STATUS_CLEAR Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.23 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_INTR_ENABLE Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.24 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_INTR_ENABLE_CLEAR Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.25 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FAULT_ADDRESS Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.26 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FAULT_TYPE_STATUS Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.27 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FAULT_ATTR_STATUS Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.28 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FAULT_CLEAR Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.29 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R0_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.30 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R4_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.31 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R5_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.32 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PID_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.33 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MMR_CFG1_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.34 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_BOOT_PROGRESS_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.35 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_DEVICE_FEATURE0_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.36 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_DEVICE_FEATURE1_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.37 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_DEVICE_FEATURE2_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.38 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_DEVICE_FEATURE3_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.39 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_DEVICE_FEATURE5_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.40 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_DEVICE_FEATURE6_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.41 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MAC_ID0_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.42 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MAC_ID1_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.43 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USB_DEVICE_ID0_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.44 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_GP_SW0_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.45 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_GP_SW1_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.46 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_GP_SW2_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.47 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_GP_SW3_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.48 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CBA_ERR_STAT_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.49 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_ACCESS_ERR_STAT_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.50 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK0_KICK0_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.51 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK0_KICK1_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.52 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_INTR_RAW_STATUS_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.53 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_INTR_ENABLED_STATUS_CLEAR_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.54 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_INTR_ENABLE_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.55 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_INTR_ENABLE_CLEAR_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.56 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FAULT_ADDRESS_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.57 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FAULT_TYPE_STATUS_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.58 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FAULT_ATTR_STATUS_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.59 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FAULT_CLEAR_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.60 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.61 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.62 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R2 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.63 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R3 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.64 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R4 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.65 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R5 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.66 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R6 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.67 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USB0_PHY_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.68 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_SDIO0_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.69 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_WKUP_TIMER1_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.70 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_WKUP_I2C0_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.71 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK1_KICK0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.72 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK1_KICK1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.73 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R0_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.74 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R3_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.75 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R4_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.76 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R5_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.77 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R12_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.78 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USB0_PHY_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.79 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_SDIO0_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.80 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_WKUP_TIMER1_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.81 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_WKUP_I2C0_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.82 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK1_KICK0_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.83 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK1_KICK1_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.84 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.85 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.86 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R2 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.87 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R3 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.88 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R4 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.89 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R5 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.90 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R6 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.91 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R7 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.92 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R8 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.93 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R9 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.94 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R10 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.95 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R11 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.96 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R12 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.97 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_WKUP_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.98 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLKOUT_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.99 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_WKUP_GTC_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.100 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USB0_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.101 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_WKUP_TIMER0_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.102 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_WKUP_TIMER1_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.103 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_WKUP_WWD0_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.104 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_WKUP_WWD0_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.105 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_WKUP_RTC_CLKSEL Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.106 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK2_KICK0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.107 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK2_KICK1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.108 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R0_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.109 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R3_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.110 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R6_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.111 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R7_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.112 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R12_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.113 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_WKUP_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.114 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLKOUT_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.115 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_WKUP_GTC_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.116 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_USB0_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.117 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_WKUP_TIMER0_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.118 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_WKUP_TIMER1_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.119 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_WKUP_WWD0_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.120 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_WKUP_WWD0_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.121 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_WKUP_RTC_CLKSEL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.122 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK2_KICK0_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.123 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK2_KICK1_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.124 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.125 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.126 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R2 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.127 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R3 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.128 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R4 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.129 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R5 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.130 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R6 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.131 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R7 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.132 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R8 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.133 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R9 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.134 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R10 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.135 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R11 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.136 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P2_R12 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.137 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_POST_STAT Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.138 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PBIST_EN Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.139 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK3_KICK0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.140 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK3_KICK1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.141 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P3_R0_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.142 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P3_R1_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.143 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P3_R2_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.144 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P3_R3_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.145 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P3_R4_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.146 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P3_R5_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.147 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P3_R6_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.148 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P3_R7_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.149 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P3_R8_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.150 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_POST_STAT_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.151 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PBIST_EN_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.152 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK3_KICK0_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.153 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK3_KICK1_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.154 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P3_R0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.155 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P3_R1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.156 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P3_R2 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.157 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P3_R3 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.158 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P3_R4 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.159 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P3_R5 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.160 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P3_R6 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.161 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P3_R7 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.162 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P3_R8 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.163 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R0_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.164 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R8_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.165 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.166 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.167 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R2 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.168 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R3 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.169 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R4 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.170 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R5 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.171 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R6 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.172 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R7 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.173 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P4_R8 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.174 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PMCTRL_SYS Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.175 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PMCTRL_IO_0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.176 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PMCTRL_IO_1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.177 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PMCTRL_MOSC Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.178 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PM_MISC_STATUS Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.179 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_RST_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.180 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_RST_STAT Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.181 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_RST_SRC Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.182 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_RST_MAGIC_WORD Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.183 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_WKUP0_EN Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.184 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLKGATE_CTRL0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.185 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLKGATE_CTRL1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.186 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CANUART_WAKE_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.187 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CANUART_WAKE_STAT0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.188 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CANUART_WAKE_STAT1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.189 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CANUART_WAKE_OFF_MODE Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.190 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CANUART_WAKE_OFF_MODE_STAT Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.191 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CANUART_WAKE_RESUME_KEY_J Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.192 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CANUART_WAKE_RESUME_KEY_STAT_J Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.193 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_WAKE_EVT_MON_CTRL Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.194 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_INTRN_POR_DUR Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.195 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_IMMED_WAKE_TIMEOUT Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.196 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_RET_RAM_STAT Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.197 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_WFI_STATUS Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.198 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_DS_MAIN Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.199 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_DS_DM_RESET Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.200 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_DS_USB0_RESET Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.201 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_DM_GRP_CLKSTOP_REQ Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.202 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_DEVICE_TYPE Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.203 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK6_KICK0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.204 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK6_KICK1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.205 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R0_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.206 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R1_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.207 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R2_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.208 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R3_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.209 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R4_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.210 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R5_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.211 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R6_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.212 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R7_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.213 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R8_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.214 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R9_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.215 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R10_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.216 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PMCTRL_SYS_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.217 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PMCTRL_IO_0_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.218 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PMCTRL_IO_1_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.219 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PMCTRL_MOSC_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.220 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PM_MISC_STATUS_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.221 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_RST_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.222 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_RST_STAT_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.223 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_RST_SRC_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.224 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_RST_MAGIC_WORD_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.225 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_WKUP0_EN_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.226 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLKGATE_CTRL0_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.227 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLKGATE_CTRL1_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.228 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CANUART_WAKE_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.229 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CANUART_WAKE_STAT0_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.230 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CANUART_WAKE_STAT1_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.231 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CANUART_WAKE_OFF_MODE_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.232 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CANUART_WAKE_OFF_MODE_STAT_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.233 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CANUART_WAKE_RESUME_KEY_PROXY_J Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.234 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CANUART_WAKE_RESUME_KEY_STAT_PROXY_J Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.235 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_WAKE_EVT_MON_CTRL_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.236 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_INTRN_POR_DUR_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.237 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_IMMED_WAKE_TIMEOUT_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.238 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_RET_RAM_STAT_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.239 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_WFI_STATUS_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.240 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_DS_MAIN_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.241 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_DS_DM_RESET_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.242 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_DS_USB0_RESET_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.243 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_DM_GRP_CLKSTOP_REQ_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.244 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_DEVICE_TYPE_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.245 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK6_KICK0_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.246 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK6_KICK1_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.247 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.248 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.249 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R2 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.250 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R3 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.251 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R4 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.252 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R5 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.253 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R6 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.254 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R7 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.255 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R8 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.256 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R9 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.257 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P6_R10 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.258 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK7_KICK0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.259 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK7_KICK1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.260 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P7_R0_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.261 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P7_R1_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.262 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P7_R2_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.263 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK7_KICK0_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.264 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK7_KICK1_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.265 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P7_R0 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.266 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P7_R1 Register
- 14.2.1.1.482.2.267 WKUP_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P7_R2 Register
- 14.2.1.1.1
MAIN_CTRL_MMR
- 14.2.1.2
Pad Configuration Registers
- 14.2.1.2.1
Pad Configuration Register Functional Description
- 14.2.1.2.1.1
PADCFG_CTRL
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.1 PADCFG_CTRL Summaries
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2
PADCFG_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.1 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PID Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.2 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MMR_CFG0 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.3 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MMR_CFG1 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.4 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK0_KICK0 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.5 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK0_KICK1 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.6 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_INTR_RAW_STATUS Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.7 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_INTR_ENABLED_STATUS_CLEAR Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.8 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_INTR_ENABLE Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.9 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_INTR_ENABLE_CLEAR Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.10 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_EOI Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.11 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FAULT_ADDRESS Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.12 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FAULT_TYPE_STATUS Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.13 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FAULT_ATTR_STATUS Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.14 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FAULT_CLEAR Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.15 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R0_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.16 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PID_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.17 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MMR_CFG0_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.18 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MMR_CFG1_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.19 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK0_KICK0_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.20 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK0_KICK1_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.21 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_INTR_RAW_STATUS_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.22 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_INTR_ENABLED_STATUS_CLEAR_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.23 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_INTR_ENABLE_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.24 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_INTR_ENABLE_CLEAR_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.25 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_EOI_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.26 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FAULT_ADDRESS_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.27 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FAULT_TYPE_STATUS_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.28 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FAULT_ATTR_STATUS_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.29 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FAULT_CLEAR_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.30 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R0 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.31 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG0 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.32 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG1 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.33 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG2 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.34 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG3 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.35 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG4 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.36 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG5 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.37 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG6 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.38 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG7 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.39 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG8 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.40 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG9 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.41 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG10 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.42 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG11 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.43 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG12 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.44 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG13 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.45 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG14 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.46 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG15 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.47 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG16 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.48 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG19 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.49 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG20 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.50 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG21 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.51 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG22 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.52 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG23 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.53 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG24 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.54 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG25 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.55 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG26 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.56 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG27 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.57 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG28 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.58 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG29 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.59 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG30 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.60 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG31 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.61 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG32 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.62 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG33 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.63 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK1_KICK0 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.64 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK1_KICK1 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.65 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R0_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.66 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R1_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.67 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG0_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.68 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG1_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.69 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG2_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.70 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG3_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.71 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG4_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.72 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG5_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.73 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG6_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.74 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG7_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.75 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG8_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.76 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG9_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.77 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG10_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.78 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG11_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.79 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG12_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.80 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG13_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.81 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG14_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.82 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG15_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.83 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG16_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.84 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG19_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.85 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG20_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.86 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG21_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.87 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG22_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.88 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG23_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.89 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG24_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.90 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG25_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.91 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG26_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.92 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG27_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.93 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG28_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.94 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG29_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.95 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG30_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.96 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG31_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.97 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG32_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.98 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG33_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.99 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK1_KICK0_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.100 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK1_KICK1_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.101 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R0 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1.2.102 MCU_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R1 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2
PADCFG_CTRL
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.1 PADCFG_CTRL Summaries
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2
PADCFG_CTRL Registers
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.1 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PID Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.2 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MMR_CFG0 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.3 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MMR_CFG1 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.4 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK0_KICK0 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.5 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK0_KICK1 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.6 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_INTR_RAW_STATUS Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.7 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_INTR_ENABLED_STATUS_CLEAR Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.8 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_INTR_ENABLE Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.9 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_INTR_ENABLE_CLEAR Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.10 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_EOI Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.11 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FAULT_ADDRESS Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.12 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FAULT_TYPE_STATUS Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.13 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FAULT_ATTR_STATUS Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.14 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FAULT_CLEAR Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.15 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R0_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.16 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PID_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.17 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MMR_CFG0_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.18 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_MMR_CFG1_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.19 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK0_KICK0_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.20 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK0_KICK1_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.21 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_INTR_RAW_STATUS_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.22 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_INTR_ENABLED_STATUS_CLEAR_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.23 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_INTR_ENABLE_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.24 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_INTR_ENABLE_CLEAR_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.25 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_EOI_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.26 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FAULT_ADDRESS_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.27 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FAULT_TYPE_STATUS_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.28 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FAULT_ATTR_STATUS_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.29 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_FAULT_CLEAR_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.30 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P0_R0 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.31 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG0 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.32 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG1 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.33 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG2 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.34 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG3 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.35 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG4 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.36 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG5 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.37 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG6 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.38 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG7 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.39 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG8 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.40 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG9 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.41 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG10 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.42 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG11 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.43 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG12 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.44 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG13 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.45 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG14 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.46 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG15 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.47 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG16 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.48 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG17 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.49 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG18 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.50 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG19 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.51 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG20 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.52 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG21 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.53 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG22 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.54 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG23 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.55 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG24 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.56 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG25 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.57 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG26 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.58 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG27 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.59 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG28 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.60 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG29 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.61 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG30 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.62 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG31 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.63 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG33 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.64 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG34 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.65 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG35 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.66 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG36 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.67 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG37 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.68 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG38 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.69 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG39 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.70 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG40 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.71 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG41 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.72 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG42 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.73 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG43 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.74 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG44 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.75 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG45 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.76 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG46 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.77 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG47 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.78 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG48 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.79 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG49 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.80 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG50 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.81 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG51 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.82 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG52 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.83 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG53 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.84 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG56 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.85 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG57 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.86 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG58 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.87 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG59 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.88 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG60 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.89 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG63 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.90 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG64 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.91 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG65 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.92 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG66 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.93 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG67 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.94 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG68 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.95 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG69 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.96 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG70 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.97 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG71 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.98 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG72 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.99 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG73 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.100 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG74 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.101 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG75 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.102 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG76 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.103 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG77 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.104 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG78 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.105 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG79 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.106 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG80 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.107 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG81 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.108 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG82 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.109 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG83 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.110 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG84 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.111 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG85 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.112 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG86 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.113 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG87 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.114 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG88 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.115 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG89 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.116 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG90 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.117 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG91 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.118 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG92 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.119 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG93 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.120 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG94 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.121 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG95 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.122 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG96 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.123 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG97 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.124 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG98 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.125 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG99 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.126 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG100 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.127 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG101 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.128 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG102 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.129 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG103 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.130 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG104 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.131 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG105 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.132 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG106 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.133 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG107 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.134 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG108 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.135 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG109 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.136 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG110 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.137 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG111 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.138 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG112 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.139 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG113 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.140 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG114 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.141 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG115 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.142 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG116 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.143 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG117 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.144 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG118 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.145 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG119 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.146 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG120 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.147 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG121 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.148 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG122 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.149 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG123 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.150 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG124 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.151 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG125 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.152 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG126 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.153 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG127 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.154 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG128 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.155 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG129 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.156 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG130 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.157 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG131 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.158 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG132 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.159 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG133 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.160 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG134 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.161 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG135 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.162 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG136 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.163 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG137 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.164 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG138 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.165 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG139 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.166 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG140 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.167 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG141 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.168 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG143 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.169 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG144 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.170 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG145 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.171 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG147 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.172 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG149 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.173 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG171 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.174 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG172 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.175 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG173 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.176 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG174 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.177 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG175 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.178 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG176 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.179 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG177 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.180 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG178 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.181 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG179 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.182 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG180 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.183 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG181 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.184 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG182 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.185 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG183 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.186 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK1_KICK0 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.187 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK1_KICK1 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.188 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R0_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.189 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R1_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.190 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R2_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.191 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R3_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.192 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R4_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.193 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R5_READONLY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.194 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG0_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.195 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG1_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.196 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG2_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.197 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG3_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.198 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG4_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.199 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG5_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.200 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG6_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.201 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG7_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.202 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG8_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.203 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG9_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.204 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG10_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.205 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG11_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.206 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG12_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.207 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG13_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.208 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG14_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.209 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG15_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.210 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG16_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.211 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG17_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.212 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG18_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.213 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG19_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.214 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG20_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.215 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG21_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.216 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG22_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.217 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG23_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.218 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG24_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.219 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG25_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.220 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG26_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.221 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG27_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.222 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG28_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.223 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG29_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.224 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG30_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.225 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG31_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.226 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG33_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.227 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG34_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.228 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG35_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.229 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG36_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.230 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG37_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.231 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG38_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.232 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG39_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.233 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG40_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.234 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG41_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.235 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG42_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.236 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG43_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.237 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG44_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.238 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG45_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.239 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG46_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.240 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG47_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.241 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG48_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.242 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG49_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.243 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG50_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.244 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG51_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.245 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG52_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.246 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG53_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.247 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG56_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.248 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG57_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.249 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG58_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.250 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG59_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.251 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG60_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.252 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG63_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.253 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG64_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.254 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG65_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.255 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG66_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.256 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG67_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.257 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG68_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.258 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG69_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.259 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG70_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.260 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG71_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.261 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG72_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.262 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG73_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.263 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG74_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.264 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG75_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.265 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG76_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.266 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG77_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.267 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG78_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.268 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG79_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.269 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG80_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.270 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG81_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.271 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG82_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.272 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG83_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.273 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG84_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.274 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG85_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.275 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG86_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.276 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG87_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.277 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG88_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.278 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG89_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.279 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG90_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.280 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG91_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.281 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG92_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.282 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG93_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.283 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG94_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.284 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG95_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.285 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG96_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.286 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG97_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.287 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG98_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.288 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG99_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.289 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG100_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.290 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG101_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.291 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG102_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.292 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG103_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.293 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG104_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.294 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG105_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.295 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG106_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.296 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG107_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.297 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG108_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.298 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG109_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.299 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG110_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.300 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG111_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.301 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG112_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.302 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG113_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.303 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG114_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.304 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG115_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.305 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG116_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.306 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG117_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.307 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG118_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.308 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG119_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.309 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG120_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.310 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG121_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.311 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG122_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.312 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG123_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.313 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG124_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.314 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG125_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.315 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG126_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.316 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG127_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.317 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG128_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.318 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG129_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.319 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG130_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.320 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG131_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.321 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG132_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.322 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG133_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.323 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG134_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.324 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG135_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.325 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG136_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.326 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG137_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.327 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG138_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.328 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG139_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.329 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG140_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.330 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG141_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.331 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG143_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.332 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG144_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.333 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG145_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.334 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG147_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.335 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG149_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.336 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG171_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.337 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG172_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.338 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG173_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.339 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG174_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.340 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG175_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.341 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG176_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.342 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG177_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.343 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG178_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.344 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG179_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.345 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG180_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.346 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG181_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.347 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG182_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.348 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_PADCONFIG183_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.349 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK1_KICK0_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.350 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_LOCK1_KICK1_PROXY Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.351 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R0 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.352 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R1 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.353 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R2 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.354 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R3 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.355 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R4 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.2.2.356 MAIN_PADCFG_CTRL_MMRCFG0_CLAIMREG_P1_R5 Register
- 14.2.1.2.1.1
PADCFG_CTRL
- 14.2.1.2.1
Pad Configuration Register Functional Description
- 14.2.1.3
Security Control Registers
- 14.2.1.3.1
MAIN_SEC_MMR
- 14.2.1.3.1.1 MAIN_SEC_MMR Summaries
- 14.2.1.3.1.2
MAIN_SEC_MMR Registers
- 14.2.1.3.1.2.1 MAIN_SEC_MMR_CFG2_CLSTR0_CORE0_DBG_CFG Register
- 14.2.1.3.1.2.2 MAIN_SEC_MMR_CFG2_CLSTR0_CORE1_DBG_CFG Register
- 14.2.1.3.1.2.3 MAIN_SEC_MMR_CFG2_CLSTR1_CORE0_DBG_CFG Register
- 14.2.1.3.1.2.4 MAIN_SEC_MMR_CFG2_CLSTR1_CORE1_DBG_CFG Register
- 14.2.1.3.1.2.5 MAIN_SEC_MMR_CFG2_CLSTR13_CORE0_DBG_CFG Register
- 14.2.1.3.1.2.6 MAIN_SEC_MMR_CFG2_CLSTR14_CORE0_DBG_CFG Register
- 14.2.1.3.1.2.7 MAIN_SEC_MMR_CFG0_PID Register
- 14.2.1.3.1.2.8 MAIN_SEC_MMR_CFG0_CLSTR0_DEF Register
- 14.2.1.3.1.2.9 MAIN_SEC_MMR_CFG0_CLSTR0_CFG Register
- 14.2.1.3.1.2.10 MAIN_SEC_MMR_CFG0_CLSTR0_PMCTRL Register
- 14.2.1.3.1.2.11 MAIN_SEC_MMR_CFG0_CLSTR0_PMSTAT Register
- 14.2.1.3.1.2.12 MAIN_SEC_MMR_CFG0_CLSTR0_CORE0_CFG Register
- 14.2.1.3.1.2.13 MAIN_SEC_MMR_CFG0_CLSTR0_CORE0_BOOTVECT_LO Register
- 14.2.1.3.1.2.14 MAIN_SEC_MMR_CFG0_CLSTR0_CORE0_BOOTVECT_HI Register
- 14.2.1.3.1.2.15 MAIN_SEC_MMR_CFG0_CLSTR0_CORE0_PMCTRL Register
- 14.2.1.3.1.2.16 MAIN_SEC_MMR_CFG0_CLSTR0_CORE0_PMSTAT Register
- 14.2.1.3.1.2.17 MAIN_SEC_MMR_CFG0_CLSTR0_CORE1_CFG Register
- 14.2.1.3.1.2.18 MAIN_SEC_MMR_CFG0_CLSTR0_CORE1_BOOTVECT_LO Register
- 14.2.1.3.1.2.19 MAIN_SEC_MMR_CFG0_CLSTR0_CORE1_BOOTVECT_HI Register
- 14.2.1.3.1.2.20 MAIN_SEC_MMR_CFG0_CLSTR0_CORE1_PMCTRL Register
- 14.2.1.3.1.2.21 MAIN_SEC_MMR_CFG0_CLSTR0_CORE1_PMSTAT Register
- 14.2.1.3.1.2.22 MAIN_SEC_MMR_CFG0_CLSTR1_DEF Register
- 14.2.1.3.1.2.23 MAIN_SEC_MMR_CFG0_CLSTR1_CFG Register
- 14.2.1.3.1.2.24 MAIN_SEC_MMR_CFG0_CLSTR1_PMCTRL Register
- 14.2.1.3.1.2.25 MAIN_SEC_MMR_CFG0_CLSTR1_PMSTAT Register
- 14.2.1.3.1.2.26 MAIN_SEC_MMR_CFG0_CLSTR1_CORE0_CFG Register
- 14.2.1.3.1.2.27 MAIN_SEC_MMR_CFG0_CLSTR1_CORE0_BOOTVECT_LO Register
- 14.2.1.3.1.2.28 MAIN_SEC_MMR_CFG0_CLSTR1_CORE0_BOOTVECT_HI Register
- 14.2.1.3.1.2.29 MAIN_SEC_MMR_CFG0_CLSTR1_CORE0_PMCTRL Register
- 14.2.1.3.1.2.30 MAIN_SEC_MMR_CFG0_CLSTR1_CORE0_PMSTAT Register
- 14.2.1.3.1.2.31 MAIN_SEC_MMR_CFG0_CLSTR1_CORE1_CFG Register
- 14.2.1.3.1.2.32 MAIN_SEC_MMR_CFG0_CLSTR1_CORE1_BOOTVECT_LO Register
- 14.2.1.3.1.2.33 MAIN_SEC_MMR_CFG0_CLSTR1_CORE1_BOOTVECT_HI Register
- 14.2.1.3.1.2.34 MAIN_SEC_MMR_CFG0_CLSTR1_CORE1_PMCTRL Register
- 14.2.1.3.1.2.35 MAIN_SEC_MMR_CFG0_CLSTR1_CORE1_PMSTAT Register
- 14.2.1.3.1.2.36 MAIN_SEC_MMR_CFG0_CLSTR13_DEF Register
- 14.2.1.3.1.2.37 MAIN_SEC_MMR_CFG0_CLSTR13_CFG Register
- 14.2.1.3.1.2.38 MAIN_SEC_MMR_CFG0_CLSTR13_PMSTAT Register
- 14.2.1.3.1.2.39 MAIN_SEC_MMR_CFG0_CLSTR13_CORE0_BOOTVECT_LO Register
- 14.2.1.3.1.2.40 MAIN_SEC_MMR_CFG0_CLSTR13_CORE0_BOOTVECT_HI Register
- 14.2.1.3.1.2.41 MAIN_SEC_MMR_CFG0_CLSTR14_DEF Register
- 14.2.1.3.1.2.42 MAIN_SEC_MMR_CFG0_CLSTR14_CFG Register
- 14.2.1.3.1.2.43 MAIN_SEC_MMR_CFG0_CLSTR14_PMSTAT Register
- 14.2.1.3.1.2.44 MAIN_SEC_MMR_CFG0_CLSTR14_CORE0_BOOTVECT_LO Register
- 14.2.1.3.1.2.45 MAIN_SEC_MMR_CFG0_CLSTR14_CORE0_BOOTVECT_HI Register
- 14.2.1.3.2
WKUP_SEC_MMR
- 14.2.1.3.2.1 WKUP_SEC_MMR Summaries
- 14.2.1.3.2.2
WKUP_SEC_MMR Registers
- 14.2.1.3.2.2.1 WKUP_SEC_MMR_CFG2_CLSTR28_CORE0_DBG_CFG Register
- 14.2.1.3.2.2.2 WKUP_SEC_MMR_CFG2_CLSTR28_CORE1_DBG_CFG Register
- 14.2.1.3.2.2.3 WKUP_SEC_MMR_CFG0_PID Register
- 14.2.1.3.2.2.4 WKUP_SEC_MMR_CFG0_CLSTR28_DEF Register
- 14.2.1.3.2.2.5 WKUP_SEC_MMR_CFG0_CLSTR28_CFG Register
- 14.2.1.3.2.2.6 WKUP_SEC_MMR_CFG0_CLSTR28_PMCTRL Register
- 14.2.1.3.2.2.7 WKUP_SEC_MMR_CFG0_CLSTR28_PMSTAT Register
- 14.2.1.3.2.2.8 WKUP_SEC_MMR_CFG0_CLSTR28_CORE0_CFG Register
- 14.2.1.3.2.2.9 WKUP_SEC_MMR_CFG0_CLSTR28_CORE0_BOOTVECT_LO Register
- 14.2.1.3.2.2.10 WKUP_SEC_MMR_CFG0_CLSTR28_CORE0_BOOTVECT_HI Register
- 14.2.1.3.2.2.11 WKUP_SEC_MMR_CFG0_CLSTR28_CORE0_PMCTRL Register
- 14.2.1.3.2.2.12 WKUP_SEC_MMR_CFG0_CLSTR28_CORE0_PMSTAT Register
- 14.2.1.3.1
MAIN_SEC_MMR
- 14.2.1.1
General Purpose Control Registers
- 14.2.2
Power Registers
- 14.2.2.1
PSC
- 14.2.2.1.1 PSC Summaries
- 14.2.2.1.2
PSC Registers
- 14.2.2.1.2.1 PSC_PID Register
- 14.2.2.1.2.2 PSC_GBLSTAT Register
- 14.2.2.1.2.3 PSC_INTEVAL Register
- 14.2.2.1.2.4 PSC_MERRPR Register
- 14.2.2.1.2.5 PSC_MERRCR Register
- 14.2.2.1.2.6 PSC_PERRPR Register
- 14.2.2.1.2.7 PSC_PERRCR Register
- 14.2.2.1.2.8 PSC_EPCPR Register
- 14.2.2.1.2.9 PSC_EPCCR Register
- 14.2.2.1.2.10 PSC_RAILSTAT Register
- 14.2.2.1.2.11 PSC_RAILCTL Register
- 14.2.2.1.2.12 PSC_RAILSEL Register
- 14.2.2.1.2.13 PSC_PTCMD Register
- 14.2.2.1.2.14 PSC_PTSTAT Register
- 14.2.2.1.2.15 PSC_PDSTAT_J Register
- 14.2.2.1.2.16 PSC_PDCTL_J Register
- 14.2.2.1.2.17 PSC_PDCFG_J Register
- 14.2.2.1.2.18 PSC_MDCFG_J Register
- 14.2.2.1.2.19 PSC_MDSTAT_J Register
- 14.2.2.1.2.20 PSC_MDCTL_J Register
- 14.2.2.2
PSC
- 14.2.2.2.1 PSC Summaries
- 14.2.2.2.2
PSC Registers
- 14.2.2.2.2.1 PSC_PID Register
- 14.2.2.2.2.2 PSC_GBLSTAT Register
- 14.2.2.2.2.3 PSC_INTEVAL Register
- 14.2.2.2.2.4 PSC_MERRPR_J Register
- 14.2.2.2.2.5 PSC_MERRCR_J Register
- 14.2.2.2.2.6 PSC_PERRPR Register
- 14.2.2.2.2.7 PSC_PERRCR Register
- 14.2.2.2.2.8 PSC_EPCPR Register
- 14.2.2.2.2.9 PSC_EPCCR Register
- 14.2.2.2.2.10 PSC_RAILSTAT Register
- 14.2.2.2.2.11 PSC_RAILCTL Register
- 14.2.2.2.2.12 PSC_RAILSEL Register
- 14.2.2.2.2.13 PSC_PTCMD Register
- 14.2.2.2.2.14 PSC_PTSTAT Register
- 14.2.2.2.2.15 PSC_PDSTAT_J Register
- 14.2.2.2.2.16 PSC_PDCTL_J Register
- 14.2.2.2.2.17 PSC_PDCFG_J Register
- 14.2.2.2.2.18 PSC_MDCFG_J Register
- 14.2.2.2.2.19 PSC_MDSTAT_J Register
- 14.2.2.2.2.20 PSC_MDCTL_J Register
- 14.2.2.3
VTM
- 14.2.2.3.1 VTM Summaries
- 14.2.2.3.2
VTM Registers
- 14.2.2.3.2.1 VTM_CFG1_PID Register
- 14.2.2.3.2.2 VTM_CFG1_DEVINFO_PWR0 Register
- 14.2.2.3.2.3 VTM_CFG1_GT_TH1_INT_RAW_STAT_SET Register
- 14.2.2.3.2.4 VTM_CFG1_GT_TH1_INT_EN_STAT_CLR Register
- 14.2.2.3.2.5 VTM_CFG1_GT_TH1_INT_EN_SET Register
- 14.2.2.3.2.6 VTM_CFG1_GT_TH1_INT_EN_CLR Register
- 14.2.2.3.2.7 VTM_CFG1_GT_TH2_INT_RAW_STAT_SET Register
- 14.2.2.3.2.8 VTM_CFG1_GT_TH2_INT_EN_STAT_CLR Register
- 14.2.2.3.2.9 VTM_CFG1_GT_TH2_INT_EN_SET Register
- 14.2.2.3.2.10 VTM_CFG1_GT_TH2_INT_EN_CLR Register
- 14.2.2.3.2.11 VTM_CFG1_LT_TH0_INT_RAW_STAT_SET Register
- 14.2.2.3.2.12 VTM_CFG1_LT_TH0_INT_EN_STAT_CLR Register
- 14.2.2.3.2.13 VTM_CFG1_LT_TH0_INT_EN_SET Register
- 14.2.2.3.2.14 VTM_CFG1_LT_TH0_INT_EN_CLR Register
- 14.2.2.3.2.15 VTM_CFG1_VD_DEVINFO_J Register
- 14.2.2.3.2.16 VTM_CFG1_VD_OPPVID_J Register
- 14.2.2.3.2.17 VTM_CFG1_VD_EVT_STAT_J Register
- 14.2.2.3.2.18 VTM_CFG1_VD_EVT_SET_J Register
- 14.2.2.3.2.19 VTM_CFG1_VD_EVT_CLR_J Register
- 14.2.2.3.2.20 VTM_CFG1_TMPSENS_CTRL_J Register
- 14.2.2.3.2.21 VTM_CFG1_TMPSENS_STAT_J Register
- 14.2.2.3.2.22 VTM_CFG1_TMPSENS_TH_J Register
- 14.2.2.3.2.23 VTM_CFG1_TMPSENS_TH2_J Register
- 14.2.2.3.2.24 VTM_CFG2_MISC_CTRL Register
- 14.2.2.3.2.25 VTM_CFG2_MISC_CTRL2 Register
- 14.2.2.3.2.26 VTM_CFG2_TMPSENS_CTRL_J Register
- 14.2.2.3.2.27 VTM_CFG2_TMPSENS_TRIM_J Register
- 14.2.2.3.2.28 ECC_AGGR_REV Register
- 14.2.2.3.2.29 ECC_AGGR_VECTOR Register
- 14.2.2.3.2.30 ECC_AGGR_STAT Register
- 14.2.2.3.2.31 ECC_AGGR_RESERVED_SVBUS_J Register
- 14.2.2.3.2.32 ECC_AGGR_SEC_EOI_REG Register
- 14.2.2.3.2.33 ECC_AGGR_SEC_STATUS_REG0 Register
- 14.2.2.3.2.34 ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Register
- 14.2.2.3.2.35 ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Register
- 14.2.2.3.2.36 ECC_AGGR_DED_EOI_REG Register
- 14.2.2.3.2.37 ECC_AGGR_DED_STATUS_REG0 Register
- 14.2.2.3.2.38 ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Register
- 14.2.2.3.2.39 ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Register
- 14.2.2.3.2.40 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_SET Register
- 14.2.2.3.2.41 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_CLR Register
- 14.2.2.3.2.42 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_STATUS_SET Register
- 14.2.2.3.2.43 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_STATUS_CLR Register
- 14.2.2.1
PSC
- 14.2.3
Clocking Registers
- 14.2.3.1
PLL
- 14.2.3.1.1 PLL Summaries
- 14.2.3.1.2
PLL Registers
- 14.2.3.1.2.1 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL0_PID Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.2 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL0_CFG Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.3 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL0_LOCKKEY0 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.4 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL0_LOCKKEY1 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.5 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL0_CTRL Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.6 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL0_STAT Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.7 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL0_FREQ_CTRL0 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.8 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL0_FREQ_CTRL1 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.9 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL0_DIV_CTRL Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.10 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL0_SS_CTRL Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.11 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL0_SS_SPREAD Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.12 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL0_CAL_CTRL Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.13 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL0_CAL_STAT Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.14 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL0_HSDIV_CTRL0 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.15 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL0_HSDIV_CTRL1 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.16 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL0_HSDIV_CTRL2 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.17 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL0_HSDIV_CTRL3 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.18 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL0_HSDIV_CTRL4 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.19 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL0_HSDIV_CTRL5 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.20 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL0_HSDIV_CTRL6 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.21 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL0_HSDIV_CTRL7 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.22 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL0_HSDIV_CTRL8 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.23 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL0_HSDIV_CTRL9 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.24 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL1_PID Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.25 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL1_CFG Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.26 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL1_LOCKKEY0 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.27 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL1_LOCKKEY1 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.28 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL1_CTRL Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.29 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL1_STAT Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.30 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL1_FREQ_CTRL0 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.31 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL1_FREQ_CTRL1 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.32 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL1_DIV_CTRL Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.33 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL1_SS_CTRL Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.34 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL1_SS_SPREAD Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.35 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL1_CAL_CTRL Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.36 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL1_CAL_STAT Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.37 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL1_HSDIV_CTRL0 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.38 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL1_HSDIV_CTRL1 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.39 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL1_HSDIV_CTRL2 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.40 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL1_HSDIV_CTRL3 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.41 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL1_HSDIV_CTRL4 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.42 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL1_HSDIV_CTRL5 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.43 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL1_HSDIV_CTRL6 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.44 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL2_PID Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.45 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL2_CFG Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.46 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL2_LOCKKEY0 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.47 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL2_LOCKKEY1 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.48 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL2_CTRL Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.49 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL2_STAT Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.50 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL2_FREQ_CTRL0 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.51 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL2_FREQ_CTRL1 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.52 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL2_DIV_CTRL Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.53 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL2_SS_CTRL Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.54 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL2_SS_SPREAD Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.55 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL2_CAL_CTRL Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.56 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL2_CAL_STAT Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.57 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL2_HSDIV_CTRL0 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.58 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL2_HSDIV_CTRL1 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.59 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL2_HSDIV_CTRL2 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.60 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL2_HSDIV_CTRL3 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.61 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL2_HSDIV_CTRL4 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.62 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL2_HSDIV_CTRL5 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.63 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL2_HSDIV_CTRL6 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.64 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL2_HSDIV_CTRL7 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.65 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL2_HSDIV_CTRL8 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.66 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL2_HSDIV_CTRL9 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.67 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL4_PID Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.68 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL4_CFG Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.69 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL4_LOCKKEY0 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.70 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL4_LOCKKEY1 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.71 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL4_CTRL Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.72 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL4_STAT Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.73 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL4_FREQ_CTRL0 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.74 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL4_FREQ_CTRL1 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.75 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL4_DIV_CTRL Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.76 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL4_SS_CTRL Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.77 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL4_SS_SPREAD Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.78 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL4_CAL_CTRL Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.79 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL4_CAL_STAT Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.80 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL4_HSDIV_CTRL0 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.81 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL4_HSDIV_CTRL1 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.82 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL4_HSDIV_CTRL2 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.83 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL4_HSDIV_CTRL3 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.84 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL7_PID Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.85 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL7_CFG Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.86 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL7_LOCKKEY0 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.87 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL7_LOCKKEY1 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.88 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL7_CTRL Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.89 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL7_STAT Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.90 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL7_FREQ_CTRL0 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.91 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL7_FREQ_CTRL1 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.92 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL7_DIV_CTRL Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.93 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL7_SS_CTRL Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.94 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL7_SS_SPREAD Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.95 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL7_CAL_CTRL Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.96 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL7_CAL_STAT Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.97 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL7_HSDIV_CTRL0 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.98 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL7_HSDIV_CTRL1 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.99 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL14_PID Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.100 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL14_CFG Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.101 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL14_LOCKKEY0 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.102 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL14_LOCKKEY1 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.103 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL14_CTRL Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.104 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL14_STAT Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.105 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL14_FREQ_CTRL0 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.106 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL14_FREQ_CTRL1 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.107 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL14_DIV_CTRL Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.108 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL14_SS_CTRL Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.109 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL14_SS_SPREAD Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.110 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL14_CAL_CTRL Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.111 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL14_CAL_STAT Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.112 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL14_HSDIV_CTRL0 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.113 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL14_HSDIV_CTRL1 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.114 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL15_PID Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.115 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL15_CFG Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.116 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL15_LOCKKEY0 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.117 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL15_LOCKKEY1 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.118 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL15_CTRL Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.119 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL15_STAT Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.120 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL15_FREQ_CTRL0 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.121 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL15_FREQ_CTRL1 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.122 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL15_DIV_CTRL Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.123 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL15_SS_CTRL Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.124 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL15_SS_SPREAD Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.125 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL15_CAL_CTRL Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.126 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL15_CAL_STAT Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.127 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL15_HSDIV_CTRL0 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.128 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL15_HSDIV_CTRL1 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.129 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL15_HSDIV_CTRL2 Register
- 14.2.3.1.2.130 MAIN_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL15_HSDIV_CTRL3 Register
- 14.2.3.2
PLL
- 14.2.3.2.1 PLL Summaries
- 14.2.3.2.2
PLL Registers
- 14.2.3.2.2.1 MCU_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL0_PID Register
- 14.2.3.2.2.2 MCU_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL0_CFG Register
- 14.2.3.2.2.3 MCU_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL0_LOCKKEY0 Register
- 14.2.3.2.2.4 MCU_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL0_LOCKKEY1 Register
- 14.2.3.2.2.5 MCU_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL0_CTRL Register
- 14.2.3.2.2.6 MCU_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL0_STAT Register
- 14.2.3.2.2.7 MCU_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL0_FREQ_CTRL0 Register
- 14.2.3.2.2.8 MCU_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL0_FREQ_CTRL1 Register
- 14.2.3.2.2.9 MCU_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL0_DIV_CTRL Register
- 14.2.3.2.2.10 MCU_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL0_SS_CTRL Register
- 14.2.3.2.2.11 MCU_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL0_SS_SPREAD Register
- 14.2.3.2.2.12 MCU_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL0_CAL_CTRL Register
- 14.2.3.2.2.13 MCU_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL0_CAL_STAT Register
- 14.2.3.2.2.14 MCU_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL0_HSDIV_CTRL0 Register
- 14.2.3.2.2.15 MCU_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL0_HSDIV_CTRL1 Register
- 14.2.3.2.2.16 MCU_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL0_HSDIV_CTRL2 Register
- 14.2.3.2.2.17 MCU_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL0_HSDIV_CTRL3 Register
- 14.2.3.2.2.18 MCU_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL0_HSDIV_CTRL4 Register
- 14.2.3.2.2.19 MCU_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL0_HSDIV_CTRL5 Register
- 14.2.3.2.2.20 MCU_PLL_MMRCFG_PLL0_HSDIV_CTRL6 Register
- 14.2.3.3 TIMESYNC_EVENT_INTROUTER
- 14.2.3.1
PLL
- 14.2.1
Control Module (CTRL_MMR)
- 14.3
Processors and Accelerators Registers
- 14.3.1
R5FSS Registers
- 14.3.1.1
R5FSS_COMMON0
- 14.3.1.1.1 R5FSS_COMMON0 Summaries
- 14.3.1.1.2
R5FSS_COMMON0 Registers
- 14.3.1.1.2.1 ECC_AGGR_REV Register
- 14.3.1.1.2.2 ECC_AGGR_VECTOR Register
- 14.3.1.1.2.3 ECC_AGGR_STAT Register
- 14.3.1.1.2.4 ECC_AGGR_RESERVED_SVBUS_J Register
- 14.3.1.1.2.5 ECC_AGGR_SEC_EOI_REG Register
- 14.3.1.1.2.6 ECC_AGGR_SEC_STATUS_REG0 Register
- 14.3.1.1.2.7 ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Register
- 14.3.1.1.2.8 ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Register
- 14.3.1.1.2.9 ECC_AGGR_DED_EOI_REG Register
- 14.3.1.1.2.10 ECC_AGGR_DED_STATUS_REG0 Register
- 14.3.1.1.2.11 ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Register
- 14.3.1.1.2.12 ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Register
- 14.3.1.1.2.13 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_SET Register
- 14.3.1.1.2.14 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_CLR Register
- 14.3.1.1.2.15 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_STATUS_SET Register
- 14.3.1.1.2.16 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_STATUS_CLR Register
- 14.3.1.2
R5FSS_COMMON0
- 14.3.1.2.1 R5FSS_COMMON0 Summaries
- 14.3.1.2.2
R5FSS_COMMON0 Registers
- 14.3.1.2.2.1 R5FSS_COMMON0_COMPARE_CFG_CCMSR1 Register
- 14.3.1.2.2.2 R5FSS_COMMON0_COMPARE_CFG_CCMKEYR1 Register
- 14.3.1.2.2.3 R5FSS_COMMON0_COMPARE_CFG_CCMSR2 Register
- 14.3.1.2.2.4 R5FSS_COMMON0_COMPARE_CFG_CCMKEYR2 Register
- 14.3.1.2.2.5 R5FSS_COMMON0_COMPARE_CFG_CCMSR3 Register
- 14.3.1.2.2.6 R5FSS_COMMON0_COMPARE_CFG_CCMKEYR3 Register
- 14.3.1.2.2.7 R5FSS_COMMON0_COMPARE_CFG_CCMPOLCNTRL Register
- 14.3.1.2.2.8 R5FSS_COMMON0_EVNT_BUS_VBUSP_MMRS_DISABLE_CR Register
- 14.3.1.2.2.9 R5FSS_COMMON0_EVNT_BUS_VBUSP_MMRS_PULSAR_CPU0_EVNT_BUS_SB_ERR_CNT_STATUS Register
- 14.3.1.2.2.10 R5FSS_COMMON0_EVNT_BUS_VBUSP_MMRS_PULSAR_CPU1_EVNT_BUS_SB_ERR_CNT_STATUS Register
- 14.3.1.2.2.11 R5FSS_COMMON0_EVNT_BUS_VBUSP_MMRS_PULSAR_CPU0_EVNT_BUS_MB_ERR_CNT_STATUS Register
- 14.3.1.2.2.12 R5FSS_COMMON0_EVNT_BUS_VBUSP_MMRS_PULSAR_CPU1_EVNT_BUS_MB_ERR_CNT_STATUS Register
- 14.3.1.2.2.13 R5FSS_COMMON0_EVNT_BUS_VBUSP_MMRS_PULSAR_EVNT_BUS_ESM_STATUS Register
- 14.3.1.2.2.14 R5FSS_COMMON0_EVNT_BUS_VBUSP_MMRS_PULSAR_EVNT_BUS_ESM_SET Register
- 14.3.1.2.2.15 R5FSS_COMMON0_EVNT_BUS_VBUSP_MMRS_PULSAR_EVNT_BUS_ESM_CLR Register
- 14.3.1.2.2.16 R5FSS_COMMON0_EVNT_BUS_VBUSP_MMRS_PULSAR_EVNT_BUS_MASK_ESM_SET Register
- 14.3.1.2.2.17 R5FSS_COMMON0_EVNT_BUS_VBUSP_MMRS_PULSAR_EVNT_BUS_MASK_ESM_CLR Register
- 14.3.1.2.2.18 R5FSS_COMMON0_EVNT_BUS_VBUSP_MMRS_PULSAR_EVT_BUS_REVID Register
- 14.3.1.3
rl2_of_cba4
- 14.3.1.3.1 rl2_of_cba4 Summaries
- 14.3.1.3.2
rl2_of_cba4 Registers
- 14.3.1.3.2.1 RL2_OF_CBA4_MOD_VER Register
- 14.3.1.3.2.2 RL2_OF_CBA4_L2_CTRL Register
- 14.3.1.3.2.3 RL2_OF_CBA4_L2_STS Register
- 14.3.1.3.2.4 RL2_OF_CBA4_L2_LO_LSW Register
- 14.3.1.3.2.5 RL2_OF_CBA4_L2_LO_MSW Register
- 14.3.1.3.2.6 RL2_OF_CBA4_L2_HI Register
- 14.3.1.3.2.7 RL2_OF_CBA4_L2_HI_MSW Register
- 14.3.1.3.2.8 RL2_OF_CBA4_L2HC Register
- 14.3.1.3.2.9 RL2_OF_CBA4_L2MC Register
- 14.3.1.3.2.10 RL2_OF_CBA4_IRQSTATUS_RAW Register
- 14.3.1.3.2.11 RL2_OF_CBA4_IRQSTATUS_MSK Register
- 14.3.1.3.2.12 RL2_OF_CBA4_IRQENABLE_SET Register
- 14.3.1.3.2.13 RL2_OF_CBA4_IRQENABLE_CLR Register
- 14.3.1.3.2.14 RL2_OF_CBA4_FLC_CFG Register
- 14.3.1.3.2.15 RL2_OF_CBA4_FLC_STS Register
- 14.3.1.3.2.16 RL2_OF_CBA4_FLC_DBG0 Register
- 14.3.1.3.2.17 RL2_OF_CBA4_FLC_DBG1 Register
- 14.3.1.3.2.18 RL2_OF_CBA4_FLC_DBG2 Register
- 14.3.1.3.2.19 RL2_OF_CBA4_RAT_CFG Register
- 14.3.1.3.2.20 RL2_OF_CBA4_TRK0_LO Register
- 14.3.1.3.2.21 RL2_OF_CBA4_TRK0_LO_MSW Register
- 14.3.1.3.2.22 RL2_OF_CBA4_TRK0_HI Register
- 14.3.1.3.2.23 RL2_OF_CBA4_TRK0_HI_MSW Register
- 14.3.1.3.2.24 RL2_OF_CBA4_TRK0_CTL Register
- 14.3.1.3.2.25 RL2_OF_CBA4_REM_ADR Register
- 14.3.1.3.2.26 RL2_OF_CBA4_REM_ADR_MSW Register
- 14.3.1.3.2.27 RL2_OF_CBA4_REM_LEN Register
- 14.3.1.3.2.28 RL2_OF_CBA4_FLC_LO_J Register
- 14.3.1.3.2.29 RL2_OF_CBA4_FLC_LO_MSW_J Register
- 14.3.1.3.2.30 RL2_OF_CBA4_FLC_HI_J Register
- 14.3.1.3.2.31 RL2_OF_CBA4_FLC_HI_MSW_J Register
- 14.3.1.3.2.32 RL2_OF_CBA4_FLC_RA_J Register
- 14.3.1.3.2.33 RL2_OF_CBA4_FLC_RA_MSW_J Register
- 14.3.1.3.2.34 RL2_OF_CBA4_FLC_CTL_J Register
- 14.3.1.1
R5FSS_COMMON0
- 14.3.2
DSP (C7x256v) Registers
- 14.3.2.1
C7X256V_CLEC
- 14.3.2.1.1 C7X256V_CLEC Summaries
- 14.3.2.1.2
C7X256V_CLEC Registers
- 14.3.2.1.2.1 CLEC_EVT_GLOBAL_PID Register
- 14.3.2.1.2.2 CLEC_EVT_GLOBAL_GELRS Register
- 14.3.2.1.2.3 CLEC_EVT_GLOBAL_GELRNS Register
- 14.3.2.1.2.4 CLEC_EVT_CFG_MRR_J Register
- 14.3.2.1.2.5 CLEC_EVT_CFG_ESR_J Register
- 14.3.2.1.2.6 CLEC_EVT_CFG_ECR_J Register
- 14.3.2.1.2.7 CLEC_EVT_GLOBAL_SET_FLAG_EFR_J Register
- 14.3.2.1.2.8 CLEC_EVT_GLOBAL_DROP_FLAG_EDR_J Register
- 14.3.2.2
C7X256V_CORE0
- 14.3.2.2.1 C7X256V_CORE0 Summaries
- 14.3.2.2.2
C7X256V_CORE0 Registers
- 14.3.2.2.2.1 DRU_ATOMIC_CHATOMIC_DEBUG_ATOMIC_SUBMIT_CURR_TR_WORD0_1_J Register
- 14.3.2.2.2.2 DRU_ATOMIC_CHATOMIC_DEBUG_ATOMIC_SUBMIT_CURR_TR_WORD2_3_J Register
- 14.3.2.2.2.3 DRU_ATOMIC_CHATOMIC_DEBUG_ATOMIC_SUBMIT_CURR_TR_WORD4_5_J Register
- 14.3.2.2.2.4 DRU_ATOMIC_CHATOMIC_DEBUG_ATOMIC_SUBMIT_CURR_TR_WORD6_7_J Register
- 14.3.2.2.2.5 DRU_ATOMIC_CHATOMIC_DEBUG_ATOMIC_SUBMIT_CURR_TR_WORD8_9_J Register
- 14.3.2.2.2.6 DRU_ATOMIC_CHATOMIC_DEBUG_ATOMIC_SUBMIT_CURR_TR_WORD10_11_J Register
- 14.3.2.2.2.7 DRU_ATOMIC_CHATOMIC_DEBUG_ATOMIC_SUBMIT_CURR_TR_WORD12_13_J Register
- 14.3.2.2.2.8 DRU_ATOMIC_CHATOMIC_DEBUG_ATOMIC_SUBMIT_CURR_TR_WORD14_15_J Register
- 14.3.2.2.2.9 DRU_ATOMIC_CHATOMIC_DEBUG_DEBUG_NEXT_TR_WORD0_1_J_K Register
- 14.3.2.2.2.10 DRU_ATOMIC_CHATOMIC_DEBUG_DEBUG_NEXT_TR_WORD2_3_J_K Register
- 14.3.2.2.2.11 DRU_ATOMIC_CHATOMIC_DEBUG_DEBUG_NEXT_TR_WORD4_5_J_K Register
- 14.3.2.2.2.12 DRU_ATOMIC_CHATOMIC_DEBUG_DEBUG_NEXT_TR_WORD6_7_J_K Register
- 14.3.2.2.2.13 DRU_ATOMIC_CHATOMIC_DEBUG_DEBUG_NEXT_TR_WORD8_9_J_K Register
- 14.3.2.2.2.14 DRU_ATOMIC_CHATOMIC_DEBUG_DEBUG_NEXT_TR_WORD10_11_J_K Register
- 14.3.2.2.2.15 DRU_ATOMIC_CHATOMIC_DEBUG_DEBUG_NEXT_TR_WORD12_13_J_K Register
- 14.3.2.2.2.16 DRU_ATOMIC_CHATOMIC_DEBUG_DEBUG_NEXT_TR_WORD14_15_J_K Register
- 14.3.2.2.2.17 DRU_CHCORE_CHCORE_CORE_SUBMIT_WORD0_1_J_K Register
- 14.3.2.2.2.18 DRU_CHCORE_CHCORE_CORE_SUBMIT_WORD2_3_J_K Register
- 14.3.2.2.2.19 DRU_CHCORE_CHCORE_CORE_SUBMIT_WORD4_5_J_K Register
- 14.3.2.2.2.20 DRU_CHCORE_CHCORE_CORE_SUBMIT_WORD6_7_J_K Register
- 14.3.2.2.2.21 DRU_CHCORE_CHCORE_CORE_SUBMIT_WORD8_9_J_K Register
- 14.3.2.2.2.22 DRU_CHCORE_CHCORE_CORE_SUBMIT_WORD10_11_J_K Register
- 14.3.2.2.2.23 DRU_CHCORE_CHCORE_CORE_SUBMIT_WORD12_13_J_K Register
- 14.3.2.2.2.24 DRU_CHCORE_CHCORE_CORE_SUBMIT_WORD14_15_J_K Register
- 14.3.2.3
C7X256V_DEBUG
- 14.3.2.3.1 C7X256V_DEBUG Summaries
- 14.3.2.3.2
C7X256V_DEBUG Registers
- 14.3.2.3.2.1 THINMAN_REG_DBG_CAP Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.2 THINMAN_REG_DBG_PID Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.3 THINMAN_REG_DBG_CNTL Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.4 THINMAN_REG_DBG_STAT Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.5 THINMAN_REG_DBG_OWN Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.6 THINMAN_REG_DBG_INDRCT_CAP0 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.7 THINMAN_REG_DBG_INDRCT_CAP1 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.8 THINMAN_REG_DBG_INDRCT_CNTL Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.9 THINMAN_REG_DBG_INDRCT_CTXT0 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.10 THINMAN_REG_DBG_INDRCT_CTXT1 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.11 THINMAN_REG_DBG_INDRCT_CTXT2 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.12 THINMAN_REG_DBG_INDRCT_ADDR0 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.13 THINMAN_REG_DBG_INDRCT_ADDR1 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.14 THINMAN_REG_DBG_INDRCT_DATA0 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.15 THINMAN_REG_DBG_INDRCT_DATA1 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.16 THINMAN_REG_DBG_HWBP_0_CNTL Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.17 THINMAN_REG_DBG_HWBP_0_CTXT0 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.18 THINMAN_REG_DBG_HWBP_0_CTXT1 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.19 THINMAN_REG_DBG_HWBP_0_CTXT2 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.20 THINMAN_REG_DBG_HWBP_0_ADDR0 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.21 THINMAN_REG_DBG_HWBP_0_ADDR1 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.22 THINMAN_REG_DBG_HWBP_0_AMASK0 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.23 THINMAN_REG_DBG_HWBP_0_AMASK1 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.24 THINMAN_REG_DBG_HWBP_1_CNTL Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.25 THINMAN_REG_DBG_HWBP_1_CTXT0 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.26 THINMAN_REG_DBG_HWBP_1_CTXT1 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.27 THINMAN_REG_DBG_HWBP_1_CTXT2 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.28 THINMAN_REG_DBG_HWBP_1_ADDR0 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.29 THINMAN_REG_DBG_HWBP_1_ADDR1 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.30 THINMAN_REG_DBG_HWBP_1_AMASK0 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.31 THINMAN_REG_DBG_HWBP_1_AMASK1 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.32 THINMAN_REG_DBG_HWBP_2_CNTL Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.33 THINMAN_REG_DBG_HWBP_2_CTXT0 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.34 THINMAN_REG_DBG_HWBP_2_CTXT1 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.35 THINMAN_REG_DBG_HWBP_2_CTXT2 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.36 THINMAN_REG_DBG_HWBP_2_ADDR0 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.37 THINMAN_REG_DBG_HWBP_2_ADDR1 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.38 THINMAN_REG_DBG_HWBP_2_AMASK0 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.39 THINMAN_REG_DBG_HWBP_2_AMASK1 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.40 THINMAN_REG_DBG_HWBP_3_CNTL Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.41 THINMAN_REG_DBG_HWBP_3_CTXT0 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.42 THINMAN_REG_DBG_HWBP_3_CTXT1 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.43 THINMAN_REG_DBG_HWBP_3_CTXT2 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.44 THINMAN_REG_DBG_HWBP_3_ADDR0 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.45 THINMAN_REG_DBG_HWBP_3_ADDR1 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.46 THINMAN_REG_DBG_HWBP_3_AMASK0 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.47 THINMAN_REG_DBG_HWBP_3_AMASK1 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.48 THINMAN_REG_DBG_HWWP_0_CNTL Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.49 THINMAN_REG_DBG_HWWP_0_CTXT0 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.50 THINMAN_REG_DBG_HWWP_0_CTXT1 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.51 THINMAN_REG_DBG_HWWP_0_CTXT2 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.52 THINMAN_REG_DBG_HWWP_0_ADDR0 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.53 THINMAN_REG_DBG_HWWP_0_ADDR1 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.54 THINMAN_REG_DBG_HWWP_0_AMASK0 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.55 THINMAN_REG_DBG_HWWP_0_AMASK1 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.56 COLUMBO_COLUMBO_REG_AET_PID Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.57 COLUMBO_COLUMBO_REG_AET_OWN Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.58 COLUMBO_COLUMBO_REG_AET_STAT Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.59 COLUMBO_COLUMBO_REG_AET_EVT Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.60 COLUMBO_COLUMBO_REG_AET_PC_0 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.61 COLUMBO_COLUMBO_REG_AET_PC_1 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.62 COLUMBO_COLUMBO_REG_IAR_ADD Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.63 COLUMBO_COLUMBO_REG_IAR_DAT Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.64 MATLOCK_REG_TRC_ID Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.65 MATLOCK_REG_TRC_OWN Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.66 MATLOCK_REG_TRC_CNTL Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.67 MATLOCK_REG_TRC_PER_CNT Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.68 MATLOCK_REG_TRC_STAT Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.69 MATLOCK_REG_TRC_TRIG0_CNTL_STAT Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.70 MATLOCK_REG_TRC_TRIG1_CNTL_STAT Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.71 MATLOCK_REG_TRC_TIMESTAMP_CNT_REG0 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.72 MATLOCK_REG_TRC_TIMESTAMP_CNT_REG1 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.73 MATLOCK_REG_TRC_EXPT_CNTL Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.74 MATLOCK_REG_TRC_EXPT_STAT Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.75 MATLOCK_REG_TRC_EXPT_ATID Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.76 CSCTI_CTICONTROL Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.77 CSCTI_CTIINTACK Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.78 CSCTI_CTIAPPSET Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.79 CSCTI_CTIAPPCLR Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.80 CSCTI_CTIAPPPULSE Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.81 CSCTI_CTIINEN0 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.82 CSCTI_CTIINEN1 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.83 CSCTI_CTIINEN2 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.84 CSCTI_CTIINEN3 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.85 CSCTI_CTIINEN4 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.86 CSCTI_CTIINEN5 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.87 CSCTI_CTIINEN6 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.88 CSCTI_CTIINEN7 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.89 CSCTI_CTIOUTEN0 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.90 CSCTI_CTIOUTEN1 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.91 CSCTI_CTIOUTEN2 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.92 CSCTI_CTIOUTEN3 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.93 CSCTI_CTIOUTEN4 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.94 CSCTI_CTIOUTEN5 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.95 CSCTI_CTIOUTEN6 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.96 CSCTI_CTIOUTEN7 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.97 CSCTI_CTITRIGINSTATUS Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.98 CSCTI_CTITRIGOUTSTATUS Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.99 CSCTI_CTICHINSTATUS Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.100 CSCTI_CTICHOUTSTATUS Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.101 CSCTI_CTIGATE Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.102 CSCTI_ASICCTL Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.103 CSCTI_ITCHINACK Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.104 CSCTI_ITTRIGINACK Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.105 CSCTI_ITCHOUT Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.106 CSCTI_ITTRIGOUT Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.107 CSCTI_ITCHOUTACK Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.108 CSCTI_ITTRIGOUTACK Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.109 CSCTI_ITCHIN Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.110 CSCTI_ITTRIGIN Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.111 CSCTI_ITCTRL Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.112 CSCTI_CLAIMSET Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.113 CSCTI_CLAIMCLR Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.114 CSCTI_LOCKACCESS Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.115 CSCTI_LOCKSTATUS Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.116 CSCTI_AUTHSTATUS Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.117 CSCTI_DEVID Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.118 CSCTI_DEVTYPE Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.119 CSCTI_PERIPHID4 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.120 CSCTI_PERIPHID0 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.121 CSCTI_PERIPHID1 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.122 CSCTI_PERIPHID2 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.123 CSCTI_PERIPHID3 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.124 CSCTI_COMPID0 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.125 CSCTI_COMPID1 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.126 CSCTI_COMPID2 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.127 CSCTI_COMPID3 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.128 CTSET2_CFG_CTSETID Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.129 CTSET2_CFG_CTSETSYSCFG Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.130 CTSET2_CFG_SETSTR Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.131 CTSET2_CFG_DBGTIMELOW Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.132 CTSET2_CFG_DBGTIMEHI Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.133 CTSET2_CFG_CTSETCFG Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.134 CTSET2_CFG_SETSPLREG Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.135 CTSET2_CFG_SETEVTENBL1 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.136 CTSET2_CFG_SETEVTENBL2 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.137 CTSET2_CFG_SETEVTENBL3 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.138 CTSET2_CFG_SETEVTENBL4 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.139 CTSET2_CFG_SETEVTENBL5 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.140 CTSET2_CFG_SETEVTENBL6 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.141 CTSET2_CFG_SETEVTENBL7 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.142 CTSET2_CFG_SETEVTENBL8 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.143 CTSET2_CFG_SETMSTID Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.144 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTL Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.145 CTSET2_CFG_CTNUMDBG Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.146 CTSET2_CFG_CTUSERACCCTL Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.147 CTSET2_CFG_CTSTMCNTL Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.148 CTSET2_CFG_CTSTMMSTID Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.149 CTSET2_CFG_CTSTMINTVL Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.150 CTSET2_CFG_CTSTMSEL0 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.151 CTSET2_CFG_CTSTMSEL1 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.152 CTSET2_CFG_CTDBGSGL0 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.153 CTSET2_CFG_CTDBGSGL1 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.154 CTSET2_CFG_CTDBGSGL2 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.155 CTSET2_CFG_CTDBGSGL3 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.156 CTSET2_CFG_CTDBGSGL4 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.157 CTSET2_CFG_CTDBGSGL5 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.158 CTSET2_CFG_CTDBGSGL6 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.159 CTSET2_CFG_CTDBGSGL7 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.160 CTSET2_CFG_CTGNBL0 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.161 CTSET2_CFG_CTGNBL1 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.162 CTSET2_CFG_CTGRST0 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.163 CTSET2_CFG_CTGRST1 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.164 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR0 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.165 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR1 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.166 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR2 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.167 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR3 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.168 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR4 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.169 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR5 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.170 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR6 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.171 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR7 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.172 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR8 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.173 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR9 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.174 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR10 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.175 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR11 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.176 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR12 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.177 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR13 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.178 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR14 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.179 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR15 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.180 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR16 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.181 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR17 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.182 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR18 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.183 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR19 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.184 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR20 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.185 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR21 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.186 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR22 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.187 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR23 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.188 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR24 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.189 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR25 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.190 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR26 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.191 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR27 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.192 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR28 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.193 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR29 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.194 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR30 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.195 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR31 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.196 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN0 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.197 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN1 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.198 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN2 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.199 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN3 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.200 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN4 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.201 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN5 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.202 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN6 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.203 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN7 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.204 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN8 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.205 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN9 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.206 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN10 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.207 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN11 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.208 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN12 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.209 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN13 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.210 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN14 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.211 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN15 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.212 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN16 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.213 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN17 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.214 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN18 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.215 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN19 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.216 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN20 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.217 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN21 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.218 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN22 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.219 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN23 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.220 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN24 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.221 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN25 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.222 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN26 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.223 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN27 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.224 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN28 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.225 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN29 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.226 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN30 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.227 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN31 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.228 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT0 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.229 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT1 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.230 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT2 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.231 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT3 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.232 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT4 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.233 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT5 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.234 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT6 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.235 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT7 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.236 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT8 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.237 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT9 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.238 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT10 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.239 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT11 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.240 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT12 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.241 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT13 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.242 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT14 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.243 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT15 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.244 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT16 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.245 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT17 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.246 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT18 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.247 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT19 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.248 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT20 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.249 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT21 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.250 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT22 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.251 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT23 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.252 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT24 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.253 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT25 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.254 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT26 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.255 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT27 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.256 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT28 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.257 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT29 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.258 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT30 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.259 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT31 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.260 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR0 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.261 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR1 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.262 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR2 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.263 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR3 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.264 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR4 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.265 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR5 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.266 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR6 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.267 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR7 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.268 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR8 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.269 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR9 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.270 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR10 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.271 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR11 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.272 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR12 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.273 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR13 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.274 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR14 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.275 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR15 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.276 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR16 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.277 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR17 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.278 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR18 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.279 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR19 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.280 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR20 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.281 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR21 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.282 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR22 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.283 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR23 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.284 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR24 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.285 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR25 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.286 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR26 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.287 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR27 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.288 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR28 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.289 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR29 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.290 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR30 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.291 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR31 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.292 CTSET2_CFG_CT_EOI Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.293 CTSET2_CFG_CTIRQSTAT_RAW Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.294 CTSET2_CFG_CTIRQSTAT Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.295 CTSET2_CFG_CTIRQENABLE_SET Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.296 CTSET2_CFG_CTIRQENABLE_CLR Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.297 CTSET2_CFG_STPTCR Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.298 CTSET2_CFG_STPTID Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.299 CTSET2_CFG_STPASYNC Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.300 CTSET2_CFG_STPFFCR Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.301 CTSET2_CFG_STPFEAT1 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.302 C7X256V_DEBUG_DBG_AGR0_MMR_AGGREGATOR_ID Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.303 C7X256V_DEBUG_DBG_AGR0_MMR_AGGREGATOR_CNTL Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.304 C7X256V_DEBUG_DBG_AGR0_MMR_AGGREGATOR_OWN Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.305 C7X256V_DEBUG_DBG_AGR0_MMR_CONT_READ_PORT0 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.306 C7X256V_DEBUG_DBG_AGR0_MMR_CONT_READ_ADDR0 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.307 C7X256V_DEBUG_DBG_AGR0_MMR_CONT_READ_DATA0 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.308 C7X256V_DEBUG_DBG_AGR0_MMR_CONT_READ_PORT1 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.309 C7X256V_DEBUG_DBG_AGR0_MMR_CONT_READ_ADDR1 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.310 C7X256V_DEBUG_DBG_AGR0_MMR_CONT_READ_DATA1 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.311 C7X256V_DEBUG_DBG_AGR0_MMR_CONT_READ_PORT2 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.312 C7X256V_DEBUG_DBG_AGR0_MMR_CONT_READ_ADDR2 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.313 C7X256V_DEBUG_DBG_AGR0_MMR_CONT_READ_DATA2 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.314 C7X256V_DEBUG_DBG_AGR0_MMR_CONT_READ_PORT3 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.315 C7X256V_DEBUG_DBG_AGR0_MMR_CONT_READ_ADDR3 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.316 C7X256V_DEBUG_DBG_AGR0_MMR_CONT_READ_DATA3 Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.317 C7X256V_DEBUG_DBG_AGR0_MEM_CFG_STP_TRACE_CONTROL Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.318 C7X256V_DEBUG_DBG_AGR0_MEM_CFG_STP_TRACE_ID Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.319 C7X256V_DEBUG_DBG_AGR0_MEM_CFG_STP_SYNC_CONTROL Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.320 C7X256V_DEBUG_DBG_AGR0_MEM_CFG_STP_FLUSH_CONTROL Register
- 14.3.2.3.2.321 C7X256V_DEBUG_DBG_AGR0_MEM_CFG_STP_FEATURES Register
- 14.3.2.4
C7X256V_DEBUG
- 14.3.2.4.1 C7X256V_DEBUG Summaries
- 14.3.2.4.2
C7X256V_DEBUG Registers
- 14.3.2.4.2.1 CTSET2_CFG_CTSETID Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.2 CTSET2_CFG_CTSETSYSCFG Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.3 CTSET2_CFG_SETSTR Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.4 CTSET2_CFG_DBGTIMELOW Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.5 CTSET2_CFG_DBGTIMEHI Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.6 CTSET2_CFG_CTSETCFG Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.7 CTSET2_CFG_SETSPLREG Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.8 CTSET2_CFG_SETEVTENBL1 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.9 CTSET2_CFG_SETEVTENBL2 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.10 CTSET2_CFG_SETEVTENBL3 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.11 CTSET2_CFG_SETEVTENBL4 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.12 CTSET2_CFG_SETEVTENBL5 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.13 CTSET2_CFG_SETEVTENBL6 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.14 CTSET2_CFG_SETEVTENBL7 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.15 CTSET2_CFG_SETEVTENBL8 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.16 CTSET2_CFG_SETMSTID Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.17 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTL Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.18 CTSET2_CFG_CTNUMDBG Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.19 CTSET2_CFG_CTUSERACCCTL Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.20 CTSET2_CFG_CTSTMCNTL Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.21 CTSET2_CFG_CTSTMMSTID Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.22 CTSET2_CFG_CTSTMINTVL Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.23 CTSET2_CFG_CTSTMSEL0 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.24 CTSET2_CFG_CTSTMSEL1 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.25 CTSET2_CFG_CTDBGSGL0 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.26 CTSET2_CFG_CTDBGSGL1 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.27 CTSET2_CFG_CTDBGSGL2 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.28 CTSET2_CFG_CTDBGSGL3 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.29 CTSET2_CFG_CTDBGSGL4 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.30 CTSET2_CFG_CTDBGSGL5 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.31 CTSET2_CFG_CTDBGSGL6 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.32 CTSET2_CFG_CTDBGSGL7 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.33 CTSET2_CFG_CTGNBL0 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.34 CTSET2_CFG_CTGNBL1 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.35 CTSET2_CFG_CTGRST0 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.36 CTSET2_CFG_CTGRST1 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.37 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR0 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.38 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR1 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.39 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR2 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.40 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR3 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.41 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR4 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.42 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR5 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.43 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR6 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.44 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR7 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.45 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR8 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.46 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR9 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.47 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR10 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.48 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR11 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.49 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR12 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.50 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR13 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.51 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR14 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.52 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR15 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.53 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR16 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.54 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR17 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.55 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR18 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.56 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR19 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.57 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR20 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.58 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR21 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.59 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR22 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.60 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR23 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.61 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR24 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.62 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR25 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.63 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR26 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.64 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR27 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.65 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR28 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.66 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR29 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.67 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR30 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.68 CTSET2_CFG_CTCR31 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.69 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN0 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.70 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN1 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.71 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN2 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.72 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN3 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.73 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN4 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.74 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN5 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.75 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN6 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.76 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN7 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.77 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN8 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.78 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN9 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.79 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN10 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.80 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN11 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.81 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN12 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.82 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN13 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.83 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN14 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.84 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN15 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.85 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN16 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.86 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN17 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.87 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN18 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.88 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN19 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.89 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN20 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.90 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN21 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.91 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN22 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.92 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN23 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.93 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN24 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.94 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN25 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.95 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN26 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.96 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN27 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.97 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN28 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.98 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN29 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.99 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN30 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.100 CTSET2_CFG_CTOWN31 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.101 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT0 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.102 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT1 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.103 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT2 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.104 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT3 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.105 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT4 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.106 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT5 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.107 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT6 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.108 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT7 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.109 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT8 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.110 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT9 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.111 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT10 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.112 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT11 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.113 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT12 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.114 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT13 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.115 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT14 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.116 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT15 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.117 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT16 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.118 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT17 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.119 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT18 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.120 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT19 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.121 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT20 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.122 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT21 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.123 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT22 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.124 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT23 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.125 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT24 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.126 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT25 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.127 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT26 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.128 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT27 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.129 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT28 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.130 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT29 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.131 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT30 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.132 CTSET2_CFG_CTFILT31 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.133 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR0 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.134 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR1 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.135 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR2 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.136 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR3 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.137 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR4 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.138 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR5 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.139 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR6 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.140 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR7 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.141 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR8 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.142 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR9 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.143 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR10 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.144 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR11 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.145 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR12 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.146 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR13 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.147 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR14 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.148 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR15 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.149 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR16 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.150 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR17 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.151 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR18 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.152 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR19 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.153 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR20 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.154 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR21 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.155 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR22 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.156 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR23 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.157 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR24 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.158 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR25 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.159 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR26 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.160 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR27 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.161 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR28 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.162 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR29 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.163 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR30 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.164 CTSET2_CFG_CTCNTR31 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.165 CTSET2_CFG_CT_EOI Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.166 CTSET2_CFG_CTIRQSTAT_RAW Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.167 CTSET2_CFG_CTIRQSTAT Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.168 CTSET2_CFG_CTIRQENABLE_SET Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.169 CTSET2_CFG_CTIRQENABLE_CLR Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.170 CTSET2_CFG_STPTCR Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.171 CTSET2_CFG_STPTID Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.172 CTSET2_CFG_STPASYNC Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.173 CTSET2_CFG_STPFFCR Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.174 CTSET2_CFG_STPFEAT1 Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.175 C7X256V_DEBUG_DBG_AGR0_MEM_CFG_STP_TRACE_CONTROL Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.176 C7X256V_DEBUG_DBG_AGR0_MEM_CFG_STP_TRACE_ID Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.177 C7X256V_DEBUG_DBG_AGR0_MEM_CFG_STP_SYNC_CONTROL Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.178 C7X256V_DEBUG_DBG_AGR0_MEM_CFG_STP_FLUSH_CONTROL Register
- 14.3.2.4.2.179 C7X256V_DEBUG_DBG_AGR0_MEM_CFG_STP_FEATURES Register
- 14.3.2.5
C7X256V_ECC_AGGR
- 14.3.2.5.1 C7X256V_ECC_AGGR Summaries
- 14.3.2.5.2
C7X256V_ECC_AGGR Registers
- 14.3.2.5.2.1 ECC_AGGR_REV Register
- 14.3.2.5.2.2 ECC_AGGR_VECTOR Register
- 14.3.2.5.2.3 ECC_AGGR_STAT Register
- 14.3.2.5.2.4 ECC_AGGR_RESERVED_SVBUS_J Register
- 14.3.2.5.2.5 ECC_AGGR_SEC_EOI_REG Register
- 14.3.2.5.2.6 ECC_AGGR_SEC_STATUS_REG0 Register
- 14.3.2.5.2.7 ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Register
- 14.3.2.5.2.8 ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Register
- 14.3.2.5.2.9 ECC_AGGR_DED_EOI_REG Register
- 14.3.2.5.2.10 ECC_AGGR_DED_STATUS_REG0 Register
- 14.3.2.5.2.11 ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Register
- 14.3.2.5.2.12 ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Register
- 14.3.2.5.2.13 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_SET Register
- 14.3.2.5.2.14 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_CLR Register
- 14.3.2.5.2.15 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_STATUS_SET Register
- 14.3.2.5.2.16 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_STATUS_CLR Register
- 14.3.2.6
C7X256V_PBIST
- 14.3.2.6.1 C7X256V_PBIST Summaries
- 14.3.2.6.2
C7X256V_PBIST Registers
- 14.3.2.6.2.1 PBIST_RF0L Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.2 PBIST_RF1L Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.3 PBIST_RF2L Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.4 PBIST_RF3L Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.5 PBIST_RF4L Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.6 PBIST_RF5L Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.7 PBIST_RF6L Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.8 PBIST_RF7L Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.9 PBIST_RF8L Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.10 PBIST_RF9L Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.11 PBIST_RF10L Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.12 PBIST_RF11L Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.13 PBIST_RF12L Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.14 PBIST_RF13L Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.15 PBIST_RF14L Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.16 PBIST_RF15L Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.17 PBIST_RF0U Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.18 PBIST_RF1U Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.19 PBIST_RF2U Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.20 PBIST_RF3U Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.21 PBIST_RF4U Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.22 PBIST_RF5U Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.23 PBIST_RF6U Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.24 PBIST_RF7U Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.25 PBIST_RF8U Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.26 PBIST_RF9U Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.27 PBIST_RF10U Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.28 PBIST_RF11U Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.29 PBIST_RF12U Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.30 PBIST_RF13U Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.31 PBIST_RF14U Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.32 PBIST_RF15U Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.33 PBIST_A0 Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.34 PBIST_A1 Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.35 PBIST_A2 Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.36 PBIST_A3 Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.37 PBIST_L0 Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.38 PBIST_L1 Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.39 PBIST_L2 Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.40 PBIST_L3 Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.41 PBIST_D Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.42 PBIST_E Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.43 PBIST_CA0 Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.44 PBIST_CA1 Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.45 PBIST_CA2 Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.46 PBIST_CA3 Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.47 PBIST_CL0 Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.48 PBIST_CL1 Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.49 PBIST_CL2 Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.50 PBIST_CL3 Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.51 PBIST_I0 Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.52 PBIST_I1 Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.53 PBIST_I2 Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.54 PBIST_I3 Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.55 PBIST_RAMT Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.56 PBIST_DLR Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.57 PBIST_CMS Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.58 PBIST_STR Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.59 PBIST_SCR Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.60 PBIST_CSR Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.61 PBIST_FDLY Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.62 PBIST_PACT Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.63 PBIST_PID Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.64 PBIST_OVER Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.65 PBIST_FSRF Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.66 PBIST_FSRC Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.67 PBIST_FSRA Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.68 PBIST_FSRDL0 Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.69 PBIST_FSRDL1 Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.70 PBIST_MARGIN_MODE Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.71 PBIST_WRENZ Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.72 PBIST_PAGE_PGS Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.73 PBIST_ROM Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.74 PBIST_ALGO Register
- 14.3.2.6.2.75 PBIST_RINFO Register
- 14.3.2.1
C7X256V_CLEC
- 14.3.1
R5FSS Registers
- 14.4
Interprocessor Communication Registers
- 14.4.1
MAILBOX_MAILBOX_CLUSTER_0
- 14.4.1.1 MAILBOX_MAILBOX_CLUSTER_0 Summaries
- 14.4.1.2
MAILBOX_MAILBOX_CLUSTER_0 Registers
- 14.4.1.2.1 MAILBOX_REVISION Register
- 14.4.1.2.2 MAILBOX_SYSCONFIG Register
- 14.4.1.2.3 MAILBOX_MESSAGE_J Register
- 14.4.1.2.4 MAILBOX_FIFO_STATUS_J Register
- 14.4.1.2.5 MAILBOX_MSG_STATUS_J Register
- 14.4.1.2.6 MAILBOX_IRQ_EOI Register
- 14.4.1.2.7 MAILBOX_USER_IRQ_STATUS_RAW_J Register
- 14.4.1.2.8 MAILBOX_USER_IRQ_STATUS_CLR_J Register
- 14.4.1.2.9 MAILBOX_USER_IRQ_ENABLE_SET_J Register
- 14.4.1.2.10 MAILBOX_USER_IRQ_ENABLE_CLR_J Register
- 14.4.2
MAILBOX_MAILBOX_CLUSTER_1
- 14.4.2.1 MAILBOX_MAILBOX_CLUSTER_1 Summaries
- 14.4.2.2
MAILBOX_MAILBOX_CLUSTER_1 Registers
- 14.4.2.2.1 MAILBOX_REVISION Register
- 14.4.2.2.2 MAILBOX_SYSCONFIG Register
- 14.4.2.2.3 MAILBOX_MESSAGE_J Register
- 14.4.2.2.4 MAILBOX_FIFO_STATUS_J Register
- 14.4.2.2.5 MAILBOX_MSG_STATUS_J Register
- 14.4.2.2.6 MAILBOX_IRQ_EOI Register
- 14.4.2.2.7 MAILBOX_USER_IRQ_STATUS_RAW_J Register
- 14.4.2.2.8 MAILBOX_USER_IRQ_STATUS_CLR_J Register
- 14.4.2.2.9 MAILBOX_USER_IRQ_ENABLE_SET_J Register
- 14.4.2.2.10 MAILBOX_USER_IRQ_ENABLE_CLR_J Register
- 14.4.3
MAILBOX_MAILBOX_CLUSTER_2
- 14.4.3.1 MAILBOX_MAILBOX_CLUSTER_2 Summaries
- 14.4.3.2
MAILBOX_MAILBOX_CLUSTER_2 Registers
- 14.4.3.2.1 MAILBOX_REVISION Register
- 14.4.3.2.2 MAILBOX_SYSCONFIG Register
- 14.4.3.2.3 MAILBOX_MESSAGE_J Register
- 14.4.3.2.4 MAILBOX_FIFO_STATUS_J Register
- 14.4.3.2.5 MAILBOX_MSG_STATUS_J Register
- 14.4.3.2.6 MAILBOX_IRQ_EOI Register
- 14.4.3.2.7 MAILBOX_USER_IRQ_STATUS_RAW_J Register
- 14.4.3.2.8 MAILBOX_USER_IRQ_STATUS_CLR_J Register
- 14.4.3.2.9 MAILBOX_USER_IRQ_ENABLE_SET_J Register
- 14.4.3.2.10 MAILBOX_USER_IRQ_ENABLE_CLR_J Register
- 14.4.4
MAILBOX_MAILBOX_CLUSTER_3
- 14.4.4.1 MAILBOX_MAILBOX_CLUSTER_3 Summaries
- 14.4.4.2
MAILBOX_MAILBOX_CLUSTER_3 Registers
- 14.4.4.2.1 MAILBOX_REVISION Register
- 14.4.4.2.2 MAILBOX_SYSCONFIG Register
- 14.4.4.2.3 MAILBOX_MESSAGE_J Register
- 14.4.4.2.4 MAILBOX_FIFO_STATUS_J Register
- 14.4.4.2.5 MAILBOX_MSG_STATUS_J Register
- 14.4.4.2.6 MAILBOX_IRQ_EOI Register
- 14.4.4.2.7 MAILBOX_USER_IRQ_STATUS_RAW_J Register
- 14.4.4.2.8 MAILBOX_USER_IRQ_STATUS_CLR_J Register
- 14.4.4.2.9 MAILBOX_USER_IRQ_ENABLE_SET_J Register
- 14.4.4.2.10 MAILBOX_USER_IRQ_ENABLE_CLR_J Register
- 14.4.5
MAILBOX_MAILBOX_CLUSTER_4
- 14.4.5.1 MAILBOX_MAILBOX_CLUSTER_4 Summaries
- 14.4.5.2
MAILBOX_MAILBOX_CLUSTER_4 Registers
- 14.4.5.2.1 MAILBOX_REVISION Register
- 14.4.5.2.2 MAILBOX_SYSCONFIG Register
- 14.4.5.2.3 MAILBOX_MESSAGE_J Register
- 14.4.5.2.4 MAILBOX_FIFO_STATUS_J Register
- 14.4.5.2.5 MAILBOX_MSG_STATUS_J Register
- 14.4.5.2.6 MAILBOX_IRQ_EOI Register
- 14.4.5.2.7 MAILBOX_USER_IRQ_STATUS_RAW_J Register
- 14.4.5.2.8 MAILBOX_USER_IRQ_STATUS_CLR_J Register
- 14.4.5.2.9 MAILBOX_USER_IRQ_ENABLE_SET_J Register
- 14.4.5.2.10 MAILBOX_USER_IRQ_ENABLE_CLR_J Register
- 14.4.6
MAILBOX_MAILBOX_CLUSTER_5
- 14.4.6.1 MAILBOX_MAILBOX_CLUSTER_5 Summaries
- 14.4.6.2
MAILBOX_MAILBOX_CLUSTER_5 Registers
- 14.4.6.2.1 MAILBOX_REVISION Register
- 14.4.6.2.2 MAILBOX_SYSCONFIG Register
- 14.4.6.2.3 MAILBOX_MESSAGE_J Register
- 14.4.6.2.4 MAILBOX_FIFO_STATUS_J Register
- 14.4.6.2.5 MAILBOX_MSG_STATUS_J Register
- 14.4.6.2.6 MAILBOX_IRQ_EOI Register
- 14.4.6.2.7 MAILBOX_USER_IRQ_STATUS_RAW_J Register
- 14.4.6.2.8 MAILBOX_USER_IRQ_STATUS_CLR_J Register
- 14.4.6.2.9 MAILBOX_USER_IRQ_ENABLE_SET_J Register
- 14.4.6.2.10 MAILBOX_USER_IRQ_ENABLE_CLR_J Register
- 14.4.7
MAILBOX_MAILBOX_CLUSTER_6
- 14.4.7.1 MAILBOX_MAILBOX_CLUSTER_6 Summaries
- 14.4.7.2
MAILBOX_MAILBOX_CLUSTER_6 Registers
- 14.4.7.2.1 MAILBOX_REVISION Register
- 14.4.7.2.2 MAILBOX_SYSCONFIG Register
- 14.4.7.2.3 MAILBOX_MESSAGE_J Register
- 14.4.7.2.4 MAILBOX_FIFO_STATUS_J Register
- 14.4.7.2.5 MAILBOX_MSG_STATUS_J Register
- 14.4.7.2.6 MAILBOX_IRQ_EOI Register
- 14.4.7.2.7 MAILBOX_USER_IRQ_STATUS_RAW_J Register
- 14.4.7.2.8 MAILBOX_USER_IRQ_STATUS_CLR_J Register
- 14.4.7.2.9 MAILBOX_USER_IRQ_ENABLE_SET_J Register
- 14.4.7.2.10 MAILBOX_USER_IRQ_ENABLE_CLR_J Register
- 14.4.8
MAILBOX_MAILBOX_CLUSTER_7
- 14.4.8.1 MAILBOX_MAILBOX_CLUSTER_7 Summaries
- 14.4.8.2
MAILBOX_MAILBOX_CLUSTER_7 Registers
- 14.4.8.2.1 MAILBOX_REVISION Register
- 14.4.8.2.2 MAILBOX_SYSCONFIG Register
- 14.4.8.2.3 MAILBOX_MESSAGE_J Register
- 14.4.8.2.4 MAILBOX_FIFO_STATUS_J Register
- 14.4.8.2.5 MAILBOX_MSG_STATUS_J Register
- 14.4.8.2.6 MAILBOX_IRQ_EOI Register
- 14.4.8.2.7 MAILBOX_USER_IRQ_STATUS_RAW_J Register
- 14.4.8.2.8 MAILBOX_USER_IRQ_STATUS_CLR_J Register
- 14.4.8.2.9 MAILBOX_USER_IRQ_ENABLE_SET_J Register
- 14.4.8.2.10 MAILBOX_USER_IRQ_ENABLE_CLR_J Register
- 14.4.9 SPINLOCK
- 14.4.1
MAILBOX_MAILBOX_CLUSTER_0
- 14.5 Interrupt Router Registers
- 14.6
DMA Controller Registers
- 14.6.1
DMASS_BCDMA_0
- 14.6.1.1 DMASS_BCDMA_0 Summaries
- 14.6.1.2
DMASS_BCDMA_0 Registers
- 14.6.1.2.1 LCDMA_RINGACC_CRED_RING_CRED_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.2 BCDMA_BCCFG_CHAN_CFG_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.3 BCDMA_BCCFG_CHAN_PRI_CTRL_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.4 BCDMA_BCCFG_CHAN_TST_SCHED_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.5 BCDMA_TXCCFG_CHAN_TCFG_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.6 BCDMA_TXCCFG_CHAN_TPRI_CTRL_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.7 BCDMA_TXCCFG_CHAN_THREAD_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.8 BCDMA_TXCCFG_CHAN_TFIFO_DEPTH_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.9 BCDMA_TXCCFG_CHAN_TST_SCHED_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.10 BCDMA_RXCCFG_CHAN_RCFG_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.11 BCDMA_RXCCFG_CHAN_RPRI_CTRL_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.12 BCDMA_RXCCFG_CHAN_THREAD_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.13 BCDMA_RXCCFG_CHAN_RST_SCHED_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.14 BCDMA_GCFG_REVISION Register
- 14.6.1.2.15 BCDMA_GCFG_PERF_CTRL Register
- 14.6.1.2.16 BCDMA_GCFG_EMU_CTRL Register
- 14.6.1.2.17 BCDMA_GCFG_PSIL_TO Register
- 14.6.1.2.18 BCDMA_GCFG_CAP0 Register
- 14.6.1.2.19 BCDMA_GCFG_CAP1 Register
- 14.6.1.2.20 BCDMA_GCFG_CAP2 Register
- 14.6.1.2.21 BCDMA_GCFG_CAP3 Register
- 14.6.1.2.22 BCDMA_GCFG_CAP4 Register
- 14.6.1.2.23 BCDMA_GCFG_PM0 Register
- 14.6.1.2.24 BCDMA_GCFG_PM1 Register
- 14.6.1.2.25 BCDMA_GCFG_DBGADDR Register
- 14.6.1.2.26 BCDMA_GCFG_DBGDATA Register
- 14.6.1.2.27 LCDMA_RINGACC_RING_CFG_RING_BA_LO_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.28 LCDMA_RINGACC_RING_CFG_RING_BA_HI_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.29 LCDMA_RINGACC_RING_CFG_RING_SIZE_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.30 BCDMA_RXCRT_CHAN_CTL_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.31 BCDMA_RXCRT_CHAN_SWTRIG_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.32 BCDMA_RXCRT_CHAN_STATUS0_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.33 BCDMA_RXCRT_CHAN_STATUS1_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.34 BCDMA_RXCRT_CHAN_STDATA_J_K Register
- 14.6.1.2.35 BCDMA_RXCRT_CHAN_PEER0_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.36 BCDMA_RXCRT_CHAN_PEER1_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.37 BCDMA_RXCRT_CHAN_PEER2_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.38 BCDMA_RXCRT_CHAN_PEER3_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.39 BCDMA_RXCRT_CHAN_PEER4_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.40 BCDMA_RXCRT_CHAN_PEER5_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.41 BCDMA_RXCRT_CHAN_PEER6_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.42 BCDMA_RXCRT_CHAN_PEER7_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.43 BCDMA_RXCRT_CHAN_PEER8_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.44 BCDMA_RXCRT_CHAN_PEER9_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.45 BCDMA_RXCRT_CHAN_PEER10_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.46 BCDMA_RXCRT_CHAN_PEER11_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.47 BCDMA_RXCRT_CHAN_PEER12_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.48 BCDMA_RXCRT_CHAN_PEER13_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.49 BCDMA_RXCRT_CHAN_PEER14_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.50 BCDMA_RXCRT_CHAN_PEER15_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.51 BCDMA_RXCRT_CHAN_PCNT_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.52 BCDMA_RXCRT_CHAN_BCNT_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.53 BCDMA_RXCRT_CHAN_SBCNT_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.54 BCDMA_TXCRT_CHAN_CTL_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.55 BCDMA_TXCRT_CHAN_SWTRIG_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.56 BCDMA_TXCRT_CHAN_STATUS0_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.57 BCDMA_TXCRT_CHAN_STATUS1_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.58 BCDMA_TXCRT_CHAN_STDATA_J_K Register
- 14.6.1.2.59 BCDMA_TXCRT_CHAN_PEER0_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.60 BCDMA_TXCRT_CHAN_PEER1_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.61 BCDMA_TXCRT_CHAN_PEER2_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.62 BCDMA_TXCRT_CHAN_PEER3_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.63 BCDMA_TXCRT_CHAN_PEER4_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.64 BCDMA_TXCRT_CHAN_PEER5_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.65 BCDMA_TXCRT_CHAN_PEER6_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.66 BCDMA_TXCRT_CHAN_PEER7_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.67 BCDMA_TXCRT_CHAN_PEER8_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.68 BCDMA_TXCRT_CHAN_PEER9_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.69 BCDMA_TXCRT_CHAN_PEER10_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.70 BCDMA_TXCRT_CHAN_PEER11_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.71 BCDMA_TXCRT_CHAN_PEER12_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.72 BCDMA_TXCRT_CHAN_PEER13_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.73 BCDMA_TXCRT_CHAN_PEER14_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.74 BCDMA_TXCRT_CHAN_PEER15_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.75 BCDMA_TXCRT_CHAN_PCNT_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.76 BCDMA_TXCRT_CHAN_BCNT_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.77 BCDMA_TXCRT_CHAN_SBCNT_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.78 LCDMA_RINGACC_RINGRT_RING_FDB_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.79 LCDMA_RINGACC_RINGRT_RING_FOCC_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.80 LCDMA_RINGACC_RINGRT_RING_RDB_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.81 LCDMA_RINGACC_RINGRT_RING_ROCC_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.82 BCDMA_BCRT_CHAN_CTL_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.83 BCDMA_BCRT_CHAN_SWTRIG_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.84 BCDMA_BCRT_CHAN_STATUS0_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.85 BCDMA_BCRT_CHAN_STATUS1_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.86 BCDMA_BCRT_CHAN_STATUS2_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.87 BCDMA_BCRT_CHAN_STATUS3_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.88 BCDMA_BCRT_CHAN_STDATA_J_K Register
- 14.6.1.2.89 BCDMA_BCRT_CHAN_STDATAW_J_K Register
- 14.6.1.2.90 BCDMA_BCRT_CHAN_PCNT_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.91 BCDMA_BCRT_CHAN_BCNT_J Register
- 14.6.1.2.92 BCDMA_BCRT_CHAN_SBCNT_J Register
- 14.6.2
DMASS_ECC_AGGR_0
- 14.6.2.1 DMASS_ECC_AGGR_0 Summaries
- 14.6.2.2
DMASS_ECC_AGGR_0 Registers
- 14.6.2.2.1 DMASS_ECC_AGGR_0_ECCAGGR_REV Register
- 14.6.2.2.2 DMASS_ECC_AGGR_0_ECCAGGR_VECTOR Register
- 14.6.2.2.3 DMASS_ECC_AGGR_0_ECCAGGR_STAT Register
- 14.6.2.2.4 DMASS_ECC_AGGR_0_ECCAGGR_RESERVED_SVBUS Register
- 14.6.2.2.5 DMASS_ECC_AGGR_0_ECCAGGR_SEC_EOI_REG Register
- 14.6.2.2.6 DMASS_ECC_AGGR_0_ECCAGGR_SEC_STATUS_REG0 Register
- 14.6.2.2.7 DMASS_ECC_AGGR_0_ECCAGGR_SEC_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Register
- 14.6.2.2.8 DMASS_ECC_AGGR_0_ECCAGGR_SEC_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Register
- 14.6.2.2.9 DMASS_ECC_AGGR_0_ECCAGGR_DED_EOI_REG Register
- 14.6.2.2.10 DMASS_ECC_AGGR_0_ECCAGGR_DED_STATUS_REG0 Register
- 14.6.2.2.11 DMASS_ECC_AGGR_0_ECCAGGR_DED_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Register
- 14.6.2.2.12 DMASS_ECC_AGGR_0_ECCAGGR_DED_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Register
- 14.6.2.2.13 DMASS_ECC_AGGR_0_ECCAGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_SET Register
- 14.6.2.2.14 DMASS_ECC_AGGR_0_ECCAGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_CLR Register
- 14.6.2.2.15 DMASS_ECC_AGGR_0_ECCAGGR_AGGR_STATUS_SET Register
- 14.6.2.2.16 DMASS_ECC_AGGR_0_ECCAGGR_AGGR_STATUS_CLR Register
- 14.6.3
DMASS_INTAGGR_0
- 14.6.3.1 DMASS_INTAGGR_0 Summaries
- 14.6.3.2
DMASS_INTAGGR_0 Registers
- 14.6.3.2.1 INTAGGR_INTR_VINT_ENABLE_SET_J Register
- 14.6.3.2.2 INTAGGR_INTR_VINT_ENABLE_CLEAR_J Register
- 14.6.3.2.3 INTAGGR_INTR_VINT_STATUS_SET_J Register
- 14.6.3.2.4 INTAGGR_INTR_VINT_STATUS_CLEAR_J Register
- 14.6.3.2.5 INTAGGR_INTR_VINT_STATUSM_J Register
- 14.6.3.2.6 INTAGGR_IMAP_GEVI_IMAP_J Register
- 14.6.3.2.7 INTAGGR_CFG_REVISION Register
- 14.6.3.2.8 INTAGGR_CFG_INTCAP Register
- 14.6.3.2.9 INTAGGR_CFG_AUXCAP Register
- 14.6.3.2.10 INTAGGR_L2G_LEVI_MAP_J Register
- 14.6.3.2.11 INTAGGR_UNMAP_UNMAP0_MAP_J Register
- 14.6.3.2.12 INTAGGR_UNMAP_UNMAP1_MAP_J Register
- 14.6.3.2.13 INTAGGR_UNMAP_UNMAP2_MAP_J Register
- 14.6.3.2.14 INTAGGR_UNMAP_UNMAP3_MAP_J Register
- 14.6.3.2.15 INTAGGR_UNMAP_UNMAP4_MAP_J Register
- 14.6.3.2.16 INTAGGR_UNMAP_UNMAP5_MAP Register
- 14.6.3.2.17 INTAGGR_UNMAP_UNMAP6_MAP_J Register
- 14.6.3.2.18 INTAGGR_UNMAP_UNMAP7_MAP_J Register
- 14.6.3.2.19 INTAGGR_UNMAP_UNMAP8_MAP_J Register
- 14.6.3.2.20 INTAGGR_UNMAP_UNMAP9_MAP_J Register
- 14.6.3.2.21 INTAGGR_UNMAP_UNMAP10_MAP_J Register
- 14.6.3.2.22 INTAGGR_UNMAP_UNMAP11_MAP_J Register
- 14.6.3.2.23 INTAGGR_UNMAP_UNMAP12_MAP_J Register
- 14.6.3.2.24 INTAGGR_UNMAP_UNMAP13_MAP_J Register
- 14.6.3.2.25 INTAGGR_UNMAP_UNMAP14_MAP_J Register
- 14.6.3.2.26 INTAGGR_MCAST_GEVI_MCMAP_J Register
- 14.6.3.2.27 INTAGGR_GCNTCFG_GEVI_MAP_J Register
- 14.6.3.2.28 INTAGGR_GCNTRTI_GEVI_COUNT_J Register
- 14.6.4
DMASS_PKTDMA_0
- 14.6.4.1 DMASS_PKTDMA_0 Summaries
- 14.6.4.2
DMASS_PKTDMA_0 Registers
- 14.6.4.2.1 LCDMA_RINGACC_CRED_RING_CRED_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.2 PKTDMA_RXFCFG_FLOW_RFA_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.3 PKTDMA_TXCCFG_CHAN_TCFG_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.4 PKTDMA_TXCCFG_CHAN_TPRI_CTRL_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.5 PKTDMA_TXCCFG_CHAN_THREAD_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.6 PKTDMA_TXCCFG_CHAN_TFIFO_DEPTH_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.7 PKTDMA_TXCCFG_CHAN_TST_SCHED_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.8 PKTDMA_RXCCFG_CHAN_RCFG_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.9 PKTDMA_RXCCFG_CHAN_RPRI_CTRL_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.10 PKTDMA_RXCCFG_CHAN_THREAD_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.11 PKTDMA_RXCCFG_CHAN_RST_SCHED_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.12 PKTDMA_GCFG_REVISION Register
- 14.6.4.2.13 PKTDMA_GCFG_PERF_CTRL Register
- 14.6.4.2.14 PKTDMA_GCFG_EMU_CTRL Register
- 14.6.4.2.15 PKTDMA_GCFG_PSIL_TO Register
- 14.6.4.2.16 PKTDMA_GCFG_CAP0 Register
- 14.6.4.2.17 PKTDMA_GCFG_CAP1 Register
- 14.6.4.2.18 PKTDMA_GCFG_CAP2 Register
- 14.6.4.2.19 PKTDMA_GCFG_CAP3 Register
- 14.6.4.2.20 PKTDMA_GCFG_CAP4 Register
- 14.6.4.2.21 PKTDMA_GCFG_PM0 Register
- 14.6.4.2.22 PKTDMA_GCFG_PM1 Register
- 14.6.4.2.23 PKTDMA_GCFG_DBGADDR Register
- 14.6.4.2.24 PKTDMA_GCFG_DBGDATA Register
- 14.6.4.2.25 PKTDMA_GCFG_RFLOWFWSTAT Register
- 14.6.4.2.26 LCDMA_RINGACC_RING_CFG_RING_BA_LO_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.27 LCDMA_RINGACC_RING_CFG_RING_BA_HI_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.28 LCDMA_RINGACC_RING_CFG_RING_SIZE_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.29 PKTDMA_RXCRT_CHAN_CTL_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.30 PKTDMA_RXCRT_CHAN_STATUS0_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.31 PKTDMA_RXCRT_CHAN_STATUS1_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.32 PKTDMA_RXCRT_CHAN_STDATA_J_K Register
- 14.6.4.2.33 PKTDMA_RXCRT_CHAN_PEER0_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.34 PKTDMA_RXCRT_CHAN_PEER1_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.35 PKTDMA_RXCRT_CHAN_PEER2_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.36 PKTDMA_RXCRT_CHAN_PEER3_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.37 PKTDMA_RXCRT_CHAN_PEER4_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.38 PKTDMA_RXCRT_CHAN_PEER5_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.39 PKTDMA_RXCRT_CHAN_PEER6_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.40 PKTDMA_RXCRT_CHAN_PEER7_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.41 PKTDMA_RXCRT_CHAN_PEER8_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.42 PKTDMA_RXCRT_CHAN_PEER9_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.43 PKTDMA_RXCRT_CHAN_PEER10_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.44 PKTDMA_RXCRT_CHAN_PEER11_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.45 PKTDMA_RXCRT_CHAN_PEER12_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.46 PKTDMA_RXCRT_CHAN_PEER13_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.47 PKTDMA_RXCRT_CHAN_PEER14_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.48 PKTDMA_RXCRT_CHAN_PEER15_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.49 PKTDMA_RXCRT_CHAN_PCNT_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.50 PKTDMA_RXCRT_CHAN_DCNT_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.51 PKTDMA_RXCRT_CHAN_BCNT_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.52 PKTDMA_RXCRT_CHAN_SBCNT_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.53 PKTDMA_TXCRT_CHAN_CTL_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.54 PKTDMA_TXCRT_CHAN_STATUS0_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.55 PKTDMA_TXCRT_CHAN_STATUS1_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.56 PKTDMA_TXCRT_CHAN_STDATA_J_K Register
- 14.6.4.2.57 PKTDMA_TXCRT_CHAN_PEER0_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.58 PKTDMA_TXCRT_CHAN_PEER1_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.59 PKTDMA_TXCRT_CHAN_PEER2_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.60 PKTDMA_TXCRT_CHAN_PEER3_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.61 PKTDMA_TXCRT_CHAN_PEER4_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.62 PKTDMA_TXCRT_CHAN_PEER5_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.63 PKTDMA_TXCRT_CHAN_PEER6_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.64 PKTDMA_TXCRT_CHAN_PEER7_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.65 PKTDMA_TXCRT_CHAN_PEER8_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.66 PKTDMA_TXCRT_CHAN_PEER9_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.67 PKTDMA_TXCRT_CHAN_PEER10_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.68 PKTDMA_TXCRT_CHAN_PEER11_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.69 PKTDMA_TXCRT_CHAN_PEER12_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.70 PKTDMA_TXCRT_CHAN_PEER13_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.71 PKTDMA_TXCRT_CHAN_PEER14_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.72 PKTDMA_TXCRT_CHAN_PEER15_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.73 PKTDMA_TXCRT_CHAN_PCNT_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.74 PKTDMA_TXCRT_CHAN_BCNT_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.75 PKTDMA_TXCRT_CHAN_SBCNT_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.76 LCDMA_RINGACC_RINGRT_RING_FDB_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.77 LCDMA_RINGACC_RINGRT_RING_FOCC_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.78 LCDMA_RINGACC_RINGRT_RING_RDB_J Register
- 14.6.4.2.79 LCDMA_RINGACC_RINGRT_RING_ROCC_J Register
- 14.6.5 DMASS_PSILCFG_0
- 14.6.6 DMASS_PSILSS_0
- 14.6.7
DMASS_RINGACC_0
- 14.6.7.1 DMASS_RINGACC_0 Summaries
- 14.6.7.2
DMASS_RINGACC_0 Registers
- 14.6.7.2.1 RINGACC_GCFG_REVISION Register
- 14.6.7.2.2 RINGACC_GCFG_TRACE_CTL Register
- 14.6.7.2.3 RINGACC_GCFG_OVRFLOW Register
- 14.6.7.2.4 RINGACC_GCFG_ERROR_EVT Register
- 14.6.7.2.5 RINGACC_GCFG_ERROR_LOG Register
- 14.6.7.2.6 RINGACC_RT_RINGRT_DB_J Register
- 14.6.7.2.7 RINGACC_RT_RINGRT_OCC_J Register
- 14.6.7.2.8 RINGACC_RT_RINGRT_INDX_J Register
- 14.6.7.2.9 RINGACC_RT_RINGRT_HWOCC_J Register
- 14.6.7.2.10 RINGACC_RT_RINGRT_HWINDX_J Register
- 14.6.7.2.11 RINGACC_CFG_RING_BA_LO_J Register
- 14.6.7.2.12 RINGACC_CFG_RING_BA_HI_J Register
- 14.6.7.2.13 RINGACC_CFG_RING_SIZE_J Register
- 14.6.7.2.14 RINGACC_CFG_RING_EVENT_J Register
- 14.6.7.2.15 RINGACC_CFG_RING_ORDERID_J Register
- 14.6.8 DMASS_SEC_PROXY_0 Summaries
- 14.6.9 Note on PDMA Instances
- 14.6.10
PDMA
- 14.6.10.1 PDMA Summaries
- 14.6.10.2
PDMA Registers
- 14.6.10.2.1 ECC_AGGR_REV Register
- 14.6.10.2.2 ECC_AGGR_VECTOR Register
- 14.6.10.2.3 ECC_AGGR_STAT Register
- 14.6.10.2.4 ECC_AGGR_RESERVED_SVBUS_J Register
- 14.6.10.2.5 ECC_AGGR_SEC_EOI_REG Register
- 14.6.10.2.6 ECC_AGGR_SEC_STATUS_REG0 Register
- 14.6.10.2.7 ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Register
- 14.6.10.2.8 ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Register
- 14.6.10.2.9 ECC_AGGR_DED_EOI_REG Register
- 14.6.10.2.10 ECC_AGGR_DED_STATUS_REG0 Register
- 14.6.10.2.11 ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Register
- 14.6.10.2.12 ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Register
- 14.6.10.2.13 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_SET Register
- 14.6.10.2.14 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_CLR Register
- 14.6.10.2.15 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_STATUS_SET Register
- 14.6.10.2.16 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_STATUS_CLR Register
- 14.6.11
PDMA
- 14.6.11.1 PDMA Summaries
- 14.6.11.2
PDMA Registers
- 14.6.11.2.1 ECC_AGGR_REV Register
- 14.6.11.2.2 ECC_AGGR_VECTOR Register
- 14.6.11.2.3 ECC_AGGR_STAT Register
- 14.6.11.2.4 ECC_AGGR_RESERVED_SVBUS_J Register
- 14.6.11.2.5 ECC_AGGR_SEC_EOI_REG Register
- 14.6.11.2.6 ECC_AGGR_SEC_STATUS_REG0 Register
- 14.6.11.2.7 ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Register
- 14.6.11.2.8 ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Register
- 14.6.11.2.9 ECC_AGGR_DED_EOI_REG Register
- 14.6.11.2.10 ECC_AGGR_DED_STATUS_REG0 Register
- 14.6.11.2.11 ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Register
- 14.6.11.2.12 ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Register
- 14.6.11.2.13 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_SET Register
- 14.6.11.2.14 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_CLR Register
- 14.6.11.2.15 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_STATUS_SET Register
- 14.6.11.2.16 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_STATUS_CLR Register
- 14.6.1
DMASS_BCDMA_0
- 14.7
Peripherals Registers
- 14.7.1
Audio Peripherals Registers
- 14.7.1.1
aasrc
- 14.7.1.1.1 aasrc Summaries
- 14.7.1.1.2
aasrc Registers
- 14.7.1.1.2.1 AASRC_CFG_AASRC_PID Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.2 AASRC_CFG_AASRC_SYSCONFIG Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.3 AASRC_CFG_IRQ_EOI_REGISTER Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.4 AASRC_CFG_INPUT_FIFO_INTERRUPT_STATUS_RAW_REGISTER Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.5 AASRC_CFG_INPUT_FIFO_INTERRUPT_STATUS_ENABLED_REGISTER Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.6 AASRC_CFG_INPUT_FIFO_INTERRUPT_ENABLE_SET_REGISTER Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.7 AASRC_CFG_INPUT_FIFO_INTERRUPT_ENABLE_CLEAR_REGISTER Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.8 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_FIFO_INTERRUPT_STATUS_RAW_REGISTER Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.9 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_FIFO_INTERRUPT_STATUS_ENABLED_REGISTER Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.10 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_FIFO_INTERRUPT_ENABLE_SET_REGISTER Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.11 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_FIFO_INTERRUPT_ENABLE_CLEAR_REGISTER Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.12 AASRC_CFG_INPUT_GROUP_INTERRUPT_STATUS_RAW_REGISTER Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.13 AASRC_CFG_INPUT_GROUP_INTERRUPT_STATUS_ENABLED_REGISTER Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.14 AASRC_CFG_INPUT_GROUP_INTERRUPT_ENABLE_SET_REGISTER Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.15 AASRC_CFG_INPUT_GROUP_INTERRUPT_ENABLE_CLEAR_REGISTER Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.16 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_GROUP_INTERRUPT_STATUS_RAW_REGISTER Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.17 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_GROUP_INTERRUPT_STATUS_ENABLED_REGISTER Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.18 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_GROUP_INTERRUPT_ENABLE_SET_REGISTER Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.19 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_GROUP_INTERRUPT_ENABLE_CLEAR_REGISTER Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.20 AASRC_CFG_ERROR_INTERRUPT_STATUS_RAW_REGISTER Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.21 AASRC_CFG_ERROR_INTERRUPT_STATUS_ENABLED_REGISTER Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.22 AASRC_CFG_ERROR_INTERRUPT_ENABLE_SET_REGISTER Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.23 AASRC_CFG_ERROR_INTERRUPT_ENABLE_CLEAR_REGISTER Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.24 AASRC_CFG_INPUT_GROUP_0_SELECT Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.25 AASRC_CFG_INPUT_GROUP_1_SELECT Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.26 AASRC_CFG_INPUT_GROUP_2_SELECT Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.27 AASRC_CFG_INPUT_GROUP_3_SELECT Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.28 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_GROUP_0_SELECT Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.29 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_GROUP_1_SELECT Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.30 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_GROUP_2_SELECT Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.31 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_GROUP_3_SELECT Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.32 AASRC_CFG_SRC_FIFO_CONTROL_0 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.33 AASRC_CFG_SRC_CONTROL_0 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.34 AASRC_CFG_SRC_STATUS_0 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.35 AASRC_CFG_SRC_FIFO_CONTROL_1 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.36 AASRC_CFG_SRC_CONTROL_1 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.37 AASRC_CFG_SRC_STATUS_1 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.38 AASRC_CFG_SRC_FIFO_CONTROL_2 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.39 AASRC_CFG_SRC_CONTROL_2 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.40 AASRC_CFG_SRC_STATUS_2 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.41 AASRC_CFG_SRC_FIFO_CONTROL_3 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.42 AASRC_CFG_SRC_CONTROL_3 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.43 AASRC_CFG_SRC_STATUS_3 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.44 AASRC_CFG_SRC_FIFO_CONTROL_4 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.45 AASRC_CFG_SRC_CONTROL_4 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.46 AASRC_CFG_SRC_STATUS_4 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.47 AASRC_CFG_SRC_FIFO_CONTROL_5 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.48 AASRC_CFG_SRC_CONTROL_5 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.49 AASRC_CFG_SRC_STATUS_5 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.50 AASRC_CFG_SRC_FIFO_CONTROL_6 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.51 AASRC_CFG_SRC_CONTROL_6 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.52 AASRC_CFG_SRC_STATUS_6 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.53 AASRC_CFG_SRC_FIFO_CONTROL_7 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.54 AASRC_CFG_SRC_CONTROL_7 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.55 AASRC_CFG_SRC_STATUS_7 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.56 AASRC_CFG_GROUP_FIFO_CONTROL_0 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.57 AASRC_CFG_GROUP_SRC_CONTROL_0 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.58 AASRC_CFG_GROUP_FIFO_CONTROL_1 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.59 AASRC_CFG_GROUP_SRC_CONTROL_1 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.60 AASRC_CFG_GROUP_FIFO_CONTROL_2 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.61 AASRC_CFG_GROUP_SRC_CONTROL_2 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.62 AASRC_CFG_GROUP_FIFO_CONTROL_3 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.63 AASRC_CFG_GROUP_SRC_CONTROL_3 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.64 AASRC_CFG_INPUT_CLOCK_GENERATOR_STAMP_LO_0 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.65 AASRC_CFG_INPUT_CLOCK_GENERATOR_STAMP_HI_0 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.66 AASRC_CFG_INPUT_CLOCK_GENERATOR_RATE_LO_0 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.67 AASRC_CFG_INPUT_CLOCK_GENERATOR_RATE_HI_0 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.68 AASRC_CFG_INPUT_CLOCK_RECOVERY_LOOP_RATE_LO_0 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.69 AASRC_CFG_INPUT_CLOCK_RECOVERY_LOOP_RATE_HI_0 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.70 AASRC_CFG_INPUT_CLOCKZONE_COUNT_0 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.71 AASRC_CFG_INPUT_CLOCKZONE_CONTROL_0 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.72 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_CLOCK_GENERATOR_STAMP_LO_0 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.73 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_CLOCK_GENERATOR_STAMP_HI_0 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.74 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_CLOCK_GENERATOR_RATE_LO_0 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.75 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_CLOCK_GENERATOR_RATE_HI_0 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.76 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_CLOCK_RECOVERY_LOOP_RATE_LO_0 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.77 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_CLOCK_RECOVERY_LOOP_RATE_HI_0 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.78 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_CLOCK_RECOVERY_LOOP_STAMP_LO_0 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.79 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_CLOCK_RECOVERY_LOOP_STAMP_HI_0 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.80 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_CLOCKZONE_COUNT_0 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.81 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_CLOCKZONE_CONTROL_0 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.82 AASRC_CFG_INPUT_CLOCK_RECOVERY_LOOP_OVERRIDE_RATE_LO_0 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.83 AASRC_CFG_INPUT_CLOCK_RECOVERY_LOOP_OVERRIDE_RATE_HI_0 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.84 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_CLOCK_RECOVERY_LOOP_OVERRIDE_RATE_LO_0 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.85 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_CLOCK_RECOVERY_LOOP_OVERRIDE_RATE_HI_0 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.86 AASRC_CFG_INPUT_CLOCK_GENERATOR_STAMP_LO_1 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.87 AASRC_CFG_INPUT_CLOCK_GENERATOR_STAMP_HI_1 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.88 AASRC_CFG_INPUT_CLOCK_GENERATOR_RATE_LO_1 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.89 AASRC_CFG_INPUT_CLOCK_GENERATOR_RATE_HI_1 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.90 AASRC_CFG_INPUT_CLOCK_RECOVERY_LOOP_RATE_LO_1 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.91 AASRC_CFG_INPUT_CLOCK_RECOVERY_LOOP_RATE_HI_1 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.92 AASRC_CFG_INPUT_CLOCKZONE_COUNT_1 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.93 AASRC_CFG_INPUT_CLOCKZONE_CONTROL_1 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.94 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_CLOCK_GENERATOR_STAMP_LO_1 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.95 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_CLOCK_GENERATOR_STAMP_HI_1 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.96 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_CLOCK_GENERATOR_RATE_LO_1 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.97 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_CLOCK_GENERATOR_RATE_HI_1 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.98 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_CLOCK_RECOVERY_LOOP_RATE_LO_1 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.99 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_CLOCK_RECOVERY_LOOP_RATE_HI_1 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.100 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_CLOCK_RECOVERY_LOOP_STAMP_LO_1 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.101 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_CLOCK_RECOVERY_LOOP_STAMP_HI_1 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.102 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_CLOCKZONE_COUNT_1 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.103 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_CLOCKZONE_CONTROL_1 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.104 AASRC_CFG_INPUT_CLOCK_RECOVERY_LOOP_OVERRIDE_RATE_LO_1 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.105 AASRC_CFG_INPUT_CLOCK_RECOVERY_LOOP_OVERRIDE_RATE_HI_1 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.106 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_CLOCK_RECOVERY_LOOP_OVERRIDE_RATE_LO_1 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.107 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_CLOCK_RECOVERY_LOOP_OVERRIDE_RATE_HI_1 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.108 AASRC_CFG_INPUT_CLOCK_GENERATOR_STAMP_LO_2 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.109 AASRC_CFG_INPUT_CLOCK_GENERATOR_STAMP_HI_2 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.110 AASRC_CFG_INPUT_CLOCK_GENERATOR_RATE_LO_2 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.111 AASRC_CFG_INPUT_CLOCK_GENERATOR_RATE_HI_2 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.112 AASRC_CFG_INPUT_CLOCK_RECOVERY_LOOP_RATE_LO_2 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.113 AASRC_CFG_INPUT_CLOCK_RECOVERY_LOOP_RATE_HI_2 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.114 AASRC_CFG_INPUT_CLOCKZONE_COUNT_2 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.115 AASRC_CFG_INPUT_CLOCKZONE_CONTROL_2 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.116 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_CLOCK_GENERATOR_STAMP_LO_2 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.117 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_CLOCK_GENERATOR_STAMP_HI_2 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.118 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_CLOCK_GENERATOR_RATE_LO_2 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.119 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_CLOCK_GENERATOR_RATE_HI_2 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.120 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_CLOCK_RECOVERY_LOOP_RATE_LO_2 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.121 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_CLOCK_RECOVERY_LOOP_RATE_HI_2 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.122 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_CLOCK_RECOVERY_LOOP_STAMP_LO_2 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.123 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_CLOCK_RECOVERY_LOOP_STAMP_HI_2 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.124 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_CLOCKZONE_COUNT_2 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.125 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_CLOCKZONE_CONTROL_2 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.126 AASRC_CFG_INPUT_CLOCK_RECOVERY_LOOP_OVERRIDE_RATE_LO_2 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.127 AASRC_CFG_INPUT_CLOCK_RECOVERY_LOOP_OVERRIDE_RATE_HI_2 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.128 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_CLOCK_RECOVERY_LOOP_OVERRIDE_RATE_LO_2 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.129 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_CLOCK_RECOVERY_LOOP_OVERRIDE_RATE_HI_2 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.130 AASRC_CFG_INPUT_CLOCK_GENERATOR_STAMP_LO_3 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.131 AASRC_CFG_INPUT_CLOCK_GENERATOR_STAMP_HI_3 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.132 AASRC_CFG_INPUT_CLOCK_GENERATOR_RATE_LO_3 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.133 AASRC_CFG_INPUT_CLOCK_GENERATOR_RATE_HI_3 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.134 AASRC_CFG_INPUT_CLOCK_RECOVERY_LOOP_RATE_LO_3 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.135 AASRC_CFG_INPUT_CLOCK_RECOVERY_LOOP_RATE_HI_3 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.136 AASRC_CFG_INPUT_CLOCKZONE_COUNT_3 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.137 AASRC_CFG_INPUT_CLOCKZONE_CONTROL_3 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.138 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_CLOCK_GENERATOR_STAMP_LO_3 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.139 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_CLOCK_GENERATOR_STAMP_HI_3 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.140 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_CLOCK_GENERATOR_RATE_LO_3 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.141 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_CLOCK_GENERATOR_RATE_HI_3 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.142 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_CLOCK_RECOVERY_LOOP_RATE_LO_3 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.143 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_CLOCK_RECOVERY_LOOP_RATE_HI_3 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.144 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_CLOCK_RECOVERY_LOOP_STAMP_LO_3 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.145 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_CLOCK_RECOVERY_LOOP_STAMP_HI_3 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.146 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_CLOCKZONE_COUNT_3 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.147 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_CLOCKZONE_CONTROL_3 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.148 AASRC_CFG_INPUT_CLOCK_RECOVERY_LOOP_OVERRIDE_RATE_LO_3 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.149 AASRC_CFG_INPUT_CLOCK_RECOVERY_LOOP_OVERRIDE_RATE_HI_3 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.150 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_CLOCK_RECOVERY_LOOP_OVERRIDE_RATE_LO_3 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.151 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_CLOCK_RECOVERY_LOOP_OVERRIDE_RATE_HI_3 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.152 AASRC_CFG_INPUT_CLOCK_ZONE_DIVIDER Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.153 AASRC_CFG_OUTPUT_CLOCK_ZONE_DIVIDER Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.154 AASRC_DATA_R0_GROUP_INPUT_FIFO_DATA_L0 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.155 AASRC_DATA_R0_GROUP_INPUT_FIFO_DATA_R0 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.156 AASRC_DATA_R0_GROUP_INPUT_FIFO_DATA_L1 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.157 AASRC_DATA_R0_GROUP_INPUT_FIFO_DATA_R1 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.158 AASRC_DATA_R0_GROUP_INPUT_FIFO_DATA_L2 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.159 AASRC_DATA_R0_GROUP_INPUT_FIFO_DATA_R2 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.160 AASRC_DATA_R0_GROUP_INPUT_FIFO_DATA_L3 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.161 AASRC_DATA_R0_GROUP_INPUT_FIFO_DATA_R3 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.162 AASRC_DATA_R0_GROUP_INPUT_FIFO_DATA_L4 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.163 AASRC_DATA_R0_GROUP_INPUT_FIFO_DATA_R4 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.164 AASRC_DATA_R0_GROUP_INPUT_FIFO_DATA_L5 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.165 AASRC_DATA_R0_GROUP_INPUT_FIFO_DATA_R5 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.166 AASRC_DATA_R0_GROUP_INPUT_FIFO_DATA_L6 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.167 AASRC_DATA_R0_GROUP_INPUT_FIFO_DATA_R6 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.168 AASRC_DATA_R0_GROUP_INPUT_FIFO_DATA_L7 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.169 AASRC_DATA_R0_GROUP_INPUT_FIFO_DATA_R7 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.170 AASRC_DATA_R0_GROUP_OUTPUT_FIFO_DATA_L0 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.171 AASRC_DATA_R0_GROUP_OUTPUT_FIFO_DATA_R0 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.172 AASRC_DATA_R0_GROUP_OUTPUT_FIFO_DATA_L1 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.173 AASRC_DATA_R0_GROUP_OUTPUT_FIFO_DATA_R1 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.174 AASRC_DATA_R0_GROUP_OUTPUT_FIFO_DATA_L2 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.175 AASRC_DATA_R0_GROUP_OUTPUT_FIFO_DATA_R2 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.176 AASRC_DATA_R0_GROUP_OUTPUT_FIFO_DATA_L3 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.177 AASRC_DATA_R0_GROUP_OUTPUT_FIFO_DATA_R3 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.178 AASRC_DATA_R0_GROUP_OUTPUT_FIFO_DATA_L4 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.179 AASRC_DATA_R0_GROUP_OUTPUT_FIFO_DATA_R4 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.180 AASRC_DATA_R0_GROUP_OUTPUT_FIFO_DATA_L5 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.181 AASRC_DATA_R0_GROUP_OUTPUT_FIFO_DATA_R5 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.182 AASRC_DATA_R0_GROUP_OUTPUT_FIFO_DATA_L6 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.183 AASRC_DATA_R0_GROUP_OUTPUT_FIFO_DATA_R6 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.184 AASRC_DATA_R0_GROUP_OUTPUT_FIFO_DATA_L7 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.185 AASRC_DATA_R0_GROUP_OUTPUT_FIFO_DATA_R7 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.186 AASRC_DATA_R1_STREAM_INPUT_FIFO_DATA_L0 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.187 AASRC_DATA_R1_STREAM_INPUT_FIFO_DATA_R0 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.188 AASRC_DATA_R1_STREAM_INPUT_FIFO_DATA_L1 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.189 AASRC_DATA_R1_STREAM_INPUT_FIFO_DATA_R1 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.190 AASRC_DATA_R1_STREAM_INPUT_FIFO_DATA_L2 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.191 AASRC_DATA_R1_STREAM_INPUT_FIFO_DATA_R2 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.192 AASRC_DATA_R1_STREAM_INPUT_FIFO_DATA_L3 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.193 AASRC_DATA_R1_STREAM_INPUT_FIFO_DATA_R3 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.194 AASRC_DATA_R1_STREAM_INPUT_FIFO_DATA_L4 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.195 AASRC_DATA_R1_STREAM_INPUT_FIFO_DATA_R4 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.196 AASRC_DATA_R1_STREAM_INPUT_FIFO_DATA_L5 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.197 AASRC_DATA_R1_STREAM_INPUT_FIFO_DATA_R5 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.198 AASRC_DATA_R1_STREAM_INPUT_FIFO_DATA_L6 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.199 AASRC_DATA_R1_STREAM_INPUT_FIFO_DATA_R6 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.200 AASRC_DATA_R1_STREAM_INPUT_FIFO_DATA_L7 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.201 AASRC_DATA_R1_STREAM_INPUT_FIFO_DATA_R7 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.202 AASRC_DATA_R1_STREAM_OUTPUT_FIFO_DATA_L0 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.203 AASRC_DATA_R1_STREAM_OUTPUT_FIFO_DATA_R0 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.204 AASRC_DATA_R1_STREAM_OUTPUT_FIFO_DATA_L1 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.205 AASRC_DATA_R1_STREAM_OUTPUT_FIFO_DATA_R1 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.206 AASRC_DATA_R1_STREAM_OUTPUT_FIFO_DATA_L2 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.207 AASRC_DATA_R1_STREAM_OUTPUT_FIFO_DATA_R2 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.208 AASRC_DATA_R1_STREAM_OUTPUT_FIFO_DATA_L3 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.209 AASRC_DATA_R1_STREAM_OUTPUT_FIFO_DATA_R3 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.210 AASRC_DATA_R1_STREAM_OUTPUT_FIFO_DATA_L4 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.211 AASRC_DATA_R1_STREAM_OUTPUT_FIFO_DATA_R4 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.212 AASRC_DATA_R1_STREAM_OUTPUT_FIFO_DATA_L5 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.213 AASRC_DATA_R1_STREAM_OUTPUT_FIFO_DATA_R5 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.214 AASRC_DATA_R1_STREAM_OUTPUT_FIFO_DATA_L6 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.215 AASRC_DATA_R1_STREAM_OUTPUT_FIFO_DATA_R6 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.216 AASRC_DATA_R1_STREAM_OUTPUT_FIFO_DATA_L7 Register
- 14.7.1.1.2.217 AASRC_DATA_R1_STREAM_OUTPUT_FIFO_DATA_R7 Register
- 14.7.1.2
MCASP
- 14.7.1.2.1 MCASP Summaries
- 14.7.1.2.2
MCASP Registers
- 14.7.1.2.2.1 MCASP_PID Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.2 MCASP_PWRIDLESYSCONFIG Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.3 MCASP_PFUNC Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.4 MCASP_PDIR Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.5 MCASP_PDOUT Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.6 MCASP_PDIN Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.7 MCASP_PDCLR Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.8 MCASP_GBLCTL Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.9 MCASP_AMUTE Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.10 MCASP_DLBCTL Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.11 MCASP_DITCTL Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.12 MCASP_RGBLCTL Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.13 MCASP_RMASK Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.14 MCASP_RFMT Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.15 MCASP_AFSRCTL Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.16 MCASP_ACLKRCTL Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.17 MCASP_AHCLKRCTL Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.18 MCASP_RTDM Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.19 MCASP_RINTCTL Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.20 MCASP_RSTAT Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.21 MCASP_RSLOT Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.22 MCASP_RCLKCHK Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.23 MCASP_XGBLCTL Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.24 MCASP_XMASK Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.25 MCASP_XFMT Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.26 MCASP_AFSXCTL Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.27 MCASP_ACLKXCTL Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.28 MCASP_AHCLKXCTL Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.29 MCASP_XTDM Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.30 MCASP_XINTCTL Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.31 MCASP_XSTAT Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.32 MCASP_XSLOT Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.33 MCASP_XCLKCHK Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.34 MCASP_XEVTCTL Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.35 MCASP_DITCSRA0 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.36 MCASP_DITCSRA1 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.37 MCASP_DITCSRA2 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.38 MCASP_DITCSRA3 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.39 MCASP_DITCSRA4 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.40 MCASP_DITCSRA5 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.41 MCASP_DITCSRB0 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.42 MCASP_DITCSRB1 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.43 MCASP_DITCSRB2 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.44 MCASP_DITCSRB3 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.45 MCASP_DITCSRB4 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.46 MCASP_DITCSRB5 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.47 MCASP_DITUDRA0 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.48 MCASP_DITUDRA1 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.49 MCASP_DITUDRA2 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.50 MCASP_DITUDRA3 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.51 MCASP_DITUDRA4 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.52 MCASP_DITUDRA5 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.53 MCASP_DITUDRB0 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.54 MCASP_DITUDRB1 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.55 MCASP_DITUDRB2 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.56 MCASP_DITUDRB3 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.57 MCASP_DITUDRB4 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.58 MCASP_DITUDRB5 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.59 MCASP_SRCTL0 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.60 MCASP_SRCTL1 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.61 MCASP_SRCTL2 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.62 MCASP_SRCTL3 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.63 MCASP_SRCTL4 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.64 MCASP_SRCTL5 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.65 MCASP_SRCTL6 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.66 MCASP_SRCTL7 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.67 MCASP_SRCTL8 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.68 MCASP_SRCTL9 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.69 MCASP_SRCTL10 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.70 MCASP_SRCTL11 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.71 MCASP_SRCTL12 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.72 MCASP_SRCTL13 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.73 MCASP_SRCTL14 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.74 MCASP_SRCTL15 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.75 MCASP_XBUF0 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.76 MCASP_XBUF1 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.77 MCASP_XBUF2 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.78 MCASP_XBUF3 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.79 MCASP_XBUF4 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.80 MCASP_XBUF5 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.81 MCASP_XBUF6 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.82 MCASP_XBUF7 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.83 MCASP_XBUF8 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.84 MCASP_XBUF9 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.85 MCASP_XBUF10 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.86 MCASP_XBUF11 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.87 MCASP_XBUF12 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.88 MCASP_XBUF13 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.89 MCASP_XBUF14 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.90 MCASP_XBUF15 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.91 MCASP_RBUF0 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.92 MCASP_RBUF1 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.93 MCASP_RBUF2 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.94 MCASP_RBUF3 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.95 MCASP_RBUF4 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.96 MCASP_RBUF5 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.97 MCASP_RBUF6 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.98 MCASP_RBUF7 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.99 MCASP_RBUF8 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.100 MCASP_RBUF9 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.101 MCASP_RBUF10 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.102 MCASP_RBUF11 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.103 MCASP_RBUF12 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.104 MCASP_RBUF13 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.105 MCASP_RBUF14 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.106 MCASP_RBUF15 Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.107 MCASP_WFIFOCTL Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.108 MCASP_WFIFOSTS Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.109 MCASP_RFIFOCTL Register
- 14.7.1.2.2.110 MCASP_RFIFOSTS Register
- 14.7.1.3
atl
- 14.7.1.3.1 atl Summaries
- 14.7.1.3.2
atl Registers
- 14.7.1.3.2.1 ATL_MMR_REVISION Register
- 14.7.1.3.2.2 ATL_MMR_ATL0_PPMR Register
- 14.7.1.3.2.3 ATL_MMR_ATL0_BBSR Register
- 14.7.1.3.2.4 ATL_MMR_ATL0_ATLCR Register
- 14.7.1.3.2.5 ATL_MMR_ATL0_SWEN Register
- 14.7.1.3.2.6 ATL_MMR_ATL0_BWSMUX Register
- 14.7.1.3.2.7 ATL_MMR_ATL0_AWSMUX Register
- 14.7.1.3.2.8 ATL_MMR_ATL0_PCLKMUX Register
- 14.7.1.3.2.9 ATL_MMR_ATL1_PPMR Register
- 14.7.1.3.2.10 ATL_MMR_ATL1_BBSR Register
- 14.7.1.3.2.11 ATL_MMR_ATL1_ATLCR Register
- 14.7.1.3.2.12 ATL_MMR_ATL1_SWEN Register
- 14.7.1.3.2.13 ATL_MMR_ATL1_BWSMUX Register
- 14.7.1.3.2.14 ATL_MMR_ATL1_AWSMUX Register
- 14.7.1.3.2.15 ATL_MMR_ATL1_PCLKMUX Register
- 14.7.1.3.2.16 ATL_MMR_ATL2_PPMR Register
- 14.7.1.3.2.17 ATL_MMR_ATL2_BBSR Register
- 14.7.1.3.2.18 ATL_MMR_ATL2_ATLCR Register
- 14.7.1.3.2.19 ATL_MMR_ATL2_SWEN Register
- 14.7.1.3.2.20 ATL_MMR_ATL2_BWSMUX Register
- 14.7.1.3.2.21 ATL_MMR_ATL2_AWSMUX Register
- 14.7.1.3.2.22 ATL_MMR_ATL2_PCLKMUX Register
- 14.7.1.3.2.23 ATL_MMR_ATL3_PPMR Register
- 14.7.1.3.2.24 ATL_MMR_ATL3_BBSR Register
- 14.7.1.3.2.25 ATL_MMR_ATL3_ATLCR Register
- 14.7.1.3.2.26 ATL_MMR_ATL3_SWEN Register
- 14.7.1.3.2.27 ATL_MMR_ATL3_BWSMUX Register
- 14.7.1.3.2.28 ATL_MMR_ATL3_AWSMUX Register
- 14.7.1.3.2.29 ATL_MMR_ATL3_PCLKMUX Register
- 14.7.1.4
MLB
- 14.7.1.4.1 MLB Summaries
- 14.7.1.4.2
MLB Registers
- 14.7.1.4.2.1 MLBSS_CFG_PID Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.2 MLBSS_CFG_STAT Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.3 MLBSS_CFG_DMA_CTRL Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.4 MLBDIM_CFG_MLBC0 Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.5 MLBDIM_CFG_MLBPC0 Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.6 MLBDIM_CFG_MS0 Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.7 MLBDIM_CFG_MS1 Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.8 MLBDIM_CFG_MSS Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.9 MLBDIM_CFG_MSD Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.10 MLBDIM_CFG_MIEN Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.11 MLBDIM_CFG_MLBPC2 Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.12 MLBDIM_CFG_MLBPC1 Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.13 MLBDIM_CFG_MLBC1 Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.14 MLBDIM_CFG_HCTL Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.15 MLBDIM_CFG_HCMR0 Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.16 MLBDIM_CFG_HCMR1 Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.17 MLBDIM_CFG_HCER0 Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.18 MLBDIM_CFG_HCER1 Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.19 MLBDIM_CFG_HCBR0 Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.20 MLBDIM_CFG_HCBR1 Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.21 MLBDIM_CFG_MDAT0 Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.22 MLBDIM_CFG_MDAT1 Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.23 MLBDIM_CFG_MDAT2 Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.24 MLBDIM_CFG_MDAT3 Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.25 MLBDIM_CFG_MDWE0 Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.26 MLBDIM_CFG_MDWE1 Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.27 MLBDIM_CFG_MDWE2 Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.28 MLBDIM_CFG_MDWE3 Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.29 MLBDIM_CFG_MCTL Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.30 MLBDIM_CFG_MADR Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.31 MLBDIM_CFG_PID Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.32 MLBDIM_CFG_ACTL Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.33 MLBDIM_CFG_ACSR0 Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.34 MLBDIM_CFG_ACSR1 Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.35 MLBDIM_CFG_ACMR0 Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.36 MLBDIM_CFG_ACMR1 Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.37 RAT_PID Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.38 RAT_CONFIG Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.39 RAT_DESTINATION_ID Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.40 RAT_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_CONTROL Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.41 RAT_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER0 Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.42 RAT_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER1 Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.43 RAT_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA0 Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.44 RAT_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA1 Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.45 RAT_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA2 Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.46 RAT_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA3 Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.47 RAT_EXCEPTION_PEND_SET Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.48 RAT_EXCEPTION_PEND_CLEAR Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.49 RAT_EXCEPTION_ENABLE_SET Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.50 RAT_EXCEPTION_ENABLE_CLEAR Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.51 RAT_EOI_REG Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.52 RAT_REGION_CTRL_J Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.53 RAT_REGION_BASE_J Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.54 RAT_REGION_TRANS_L_J Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.55 RAT_REGION_TRANS_U_J Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.56 ECC_AGGR_REV Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.57 ECC_AGGR_VECTOR Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.58 ECC_AGGR_STAT Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.59 ECC_AGGR_RESERVED_SVBUS_J Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.60 ECC_AGGR_SEC_EOI_REG Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.61 ECC_AGGR_SEC_STATUS_REG0 Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.62 ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.63 ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.64 ECC_AGGR_DED_EOI_REG Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.65 ECC_AGGR_DED_STATUS_REG0 Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.66 ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.67 ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.68 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_SET Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.69 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_CLR Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.70 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_STATUS_SET Register
- 14.7.1.4.2.71 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_STATUS_CLR Register
- 14.7.1.1
aasrc
- 14.7.2
General Connectivity Peripherals Registers
- 14.7.2.1
GPIO
- 14.7.2.1.1 GPIO Summaries
- 14.7.2.1.2
GPIO Registers
- 14.7.2.1.2.1 GPIO_PID Register
- 14.7.2.1.2.2 GPIO_PCR Register
- 14.7.2.1.2.3 GPIO_BINTEN Register
- 14.7.2.1.2.4 GPIO_DIR01 Register
- 14.7.2.1.2.5 GPIO_OUT_DATA01 Register
- 14.7.2.1.2.6 GPIO_SET_DATA01 Register
- 14.7.2.1.2.7 GPIO_CLR_DATA01 Register
- 14.7.2.1.2.8 GPIO_IN_DATA01 Register
- 14.7.2.1.2.9 GPIO_SET_RIS_TRIG01 Register
- 14.7.2.1.2.10 GPIO_CLR_RIS_TRIG01 Register
- 14.7.2.1.2.11 GPIO_SET_FAL_TRIG01 Register
- 14.7.2.1.2.12 GPIO_CLR_FAL_TRIG01 Register
- 14.7.2.1.2.13 GPIO_INTSTAT01 Register
- 14.7.2.1.2.14 GPIO_DIR23 Register
- 14.7.2.1.2.15 GPIO_OUT_DATA23 Register
- 14.7.2.1.2.16 GPIO_SET_DATA23 Register
- 14.7.2.1.2.17 GPIO_CLR_DATA23 Register
- 14.7.2.1.2.18 GPIO_IN_DATA23 Register
- 14.7.2.1.2.19 GPIO_SET_RIS_TRIG23 Register
- 14.7.2.1.2.20 GPIO_CLR_RIS_TRIG23 Register
- 14.7.2.1.2.21 GPIO_SET_FAL_TRIG23 Register
- 14.7.2.1.2.22 GPIO_CLR_FAL_TRIG23 Register
- 14.7.2.1.2.23 GPIO_INTSTAT23 Register
- 14.7.2.1.2.24 GPIO_DIR45 Register
- 14.7.2.1.2.25 GPIO_OUT_DATA45 Register
- 14.7.2.1.2.26 GPIO_SET_DATA45 Register
- 14.7.2.1.2.27 GPIO_CLR_DATA45 Register
- 14.7.2.1.2.28 GPIO_IN_DATA45 Register
- 14.7.2.1.2.29 GPIO_SET_RIS_TRIG45 Register
- 14.7.2.1.2.30 GPIO_CLR_RIS_TRIG45 Register
- 14.7.2.1.2.31 GPIO_SET_FAL_TRIG45 Register
- 14.7.2.1.2.32 GPIO_CLR_FAL_TRIG45 Register
- 14.7.2.1.2.33 GPIO_INTSTAT45 Register
- 14.7.2.1.2.34 GPIO_DIR67 Register
- 14.7.2.1.2.35 GPIO_OUT_DATA67 Register
- 14.7.2.1.2.36 GPIO_SET_DATA67 Register
- 14.7.2.1.2.37 GPIO_CLR_DATA67 Register
- 14.7.2.1.2.38 GPIO_IN_DATA67 Register
- 14.7.2.1.2.39 GPIO_SET_RIS_TRIG67 Register
- 14.7.2.1.2.40 GPIO_CLR_RIS_TRIG67 Register
- 14.7.2.1.2.41 GPIO_SET_FAL_TRIG67 Register
- 14.7.2.1.2.42 GPIO_CLR_FAL_TRIG67 Register
- 14.7.2.1.2.43 GPIO_INTSTAT67 Register
- 14.7.2.1.2.44 GPIO_DIR8 Register
- 14.7.2.1.2.45 GPIO_OUT_DATA8 Register
- 14.7.2.1.2.46 GPIO_SET_DATA8 Register
- 14.7.2.1.2.47 GPIO_CLR_DATA8 Register
- 14.7.2.1.2.48 GPIO_IN_DATA8 Register
- 14.7.2.1.2.49 GPIO_SET_RIS_TRIG8 Register
- 14.7.2.1.2.50 GPIO_CLR_RIS_TRIG8 Register
- 14.7.2.1.2.51 GPIO_SET_FAL_TRIG8 Register
- 14.7.2.1.2.52 GPIO_CLR_FAL_TRIG8 Register
- 14.7.2.1.2.53 GPIO_INTSTAT8 Register
- 14.7.2.2
I2C
- 14.7.2.2.1 I2C Summaries
- 14.7.2.2.2
I2C Registers
- 14.7.2.2.2.1 I2C_REVNB_LO Register
- 14.7.2.2.2.2 I2C_REVNB_HI Register
- 14.7.2.2.2.3 I2C_SYSC Register
- 14.7.2.2.2.4 I2C_EOI Register
- 14.7.2.2.2.5 I2C_IRQSTATUS_RAW Register
- 14.7.2.2.2.6 I2C_IRQSTATUS Register
- 14.7.2.2.2.7 I2C_IRQENABLE_SET Register
- 14.7.2.2.2.8 I2C_IRQENABLE_CLR Register
- 14.7.2.2.2.9 I2C_WE Register
- 14.7.2.2.2.10 I2C_DMARXENABLE_SET Register
- 14.7.2.2.2.11 I2C_DMATXENABLE_SET Register
- 14.7.2.2.2.12 I2C_DMARXENABLE_CLR Register
- 14.7.2.2.2.13 I2C_DMATXENABLE_CLR Register
- 14.7.2.2.2.14 I2C_DMARXWAKE_EN Register
- 14.7.2.2.2.15 I2C_DMATXWAKE_EN Register
- 14.7.2.2.2.16 I2C_IE Register
- 14.7.2.2.2.17 I2C_STAT Register
- 14.7.2.2.2.18 I2C_SYSS Register
- 14.7.2.2.2.19 I2C_BUF Register
- 14.7.2.2.2.20 I2C_CNT Register
- 14.7.2.2.2.21 I2C_DATA Register
- 14.7.2.2.2.22 I2C_CON Register
- 14.7.2.2.2.23 I2C_OA Register
- 14.7.2.2.2.24 I2C_SA Register
- 14.7.2.2.2.25 I2C_PSC Register
- 14.7.2.2.2.26 I2C_SCLL Register
- 14.7.2.2.2.27 I2C_SCLH Register
- 14.7.2.2.2.28 I2C_SYSTEST Register
- 14.7.2.2.2.29 I2C_BUFSTAT Register
- 14.7.2.2.2.30 I2C_OA1 Register
- 14.7.2.2.2.31 I2C_OA2 Register
- 14.7.2.2.2.32 I2C_OA3 Register
- 14.7.2.2.2.33 I2C_ACTOA Register
- 14.7.2.2.2.34 I2C_SBLOCK Register
- 14.7.2.3
MCSPI
- 14.7.2.3.1 MCSPI Summaries
- 14.7.2.3.2
MCSPI Registers
- 14.7.2.3.2.1 MCSPI_HL_REV Register
- 14.7.2.3.2.2 MCSPI_HL_HWINFO Register
- 14.7.2.3.2.3 MCSPI_HL_SYSCONFIG Register
- 14.7.2.3.2.4 MCSPI_REVISION Register
- 14.7.2.3.2.5 MCSPI_SYSCONFIG Register
- 14.7.2.3.2.6 MCSPI_SYSSTATUS Register
- 14.7.2.3.2.7 MCSPI_IRQSTATUS Register
- 14.7.2.3.2.8 MCSPI_IRQENABLE Register
- 14.7.2.3.2.9 MCSPI_WAKEUPENABLE Register
- 14.7.2.3.2.10 MCSPI_SYST Register
- 14.7.2.3.2.11 MCSPI_MODULCTRL Register
- 14.7.2.3.2.12 MCSPI_CH0CONF Register
- 14.7.2.3.2.13 MCSPI_CH0STAT Register
- 14.7.2.3.2.14 MCSPI_CH0CTRL Register
- 14.7.2.3.2.15 MCSPI_TX0 Register
- 14.7.2.3.2.16 MCSPI_RX0 Register
- 14.7.2.3.2.17 MCSPI_CH1CONF Register
- 14.7.2.3.2.18 MCSPI_CH1STAT Register
- 14.7.2.3.2.19 MCSPI_CH1CTRL Register
- 14.7.2.3.2.20 MCSPI_TX1 Register
- 14.7.2.3.2.21 MCSPI_RX1 Register
- 14.7.2.3.2.22 MCSPI_CH2CONF Register
- 14.7.2.3.2.23 MCSPI_CH2STAT Register
- 14.7.2.3.2.24 MCSPI_CH2CTRL Register
- 14.7.2.3.2.25 MCSPI_TX2 Register
- 14.7.2.3.2.26 MCSPI_RX2 Register
- 14.7.2.3.2.27 MCSPI_CH3CONF Register
- 14.7.2.3.2.28 MCSPI_CH3STAT Register
- 14.7.2.3.2.29 MCSPI_CH3CTRL Register
- 14.7.2.3.2.30 MCSPI_TX3 Register
- 14.7.2.3.2.31 MCSPI_RX3 Register
- 14.7.2.3.2.32 MCSPI_XFERLEVEL Register
- 14.7.2.3.2.33 MCSPI_DAFTX Register
- 14.7.2.3.2.34 MCSPI_DAFRX Register
- 14.7.2.4
UART
- 14.7.2.4.1 UART Summaries
- 14.7.2.4.2
UART Registers
- 14.7.2.4.2.1 UART_DLL Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.2 UART_RHR Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.3 UART_THR Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.4 UART_DLH Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.5 UART_IER_CIR Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.6 UART_IER_IRDA Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.7 UART_IER_UART Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.8 UART_EFR Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.9 UART_FCR Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.10 UART_IIR_CIR Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.11 UART_IIR_IRDA Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.12 UART_IIR_UART Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.13 UART_LCR Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.14 UART_MCR Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.15 UART_XON1_ADDR1 Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.16 UART_LSR_CIR Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.17 UART_LSR_IRDA Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.18 UART_LSR_UART Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.19 UART_XON2_ADDR2 Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.20 UART_MSR Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.21 UART_TCR Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.22 UART_XOFF1 Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.23 UART_SPR Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.24 UART_TLR Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.25 UART_XOFF2 Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.26 UART_MDR1 Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.27 UART_MDR2 Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.28 UART_SFLSR Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.29 UART_TXFLL Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.30 UART_RESUME Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.31 UART_TXFLH Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.32 UART_RXFLL Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.33 UART_SFREGL Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.34 UART_RXFLH Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.35 UART_SFREGH Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.36 UART_BLR Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.37 UART_UASR Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.38 UART_ACREG Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.39 UART_SCR Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.40 UART_SSR Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.41 UART_EBLR Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.42 UART_MVR Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.43 UART_SYSC Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.44 UART_SYSS Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.45 UART_WER Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.46 UART_CFPS Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.47 UART_RXFIFO_LVL Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.48 UART_TXFIFO_LVL Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.49 UART_IER2 Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.50 UART_ISR2 Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.51 UART_FREQ_SEL Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.52 UART_ABAUD_1ST_CHAR Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.53 UART_BAUD_2ND_CHAR Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.54 UART_MDR3 Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.55 UART_TX_DMA_THRESHOLD Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.56 UART_MDR4 Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.57 UART_EFR2 Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.58 UART_ECR Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.59 UART_TIMEGUARD Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.60 UART_TIMEOUTL Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.61 UART_TIMEOUTH Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.62 UART_SCCR Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.63 UART_ERHR Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.64 UART_ETHR Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.65 UART_MAR Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.66 UART_MMR Register
- 14.7.2.4.2.67 UART_MBR Register
- 14.7.2.1
GPIO
- 14.7.3
High-Speed Serial Interfaces Registers
- 14.7.3.1
CPSW
- 14.7.3.1.1 CPSW Summaries
- 14.7.3.1.2
CPSW Registers
- 14.7.3.1.2.1 CPSW3_ECC_ECC_REV Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.2 CPSW3_ECC_ECC_VECTOR Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.3 CPSW3_ECC_ECC_STAT Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.4 CPSW3_ECC_ECC_RESERVED_SVBUS_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.5 CPSW3_ECC_ECC_SEC_EOI_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.6 CPSW3_ECC_ECC_SEC_STATUS_REG0 Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.7 CPSW3_ECC_ECC_SEC_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.8 CPSW3_ECC_ECC_SEC_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.9 CPSW3_ECC_ECC_DED_EOI_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.10 CPSW3_ECC_ECC_DED_STATUS_REG0 Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.11 CPSW3_ECC_ECC_DED_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.12 CPSW3_ECC_ECC_DED_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.13 CPSW3_ECC_ECC_AGGR_ENABLE_SET Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.14 CPSW3_ECC_ECC_AGGR_ENABLE_CLR Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.15 CPSW3_ECC_ECC_AGGR_STATUS_SET Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.16 CPSW3_ECC_ECC_AGGR_STATUS_CLR Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.17 CPSW3_CPSW_NUSS_IDVER_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.18 CPSW3_SYNCE_COUNT_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.19 CPSW3_SYNCE_MUX_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.20 CPSW3_CONTROL_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.21 CPSW3_SUBSSYSTEM_STATUS_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.22 CPSW3_SUBSYSTEM_CONFIG_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.23 CPSW3_RGMII1_STATUS_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.24 CPSW3_RGMII2_STATUS_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.25 CPSW3_MDIO_MDIO_VERSION_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.26 CPSW3_MDIO_CONTROL_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.27 CPSW3_MDIO_ALIVE_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.28 CPSW3_MDIO_LINK_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.29 CPSW3_MDIO_LINK_INT_RAW_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.30 CPSW3_MDIO_LINK_INT_MASKED_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.31 CPSW3_MDIO_LINK_INT_MASK_SET_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.32 CPSW3_MDIO_LINK_INT_MASK_CLEAR_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.33 CPSW3_MDIO_USER_INT_RAW_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.34 CPSW3_MDIO_USER_INT_MASKED_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.35 CPSW3_MDIO_USER_INT_MASK_SET_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.36 CPSW3_MDIO_USER_INT_MASK_CLEAR_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.37 CPSW3_MDIO_MANUAL_IF_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.38 CPSW3_MDIO_POLL_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.39 CPSW3_MDIO_POLL_EN_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.40 CPSW3_MDIO_CLAUS45_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.41 CPSW3_MDIO_USER_ADDR0_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.42 CPSW3_MDIO_USER_ADDR1_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.43 CPSW3_INTD_REVISION Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.44 CPSW3_INTD_EOI_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.45 CPSW3_INTD_INTR_VECTOR_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.46 CPSW3_INTD_ENABLE_REG_OUT_PULSE_0 Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.47 CPSW3_INTD_ENABLE_CLR_REG_OUT_PULSE_0 Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.48 CPSW3_INTD_STATUS_REG_OUT_PULSE_0 Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.49 CPSW3_INTD_INTR_VECTOR_REG_OUT_PULSE Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.50 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_ID_VER_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.51 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CONTROL_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.52 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_EM_CONTROL_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.53 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_STAT_PORT_EN_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.54 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_PTYPE_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.55 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_SOFT_IDLE_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.56 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_THRU_RATE_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.57 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_GAP_THRESH_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.58 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_EEE_PRESCALE_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.59 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_TX_G_OFLOW_THRESH_SET_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.60 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_TX_G_OFLOW_THRESH_CLR_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.61 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_TX_G_BUF_THRESH_SET_L_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.62 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_TX_G_BUF_THRESH_SET_H_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.63 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_TX_G_BUF_THRESH_CLR_L_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.64 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_TX_G_BUF_THRESH_CLR_H_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.65 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_VLAN_LTYPE_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.66 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_EST_TS_DOMAIN_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.67 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CUT_THRESHOLD_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.68 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_FREQUENCY_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.69 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_IET_HOLD_CNT_LD_VAL_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.70 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_TX_PRI0_MAXLEN_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.71 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_TX_PRI1_MAXLEN_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.72 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_TX_PRI2_MAXLEN_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.73 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_TX_PRI3_MAXLEN_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.74 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_TX_PRI4_MAXLEN_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.75 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_TX_PRI5_MAXLEN_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.76 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_TX_PRI6_MAXLEN_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.77 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_TX_PRI7_MAXLEN_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.78 CPSW3_MDIO_USER_GROUP_USER_ACCESS_REG_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.79 CPSW3_MDIO_USER_GROUP_USER_PHY_SEL_REG_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.80 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPPI_P0_CONTROL_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.81 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPPI_P0_FLOW_ID_OFFSET_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.82 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPPI_P0_BLK_CNT_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.83 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPPI_P0_PORT_VLAN_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.84 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPPI_P0_TX_PRI_MAP_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.85 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPPI_P0_PRI_CTL_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.86 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPPI_P0_RX_PRI_MAP_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.87 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPPI_P0_RX_MAXLEN_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.88 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPPI_P0_TX_BLKS_PRI_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.89 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPPI_P0_IDLE2LPI_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.90 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPPI_P0_LPI2WAKE_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.91 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPPI_P0_EEE_STATUS_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.92 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPPI_P0_FIFO_STATUS_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.93 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPPI_P0_MAX_BLKS_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.94 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPPI_P0_RX_DSCP_MAP_REG_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.95 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPPI_P0_PRI_CIR_REG_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.96 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPPI_P0_PRI_EIR_REG_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.97 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPPI_P0_TX_D_THRESH_SET_L_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.98 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPPI_P0_TX_D_THRESH_SET_H_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.99 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPPI_P0_TX_D_THRESH_CLR_L_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.100 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPPI_P0_TX_D_THRESH_CLR_H_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.101 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPPI_P0_TX_G_BUF_THRESH_SET_L_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.102 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPPI_P0_TX_G_BUF_THRESH_SET_H_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.103 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPPI_P0_TX_G_BUF_THRESH_CLR_L_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.104 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPPI_P0_TX_G_BUF_THRESH_CLR_H_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.105 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPPI_P0_SRC_ID_A_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.106 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPPI_P0_SRC_ID_B_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.107 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_CPPI_P0_HOST_BLKS_PRI_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.108 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_RESERVED_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.109 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_CONTROL_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.110 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_MAX_BLKS_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.111 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_BLK_CNT_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.112 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_PORT_VLAN_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.113 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_TX_PRI_MAP_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.114 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_PRI_CTL_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.115 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_RX_PRI_MAP_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.116 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_RX_MAXLEN_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.117 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_TX_BLKS_PRI_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.118 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_IDLE2LPI_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.119 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_LPI2WAKE_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.120 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_EEE_STATUS_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.121 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_IET_CONTROL_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.122 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_IET_STATUS_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.123 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_IET_VERIFY_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.124 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_FIFO_STATUS_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.125 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_EST_CONTROL_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.126 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_RX_DSCP_MAP_REG_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.127 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_PRI_CIR_REG_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.128 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_PRI_EIR_REG_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.129 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_TX_D_THRESH_SET_L_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.130 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_TX_D_THRESH_SET_H_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.131 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_TX_D_THRESH_CLR_L_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.132 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_TX_D_THRESH_CLR_H_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.133 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_TX_G_BUF_THRESH_SET_L_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.134 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_TX_G_BUF_THRESH_SET_H_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.135 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_TX_G_BUF_THRESH_CLR_L_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.136 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_TX_G_BUF_THRESH_CLR_H_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.137 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_TX_D_OFLOW_ADDVAL_L_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.138 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_TX_D_OFLOW_ADDVAL_H_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.139 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_SA_L_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.140 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_SA_H_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.141 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_TS_CTL_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.142 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_TS_SEQ_LTYPE_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.143 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_TS_VLAN_LTYPE_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.144 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_TS_CTL_LTYPE2_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.145 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_TS_CTL2_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.146 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_MAC_CONTROL_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.147 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_MAC_STATUS_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.148 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_MAC_SOFT_RESET_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.149 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_MAC_BOFFTEST_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.150 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_MAC_RX_PAUSETIMER_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.151 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_MAC_RXN_PAUSETIMER_REG_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.152 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_MAC_TX_PAUSETIMER_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.153 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_MAC_TXN_PAUSETIMER_REG_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.154 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_MAC_EMCONTROL_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.155 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_MAC_TX_GAP_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.156 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_MAC_PORT_CONFIG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.157 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_INTERVLAN_OPX_POINTER_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.158 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_INTERVLAN_OPX_A_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.159 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_INTERVLAN_OPX_B_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.160 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_INTERVLAN_OPX_C_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.161 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_INTERVLAN_OPX_D_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.162 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_CUT_THRU_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.163 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_0_PN_PORT_SPEED_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.164 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_RESERVED_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.165 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_CONTROL_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.166 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_MAX_BLKS_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.167 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_BLK_CNT_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.168 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_PORT_VLAN_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.169 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_TX_PRI_MAP_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.170 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_PRI_CTL_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.171 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_RX_PRI_MAP_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.172 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_RX_MAXLEN_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.173 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_TX_BLKS_PRI_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.174 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_IDLE2LPI_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.175 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_LPI2WAKE_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.176 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_EEE_STATUS_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.177 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_IET_CONTROL_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.178 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_IET_STATUS_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.179 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_IET_VERIFY_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.180 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_FIFO_STATUS_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.181 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_EST_CONTROL_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.182 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_RX_DSCP_MAP_REG_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.183 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_PRI_CIR_REG_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.184 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_PRI_EIR_REG_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.185 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_TX_D_THRESH_SET_L_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.186 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_TX_D_THRESH_SET_H_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.187 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_TX_D_THRESH_CLR_L_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.188 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_TX_D_THRESH_CLR_H_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.189 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_TX_G_BUF_THRESH_SET_L_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.190 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_TX_G_BUF_THRESH_SET_H_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.191 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_TX_G_BUF_THRESH_CLR_L_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.192 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_TX_G_BUF_THRESH_CLR_H_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.193 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_TX_D_OFLOW_ADDVAL_L_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.194 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_TX_D_OFLOW_ADDVAL_H_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.195 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_SA_L_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.196 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_SA_H_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.197 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_TS_CTL_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.198 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_TS_SEQ_LTYPE_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.199 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_TS_VLAN_LTYPE_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.200 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_TS_CTL_LTYPE2_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.201 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_TS_CTL2_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.202 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_MAC_CONTROL_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.203 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_MAC_STATUS_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.204 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_MAC_SOFT_RESET_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.205 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_MAC_BOFFTEST_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.206 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_MAC_RX_PAUSETIMER_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.207 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_MAC_RXN_PAUSETIMER_REG_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.208 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_MAC_TX_PAUSETIMER_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.209 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_MAC_TXN_PAUSETIMER_REG_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.210 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_MAC_EMCONTROL_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.211 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_MAC_TX_GAP_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.212 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_MAC_PORT_CONFIG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.213 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_INTERVLAN_OPX_POINTER_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.214 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_INTERVLAN_OPX_A_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.215 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_INTERVLAN_OPX_B_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.216 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_INTERVLAN_OPX_C_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.217 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_INTERVLAN_OPX_D_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.218 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_CUT_THRU_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.219 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_ETH_MAC_1_PN_PORT_SPEED_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.220 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_EST_FETCH_LOC_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.221 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_RXGOODFRAMES_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.222 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_RXBROADCASTFRAMES_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.223 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_RXMULTICASTFRAMES_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.224 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_RXPAUSEFRAMES_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.225 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_RXCRCERRORS_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.226 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_RXALIGNCODEERRORS_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.227 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_RXOVERSIZEDFRAMES_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.228 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_RXJABBERFRAMES_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.229 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_RXUNDERSIZEDFRAMES_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.230 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_RXFRAGMENTS_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.231 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_ALE_DROP_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.232 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_ALE_OVERRUN_DROP_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.233 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_RXOCTETS_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.234 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_TXGOODFRAMES_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.235 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_TXBROADCASTFRAMES_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.236 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_TXMULTICASTFRAMES_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.237 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_TXPAUSEFRAMES_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.238 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_TXDEFERREDFRAMES_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.239 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_TXCOLLISIONFRAMES_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.240 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_TXSINGLECOLLFRAMES_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.241 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_TXMULTCOLLFRAMES_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.242 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_TXEXCESSIVECOLLISIONS_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.243 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_TXLATECOLLISIONS_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.244 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_RXIPGERROR_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.245 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_TXCARRIERSENSEERRORS_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.246 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_TXOCTETS_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.247 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_OCTETFRAMES64_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.248 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_OCTETFRAMES65T127_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.249 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_OCTETFRAMES128T255_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.250 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_OCTETFRAMES256T511_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.251 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_OCTETFRAMES512T1023_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.252 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_OCTETFRAMES1024TUP_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.253 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_NETOCTETS_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.254 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_RX_BOTTOM_OF_FIFO_DROP_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.255 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_PORTMASK_DROP_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.256 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_RX_TOP_OF_FIFO_DROP_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.257 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_ALE_RATE_LIMIT_DROP_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.258 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_ALE_VID_INGRESS_DROP_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.259 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_ALE_DA_EQ_SA_DROP_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.260 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_ALE_BLOCK_DROP_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.261 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_ALE_SECURE_DROP_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.262 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_ALE_AUTH_DROP_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.263 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_ALE_UNKN_UNI_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.264 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_ALE_UNKN_UNI_BCNT_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.265 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_ALE_UNKN_MLT_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.266 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_ALE_UNKN_MLT_BCNT_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.267 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_ALE_UNKN_BRD_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.268 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_ALE_UNKN_BRD_BCNT_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.269 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_ALE_POL_MATCH_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.270 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_ALE_POL_MATCH_RED_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.271 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_ALE_POL_MATCH_YELLOW_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.272 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_ALE_MULT_SA_DROP_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.273 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_ALE_DUAL_VLAN_DROP_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.274 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_ALE_LEN_ERROR_DROP_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.275 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_ALE_IP_NEXT_HDR_DROP_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.276 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_ALE_IPV4_FRAG_DROP_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.277 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_IET_RX_ASSEMBLY_ERROR_REG_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.278 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_IET_RX_ASSEMBLY_OK_REG_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.279 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_IET_RX_SMD_ERROR_REG_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.280 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_IET_RX_FRAG_REG_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.281 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_IET_TX_HOLD_REG_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.282 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_IET_TX_FRAG_REG_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.283 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_TX_MEMORY_PROTECT_ERROR_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.284 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_ENET_PN_TX_PRI_REG_J_K Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.285 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_ENET_PN_TX_PRI_BCNT_REG_J_K Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.286 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_ENET_PN_TX_PRI_DROP_REG_J_K Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.287 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPSW_NU_STAT_ENET_PN_TX_PRI_DROP_BCNT_REG_J_K Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.288 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPTS_IDVER_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.289 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPTS_CONTROL_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.290 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPTS_RFTCLK_SEL_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.291 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPTS_TS_PUSH_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.292 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPTS_TS_LOAD_VAL_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.293 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPTS_TS_LOAD_EN_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.294 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPTS_TS_COMP_VAL_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.295 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPTS_TS_COMP_LEN_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.296 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPTS_INTSTAT_RAW_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.297 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPTS_INTSTAT_MASKED_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.298 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPTS_INT_ENABLE_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.299 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPTS_TS_COMP_NUDGE_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.300 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPTS_EVENT_POP_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.301 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPTS_EVENT_0_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.302 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPTS_EVENT_1_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.303 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPTS_EVENT_2_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.304 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPTS_EVENT_3_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.305 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPTS_TS_LOAD_HIGH_VAL_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.306 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPTS_TS_COMP_HIGH_VAL_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.307 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPTS_TS_ADD_VAL_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.308 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPTS_TS_PPM_LOW_VAL_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.309 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPTS_TS_PPM_HIGH_VAL_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.310 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPTS_TS_NUDGE_VAL_REG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.311 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPTS_TS_CONFIG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.312 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_ALE_MOD_VER Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.313 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_ALE_ALE_STATUS Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.314 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_ALE_ALE_CONTROL Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.315 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_ALE_ALE_CTRL2 Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.316 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_ALE_ALE_PRESCALE Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.317 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_ALE_ALE_AGING_CTRL Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.318 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_ALE_ALE_NXT_HDR Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.319 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_ALE_ALE_TBLCTL Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.320 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_ALE_ALE_TBLW2 Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.321 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_ALE_ALE_TBLW1 Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.322 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_ALE_ALE_TBLW0 Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.323 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_ALE_I0_ALE_PORTCTL0_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.324 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_ALE_ALE_UVLAN_MEMBER Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.325 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_ALE_ALE_UVLAN_URCAST Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.326 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_ALE_ALE_UVLAN_RMCAST Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.327 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_ALE_ALE_UVLAN_UNTAG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.328 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_ALE_ALE_FAST_LUT Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.329 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_ALE_ALE_STAT_DIAG Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.330 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_ALE_ALE_OAM_LB_CTRL Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.331 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_ALE_EGRESSOP Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.332 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_ALE_POLICECFG0 Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.333 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_ALE_POLICECFG1 Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.334 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_ALE_POLICECFG2 Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.335 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_ALE_POLICECFG3 Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.336 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_ALE_POLICECFG4 Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.337 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_ALE_POLICECFG6 Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.338 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_ALE_POLICECFG7 Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.339 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_ALE_POLICETBLCTL Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.340 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_ALE_POLICECONTROL Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.341 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_ALE_POLICETESTCTL Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.342 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_ALE_POLICEHSTAT Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.343 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_ALE_THREADMAPDEF Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.344 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_ALE_THREADMAPCTL Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.345 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_ALE_THREADMAPVAL Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.346 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPTS_TS_GENF_COMP_LOW_REG_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.347 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPTS_TS_GENF_COMP_HIGH_REG_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.348 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPTS_TS_GENF_CONTROL_REG_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.349 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPTS_TS_GENF_LENGTH_REG_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.350 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPTS_TS_GENF_PPM_LOW_REG_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.351 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPTS_TS_GENF_PPM_HIGH_REG_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.352 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPTS_TS_GENF_NUDGE_REG_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.353 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPTS_TS_ESTF_COMP_LOW_REG_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.354 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPTS_TS_ESTF_COMP_HIGH_REG_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.355 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPTS_TS_ESTF_CONTROL_REG_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.356 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPTS_TS_ESTF_LENGTH_REG_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.357 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPTS_TS_ESTF_PPM_LOW_REG_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.358 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPTS_TS_ESTF_PPM_HIGH_REG_J Register
- 14.7.3.1.2.359 CPSW3_CPSW_NU_CPTS_TS_ESTF_NUDGE_REG_J Register
- 14.7.3.2
USB
- 14.7.3.2.1 USB Summaries
- 14.7.3.2.2
USB Registers
- 14.7.3.2.2.1 USB2SS_USB2SS_DEBUG_TRACE_TRACE_CTRL Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.2 USB2SS_USB2SS_DEBUG_TRACE_EP_TRB0_W0_J Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.3 USB2SS_USB2SS_DEBUG_TRACE_EP_TRB0_W1_J Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.4 USB2SS_USB2SS_DEBUG_TRACE_EP_TRB0_W2_J Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.5 USB2SS_USB2SS_DEBUG_TRACE_EP_TRB0_W3_J Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.6 USB2SS_USB2SS_DEBUG_TRACE_EP_TRB1_W0_J Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.7 USB2SS_USB2SS_DEBUG_TRACE_EP_TRB1_W1_J Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.8 USB2SS_USB2SS_DEBUG_TRACE_EP_TRB1_W2_J Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.9 USB2SS_USB2SS_DEBUG_TRACE_EP_TRB1_W3_J Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.10 USB2SS_USB2SS_DEBUG_TRACE_EP_TRB2_W0_J Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.11 USB2SS_USB2SS_DEBUG_TRACE_EP_TRB2_W1_J Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.12 USB2SS_USB2SS_DEBUG_TRACE_EP_TRB2_W2_J Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.13 USB2SS_USB2SS_DEBUG_TRACE_EP_TRB2_W3_J Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.14 USB2SS_USB2SS_DEBUG_TRACE_EP_TRB3_W0_J Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.15 USB2SS_USB2SS_DEBUG_TRACE_EP_TRB3_W1_J Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.16 USB2SS_USB2SS_DEBUG_TRACE_EP_TRB3_W2_J Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.17 USB2SS_USB2SS_DEBUG_TRACE_EP_TRB3_W3_J Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.18 USB2SS_USB2SS_CFG_REVISION Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.19 USB2SS_USB2SS_CFG_OVERCURRENT_CONTROL Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.20 USB2SS_USB2SS_CFG_PHY_CONFIG Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.21 USB2SS_USB2SS_CFG_PHY_TEST Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.22 USB2SS_USB2SS_CFG_CORE_STAT Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.23 USB2SS_USB2SS_CFG_HOST_VBUS_CTRL Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.24 USB2SS_USB2SS_CFG_MODE_CONTROL Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.25 USB2SS_USB2SS_CFG_WAKEUP_CONFIG Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.26 USB2SS_USB2SS_CFG_WAKEUP_STAT Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.27 USB2SS_USB2SS_CFG_OVERRIDE_CONFIG Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.28 USB2SS_USB2SS_CFG_IRQ_MISC_STATUS_RAW Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.29 USB2SS_USB2SS_CFG_IRQ_MISC_STATUS Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.30 USB2SS_USB2SS_CFG_IRQ_MISC_ENABLE_SET Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.31 USB2SS_USB2SS_CFG_IRQ_MISC_ENABLE_CLR Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.32 USB2SS_USB2SS_CFG_IRQ_MISC_EOI Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.33 USB2SS_USB2SS_CFG_INTR_TEST Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.34 USB2SS_USB2SS_CFG_VBUS_FILTER Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.35 USB2SS_USB2SS_CFG_VBUS_STAT Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.36 USB2SS_USB2SS_CFG_DEBUG_CFG Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.37 USB2SS_USB2SS_CFG_DEBUG_DATA Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.38 USB2SS_USB2SS_CFG_HOST_HUB_CTRL Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.39 USB2SS_PHY2_AFE_TX_REG0 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.40 USB2SS_PHY2_AFE_TX_REG1 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.41 USB2SS_PHY2_AFE_TX_REG2 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.42 USB2SS_PHY2_AFE_TX_REG3 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.43 USB2SS_PHY2_AFE_TX_REG4 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.44 USB2SS_PHY2_AFE_TX_REG5 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.45 USB2SS_PHY2_AFE_TX_REG6 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.46 USB2SS_PHY2_AFE_TX_REG7 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.47 USB2SS_PHY2_AFE_TX_REG8 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.48 USB2SS_PHY2_AFE_TX_REG9 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.49 USB2SS_PHY2_AFE_TX_REG10 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.50 USB2SS_PHY2_AFE_TX_REG11 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.51 USB2SS_PHY2_AFE_TX_REG12 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.52 USB2SS_PHY2_AFE_RX_REG0 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.53 USB2SS_PHY2_AFE_RX_REG1 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.54 USB2SS_PHY2_AFE_RX_REG2 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.55 USB2SS_PHY2_AFE_RX_REG3 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.56 USB2SS_PHY2_AFE_RX_REG4 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.57 USB2SS_PHY2_AFE_RX_REG5 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.58 USB2SS_PHY2_AFE_RX_REG6 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.59 USB2SS_PHY2_AFE_TX_REG13 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.60 USB2SS_PHY2_AFE_TX_REG14 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.61 USB2SS_PHY2_AFE_RX_REG7 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.62 USB2SS_PHY2_AFE_RX_REG8 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.63 USB2SS_PHY2_AFE_UNUSED_REG0 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.64 USB2SS_PHY2_AFE_UNUSED_REG1 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.65 USB2SS_PHY2_AFE_BG_REG0 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.66 USB2SS_PHY2_AFE_BG_REG1 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.67 USB2SS_PHY2_AFE_BG_REG2 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.68 USB2SS_PHY2_AFE_BG_REG3 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.69 USB2SS_PHY2_AFE_CALIB_REG0 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.70 USB2SS_PHY2_AFE_BC_REG0 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.71 USB2SS_PHY2_AFE_BC_REG1 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.72 USB2SS_PHY2_AFE_BC_REG2 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.73 USB2SS_PHY2_AFE_BC_REG3 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.74 USB2SS_PHY2_AFE_BC_REG4 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.75 USB2SS_PHY2_AFE_BC_REG5 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.76 USB2SS_PHY2_AFE_BC_REG6 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.77 USB2SS_PHY2_AFE_PLL_REG0 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.78 USB2SS_PHY2_AFE_PLL_REG1 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.79 USB2SS_PHY2_AFE_PLL_REG2 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.80 USB2SS_PHY2_AFE_PLL_REG3 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.81 USB2SS_PHY2_AFE_PLL_REG4 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.82 USB2SS_PHY2_AFE_PLL_REG5 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.83 USB2SS_PHY2_AFE_BG_REG4 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.84 USB2SS_PHY2_AFE_CALIB_REG1 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.85 USB2SS_PHY2_AFE_BC_REG7 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.86 USB2SS_PHY2_AFE_PLL_REG6 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.87 USB2SS_PHY2_AFE_UNUSED_REG2 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.88 USB2SS_PHY2_AFE_UNUSED_REG3 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.89 USB2SS_PHY2_PLL_REG0 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.90 USB2SS_PHY2_PLL_REG1 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.91 USB2SS_PHY2_PLL_REG2 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.92 USB2SS_PHY2_PLL_REG3 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.93 USB2SS_PHY2_PLL_REG4 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.94 USB2SS_PHY2_PLL_REG5 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.95 USB2SS_PHY2_PLL_REG6 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.96 USB2SS_PHY2_PLL_REG7 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.97 USB2SS_PHY2_PLL_REG8 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.98 USB2SS_PHY2_PLL_REG9 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.99 USB2SS_PHY2_PLL_REG10 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.100 USB2SS_PHY2_PLL_REG11 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.101 USB2SS_PHY2_PLL_REG12 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.102 USB2SS_PHY2_PLL_REG13 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.103 USB2SS_PHY2_PLL_REG14 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.104 USB2SS_PHY2_PLL_UNUSED_REG0 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.105 USB2SS_PHY2_PLL_UNUSED_REG1 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.106 USB2SS_PHY2_PLL_REG15 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.107 USB2SS_PHY2_PLL_REG16 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.108 USB2SS_PHY2_PLL_UNUSED_REG2 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.109 USB2SS_PHY2_CALIB_REG0 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.110 USB2SS_PHY2_CALIB_REG1 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.111 USB2SS_PHY2_BC_REG0 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.112 USB2SS_PHY2_BC_REG1 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.113 USB2SS_PHY2_BC_REG2 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.114 USB2SS_PHY2_BC_REG3 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.115 USB2SS_PHY2_BC_REG4 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.116 USB2SS_PHY2_BC_REG5 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.117 USB2SS_PHY2_BC_REG6 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.118 USB2SS_PHY2_BC_REG7 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.119 USB2SS_PHY2_TED_REG0 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.120 USB2SS_PHY2_TED_REG1 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.121 USB2SS_PHY2_TED_REG2 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.122 USB2SS_PHY2_CALIB_REG2 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.123 USB2SS_PHY2_CALIB_REG3 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.124 USB2SS_PHY2_BC_REG8 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.125 USB2SS_PHY2_BC_REG9 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.126 USB2SS_PHY2_BC_REG10 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.127 USB2SS_PHY2_BC_REG11 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.128 USB2SS_PHY2_BC_REG12 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.129 USB2SS_PHY2_TED_REG3 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.130 USB2SS_PHY2_TED_REG4 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.131 USB2SS_PHY2_DIG_UNUSED_REG0 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.132 USB2SS_PHY2_DIG_UNUSED_REG1 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.133 USB2SS_PHY2_DIG_UNUSED_REG2 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.134 USB2SS_PHY2_DIG_UNUSED_REG3 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.135 USB2SS_PHY2_INTERRUPT_REG1 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.136 USB2SS_PHY2_INTERRUPT_REG2 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.137 USB2SS_PHY2_RX_REG0 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.138 USB2SS_PHY2_RX_REG1 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.139 USB2SS_PHY2_TX_REG0 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.140 USB2SS_PHY2_TX_REG1 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.141 USB2SS_PHY2_CDR_REG0 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.142 USB2SS_PHY2_CDR_REG1 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.143 USB2SS_PHY2_CDR_REG2 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.144 USB2SS_PHY2_CDR_REG3 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.145 USB2SS_PHY2_CDR_REG4 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.146 USB2SS_PHY2_CDR_REG5 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.147 USB2SS_PHY2_CDR_REG6 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.148 USB2SS_PHY2_CDR_REG7 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.149 USB2SS_PHY2_CDR_REG8 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.150 USB2SS_PHY2_RX_REG2 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.151 USB2SS_PHY2_RX_REG3 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.152 USB2SS_PHY2_RX_REG4 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.153 USB2SS_PHY2_RX_REG5 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.154 USB2SS_PHY2_RX_REG6 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.155 USB2SS_PHY2_RX_REG7 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.156 USB2SS_PHY2_TX_REG2 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.157 USB2SS_PHY2_TX_REG3 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.158 USB2SS_PHY2_TX_REG4 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.159 USB2SS_PHY2_CDR_REG9 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.160 USB2SS_PHY2_CDR_REG10 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.161 USB2SS_PHY2_CDR_REG11 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.162 USB2SS_PHY2_CDR_RE12 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.163 USB2SS_PHY2_DIG_TXRX_UNUSED_REG0 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.164 USB2SS_PHY2_DIG_TXRX_UNUSED_REG1 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.165 USB2SS_PHY2_DIG_TXRX_UNUSED_REG2 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.166 USB2SS_PHY2_DIG_TXRX_UNUSED_REG3 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.167 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG0 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.168 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG1 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.169 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG2 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.170 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG3 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.171 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG4 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.172 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG5 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.173 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG6 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.174 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG7 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.175 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG8 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.176 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG9 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.177 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG10 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.178 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG11 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.179 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG12 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.180 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG13 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.181 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG14 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.182 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG15 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.183 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG16 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.184 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG17 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.185 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG18 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.186 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG19 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.187 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG20 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.188 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG21 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.189 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG22 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.190 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG23 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.191 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG24 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.192 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG25 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.193 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG26 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.194 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG27 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.195 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG28 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.196 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG29 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.197 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG30 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.198 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_UNUSED_REG0 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.199 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_UNUSED_REG1 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.200 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_UNUSED_REG2 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.201 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_UNUSED_REG3 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.202 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG31 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.203 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG32 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.204 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG33 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.205 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG34 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.206 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG35 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.207 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG36 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.208 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG37 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.209 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG38 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.210 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG39 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.211 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG40 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.212 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG41 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.213 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG42 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.214 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG43 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.215 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG44 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.216 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG45 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.217 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG46 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.218 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG47 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.219 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG48 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.220 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG49 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.221 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG50 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.222 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG51 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.223 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG52 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.224 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG53 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.225 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG54 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.226 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG55 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.227 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG56 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.228 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG57 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.229 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG58 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.230 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_REG59 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.231 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_UNUSED_REG6 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.232 USB2SS_PHY2_UTMI_UNUSED_REG7 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.233 ECC_AGGR_REV Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.234 ECC_AGGR_VECTOR Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.235 ECC_AGGR_STAT Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.236 ECC_AGGR_RESERVED_SVBUS_J Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.237 ECC_AGGR_SEC_EOI_REG Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.238 ECC_AGGR_SEC_STATUS_REG0 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.239 ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.240 ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.241 ECC_AGGR_DED_EOI_REG Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.242 ECC_AGGR_DED_STATUS_REG0 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.243 ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.244 ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.245 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_SET Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.246 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_CLR Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.247 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_STATUS_SET Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.248 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_STATUS_CLR Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.249 USB2SS_CAP_CAPLENGTH Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.250 USB2SS_CAP_HCSPARAMS1 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.251 USB2SS_CAP_HCSPARAMS2 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.252 USB2SS_CAP_HCSPARAMS3 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.253 USB2SS_CAP_HCCPARAMS1 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.254 USB2SS_CAP_DBOFF Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.255 USB2SS_CAP_RTSOFF Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.256 USB2SS_CAP_HCCPARAMS2 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.257 USB2SS_OPER_USBCMD Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.258 USB2SS_OPER_USBSTS Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.259 USB2SS_OPER_PAGESIZE Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.260 USB2SS_OPER_DNCTRL Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.261 USB2SS_OPER_CRCR_LO Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.262 USB2SS_OPER_CRCR_HI Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.263 USB2SS_OPER_DCBAAP_LO Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.264 USB2SS_OPER_DCBAAP_HI Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.265 USB2SS_OPER_CONFIG Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.266 USB2SS_PORT_XHCI_PORT_20_PORTSC_20 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.267 USB2SS_PORT_XHCI_PORT_20_PORTPMSC_20 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.268 USB2SS_PORT_XHCI_PORT_20_PORTLI_20 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.269 USB2SS_PORT_XHCI_PORT_20_PORTHLPMC_20 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.270 USB2SS_PORT_XHCI_PORT_30_PORTPMSC_30 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.271 USB2SS_PORT_XHCI_PORT_30_PORTLI_30 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.272 USB2SS_PORT_XHCI_PORT_30_PORTHLPMC_30 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.273 USB2SS_RUNTIME_MFINDEX Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.274 USB2SS_RUNTIME_RSVDZ Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.275 USB2SS_INTR_XHCI_INTR_IMAN_J Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.276 USB2SS_INTR_XHCI_INTR_IMOD_J Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.277 USB2SS_INTR_XHCI_INTR_ERSTSZ_J Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.278 USB2SS_INTR_XHCI_INTR_RSVDP_J Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.279 USB2SS_INTR_XHCI_INTR_ERSTBA_LO_J Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.280 USB2SS_INTR_XHCI_INTR_ERSTBA_HI_J Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.281 USB2SS_INTR_XHCI_INTR_ERDP_LO_J Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.282 USB2SS_INTR_XHCI_INTR_ERDP_HI_J Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.283 USB2SS_DBARR_XHCI_DB_DB_J Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.284 USB2SS_EXTCAP_USBLEGSUP Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.285 USB2SS_EXTCAP_USBLEGCTLSTS Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.286 USB2SS_SUPPRTCAP2_SUPTPRT2_DW0 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.287 USB2SS_SUPPRTCAP2_SUPTPRT2_DW1 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.288 USB2SS_SUPPRTCAP2_SUPTPRT2_DW2 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.289 USB2SS_SUPPRTCAP2_SUPTPRT2_DW3 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.290 USB2SS_SUPPRTCAP3_SUPTPRT3_DW0 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.291 USB2SS_SUPPRTCAP3_SUPTPRT3_DW1 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.292 USB2SS_SUPPRTCAP3_SUPTPRT3_DW2 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.293 USB2SS_SUPPRTCAP3_SUPTPRT3_DW3 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.294 USB2SS_GBL_GSBUSCFG0 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.295 USB2SS_GBL_GSBUSCFG1 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.296 USB2SS_GBL_GTXTHRCFG Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.297 USB2SS_GBL_GRXTHRCFG Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.298 USB2SS_GBL_GCTL Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.299 USB2SS_GBL_GPMSTS Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.300 USB2SS_GBL_GSTS Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.301 USB2SS_GBL_GUCTL1 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.302 USB2SS_GBL_GSNPSID Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.303 USB2SS_GBL_GGPIO Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.304 USB2SS_GBL_GUID Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.305 USB2SS_GBL_GUCTL Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.306 USB2SS_GBL_GBUSERRADDRLO Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.307 USB2SS_GBL_GBUSERRADDRHI Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.308 USB2SS_GBL_GPRTBIMAPLO Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.309 USB2SS_GBL_GPRTBIMAPHI Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.310 USB2SS_GBL_GHWPARAMS0 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.311 USB2SS_GBL_GHWPARAMS1 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.312 USB2SS_GBL_GHWPARAMS2 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.313 USB2SS_GBL_GHWPARAMS3 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.314 USB2SS_GBL_GHWPARAMS4 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.315 USB2SS_GBL_GHWPARAMS5 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.316 USB2SS_GBL_GHWPARAMS6 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.317 USB2SS_GBL_GHWPARAMS7 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.318 USB2SS_GBL_GDBGFIFOSPACE Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.319 USB2SS_GBL_GDBGLTSSM Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.320 USB2SS_GBL_GDBGLNMCC Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.321 USB2SS_GBL_GDBGBMU Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.322 USB2SS_GBL_GDBGLSPMUX_HST Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.323 USB2SS_GBL_GDBGLSP Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.324 USB2SS_GBL_GDBGEPINFO0 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.325 USB2SS_GBL_GDBGEPINFO1 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.326 USB2SS_GBL_GPRTBIMAP_HSLO Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.327 USB2SS_GBL_GPRTBIMAP_HSHI Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.328 USB2SS_GBL_GPRTBIMAP_FSLO Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.329 USB2SS_GBL_GPRTBIMAP_FSHI Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.330 USB2SS_GBL_RESERVED_94 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.331 USB2SS_GBL_RESERVED_98 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.332 USB2SS_GBL_GUCTL2 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.333 USB2SS_GBL_GHWPARAMS8 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.334 USB2SS_GBL_GUCTL3 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.335 USB2SS_GBL_GTXFIFOPRIDEV Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.336 USB2SS_GBL_GTXFIFOPRIHST Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.337 USB2SS_GBL_GRXFIFOPRIHST Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.338 USB2SS_GBL_GDMAHLRATIO Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.339 USB2SS_GBL_GFLADJ Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.340 USB2SS_GBL_GPHY_GUSB2PHYCFG Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.341 USB2SS_GBL_GI2C_GUSB2I2CCTL Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.342 USB2SS_GBL_GULPI_GUSB2PHYACC_ULPI Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.343 USB2SS_GBL_GPIPE_GUSB3PIPECTL Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.344 USB2SS_GBL_GTXFIFO_GTXFIFOSIZ0 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.345 USB2SS_GBL_GTXFIFO_GTXFIFOSIZ1 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.346 USB2SS_GBL_GTXFIFO_GTXFIFOSIZ2 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.347 USB2SS_GBL_GTXFIFO_GTXFIFOSIZ3 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.348 USB2SS_GBL_GTXFIFO_GTXFIFOSIZ4 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.349 USB2SS_GBL_GTXFIFO_GTXFIFOSIZ5 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.350 USB2SS_GBL_GTXFIFO_GTXFIFOSIZ6 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.351 USB2SS_GBL_GTXFIFO_GTXFIFOSIZ7 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.352 USB2SS_GBL_GTXFIFO_GTXFIFOSIZ8 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.353 USB2SS_GBL_GTXFIFO_GTXFIFOSIZ9 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.354 USB2SS_GBL_GTXFIFO_GTXFIFOSIZ10 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.355 USB2SS_GBL_GTXFIFO_GTXFIFOSIZ11 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.356 USB2SS_GBL_GTXFIFO_GTXFIFOSIZ12 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.357 USB2SS_GBL_GTXFIFO_GTXFIFOSIZ13 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.358 USB2SS_GBL_GTXFIFO_GTXFIFOSIZ14 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.359 USB2SS_GBL_GTXFIFO_GTXFIFOSIZ15 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.360 USB2SS_GBL_GRXFIFO_GRXFIFOSIZ0 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.361 USB2SS_GBL_GRXFIFO_GRXFIFOSIZ1 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.362 USB2SS_GBL_GRXFIFO_GRXFIFOSIZ2 Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.363 USB2SS_GBL_GEVNT_GEVNTADRLO_J Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.364 USB2SS_GBL_GEVNT_GEVNTADRHI_J Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.365 USB2SS_GBL_GEVNT_GEVNTSIZ_J Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.366 USB2SS_GBL_GEVNT_GEVNTCOUNT_J Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.367 USB2SS_GBL_GRHB_GUSB2RHBCTL Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.368 USB2SS_DEV_DCFG Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.369 USB2SS_DEV_DCTL Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.370 USB2SS_DEV_DEVTEN Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.371 USB2SS_DEV_DSTS Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.372 USB2SS_DEV_DGCMDPAR Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.373 USB2SS_DEV_DGCMD Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.374 USB2SS_DEV_DALEPENA Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.375 USB2SS_DEV_DEV_RESERVED_RSVD_J Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.376 USB2SS_DEV_DEPCMDPAR_EP_DEPCMDPAR2_J Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.377 USB2SS_DEV_DEPCMDPAR_EP_DEPCMDPAR1_J Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.378 USB2SS_DEV_DEPCMDPAR_EP_DEPCMDPAR0_J Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.379 USB2SS_DEV_DEPCMDPAR_EP_DEPCMD_J Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.380 USB2SS_DEV_DEV_INTR_DEV_IMOD_J Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.381 USB2SS_LINK_LINK_LU1LFPSRXTIM Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.382 USB2SS_LINK_LINK_LINK_SETTINGS Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.383 USB2SS_LINK_LINK_LLUCTL Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.384 USB2SS_LINK_LINK_LPTMDPDELAY Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.385 USB2SS_DEBUG_DEBUG_U3RHBDBG Register
- 14.7.3.2.2.386 USB2SS_DEBUG_RAM0_RAM0_J Register
- 14.7.3.1
CPSW
- 14.7.4
Memory Interfaces Registers
- 14.7.4.1
FSS0
- 14.7.4.1.1 FSS0 Summaries
- 14.7.4.1.2
FSS0 Registers
- 14.7.4.1.2.1 ECC_AGGR_REV Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.2 ECC_AGGR_VECTOR Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.3 ECC_AGGR_STAT Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.4 ECC_AGGR_RESERVED_SVBUS_J Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.5 ECC_AGGR_SEC_EOI_REG Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.6 ECC_AGGR_SEC_STATUS_REG0 Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.7 ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.8 ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.9 ECC_AGGR_DED_EOI_REG Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.10 ECC_AGGR_DED_STATUS_REG0 Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.11 ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.12 ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.13 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_SET Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.14 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_CLR Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.15 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_STATUS_SET Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.16 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_STATUS_CLR Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.17 ECC_AGGR_REV Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.18 ECC_AGGR_VECTOR Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.19 ECC_AGGR_STAT Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.20 ECC_AGGR_RESERVED_SVBUS_J Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.21 ECC_AGGR_SEC_EOI_REG Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.22 ECC_AGGR_SEC_STATUS_REG0 Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.23 ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.24 ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.25 ECC_AGGR_DED_EOI_REG Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.26 ECC_AGGR_DED_STATUS_REG0 Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.27 ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.28 ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.29 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_SET Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.30 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_CLR Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.31 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_STATUS_SET Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.32 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_STATUS_CLR Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.33 FSS_GENREGS_REVISION Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.34 FSS0_FSAS_GENREGS_REVISION Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.35 FSS0_FSAS_GENREGS_SYSCONFIG Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.36 FSS0_FSAS_GENREGS_DP_ERR_INJ_CTRL Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.37 FSS0_FSAS_GENREGS_IRQ_EOI Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.38 FSS0_FSAS_GENREGS_IRQ_STATUS_RAW Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.39 FSS0_FSAS_GENREGS_IRQ_STATUS Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.40 FSS0_FSAS_GENREGS_IRQ_ENABLE_SET Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.41 FSS0_FSAS_GENREGS_IRQ_ENABLE_CLR Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.42 FSS0_FSAS_GENREGS_ECC_REGCTRL_ECC_RGSTRT_J Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.43 FSS0_FSAS_GENREGS_ECC_REGCTRL_ECC_RGSIZ_J Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.44 FSS0_FSAS_GENREGS_ERR_ECC_BLOCK_ADR Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.45 FSS0_FSAS_GENREGS_ERR_ECC_TYPE Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.46 FSS0_FSAS_GENREGS_ERR_WRT_TYPE Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.47 FSAS_OTFA_REGS_REVID Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.48 FSAS_OTFA_REGS_SCFG Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.49 FSAS_OTFA_REGS_ISR Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.50 FSAS_OTFA_REGS_IS Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.51 FSAS_OTFA_REGS_IES Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.52 FSAS_OTFA_REGS_IEC Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.53 FSAS_OTFA_REGS_CCFG Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.54 FSAS_OTFA_REGS_CSTATUS Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.55 FSAS_OTFA_REGS_IRQADDINFO0 Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.56 FSAS_OTFA_REGS_IRQADDINFO1 Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.57 FSAS_OTFA_REGS_MACCACHEINFO Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.58 FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RMWRMCNT Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.59 FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RG_RGCFG_J Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.60 FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RG_RGMACST_J Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.61 FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RG_RGST_J Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.62 FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RG_RGSI_J Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.63 FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RG_RKEYE_J_K Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.64 FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RG_RKEYEP_J_K Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.65 FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RG_RKEYA_J_K Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.66 FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RG_RKEYAP_J_K Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.67 FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RG_RIV_J_K Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.68 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_CONFIG_REG Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.69 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_DEV_INSTR_RD_CONFIG_REG Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.70 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_DEV_INSTR_WR_CONFIG_REG Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.71 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_DEV_DELAY_REG Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.72 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_RD_DATA_CAPTURE_REG Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.73 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_DEV_SIZE_CONFIG_REG Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.74 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_SRAM_PARTITION_CFG_REG Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.75 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_IND_AHB_ADDR_TRIGGER_REG Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.76 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_DMA_PERIPH_CONFIG_REG Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.77 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_REMAP_ADDR_REG Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.78 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_MODE_BIT_CONFIG_REG Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.79 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_SRAM_FILL_REG Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.80 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_TX_THRESH_REG Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.81 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_RX_THRESH_REG Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.82 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_WRITE_COMPLETION_CTRL_REG Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.83 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_NO_OF_POLLS_BEF_EXP_REG Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.84 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_IRQ_STATUS_REG Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.85 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_IRQ_MASK_REG Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.86 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_LOWER_WR_PROT_REG Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.87 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_UPPER_WR_PROT_REG Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.88 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_WR_PROT_CTRL_REG Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.89 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_INDIRECT_READ_XFER_CTRL_REG Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.90 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_INDIRECT_READ_XFER_WATERMARK_REG Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.91 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_INDIRECT_READ_XFER_START_REG Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.92 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_INDIRECT_READ_XFER_NUM_BYTES_REG Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.93 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_INDIRECT_WRITE_XFER_CTRL_REG Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.94 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_INDIRECT_WRITE_XFER_WATERMARK_REG Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.95 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_INDIRECT_WRITE_XFER_START_REG Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.96 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_INDIRECT_WRITE_XFER_NUM_BYTES_REG Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.97 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_INDIRECT_TRIGGER_ADDR_RANGE_REG Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.98 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_FLASH_COMMAND_CTRL_MEM_REG Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.99 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_FLASH_CMD_CTRL_REG Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.100 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_FLASH_CMD_ADDR_REG Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.101 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_FLASH_RD_DATA_LOWER_REG Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.102 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_FLASH_RD_DATA_UPPER_REG Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.103 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_FLASH_WR_DATA_LOWER_REG Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.104 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_FLASH_WR_DATA_UPPER_REG Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.105 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_POLLING_FLASH_STATUS_REG Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.106 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_PHY_CONFIGURATION_REG Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.107 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_PHY_MASTER_CONTROL_REG Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.108 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_DLL_OBSERVABLE_LOWER_REG Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.109 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_DLL_OBSERVABLE_UPPER_REG Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.110 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_OPCODE_EXT_LOWER_REG Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.111 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_OPCODE_EXT_UPPER_REG Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.112 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_MODULE_ID_REG Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.113 OSPI_CFG_PID Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.114 OSPI_CFG_CTRL Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.115 OSPI_CFG_STAT Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.116 OSPI_CFG_EOI Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.117 FSS0_FOTA_GENREGS_FOTA_INIT Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.118 FSS0_FOTA_GENREGS_FOTA_CTRL Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.119 FSS0_FOTA_GENREGS_FOTA_ERR_INFO Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.120 FSS0_FOTA_GENREGS_FOTA_GP0 Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.121 FSS0_FOTA_GENREGS_FOTA_GP1 Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.122 FSS0_FOTA_GENREGS_FOTA_ADDR Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.123 FSS0_FOTA_GENREGS_FOTA_CNT Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.124 FSS0_FOTA_GENREGS_STS_IRQ_EOI Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.125 FSS0_FOTA_GENREGS_STS_IRQ_STATUS_RAW Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.126 FSS0_FOTA_GENREGS_STS_IRQ_STATUS Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.127 FSS0_FOTA_GENREGS_STS_IRQ_ENABLE_SET Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.128 FSS0_FOTA_GENREGS_STS_IRQ_ENABLE_CLR Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.129 FSS0_FOTA_GENREGS_ERR_STS_IRQ_EOI Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.130 FSS0_FOTA_GENREGS_ERR_STS_IRQ_STATUS_RAW Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.131 FSS0_FOTA_GENREGS_ERR_STS_IRQ_STATUS Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.132 FSS0_FOTA_GENREGS_ERR_STS_IRQ_ENABLE_SET Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.133 FSS0_FOTA_GENREGS_ERR_STS_IRQ_ENABLE_CLR Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.134 FSS0_PDMEM_GENREGS_LOC_J Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.135 FSS0_IMEM_GENREGS_LOC_J Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.136 FSS0_WBUF_GENREGS_LOC_J Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.137 DAT_REG1_HPB_DATA_MEM_J Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.138 DAT_REG0_HPB_DATA_MEM_J Register
- 14.7.4.1.2.139 DAT_REG3_HPB_DATA_MEM_J Register
- 14.7.4.2
FSS1
- 14.7.4.2.1 FSS1 Summaries
- 14.7.4.2.2
FSS1 Registers
- 14.7.4.2.2.1 FSS_GENREGS_REVISION Register
- 14.7.4.2.2.2 FSS_GENREGS_SYSCONFIG Register
- 14.7.4.2.2.3 FSS_GENREGS_IRQ_EOI Register
- 14.7.4.2.2.4 FSS_GENREGS_IRQ_STATUS_RAW Register
- 14.7.4.2.2.5 FSS_GENREGS_IRQ_STATUS Register
- 14.7.4.2.2.6 FSS_GENREGS_IRQ_ENABLE_SET Register
- 14.7.4.2.2.7 FSS_GENREGS_IRQ_ENABLE_CLR Register
- 14.7.4.2.2.8 FSS_GENREGS_ECC_REGCTRL_ECC_RGSTRT_J Register
- 14.7.4.2.2.9 FSS_GENREGS_ECC_REGCTRL_ECC_RGSIZ_J Register
- 14.7.4.2.2.10 FSS_GENREGS_ERR_ECC_BLOCK_ADR Register
- 14.7.4.2.2.11 FSS_GENREGS_ERR_ECC_TYPE Register
- 14.7.4.2.2.12 FSS_GENREGS_ERR_WRT_TYPE Register
- 14.7.4.3
OSPI1
- 14.7.4.3.1 OSPI1 Summaries
- 14.7.4.3.2
OSPI1 Registers
- 14.7.4.3.2.1 ECC_AGGR_REV Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.2 ECC_AGGR_VECTOR Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.3 ECC_AGGR_STAT Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.4 ECC_AGGR_RESERVED_SVBUS_J Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.5 ECC_AGGR_SEC_EOI_REG Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.6 ECC_AGGR_SEC_STATUS_REG0 Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.7 ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.8 ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.9 ECC_AGGR_DED_EOI_REG Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.10 ECC_AGGR_DED_STATUS_REG0 Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.11 ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.12 ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.13 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_SET Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.14 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_CLR Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.15 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_STATUS_SET Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.16 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_STATUS_CLR Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.17 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_CONFIG_REG Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.18 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_DEV_INSTR_RD_CONFIG_REG Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.19 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_DEV_INSTR_WR_CONFIG_REG Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.20 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_DEV_DELAY_REG Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.21 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_RD_DATA_CAPTURE_REG Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.22 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_DEV_SIZE_CONFIG_REG Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.23 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_SRAM_PARTITION_CFG_REG Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.24 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_IND_AHB_ADDR_TRIGGER_REG Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.25 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_DMA_PERIPH_CONFIG_REG Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.26 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_REMAP_ADDR_REG Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.27 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_MODE_BIT_CONFIG_REG Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.28 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_SRAM_FILL_REG Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.29 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_TX_THRESH_REG Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.30 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_RX_THRESH_REG Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.31 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_WRITE_COMPLETION_CTRL_REG Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.32 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_NO_OF_POLLS_BEF_EXP_REG Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.33 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_IRQ_STATUS_REG Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.34 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_IRQ_MASK_REG Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.35 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_LOWER_WR_PROT_REG Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.36 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_UPPER_WR_PROT_REG Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.37 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_WR_PROT_CTRL_REG Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.38 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_INDIRECT_READ_XFER_CTRL_REG Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.39 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_INDIRECT_READ_XFER_WATERMARK_REG Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.40 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_INDIRECT_READ_XFER_START_REG Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.41 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_INDIRECT_READ_XFER_NUM_BYTES_REG Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.42 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_INDIRECT_WRITE_XFER_CTRL_REG Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.43 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_INDIRECT_WRITE_XFER_WATERMARK_REG Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.44 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_INDIRECT_WRITE_XFER_START_REG Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.45 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_INDIRECT_WRITE_XFER_NUM_BYTES_REG Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.46 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_INDIRECT_TRIGGER_ADDR_RANGE_REG Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.47 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_FLASH_COMMAND_CTRL_MEM_REG Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.48 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_FLASH_CMD_CTRL_REG Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.49 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_FLASH_CMD_ADDR_REG Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.50 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_FLASH_RD_DATA_LOWER_REG Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.51 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_FLASH_RD_DATA_UPPER_REG Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.52 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_FLASH_WR_DATA_LOWER_REG Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.53 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_FLASH_WR_DATA_UPPER_REG Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.54 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_POLLING_FLASH_STATUS_REG Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.55 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_PHY_CONFIGURATION_REG Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.56 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_PHY_MASTER_CONTROL_REG Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.57 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_DLL_OBSERVABLE_LOWER_REG Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.58 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_DLL_OBSERVABLE_UPPER_REG Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.59 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_OPCODE_EXT_LOWER_REG Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.60 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_OPCODE_EXT_UPPER_REG Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.61 OSPI_FLASH_CFG_MODULE_ID_REG Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.62 OSPI_CFG_PID Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.63 OSPI_CFG_CTRL Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.64 OSPI_CFG_STAT Register
- 14.7.4.3.2.65 OSPI_CFG_EOI Register
- 14.7.4.4
FSS_HYPERBUS1P0_0
- 14.7.4.4.1 FSS_HYPERBUS1P0_0 Summaries
- 14.7.4.4.2
FSS_HYPERBUS1P0_0 Registers
- 14.7.4.4.2.1 ECC_AGGR_REV Register
- 14.7.4.4.2.2 ECC_AGGR_VECTOR Register
- 14.7.4.4.2.3 ECC_AGGR_STAT Register
- 14.7.4.4.2.4 ECC_AGGR_RESERVED_SVBUS_J Register
- 14.7.4.4.2.5 ECC_AGGR_SEC_EOI_REG Register
- 14.7.4.4.2.6 ECC_AGGR_SEC_STATUS_REG0 Register
- 14.7.4.4.2.7 ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Register
- 14.7.4.4.2.8 ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Register
- 14.7.4.4.2.9 ECC_AGGR_DED_EOI_REG Register
- 14.7.4.4.2.10 ECC_AGGR_DED_STATUS_REG0 Register
- 14.7.4.4.2.11 ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Register
- 14.7.4.4.2.12 ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Register
- 14.7.4.4.2.13 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_SET Register
- 14.7.4.4.2.14 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_CLR Register
- 14.7.4.4.2.15 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_STATUS_SET Register
- 14.7.4.4.2.16 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_STATUS_CLR Register
- 14.7.4.4.2.17 HYPERBUS_SYSCFG_REVISION_REG Register
- 14.7.4.4.2.18 HYPERBUS_SYSCFG_DLL_STAT_REG Register
- 14.7.4.4.2.19 HYPERBUS_SYSCFG_RAM_STAT_REG Register
- 14.7.4.4.2.20 HYPERBUS_CORE_CSR Register
- 14.7.4.4.2.21 HYPERBUS_CORE_IER Register
- 14.7.4.4.2.22 HYPERBUS_CORE_ISR Register
- 14.7.4.4.2.23 HYPERBUS_CORE_MBAR_J Register
- 14.7.4.4.2.24 HYPERBUS_CORE_MCR_J Register
- 14.7.4.4.2.25 HYPERBUS_CORE_MTR_J Register
- 14.7.4.4.2.26 HYPERBUS_CORE_GPOR Register
- 14.7.4.4.2.27 HYPERBUS_CORE_WPR Register
- 14.7.4.4.2.28 HYPERBUS_CORE_LBR Register
- 14.7.4.5
FSS_FSAS_0
- 14.7.4.5.1 FSS_FSAS_0 Summaries
- 14.7.4.5.2
FSS_FSAS_0 Registers
- 14.7.4.5.2.1 FSS_FSAS_GENREGS_SYSCONFIG Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.2 FSS_FSAS_GENREGS_FRAG_ADR Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.3 FSS_FSAS_GENREGS_FRAG_CTL Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.4 FSS_FSAS_GENREGS_IRQ_EOI Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.5 FSS_FSAS_GENREGS_IRQ_STATUS_RAW Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.6 FSS_FSAS_GENREGS_IRQ_STATUS Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.7 FSS_FSAS_GENREGS_IRQ_ENABLE_SET Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.8 FSS_FSAS_GENREGS_IRQ_ENABLE_CLR Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.9 FSS_FSAS_GENREGS_ECC_REGCTRL_ECC_RGSTRT_J Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.10 FSS_FSAS_GENREGS_ECC_REGCTRL_ECC_RGSIZ_J Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.11 FSS_FSAS_GENREGS_ERR_ECC_BLOCK_ADR Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.12 FSS_FSAS_GENREGS_ERR_ECC_TYPE Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.13 FSS_FSAS_GENREGS_ERR_WRT_TYPE Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.14 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_REVID Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.15 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_SCFG Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.16 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_ISR Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.17 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_IS Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.18 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_IES Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.19 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_IEC Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.20 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_CCFG Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.21 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_CSTATUS Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.22 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RGCFG0 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.23 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RGMACST0 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.24 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RGST0 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.25 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RGSI0 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.26 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYE00 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.27 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYE01 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.28 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYE02 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.29 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYE03 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.30 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYE04 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.31 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYE05 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.32 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYE06 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.33 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYE07 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.34 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYEP00 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.35 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYEP01 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.36 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYEP02 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.37 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYEP03 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.38 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYEP04 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.39 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYEP05 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.40 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYEP06 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.41 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYEP07 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.42 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYA00 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.43 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYA01 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.44 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYA02 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.45 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYA03 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.46 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYAP00 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.47 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYAP01 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.48 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYAP02 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.49 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYAP03 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.50 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RIV00 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.51 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RIV01 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.52 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RIV02 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.53 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RIV03 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.54 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RGCFG1 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.55 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RGMACST1 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.56 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RGST1 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.57 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RGSI1 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.58 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYE10 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.59 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYE11 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.60 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYE12 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.61 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYE13 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.62 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYE14 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.63 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYE15 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.64 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYE16 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.65 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYE17 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.66 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYEP10 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.67 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYEP11 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.68 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYEP12 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.69 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYEP13 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.70 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYEP14 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.71 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYEP15 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.72 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYEP16 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.73 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYEP17 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.74 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYA10 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.75 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYA11 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.76 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYA12 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.77 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYA13 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.78 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYAP10 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.79 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYAP11 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.80 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYAP12 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.81 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYAP13 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.82 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RIV10 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.83 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RIV11 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.84 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RIV12 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.85 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RIV13 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.86 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RGCFG2 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.87 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RGMACST2 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.88 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RGST2 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.89 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RGSI2 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.90 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYE20 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.91 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYE21 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.92 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYE22 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.93 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYE23 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.94 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYE24 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.95 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYE25 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.96 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYE26 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.97 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYE27 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.98 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYEP20 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.99 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYEP21 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.100 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYEP22 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.101 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYEP23 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.102 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYEP24 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.103 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYEP25 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.104 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYEP26 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.105 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYEP27 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.106 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYA20 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.107 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYA21 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.108 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYA22 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.109 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYA23 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.110 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYAP20 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.111 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYAP21 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.112 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYAP22 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.113 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYAP23 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.114 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RIV20 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.115 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RIV21 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.116 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RIV22 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.117 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RIV23 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.118 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RGCFG3 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.119 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RGMACST3 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.120 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RGST3 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.121 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RGSI3 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.122 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYE30 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.123 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYE31 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.124 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYE32 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.125 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYE33 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.126 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYE34 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.127 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYE35 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.128 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYE36 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.129 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYE37 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.130 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYEP30 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.131 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYEP31 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.132 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYEP32 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.133 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYEP33 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.134 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYEP34 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.135 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYEP35 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.136 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYEP36 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.137 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYEP37 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.138 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYA30 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.139 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYA31 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.140 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYA32 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.141 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYA33 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.142 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYAP30 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.143 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYAP31 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.144 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYAP32 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.145 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RKEYAP33 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.146 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RIV30 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.147 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RIV31 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.148 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RIV32 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.149 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RIV33 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.150 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_IRQADDINFO0 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.151 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_IRQADDINFO1 Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.152 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_MACCACHEINFO Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.153 FSS_FSAS_OTFA_REGS_RMWRMCNT Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.154 FSS_DAT_REG1_HPB_DATA_MEM_J Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.155 FSS_DAT_REG0_HPB_DATA_MEM_J Register
- 14.7.4.5.2.156 FSS_DAT_REG3_HPB_DATA_MEM_J Register
- 14.7.4.6
MMCSD
- 14.7.4.6.1 MMCSD Summaries
- 14.7.4.6.2
MMCSD Registers
- 14.7.4.6.2.1 MMCSD_ECC_AGGR_RXMEM_REV Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.2 MMCSD_ECC_AGGR_RXMEM_VECTOR Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.3 MMCSD_ECC_AGGR_RXMEM_STAT Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.4 MMCSD_ECC_AGGR_RXMEM_RESERVED_SVBUS Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.5 MMCSD_ECC_AGGR_RXMEM_SEC_EOI_REG Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.6 MMCSD_ECC_AGGR_RXMEM_SEC_STATUS_REG0 Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.7 MMCSD_ECC_AGGR_RXMEM_SEC_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.8 MMCSD_ECC_AGGR_RXMEM_SEC_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.9 MMCSD_ECC_AGGR_RXMEM_DED_EOI_REG Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.10 MMCSD_ECC_AGGR_RXMEM_DED_STATUS_REG0 Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.11 MMCSD_ECC_AGGR_RXMEM_DED_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.12 MMCSD_ECC_AGGR_RXMEM_DED_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.13 MMCSD_ECC_AGGR_RXMEM_AGGR_ENABLE_SET Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.14 MMCSD_ECC_AGGR_RXMEM_AGGR_ENABLE_CLR Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.15 MMCSD_ECC_AGGR_RXMEM_AGGR_STATUS_SET Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.16 MMCSD_ECC_AGGR_RXMEM_AGGR_STATUS_CLR Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.17 MMCSD_ECC_AGGR_TXMEM_REV Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.18 MMCSD_ECC_AGGR_TXMEM_VECTOR Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.19 MMCSD_ECC_AGGR_TXMEM_STAT Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.20 MMCSD_ECC_AGGR_TXMEM_RESERVED_SVBUS Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.21 MMCSD_ECC_AGGR_TXMEM_SEC_EOI_REG Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.22 MMCSD_ECC_AGGR_TXMEM_SEC_STATUS_REG0 Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.23 MMCSD_ECC_AGGR_TXMEM_SEC_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.24 MMCSD_ECC_AGGR_TXMEM_SEC_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.25 MMCSD_ECC_AGGR_TXMEM_DED_EOI_REG Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.26 MMCSD_ECC_AGGR_TXMEM_DED_STATUS_REG0 Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.27 MMCSD_ECC_AGGR_TXMEM_DED_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.28 MMCSD_ECC_AGGR_TXMEM_DED_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.29 MMCSD_ECC_AGGR_TXMEM_AGGR_ENABLE_SET Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.30 MMCSD_ECC_AGGR_TXMEM_AGGR_ENABLE_CLR Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.31 MMCSD_ECC_AGGR_TXMEM_AGGR_STATUS_SET Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.32 MMCSD_ECC_AGGR_TXMEM_AGGR_STATUS_CLR Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.33 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_SDMA_SYS_ADDR_LO Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.34 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_SDMA_SYS_ADDR_HI Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.35 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_BLOCK_SIZE Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.36 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_BLOCK_COUNT Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.37 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_ARGUMENT1_LO Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.38 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_ARGUMENT1_HI Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.39 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_TRANSFER_MODE Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.40 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_COMMAND Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.41 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_RESPONSE Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.42 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_DATA_PORT Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.43 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_PRESENTSTATE Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.44 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_HOST_CONTROL1 Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.45 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_POWER_CONTROL Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.46 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_BLOCK_GAP_CONTROL Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.47 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_WAKEUP_CONTROL Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.48 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_CLOCK_CONTROL Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.49 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_TIMEOUT_CONTROL Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.50 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_SOFTWARE_RESET Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.51 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_NORMAL_INTR_STS Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.52 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_ERROR_INTR_STS Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.53 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_NORMAL_INTR_STS_ENA Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.54 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_ERROR_INTR_STS_ENA Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.55 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_NORMAL_INTR_SIG_ENA Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.56 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_ERROR_INTR_SIG_ENA Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.57 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_AUTOCMD_ERR_STS Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.58 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_HOST_CONTROL2 Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.59 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_CAPABILITIES Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.60 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_MAX_CURRENT_CAP Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.61 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_FORCE_EVNT_ACMD_ERR_STS Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.62 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_FORCE_EVNT_ERR_INT_STS Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.63 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_ADMA_ERR_STATUS Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.64 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_ADMA_SYS_ADDRESS Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.65 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_PRESET_VALUE0 Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.66 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_PRESET_VALUE1 Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.67 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_PRESET_VALUE2 Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.68 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_PRESET_VALUE3 Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.69 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_PRESET_VALUE4 Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.70 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_PRESET_VALUE5 Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.71 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_PRESET_VALUE6 Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.72 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_PRESET_VALUE7 Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.73 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_PRESET_VALUE8 Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.74 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_PRESET_VALUE10 Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.75 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_ADMA3_DESC_ADDRESS Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.76 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_UHS2_BLOCK_SIZE Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.77 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_UHS2_BLOCK_COUNT Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.78 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_UHS2_COMMAND_PKT Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.79 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_UHS2_XFER_MODE Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.80 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_UHS2_COMMAND Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.81 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_UHS2_RESPONSE Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.82 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_UHS2_MESSAGE_SELECT Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.83 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_UHS2_MESSAGE Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.84 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_UHS2_DEVICE_INTR_STATUS Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.85 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_UHS2_DEVICE_SELECT Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.86 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_UHS2_DEVICE_INT_CODE Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.87 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_UHS2_SOFTWARE_RESET Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.88 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_UHS2_TIMER_CONTROL Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.89 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_UHS2_ERR_INTR_STS Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.90 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_UHS2_ERR_INTR_STS_ENA Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.91 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_UHS2_ERR_INTR_SIG_ENA Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.92 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_UHS2_SETTINGS_PTR Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.93 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_UHS2_CAPABILITIES_PTR Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.94 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_UHS2_TEST_PTR Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.95 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_SHARED_BUS_CTRL_PTR Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.96 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_VENDOR_SPECFIC_PTR Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.97 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_BOOT_TIMEOUT_CONTROL Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.98 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_VENDOR_REGISTER Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.99 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_SLOT_INT_STS Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.100 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_HOST_CONTROLLER_VER Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.101 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_UHS2_GEN_SETTINGS Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.102 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_UHS2_PHY_SETTINGS Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.103 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_UHS2_LNK_TRN_SETTINGS Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.104 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_UHS2_GEN_CAP Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.105 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_UHS2_PHY_CAP Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.106 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_UHS2_LNK_TRN_CAP Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.107 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_FORCE_UHSII_ERR_INT_STS Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.108 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_CQ_VERSION Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.109 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_CQ_CAPABILITIES Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.110 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_CQ_CONFIG Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.111 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_CQ_CONTROL Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.112 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_CQ_INTR_STS Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.113 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_CQ_INTR_STS_ENA Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.114 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_CQ_INTR_SIG_ENA Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.115 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_CQ_INTR_COALESCING Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.116 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_CQ_TDL_BASE_ADDR Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.117 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_CQ_TDL_BASE_ADDR_UPBITS Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.118 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_CQ_TASK_DOOR_BELL Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.119 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_CQ_TASK_COMP_NOTIF Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.120 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_CQ_DEV_QUEUE_STATUS Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.121 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_CQ_DEV_PENDING_TASKS Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.122 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_CQ_TASK_CLEAR Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.123 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_CQ_SEND_STS_CONFIG1 Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.124 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_CQ_SEND_STS_CONFIG2 Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.125 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_CQ_DCMD_RESPONSE Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.126 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_CQ_RESP_ERR_MASK Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.127 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_CQ_TASK_ERR_INFO Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.128 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_CQ_CMD_RESP_INDEX Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.129 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_CQ_CMD_RESP_ARG Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.130 MMCSD_CTL_CFG_CQ_ERROR_TASK_ID Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.131 MMCSD_SS_CFG_SS_ID_REV_REG Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.132 MMCSD_SS_CFG_CTL_CFG_1_REG Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.133 MMCSD_SS_CFG_CTL_CFG_2_REG Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.134 MMCSD_SS_CFG_CTL_CFG_3_REG Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.135 MMCSD_SS_CFG_CTL_CFG_4_REG Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.136 MMCSD_SS_CFG_CTL_CFG_5_REG Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.137 MMCSD_SS_CFG_CTL_CFG_6_REG Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.138 MMCSD_SS_CFG_CTL_CFG_7_REG Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.139 MMCSD_SS_CFG_CTL_CFG_8_REG Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.140 MMCSD_SS_CFG_CTL_CFG_9_REG Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.141 MMCSD_SS_CFG_CTL_CFG_10_REG Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.142 MMCSD_SS_CFG_CTL_CFG_11_REG Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.143 MMCSD_SS_CFG_CTL_CFG_12_REG Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.144 MMCSD_SS_CFG_CTL_CFG_13_REG Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.145 MMCSD_SS_CFG_CTL_CFG_14_REG Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.146 MMCSD_SS_CFG_CTL_STAT_1_REG Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.147 MMCSD_SS_CFG_CTL_STAT_2_REG Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.148 MMCSD_SS_CFG_CTL_STAT_3_REG Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.149 MMCSD_SS_CFG_CTL_STAT_4_REG Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.150 MMCSD_SS_CFG_CTL_STAT_5_REG Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.151 MMCSD_SS_CFG_CTL_STAT_6_REG Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.152 MMCSD_SS_CFG_PHY_CTRL_1_REG Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.153 MMCSD_SS_CFG_PHY_CTRL_2_REG Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.154 MMCSD_SS_CFG_PHY_CTRL_3_REG Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.155 MMCSD_SS_CFG_PHY_CTRL_4_REG Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.156 MMCSD_SS_CFG_PHY_CTRL_5_REG Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.157 MMCSD_SS_CFG_PHY_CTRL_6_REG Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.158 MMCSD_SS_CFG_PHY_STAT_1_REG Register
- 14.7.4.6.2.159 MMCSD_SS_CFG_PHY_STAT_2_REG Register
- 14.7.4.1
FSS0
- 14.7.5
Industrial and Control Interfaces Registers
- 14.7.5.1
MCAN
- 14.7.5.1.1 MCAN Summaries
- 14.7.5.1.2
MCAN Registers
- 14.7.5.1.2.1 MCAN_PID Register
- 14.7.5.1.2.2 MCAN_CTRL Register
- 14.7.5.1.2.3 MCAN_STAT Register
- 14.7.5.1.2.4 MCAN_ICS Register
- 14.7.5.1.2.5 MCAN_IRS Register
- 14.7.5.1.2.6 MCAN_IECS Register
- 14.7.5.1.2.7 MCAN_IE Register
- 14.7.5.1.2.8 MCAN_IES Register
- 14.7.5.1.2.9 MCAN_EOI Register
- 14.7.5.1.2.10 MCAN_EXT_TS_PRESCALER Register
- 14.7.5.1.2.11 MCAN_EXT_TS_UNSERVICED_INTR_CNTR Register
- 14.7.5.1.2.12 MMCSD_ECC_AGGR_RXMEM_REV Register
- 14.7.5.1.2.13 MMCSD_ECC_AGGR_RXMEM_VECTOR Register
- 14.7.5.1.2.14 MMCSD_ECC_AGGR_RXMEM_STAT Register
- 14.7.5.1.2.15 MMCSD_ECC_AGGR_RXMEM_RESERVED_SVBUS Register
- 14.7.5.1.2.16 MMCSD_ECC_AGGR_RXMEM_SEC_EOI_REG Register
- 14.7.5.1.2.17 MMCSD_ECC_AGGR_RXMEM_SEC_STATUS_REG0 Register
- 14.7.5.1.2.18 MMCSD_ECC_AGGR_RXMEM_SEC_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Register
- 14.7.5.1.2.19 MMCSD_ECC_AGGR_RXMEM_SEC_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Register
- 14.7.5.1.2.20 MMCSD_ECC_AGGR_RXMEM_DED_EOI_REG Register
- 14.7.5.1.2.21 MMCSD_ECC_AGGR_RXMEM_DED_STATUS_REG0 Register
- 14.7.5.1.2.22 MMCSD_ECC_AGGR_RXMEM_DED_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Register
- 14.7.5.1.2.23 MMCSD_ECC_AGGR_RXMEM_DED_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Register
- 14.7.5.1.2.24 MMCSD_ECC_AGGR_RXMEM_AGGR_ENABLE_SET Register
- 14.7.5.1.2.25 MMCSD_ECC_AGGR_RXMEM_AGGR_ENABLE_CLR Register
- 14.7.5.1.2.26 MMCSD_ECC_AGGR_RXMEM_AGGR_STATUS_SET Register
- 14.7.5.1.2.27 MMCSD_ECC_AGGR_RXMEM_AGGR_STATUS_CLR Register
- 14.7.5.1.2.28 MCAN_MSGMEM_RAM_RAM_REG_J Register
- 14.7.5.1.2.29 ECC_AGGR_REV Register
- 14.7.5.1.2.30 ECC_AGGR_VECTOR Register
- 14.7.5.1.2.31 ECC_AGGR_STAT Register
- 14.7.5.1.2.32 ECC_AGGR_SEC_EOI_REG Register
- 14.7.5.1.2.33 ECC_AGGR_SEC_STATUS_REG0 Register
- 14.7.5.1.2.34 ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Register
- 14.7.5.1.2.35 ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Register
- 14.7.5.1.2.36 ECC_AGGR_DED_EOI_REG Register
- 14.7.5.1.2.37 ECC_AGGR_DED_STATUS_REG0 Register
- 14.7.5.1.2.38 ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Register
- 14.7.5.1.2.39 ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Register
- 14.7.5.1.2.40 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_SET Register
- 14.7.5.1.2.41 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_CLR Register
- 14.7.5.1.2.42 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_STATUS_SET Register
- 14.7.5.1.2.43 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_STATUS_CLR Register
- 14.7.5.2
ECAP
- 14.7.5.2.1 ECAP Summaries
- 14.7.5.2.2
CBASS_QOS_IPULSAR_UL_WKUP_0_CPU0_WMST_MAP0 Register
- 14.7.5.2.2.1 CBASS_SAFE_ERR_PID Register
- 14.7.5.2.2.2 CBASS_SAFE_ERR_DESTINATION_ID Register
- 14.7.5.2.2.3 CBASS_SAFE_ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER0 Register
- 14.7.5.2.2.4 CBASS_SAFE_ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_HEADER1 Register
- 14.7.5.2.2.5 CBASS_SAFE_ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA0 Register
- 14.7.5.2.2.6 CBASS_SAFE_ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA1 Register
- 14.7.5.2.2.7 CBASS_SAFE_ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA2 Register
- 14.7.5.2.2.8 CBASS_SAFE_ERR_EXCEPTION_LOGGING_DATA3 Register
- 14.7.5.2.2.9 CBASS_SAFE_ERR_ERR_INTR_RAW_STAT Register
- 14.7.5.2.2.10 CBASS_SAFE_ERR_ERR_INTR_ENABLED_STAT Register
- 14.7.5.2.2.11 CBASS_SAFE_ERR_ERR_INTR_ENABLE_SET Register
- 14.7.5.2.2.12 CBASS_SAFE_ERR_ERR_INTR_ENABLE_CLR Register
- 14.7.5.2.2.13 CBASS_SAFE_ERR_EOI Register
- 14.7.5.3
EPWM
- 14.7.5.3.1 EPWM Summaries
- 14.7.5.3.2
EPWM Registers
- 14.7.5.3.2.1 EPWM_TBCTL Register
- 14.7.5.3.2.2 EPWM_TBSTS Register
- 14.7.5.3.2.3 EPWM_TBPHSHR Register
- 14.7.5.3.2.4 EPWM_TBPHS Register
- 14.7.5.3.2.5 EPWM_TBCNT Register
- 14.7.5.3.2.6 EPWM_TBPRD Register
- 14.7.5.3.2.7 EPWM_CMPCTL Register
- 14.7.5.3.2.8 EPWM_CMPAHR Register
- 14.7.5.3.2.9 EPWM_CMPA Register
- 14.7.5.3.2.10 EPWM_CMPB Register
- 14.7.5.3.2.11 EPWM_AQCTLA Register
- 14.7.5.3.2.12 EPWM_AQCTLB Register
- 14.7.5.3.2.13 EPWM_AQSFRC Register
- 14.7.5.3.2.14 EPWM_AQCSFRC Register
- 14.7.5.3.2.15 EPWM_DBCTL Register
- 14.7.5.3.2.16 EPWM_DBRED Register
- 14.7.5.3.2.17 EPWM_DBFED Register
- 14.7.5.3.2.18 EPWM_TZSEL Register
- 14.7.5.3.2.19 EPWM_TZCTL Register
- 14.7.5.3.2.20 EPWM_TZEINT Register
- 14.7.5.3.2.21 EPWM_TZFLG Register
- 14.7.5.3.2.22 EPWM_TZCLR Register
- 14.7.5.3.2.23 EPWM_TZFRC Register
- 14.7.5.3.2.24 EPWM_ETSEL Register
- 14.7.5.3.2.25 EPWM_ETPS Register
- 14.7.5.3.2.26 EPWM_ETFLG Register
- 14.7.5.3.2.27 EPWM_ETCLR Register
- 14.7.5.3.2.28 EPWM_ETFRC Register
- 14.7.5.3.2.29 EPWM_PCCTL Register
- 14.7.5.3.2.30 EPWM_PID Register
- 14.7.5.4
adcss
- 14.7.5.4.1 adcss Summaries
- 14.7.5.4.2
adcss Registers
- 14.7.5.4.2.1 ADCSS_ECC_AGGR_ADCSS_ECC_AGGR Register
- 14.7.5.4.2.2 ADCSS_ECC_AGGR_ADCSS_ECC_AGGR Register
- 14.7.5.4.2.3 ADCSS_ECC_AGGR_ADCSS_ECC_AGGR Register
- 14.7.5.4.2.4 ADCSS_ECC_AGGR_SEC_EOI_REG Register
- 14.7.5.4.2.5 ADCSS_ECC_AGGR_SEC_STATUS_REG0 Register
- 14.7.5.4.2.6 ADCSS_ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Register
- 14.7.5.4.2.7 ADCSS_ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Register
- 14.7.5.4.2.8 ADCSS_ECC_AGGR_DED_EOI_REG Register
- 14.7.5.4.2.9 ADCSS_ECC_AGGR_DED_STATUS_REG0 Register
- 14.7.5.4.2.10 ADCSS_ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Register
- 14.7.5.4.2.11 ADCSS_ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Register
- 14.7.5.4.2.12 ADCSS_ECC_AGGR_ADCSS_ECC_AGGR Register
- 14.7.5.4.2.13 ADCSS_ECC_AGGR_ADCSS_ECC_AGGR Register
- 14.7.5.4.2.14 ADCSS_ECC_AGGR_ADCSS_ECC_AGGR Register
- 14.7.5.4.2.15 ADCSS_ECC_AGGR_ADCSS_ECC_AGGR Register
- 14.7.5.4.2.16 ADC_DATA0 Register
- 14.7.5.4.2.17 ADC_DATA1 Register
- 14.7.5.4.2.18 ADC_DATA0 Register
- 14.7.5.4.2.19 ADC_DATA1 Register
- 14.7.5.1
MCAN
- 14.7.6
Timer Module Registers
- 14.7.6.1
DMASS_BCDMA_0_BCDMA_GCFG_CAP1 Register
- 14.7.6.1.1 DMASS_BCDMA_0_BCDMA_GCFG_CAP0 Register
- 14.7.6.1.2
DMASS_BCDMA_0_BCDMA_GCFG_EMU_CTRL Register
- 14.7.6.1.2.1 DMASS_BCDMA_0_BCDMA_RING_RING_BA_LO_J Register
- 14.7.6.1.2.2 DMASS_BCDMA_0_BCDMA_RING_RING_BA_HI_J Register
- 14.7.6.1.2.3 DMASS_BCDMA_0_BCDMA_RING_RING_SIZE_J Register
- 14.7.6.1.2.4 GTC_CFG1_CNTCR Register
- 14.7.6.1.2.5 GTC_CFG1_CNTSR Register
- 14.7.6.1.2.6 GTC_CFG1_CNTCV_LO Register
- 14.7.6.1.2.7 GTC_CFG1_CNTCV_HI Register
- 14.7.6.1.2.8 GTC_CFG1_CNTFID0 Register
- 14.7.6.1.2.9 GTC_CFG1_CNTFID1 Register
- 14.7.6.1.2.10 DMASS_BCDMA_0_BCDMA_RINGRT_RINGRT_FDB_J Register
- 14.7.6.1.2.11 DMASS_BCDMA_0_BCDMA_RINGRT_RINGRT_FOCC_J Register
- 14.7.6.1.2.12 DMASS_BCDMA_0_BCDMA_RINGRT_RINGRT_RDB_J Register
- 14.7.6.1.2.13 DMASS_BCDMA_0_BCDMA_RINGRT_RINGRT_ROCC_J Register
- 14.7.6.1.2.14 GTC_CFG3_CNTTIDR Register
- 14.7.6.2
RTI
- 14.7.6.2.1 RTI Summaries
- 14.7.6.2.2
RTI Registers
- 14.7.6.2.2.1 SMS_HSM_WDT_RTI_GCTRL Register
- 14.7.6.2.2.2 SMS_HSM_WDT_RTI_TBCTRL Register
- 14.7.6.2.2.3 SMS_HSM_WDT_RTI_CAPCTRL Register
- 14.7.6.2.2.4 SMS_HSM_WDT_RTI_COMPCTRL Register
- 14.7.6.2.2.5 SMS_HSM_WDT_RTI_FRC0 Register
- 14.7.6.2.2.6 SMS_HSM_WDT_RTI_UC0 Register
- 14.7.6.2.2.7 SMS_HSM_WDT_RTI_CPUC0 Register
- 14.7.6.2.2.8 SMS_HSM_WDT_RTI_CAFRC0 Register
- 14.7.6.2.2.9 SMS_HSM_WDT_RTI_CAUC0 Register
- 14.7.6.2.2.10 SMS_HSM_WDT_RTI_FRC1 Register
- 14.7.6.2.2.11 SMS_HSM_WDT_RTI_UC1 Register
- 14.7.6.2.2.12 SMS_HSM_WDT_RTI_CPUC1 Register
- 14.7.6.2.2.13 SMS_HSM_WDT_RTI_CAFRC1 Register
- 14.7.6.2.2.14 SMS_HSM_WDT_RTI_CAUC1 Register
- 14.7.6.2.2.15 SMS_HSM_WDT_RTI_COMP0 Register
- 14.7.6.2.2.16 SMS_HSM_WDT_RTI_UDCP0 Register
- 14.7.6.2.2.17 SMS_HSM_WDT_RTI_COMP1 Register
- 14.7.6.2.2.18 SMS_HSM_WDT_RTI_UDCP1 Register
- 14.7.6.2.2.19 SMS_HSM_WDT_RTI_COMP2 Register
- 14.7.6.2.2.20 SMS_HSM_WDT_RTI_UDCP2 Register
- 14.7.6.2.2.21 SMS_HSM_WDT_RTI_COMP3 Register
- 14.7.6.2.2.22 SMS_HSM_WDT_RTI_UDCP3 Register
- 14.7.6.2.2.23 SMS_HSM_WDT_RTI_TBLCOMP Register
- 14.7.6.2.2.24 SMS_HSM_WDT_RTI_TBHCOMP Register
- 14.7.6.2.2.25 SMS_HSM_WDT_RTI_SETINT Register
- 14.7.6.2.2.26 SMS_HSM_WDT_RTI_CLEARINT Register
- 14.7.6.2.2.27 SMS_HSM_WDT_RTI_INTFLAG Register
- 14.7.6.2.2.28 SMS_HSM_WDT_RTI_DWDCTRL Register
- 14.7.6.2.2.29 SMS_HSM_WDT_RTI_DWDPRLD Register
- 14.7.6.2.2.30 SMS_HSM_WDT_RTI_WDSTATUS Register
- 14.7.6.2.2.31 SMS_HSM_WDT_RTI_WDKEY Register
- 14.7.6.2.2.32 SMS_HSM_WDT_RTI_DWDCNTR Register
- 14.7.6.2.2.33 SMS_HSM_WDT_RTI_WWDRXNCTRL Register
- 14.7.6.2.2.34 SMS_HSM_WDT_RTI_WWDSIZECTRL Register
- 14.7.6.2.2.35 SMS_HSM_WDT_RTI_INTCLRENABLE Register
- 14.7.6.2.2.36 SMS_HSM_WDT_RTI_COMP0CLR Register
- 14.7.6.2.2.37 SMS_HSM_WDT_RTI_COMP1CLR Register
- 14.7.6.2.2.38 SMS_HSM_WDT_RTI_COMP2CLR Register
- 14.7.6.2.2.39 SMS_HSM_WDT_RTI_COMP3CLR Register
- 14.7.6.3
rtcss
- 14.7.6.3.1 rtcss Summaries
- 14.7.6.3.2
rtcss Registers
- 14.7.6.3.2.1 RTC_MOD_VER Register
- 14.7.6.3.2.2 RTC_SUB_S_CNT Register
- 14.7.6.3.2.3 RTC_S_CNT_LSW Register
- 14.7.6.3.2.4 RTC_S_CNT_MSW Register
- 14.7.6.3.2.5 RTC_COMP Register
- 14.7.6.3.2.6 RTC_OFF_ON_S_CNT_LSW Register
- 14.7.6.3.2.7 RTC_OFF_ON_S_CNT_MSW Register
- 14.7.6.3.2.8 RTC_ON_OFF_S_CNT_LSW Register
- 14.7.6.3.2.9 RTC_ON_OFF_S_CNT_MSW Register
- 14.7.6.3.2.10 RTC_DEBOUNCE Register
- 14.7.6.3.2.11 RTC_ANALOG Register
- 14.7.6.3.2.12 RTC_SCRATCH0_J Register
- 14.7.6.3.2.13 RTC_GENRAL_CTL Register
- 14.7.6.3.2.14 RTC_IRQSTATUS_RAW_SYS Register
- 14.7.6.3.2.15 RTC_IRQSTATUS_SYS Register
- 14.7.6.3.2.16 RTC_IRQENABLE_SET_SYS Register
- 14.7.6.3.2.17 RTC_IRQENABLE_CLR_SYS Register
- 14.7.6.3.2.18 RTC_SYNCPEND Register
- 14.7.6.3.2.19 RTC_KICK0 Register
- 14.7.6.3.2.20 RTC_KICK1 Register
- 14.7.6.4
TIMER
- 14.7.6.4.1 TIMER Summaries
- 14.7.6.4.2
TIMER Registers
- 14.7.6.4.2.1 DMTIMER1MS_TIDR Register
- 14.7.6.4.2.2 DMTIMER1MS_TIOCP_CFG Register
- 14.7.6.4.2.3 DMTIMER1MS_IRQ_EOI Register
- 14.7.6.4.2.4 DMTIMER1MS_IRQSTATUS_RAW Register
- 14.7.6.4.2.5 DMTIMER1MS_IRQSTATUS Register
- 14.7.6.4.2.6 DMTIMER1MS_IRQSTATUS_SET Register
- 14.7.6.4.2.7 DMTIMER1MS_IRQSTATUS_CLR Register
- 14.7.6.4.2.8 DMTIMER1MS_IRQWAKEEN Register
- 14.7.6.4.2.9 DMTIMER1MS_TCLR Register
- 14.7.6.4.2.10 DMTIMER1MS_TCRR Register
- 14.7.6.4.2.11 DMTIMER1MS_TLDR Register
- 14.7.6.4.2.12 DMTIMER1MS_TTGR Register
- 14.7.6.4.2.13 DMTIMER1MS_TWPS Register
- 14.7.6.4.2.14 DMTIMER1MS_TMAR Register
- 14.7.6.4.2.15 DMTIMER1MS_TCAR1 Register
- 14.7.6.4.2.16 DMTIMER1MS_TSICR Register
- 14.7.6.4.2.17 DMTIMER1MS_TCAR2 Register
- 14.7.6.4.2.18 DMTIMER1MS_TPIR Register
- 14.7.6.4.2.19 DMTIMER1MS_TNIR Register
- 14.7.6.4.2.20 DMTIMER1MS_TCVR Register
- 14.7.6.4.2.21 DMTIMER1MS_TOCR Register
- 14.7.6.4.2.22 DMTIMER1MS_TOWR Register
- 14.7.6.1
DMASS_BCDMA_0_BCDMA_GCFG_CAP1 Register
- 14.7.7
Internal Diagnostics Modules Registers
- 14.7.7.1
DCC
- 14.7.7.1.1 DCC Summaries
- 14.7.7.1.2
DCC Registers
- 14.7.7.1.2.1 DCC2_DCCGCTRL Register
- 14.7.7.1.2.2 DCC2_DCCREV Register
- 14.7.7.1.2.3 DCC2_DCCCNTSEED0 Register
- 14.7.7.1.2.4 DCC2_DCCVALIDSEED0 Register
- 14.7.7.1.2.5 DCC2_DCCCNTSEED1 Register
- 14.7.7.1.2.6 DCC2_DCCSTATUS Register
- 14.7.7.1.2.7 DCC2_DCCCNT0 Register
- 14.7.7.1.2.8 DCC2_DCCVALID0 Register
- 14.7.7.1.2.9 DCC2_DCCCNT1 Register
- 14.7.7.1.2.10 DCC2_DCCCLKSRC1 Register
- 14.7.7.1.2.11 DCC2_DCCCLKSRC0 Register
- 14.7.7.1.2.12 DCC2_DCCGCTRL2 Register
- 14.7.7.1.2.13 DCC2_DCCSTATUS2 Register
- 14.7.7.1.2.14 DCC2_DCCERRCNT Register
- 14.7.7.2
ESM
- 14.7.7.2.1 ESM Summaries
- 14.7.7.2.2
ESM Registers
- 14.7.7.2.2.1 ESM_PID Register
- 14.7.7.2.2.2 ESM_INFO Register
- 14.7.7.2.2.3 ESM_EN Register
- 14.7.7.2.2.4 ESM_SFT_RST Register
- 14.7.7.2.2.5 ESM_ERR_RAW Register
- 14.7.7.2.2.6 ESM_ERR_STS Register
- 14.7.7.2.2.7 ESM_ERR_EN_SET Register
- 14.7.7.2.2.8 ESM_ERR_EN_CLR Register
- 14.7.7.2.2.9 ESM_LOW_PRI Register
- 14.7.7.2.2.10 ESM_HI_PRI Register
- 14.7.7.2.2.11 ESM_LOW Register
- 14.7.7.2.2.12 ESM_HI Register
- 14.7.7.2.2.13 ESM_EOI Register
- 14.7.7.2.2.14 ESM_PIN_CTRL Register
- 14.7.7.2.2.15 ESM_PIN_STS Register
- 14.7.7.2.2.16 ESM_PIN_CNTR Register
- 14.7.7.2.2.17 ESM_PIN_CNTR_PRE Register
- 14.7.7.2.2.18 ESM_PWMH_PIN_CNTR Register
- 14.7.7.2.2.19 ESM_PWMH_PIN_CNTR_PRE Register
- 14.7.7.2.2.20 ESM_PWML_PIN_CNTR Register
- 14.7.7.2.2.21 ESM_PWML_PIN_CNTR_PRE Register
- 14.7.7.2.2.22 ESM_ERR_GRP_RAW_J Register
- 14.7.7.2.2.23 ESM_ERR_GRP_STS_J Register
- 14.7.7.2.2.24 ESM_ERR_GRP_INTR_EN_SET_J Register
- 14.7.7.2.2.25 ESM_ERR_GRP_INTR_EN_CLR_J Register
- 14.7.7.2.2.26 ESM_ERR_GRP_INT_PRIO_J Register
- 14.7.7.2.2.27 ESM_ERR_GRP_PIN_EN_SET_J Register
- 14.7.7.2.2.28 ESM_ERR_GRP_PIN_EN_CLR_J Register
- 14.7.7.3
ESM
- 14.7.7.3.1 ESM Summaries
- 14.7.7.3.2
ESM Registers
- 14.7.7.3.2.1 ESM_PID Register
- 14.7.7.3.2.2 ESM_INFO Register
- 14.7.7.3.2.3 ESM_EN Register
- 14.7.7.3.2.4 ESM_SFT_RST Register
- 14.7.7.3.2.5 ESM_ERR_RAW Register
- 14.7.7.3.2.6 ESM_ERR_STS Register
- 14.7.7.3.2.7 ESM_ERR_EN_SET Register
- 14.7.7.3.2.8 ESM_ERR_EN_CLR Register
- 14.7.7.3.2.9 ESM_LOW_PRI Register
- 14.7.7.3.2.10 ESM_HI_PRI Register
- 14.7.7.3.2.11 ESM_LOW Register
- 14.7.7.3.2.12 ESM_HI Register
- 14.7.7.3.2.13 ESM_EOI Register
- 14.7.7.3.2.14 ESM_PIN_CTRL Register
- 14.7.7.3.2.15 ESM_PIN_STS Register
- 14.7.7.3.2.16 ESM_PIN_CNTR Register
- 14.7.7.3.2.17 ESM_PIN_CNTR_PRE Register
- 14.7.7.3.2.18 ESM_PWMH_PIN_CNTR Register
- 14.7.7.3.2.19 ESM_PWMH_PIN_CNTR_PRE Register
- 14.7.7.3.2.20 ESM_PWML_PIN_CNTR Register
- 14.7.7.3.2.21 ESM_PWML_PIN_CNTR_PRE Register
- 14.7.7.3.2.22 ESM_ERR_GRP_RAW_J Register
- 14.7.7.3.2.23 ESM_ERR_GRP_STS_J Register
- 14.7.7.3.2.24 ESM_ERR_GRP_INTR_EN_SET_J Register
- 14.7.7.3.2.25 ESM_ERR_GRP_INTR_EN_CLR_J Register
- 14.7.7.3.2.26 ESM_ERR_GRP_INT_PRIO_J Register
- 14.7.7.3.2.27 ESM_ERR_GRP_PIN_EN_SET_J Register
- 14.7.7.3.2.28 ESM_ERR_GRP_PIN_EN_CLR_J Register
- 14.7.7.4
MCRC64
- 14.7.7.4.1 MCRC64 Summaries
- 14.7.7.4.2
MCRC64 Registers
- 14.7.7.4.2.1 CRC_CTRL0 Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.2 CRC_CTRL1 Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.3 CRC_CTRL2 Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.4 CRC_INTS Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.5 CRC_INTR Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.6 CRC_STATUS Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.7 CRC_INT_OFFSET_REG Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.8 CRC_BUSY Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.9 CRC_PCOUNT_REG1 Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.10 CRC_SCOUNT_REG1 Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.11 CRC_CURSEC_REG1 Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.12 CRC_WDTOPLD1 Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.13 CRC_BCTOPLD1 Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.14 CRC_PSA_SIGREGL1 Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.15 CRC_PSA_SIGREGH1 Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.16 CRC_REGL1 Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.17 CRC_REGH1 Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.18 CRC_PSA_SECSIGREGL1 Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.19 CRC_PSA_SECSIGREGH1 Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.20 CRC_RAW_DATAREGL1 Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.21 CRC_RAW_DATAREGH1 Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.22 CRC_PCOUNT_REG2 Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.23 CRC_SCOUNT_REG2 Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.24 CRC_CURSEC_REG2 Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.25 CRC_WDTOPLD2 Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.26 CRC_BCTOPLD2 Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.27 CRC_PSA_SIGREGL2 Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.28 CRC_PSA_SIGREGH2 Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.29 CRC_REGL2 Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.30 CRC_REGH2 Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.31 CRC_PSA_SECSIGREGL2 Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.32 CRC_PSA_SECSIGREGH2 Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.33 CRC_RAW_DATAREGL2 Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.34 CRC_RAW_DATAREGH2 Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.35 CRC_PCOUNT_REG3 Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.36 CRC_SCOUNT_REG3 Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.37 CRC_CURSEC_REG3 Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.38 CRC_WDTOPLD3 Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.39 CRC_BCTOPLD3 Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.40 CRC_PSA_SIGREGL3 Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.41 CRC_PSA_SIGREGH3 Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.42 CRC_REGL3 Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.43 CRC_REGH3 Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.44 CRC_PSA_SECSIGREGL3 Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.45 CRC_PSA_SECSIGREGH3 Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.46 CRC_RAW_DATAREGL3 Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.47 CRC_RAW_DATAREGH3 Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.48 CRC_PCOUNT_REG4 Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.49 CRC_SCOUNT_REG4 Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.50 CRC_CURSEC_REG4 Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.51 CRC_WDTOPLD4 Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.52 CRC_BCTOPLD4 Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.53 CRC_PSA_SIGREGL4 Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.54 CRC_PSA_SIGREGH4 Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.55 CRC_REGL4 Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.56 CRC_REGH4 Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.57 CRC_PSA_SECSIGREGL4 Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.58 CRC_PSA_SECSIGREGH4 Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.59 CRC_RAW_DATAREGL4 Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.60 CRC_RAW_DATAREGH4 Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.61 CRC_MBUS_SEL Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.62 CRC_I0_PSA_SIGREG1_CPY_J Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.63 CRC_I0_PSA_SIGREG2_CPY_J Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.64 CRC_I0_PSA_SIGREG3_CPY_J Register
- 14.7.7.4.2.65 CRC_I0_PSA_SIGREG4_CPY_J Register
- 14.7.7.5
ECC_AGGR
- 14.7.7.5.1 ECC_AGGR Summaries
- 14.7.7.5.2
ECC_AGGR Registers
- 14.7.7.5.2.1 ECC_AGGR_REV Register
- 14.7.7.5.2.2 ECC_AGGR_VECTOR Register
- 14.7.7.5.2.3 ECC_AGGR_STAT Register
- 14.7.7.5.2.4 ECC_AGGR_RESERVED_SVBUS_J Register
- 14.7.7.5.2.5 ECC_AGGR_SEC_EOI_REG Register
- 14.7.7.5.2.6 ECC_AGGR_SEC_STATUS_REG0 Register
- 14.7.7.5.2.7 ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Register
- 14.7.7.5.2.8 ECC_AGGR_SEC_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Register
- 14.7.7.5.2.9 ECC_AGGR_DED_EOI_REG Register
- 14.7.7.5.2.10 ECC_AGGR_DED_STATUS_REG0 Register
- 14.7.7.5.2.11 ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_SET_REG0 Register
- 14.7.7.5.2.12 ECC_AGGR_DED_ENABLE_CLR_REG0 Register
- 14.7.7.5.2.13 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_SET Register
- 14.7.7.5.2.14 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_ENABLE_CLR Register
- 14.7.7.5.2.15 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_STATUS_SET Register
- 14.7.7.5.2.16 ECC_AGGR_AGGR_STATUS_CLR Register
- 14.7.7.1
DCC
- 14.7.1
Audio Peripherals Registers
- 14.8
On-Chip Debug Registers
- 14.8.1
DEBUGSS_WRAP
- 14.8.1.1 DEBUGSS_WRAP Summaries
- 14.8.1.2
DEBUGSS_WRAP Registers
- 14.8.1.2.1 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_ENTRY0 Register
- 14.8.1.2.2 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_ENTRY1 Register
- 14.8.1.2.3 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_ENTRY2 Register
- 14.8.1.2.4 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY0 Register
- 14.8.1.2.5 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY1 Register
- 14.8.1.2.6 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY2 Register
- 14.8.1.2.7 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY3 Register
- 14.8.1.2.8 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY4 Register
- 14.8.1.2.9 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY5 Register
- 14.8.1.2.10 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY6 Register
- 14.8.1.2.11 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY7 Register
- 14.8.1.2.12 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY8 Register
- 14.8.1.2.13 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY9 Register
- 14.8.1.2.14 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY10 Register
- 14.8.1.2.15 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY11 Register
- 14.8.1.2.16 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY12 Register
- 14.8.1.2.17 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY13 Register
- 14.8.1.2.18 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY14 Register
- 14.8.1.2.19 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY15 Register
- 14.8.1.2.20 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY16 Register
- 14.8.1.2.21 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY17 Register
- 14.8.1.2.22 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY18 Register
- 14.8.1.2.23 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY19 Register
- 14.8.1.2.24 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY20 Register
- 14.8.1.2.25 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY21 Register
- 14.8.1.2.26 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY22 Register
- 14.8.1.2.27 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY23 Register
- 14.8.1.2.28 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY24 Register
- 14.8.1.2.29 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY25 Register
- 14.8.1.2.30 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY26 Register
- 14.8.1.2.31 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY27 Register
- 14.8.1.2.32 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY28 Register
- 14.8.1.2.33 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY29 Register
- 14.8.1.2.34 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY30 Register
- 14.8.1.2.35 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY31 Register
- 14.8.1.2.36 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY32 Register
- 14.8.1.2.37 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY33 Register
- 14.8.1.2.38 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY34 Register
- 14.8.1.2.39 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY35 Register
- 14.8.1.2.40 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY36 Register
- 14.8.1.2.41 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY37 Register
- 14.8.1.2.42 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY38 Register
- 14.8.1.2.43 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY39 Register
- 14.8.1.2.44 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY40 Register
- 14.8.1.2.45 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY41 Register
- 14.8.1.2.46 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY42 Register
- 14.8.1.2.47 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY43 Register
- 14.8.1.2.48 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY44 Register
- 14.8.1.2.49 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY45 Register
- 14.8.1.2.50 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY46 Register
- 14.8.1.2.51 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY47 Register
- 14.8.1.2.52 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY48 Register
- 14.8.1.2.53 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY49 Register
- 14.8.1.2.54 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY50 Register
- 14.8.1.2.55 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY51 Register
- 14.8.1.2.56 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY52 Register
- 14.8.1.2.57 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY53 Register
- 14.8.1.2.58 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY54 Register
- 14.8.1.2.59 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY55 Register
- 14.8.1.2.60 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY56 Register
- 14.8.1.2.61 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY57 Register
- 14.8.1.2.62 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY58 Register
- 14.8.1.2.63 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY59 Register
- 14.8.1.2.64 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY60 Register
- 14.8.1.2.65 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY61 Register
- 14.8.1.2.66 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY62 Register
- 14.8.1.2.67 ROM_TABLE_0_0_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY63 Register
- 14.8.1.2.68 ROM_TABLE_0_0_PERIPHID0 Register
- 14.8.1.2.69 ROM_TABLE_0_0_PERIPHID1 Register
- 14.8.1.2.70 ROM_TABLE_0_0_PERIPHID2 Register
- 14.8.1.2.71 ROM_TABLE_0_0_PERIPHID3 Register
- 14.8.1.2.72 ROM_TABLE_0_0_PERIPHID4 Register
- 14.8.1.2.73 ROM_TABLE_0_0_COMPID0 Register
- 14.8.1.2.74 ROM_TABLE_0_0_COMPID1 Register
- 14.8.1.2.75 ROM_TABLE_0_0_COMPID2 Register
- 14.8.1.2.76 ROM_TABLE_0_0_COMPID3 Register
- 14.8.1.2.77 CFGAP_CFG_0_JTAGID_REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.78 CFGAP_CFG_0_USERID_REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.79 CFGAP_CFG_0_VERSION_REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.80 CFGAP_CFG_0_APID_REGISTER Register
- 14.8.1.2.81 APBAP_CFG_0_CSWREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.82 APBAP_CFG_0_DRWREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.83 APBAP_CFG_0_BD0REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.84 APBAP_CFG_0_BD1REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.85 APBAP_CFG_0_BD2REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.86 APBAP_CFG_0_BD3REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.87 APBAP_CFG_0_ROM_REGISTER Register
- 14.8.1.2.88 APBAP_CFG_0_ID_REGISTER Register
- 14.8.1.2.89 AXIAP_CFG_0_CSWREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.90 AXIAP_CFG_0_DRWREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.91 AXIAP_CFG_0_BD0REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.92 AXIAP_CFG_0_BD1REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.93 AXIAP_CFG_0_BD2REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.94 AXIAP_CFG_0_BD3REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.95 AXIAP_CFG_0_MBT_REGISTER Register
- 14.8.1.2.96 AXIAP_CFG_0_ROM_HI_REGISTER Register
- 14.8.1.2.97 AXIAP_CFG_0_CFG_REGISTER Register
- 14.8.1.2.98 AXIAP_CFG_0_ROM_LO_REGISTER Register
- 14.8.1.2.99 AXIAP_CFG_0_ID_REGISTER Register
- 14.8.1.2.100 PWRAP_CFG_0_ID_REGISTER Register
- 14.8.1.2.101 PVIEW_CFG_0_PVIEW_STATE0 Register
- 14.8.1.2.102 PVIEW_CFG_0_PVIEW_CAPABILITY Register
- 14.8.1.2.103 PVIEW_CFG_0_ID_REGISTER Register
- 14.8.1.2.104 JTAGAP_CFG_0_CSW Register
- 14.8.1.2.105 JTAGAP_CFG_0_PSEL_REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.106 JTAGAP_CFG_0_PSTA_REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.107 JTAGAP_CFG_0_BYTEFIFO1 Register
- 14.8.1.2.108 JTAGAP_CFG_0_BYTEFIFO2 Register
- 14.8.1.2.109 JTAGAP_CFG_0_BYTEFIFO3 Register
- 14.8.1.2.110 JTAGAP_CFG_0_BYTEFIFO4 Register
- 14.8.1.2.111 JTAGAP_CFG_0_ID_REGISTER Register
- 14.8.1.2.112 SECAP_CFG_0_TXDATA Register
- 14.8.1.2.113 SECAP_CFG_0_TXCTRL Register
- 14.8.1.2.114 SECAP_CFG_0_RXDATA Register
- 14.8.1.2.115 SECAP_CFG_0_RXCTRL Register
- 14.8.1.2.116 CORTEX0_CFG_0_CSWREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.117 CORTEX0_CFG_0_DRWREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.118 CORTEX0_CFG_0_BD0REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.119 CORTEX0_CFG_0_BD1REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.120 CORTEX0_CFG_0_BD2REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.121 CORTEX0_CFG_0_BD3REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.122 CORTEX0_CFG_0_ROM_REGISTER Register
- 14.8.1.2.123 CORTEX0_CFG_0_ID_REGISTER Register
- 14.8.1.2.124 CORTEX1_CFG_0_CSWREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.125 CORTEX1_CFG_0_DRWREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.126 CORTEX1_CFG_0_BD0REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.127 CORTEX1_CFG_0_BD1REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.128 CORTEX1_CFG_0_BD2REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.129 CORTEX1_CFG_0_BD3REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.130 CORTEX1_CFG_0_ROM_REGISTER Register
- 14.8.1.2.131 CORTEX1_CFG_0_ID_REGISTER Register
- 14.8.1.2.132 CORTEX2_CFG_0_CSWREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.133 CORTEX2_CFG_0_DRWREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.134 CORTEX2_CFG_0_BD0REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.135 CORTEX2_CFG_0_BD1REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.136 CORTEX2_CFG_0_BD2REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.137 CORTEX2_CFG_0_BD3REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.138 CORTEX2_CFG_0_ROM_REGISTER Register
- 14.8.1.2.139 CORTEX2_CFG_0_ID_REGISTER Register
- 14.8.1.2.140 CORTEX3_CFG_0_CSWREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.141 CORTEX3_CFG_0_DRWREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.142 CORTEX3_CFG_0_BD0REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.143 CORTEX3_CFG_0_BD1REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.144 CORTEX3_CFG_0_BD2REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.145 CORTEX3_CFG_0_BD3REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.146 CORTEX3_CFG_0_ROM_REGISTER Register
- 14.8.1.2.147 CORTEX3_CFG_0_ID_REGISTER Register
- 14.8.1.2.148 CORTEX4_CFG_0_CSWREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.149 CORTEX4_CFG_0_DRWREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.150 CORTEX4_CFG_0_BD0REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.151 CORTEX4_CFG_0_BD1REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.152 CORTEX4_CFG_0_BD2REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.153 CORTEX4_CFG_0_BD3REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.154 CORTEX4_CFG_0_ROM_REGISTER Register
- 14.8.1.2.155 CORTEX4_CFG_0_ID_REGISTER Register
- 14.8.1.2.156 CORTEX5_CFG_0_CSWREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.157 CORTEX5_CFG_0_DRWREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.158 CORTEX5_CFG_0_BD0REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.159 CORTEX5_CFG_0_BD1REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.160 CORTEX5_CFG_0_BD2REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.161 CORTEX5_CFG_0_BD3REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.162 CORTEX5_CFG_0_ROM_REGISTER Register
- 14.8.1.2.163 CORTEX5_CFG_0_ID_REGISTER Register
- 14.8.1.2.164 CORTEX6_CFG_0_CSWREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.165 CORTEX6_CFG_0_DRWREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.166 CORTEX6_CFG_0_BD0REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.167 CORTEX6_CFG_0_BD1REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.168 CORTEX6_CFG_0_BD2REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.169 CORTEX6_CFG_0_BD3REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.170 CORTEX6_CFG_0_ROM_REGISTER Register
- 14.8.1.2.171 CORTEX6_CFG_0_ID_REGISTER Register
- 14.8.1.2.172 CORTEX7_CFG_0_CSWREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.173 CORTEX7_CFG_0_DRWREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.174 CORTEX7_CFG_0_BD0REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.175 CORTEX7_CFG_0_BD1REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.176 CORTEX7_CFG_0_BD2REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.177 CORTEX7_CFG_0_BD3REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.178 CORTEX7_CFG_0_ROM_REGISTER Register
- 14.8.1.2.179 CORTEX7_CFG_0_ID_REGISTER Register
- 14.8.1.2.180 CORTEX8_CFG_0_CSWREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.181 CORTEX8_CFG_0_DRWREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.182 CORTEX8_CFG_0_BD0REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.183 CORTEX8_CFG_0_BD1REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.184 CORTEX8_CFG_0_BD2REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.185 CORTEX8_CFG_0_BD3REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.186 CORTEX8_CFG_0_ROM_REGISTER Register
- 14.8.1.2.187 CORTEX8_CFG_0_ID_REGISTER Register
- 14.8.1.2.188 ROM_TABLE_1_0_ROM_ENTRY0 Register
- 14.8.1.2.189 ROM_TABLE_1_0_ROM_ENTRY1 Register
- 14.8.1.2.190 ROM_TABLE_1_0_ROM_ENTRY2 Register
- 14.8.1.2.191 ROM_TABLE_1_0_ROM_ENTRY3 Register
- 14.8.1.2.192 ROM_TABLE_1_0_ROM_ENTRY4 Register
- 14.8.1.2.193 ROM_TABLE_1_0_ROM_ENTRY5 Register
- 14.8.1.2.194 ROM_TABLE_1_0_COMPUTE_CLUSTER0 Register
- 14.8.1.2.195 ROM_TABLE_1_0_COMPUTE_CLUSTER1 Register
- 14.8.1.2.196 ROM_TABLE_1_0_COMPUTE_CLUSTER2 Register
- 14.8.1.2.197 ROM_TABLE_1_0_DEBUG_CELL0 Register
- 14.8.1.2.198 ROM_TABLE_1_0_DEBUG_CELL1 Register
- 14.8.1.2.199 ROM_TABLE_1_0_DEBUG_CELL2 Register
- 14.8.1.2.200 ROM_TABLE_1_0_DEBUG_CELL3 Register
- 14.8.1.2.201 ROM_TABLE_1_0_DEBUG_CELL4 Register
- 14.8.1.2.202 ROM_TABLE_1_0_DEBUG_CELL5 Register
- 14.8.1.2.203 ROM_TABLE_1_0_DEBUG_CELL6 Register
- 14.8.1.2.204 ROM_TABLE_1_0_DEBUG_CELL7 Register
- 14.8.1.2.205 ROM_TABLE_1_0_DEBUG_CELL8 Register
- 14.8.1.2.206 ROM_TABLE_1_0_DEBUG_CELL9 Register
- 14.8.1.2.207 ROM_TABLE_1_0_DEBUG_CELL10 Register
- 14.8.1.2.208 ROM_TABLE_1_0_DEBUG_CELL11 Register
- 14.8.1.2.209 ROM_TABLE_1_0_EXTCSCOMP0 Register
- 14.8.1.2.210 ROM_TABLE_1_0_EXTCSCOMP1 Register
- 14.8.1.2.211 ROM_TABLE_1_0_EXTCSCOMP2 Register
- 14.8.1.2.212 ROM_TABLE_1_0_EXTCSCOMP3 Register
- 14.8.1.2.213 ROM_TABLE_1_0_EXTCSCOMP4 Register
- 14.8.1.2.214 ROM_TABLE_1_0_EXTCSCOMP5 Register
- 14.8.1.2.215 ROM_TABLE_1_0_EXTCSCOMP6 Register
- 14.8.1.2.216 ROM_TABLE_1_0_EXTCSCOMP7 Register
- 14.8.1.2.217 ROM_TABLE_1_0_EXTCSCOMP8 Register
- 14.8.1.2.218 ROM_TABLE_1_0_EXTCSCOMP9 Register
- 14.8.1.2.219 ROM_TABLE_1_0_EXTCSCOMP10 Register
- 14.8.1.2.220 ROM_TABLE_1_0_EXTCSCOMP11 Register
- 14.8.1.2.221 CSCTI_CTICONTROL Register
- 14.8.1.2.222 CSCTI_CTIINTACK Register
- 14.8.1.2.223 CSCTI_CTIAPPSET Register
- 14.8.1.2.224 CSCTI_CTIAPPCLR Register
- 14.8.1.2.225 CSCTI_CTIAPPPULSE Register
- 14.8.1.2.226 CSCTI_CTIINEN0 Register
- 14.8.1.2.227 CSCTI_CTIINEN1 Register
- 14.8.1.2.228 CSCTI_CTIINEN2 Register
- 14.8.1.2.229 CSCTI_CTIINEN3 Register
- 14.8.1.2.230 CSCTI_CTIINEN4 Register
- 14.8.1.2.231 CSCTI_CTIINEN5 Register
- 14.8.1.2.232 CSCTI_CTIINEN6 Register
- 14.8.1.2.233 CSCTI_CTIINEN7 Register
- 14.8.1.2.234 CSCTI_CTIOUTEN0 Register
- 14.8.1.2.235 CSCTI_CTIOUTEN1 Register
- 14.8.1.2.236 CSCTI_CTIOUTEN2 Register
- 14.8.1.2.237 CSCTI_CTIOUTEN3 Register
- 14.8.1.2.238 CSCTI_CTIOUTEN4 Register
- 14.8.1.2.239 CSCTI_CTIOUTEN5 Register
- 14.8.1.2.240 CSCTI_CTIOUTEN6 Register
- 14.8.1.2.241 CSCTI_CTIOUTEN7 Register
- 14.8.1.2.242 CSCTI_CTITRIGINSTATUS Register
- 14.8.1.2.243 CSCTI_CTITRIGOUTSTATUS Register
- 14.8.1.2.244 CSCTI_CTICHINSTATUS Register
- 14.8.1.2.245 CSCTI_CTICHOUTSTATUS Register
- 14.8.1.2.246 CSCTI_CTIGATE Register
- 14.8.1.2.247 CSCTI_ASICCTL Register
- 14.8.1.2.248 CSCTI_ITCHINACK Register
- 14.8.1.2.249 CSCTI_ITTRIGINACK Register
- 14.8.1.2.250 CSCTI_ITCHOUT Register
- 14.8.1.2.251 CSCTI_ITTRIGOUT Register
- 14.8.1.2.252 CSCTI_ITCHOUTACK Register
- 14.8.1.2.253 CSCTI_ITTRIGOUTACK Register
- 14.8.1.2.254 CSCTI_ITCHIN Register
- 14.8.1.2.255 CSCTI_ITTRIGIN Register
- 14.8.1.2.256 CSCTI_ITCTRL Register
- 14.8.1.2.257 CSCTI_CLAIMSET Register
- 14.8.1.2.258 CSCTI_CLAIMCLR Register
- 14.8.1.2.259 CSCTI_LOCKACCESS Register
- 14.8.1.2.260 CSCTI_LOCKSTATUS Register
- 14.8.1.2.261 CSCTI_AUTHSTATUS Register
- 14.8.1.2.262 CSCTI_DEVID Register
- 14.8.1.2.263 CSCTI_DEVTYPE Register
- 14.8.1.2.264 CSCTI_PERIPHID4 Register
- 14.8.1.2.265 CSCTI_PERIPHID0 Register
- 14.8.1.2.266 CSCTI_PERIPHID1 Register
- 14.8.1.2.267 CSCTI_PERIPHID2 Register
- 14.8.1.2.268 CSCTI_PERIPHID3 Register
- 14.8.1.2.269 CSCTI_COMPONID0 Register
- 14.8.1.2.270 CSCTI_COMPONID1 Register
- 14.8.1.2.271 CSCTI_COMPONID2 Register
- 14.8.1.2.272 CSCTI_COMPONID3 Register
- 14.8.1.2.273 DRM_CFG_0_PERIPH_ID Register
- 14.8.1.2.274 DRM_CFG_0_VERSION Register
- 14.8.1.2.275 DRM_CFG_0_CAPABILITY Register
- 14.8.1.2.276 DRM_CFG_0_TRACE_CTRL Register
- 14.8.1.2.277 DRM_CFG_0_VBUSM_CTRL Register
- 14.8.1.2.278 DRM_CFG_0_DAP_TIMEOUT Register
- 14.8.1.2.279 DRM_CFG_0_CONFIG Register
- 14.8.1.2.280 DRM_CFG_0_EMUTRIGEN Register
- 14.8.1.2.281 DRM_CFG_0_BINVALLO Register
- 14.8.1.2.282 DRM_CFG_0_BINVALHI Register
- 14.8.1.2.283 DRM_CFG_0_SUSPEND_REG0 Register
- 14.8.1.2.284 DRM_CFG_0_SUSPEND_REG1 Register
- 14.8.1.2.285 DRM_CFG_0_SUSPEND_REG2 Register
- 14.8.1.2.286 DRM_CFG_0_SUSPEND_REG3 Register
- 14.8.1.2.287 DRM_CFG_0_SUSPEND_REG4 Register
- 14.8.1.2.288 DRM_CFG_0_SUSPEND_REG5 Register
- 14.8.1.2.289 DRM_CFG_0_SUSPEND_REG6 Register
- 14.8.1.2.290 DRM_CFG_0_SUSPEND_REG7 Register
- 14.8.1.2.291 DRM_CFG_0_SUSPEND_REG8 Register
- 14.8.1.2.292 DRM_CFG_0_SUSPEND_REG9 Register
- 14.8.1.2.293 DRM_CFG_0_SUSPEND_REG10 Register
- 14.8.1.2.294 DRM_CFG_0_SUSPEND_REG11 Register
- 14.8.1.2.295 DRM_CFG_0_SUSPEND_REG12 Register
- 14.8.1.2.296 DRM_CFG_0_SUSPEND_REG13 Register
- 14.8.1.2.297 DRM_CFG_0_SUSPEND_REG14 Register
- 14.8.1.2.298 DRM_CFG_0_SUSPEND_REG15 Register
- 14.8.1.2.299 DRM_CFG_0_SUSPEND_REG16 Register
- 14.8.1.2.300 DRM_CFG_0_SUSPEND_REG17 Register
- 14.8.1.2.301 DRM_CFG_0_SUSPEND_REG18 Register
- 14.8.1.2.302 DRM_CFG_0_SUSPEND_REG19 Register
- 14.8.1.2.303 DRM_CFG_0_SUSPEND_REG20 Register
- 14.8.1.2.304 DRM_CFG_0_SUSPEND_REG21 Register
- 14.8.1.2.305 DRM_CFG_0_SUSPEND_REG22 Register
- 14.8.1.2.306 DRM_CFG_0_SUSPEND_REG23 Register
- 14.8.1.2.307 DRM_CFG_0_SUSPEND_REG24 Register
- 14.8.1.2.308 DRM_CFG_0_SUSPEND_REG25 Register
- 14.8.1.2.309 DRM_CFG_0_SUSPEND_REG26 Register
- 14.8.1.2.310 DRM_CFG_0_SUSPEND_REG27 Register
- 14.8.1.2.311 DRM_CFG_0_SUSPEND_REG28 Register
- 14.8.1.2.312 DRM_CFG_0_SUSPEND_REG29 Register
- 14.8.1.2.313 DRM_CFG_0_SUSPEND_REG30 Register
- 14.8.1.2.314 DRM_CFG_0_SUSPEND_REG31 Register
- 14.8.1.2.315 CSTPIU_CFG_0_SUPPORTSIZE Register
- 14.8.1.2.316 CSTPIU_CFG_0_CURPORTSIZE Register
- 14.8.1.2.317 CSTPIU_CFG_0_TRIGMODEREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.318 CSTPIU_CFG_0_TRIGCTRREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.319 CSTPIU_CFG_0_TRIGMPYREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.320 CSTPIU_CFG_0_SUPTESTPAT Register
- 14.8.1.2.321 CSTPIU_CFG_0_CURTESTPAT Register
- 14.8.1.2.322 CSTPIU_CFG_0_TESTPATCNT Register
- 14.8.1.2.323 CSTPIU_CFG_0_FORMFLUSHSTAT Register
- 14.8.1.2.324 CSTPIU_CFG_0_FORMFLUSHCTL Register
- 14.8.1.2.325 CSTPIU_CFG_0_FORMSYNCCTR Register
- 14.8.1.2.326 CSTPIU_CFG_0_EXTCTLIN Register
- 14.8.1.2.327 CSTPIU_CFG_0_EXTCTLOUT Register
- 14.8.1.2.328 CSTPIU_CFG_0_ITTRFLINACK Register
- 14.8.1.2.329 CSTPIU_CFG_0_ITTRFLIN Register
- 14.8.1.2.330 CSTPIU_CFG_0_ITATBDATA0 Register
- 14.8.1.2.331 CSTPIU_CFG_0_ITATBCTR2 Register
- 14.8.1.2.332 CSTPIU_CFG_0_ITATBCTR1 Register
- 14.8.1.2.333 CSTPIU_CFG_0_ITATBCTR0 Register
- 14.8.1.2.334 CSTPIU_CFG_0_INTCTRL Register
- 14.8.1.2.335 CSTPIU_CFG_0_CTSET Register
- 14.8.1.2.336 CSTPIU_CFG_0_CTCLR Register
- 14.8.1.2.337 CSTPIU_CFG_0_LAREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.338 CSTPIU_CFG_0_LSREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.339 CSTPIU_CFG_0_AUTHST Register
- 14.8.1.2.340 CSTPIU_CFG_0_DEVID Register
- 14.8.1.2.341 CSTPIU_CFG_0_DEVTYPE Register
- 14.8.1.2.342 CSTPIU_CFG_0_PERID4 Register
- 14.8.1.2.343 CSTPIU_CFG_0_PERID0 Register
- 14.8.1.2.344 CSTPIU_CFG_0_PERID1 Register
- 14.8.1.2.345 CSTPIU_CFG_0_PERID2 Register
- 14.8.1.2.346 CSTPIU_CFG_0_PERID3 Register
- 14.8.1.2.347 CSTPIU_CFG_0_COMPID0 Register
- 14.8.1.2.348 CSTPIU_CFG_0_COMPID1 Register
- 14.8.1.2.349 CSTPIU_CFG_0_COMPID2 Register
- 14.8.1.2.350 CSTPIU_CFG_0_COMPID3 Register
- 14.8.1.2.351 CTF_CFG_0_CSTFCTLREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.352 CTF_CFG_0_PRIORCTLREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.353 CTF_CFG_0_ITATBDATA0 Register
- 14.8.1.2.354 CTF_CFG_0_ITATBCTR2 Register
- 14.8.1.2.355 CTF_CFG_0_ITATBCTR1 Register
- 14.8.1.2.356 CTF_CFG_0_ITATBCTR0 Register
- 14.8.1.2.357 CTF_CFG_0_INTCTRL Register
- 14.8.1.2.358 CTF_CFG_0_CTSET Register
- 14.8.1.2.359 CTF_CFG_0_CTCLR Register
- 14.8.1.2.360 CTF_CFG_0_LAREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.361 CTF_CFG_0_LSREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.362 CTF_CFG_0_AUTHST Register
- 14.8.1.2.363 CTF_CFG_0_DEVID Register
- 14.8.1.2.364 CTF_CFG_0_DEVTYPEID Register
- 14.8.1.2.365 CTF_CFG_0_PERID4 Register
- 14.8.1.2.366 CTF_CFG_0_PERID5 Register
- 14.8.1.2.367 CTF_CFG_0_PERID6 Register
- 14.8.1.2.368 CTF_CFG_0_PERID7 Register
- 14.8.1.2.369 CTF_CFG_0_PERID0 Register
- 14.8.1.2.370 CTF_CFG_0_PERID1 Register
- 14.8.1.2.371 CTF_CFG_0_PERID2 Register
- 14.8.1.2.372 CTF_CFG_0_PERID3 Register
- 14.8.1.2.373 CTF_CFG_0_COMPID0 Register
- 14.8.1.2.374 CTF_CFG_0_COMPID1 Register
- 14.8.1.2.375 CTF_CFG_0_COMPID2 Register
- 14.8.1.2.376 CTF_CFG_0_COMPID3 Register
- 14.8.1.2.377 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_ENTRY0 Register
- 14.8.1.2.378 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_ENTRY1 Register
- 14.8.1.2.379 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_ENTRY2 Register
- 14.8.1.2.380 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY0 Register
- 14.8.1.2.381 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY1 Register
- 14.8.1.2.382 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY2 Register
- 14.8.1.2.383 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY3 Register
- 14.8.1.2.384 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY4 Register
- 14.8.1.2.385 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY5 Register
- 14.8.1.2.386 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY6 Register
- 14.8.1.2.387 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY7 Register
- 14.8.1.2.388 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY8 Register
- 14.8.1.2.389 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY9 Register
- 14.8.1.2.390 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY10 Register
- 14.8.1.2.391 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY11 Register
- 14.8.1.2.392 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY12 Register
- 14.8.1.2.393 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY13 Register
- 14.8.1.2.394 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY14 Register
- 14.8.1.2.395 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY15 Register
- 14.8.1.2.396 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY16 Register
- 14.8.1.2.397 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY17 Register
- 14.8.1.2.398 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY18 Register
- 14.8.1.2.399 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY19 Register
- 14.8.1.2.400 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY20 Register
- 14.8.1.2.401 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY21 Register
- 14.8.1.2.402 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY22 Register
- 14.8.1.2.403 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY23 Register
- 14.8.1.2.404 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY24 Register
- 14.8.1.2.405 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY25 Register
- 14.8.1.2.406 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY26 Register
- 14.8.1.2.407 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY27 Register
- 14.8.1.2.408 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY28 Register
- 14.8.1.2.409 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY29 Register
- 14.8.1.2.410 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY30 Register
- 14.8.1.2.411 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY31 Register
- 14.8.1.2.412 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY32 Register
- 14.8.1.2.413 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY33 Register
- 14.8.1.2.414 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY34 Register
- 14.8.1.2.415 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY35 Register
- 14.8.1.2.416 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY36 Register
- 14.8.1.2.417 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY37 Register
- 14.8.1.2.418 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY38 Register
- 14.8.1.2.419 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY39 Register
- 14.8.1.2.420 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY40 Register
- 14.8.1.2.421 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY41 Register
- 14.8.1.2.422 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY42 Register
- 14.8.1.2.423 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY43 Register
- 14.8.1.2.424 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY44 Register
- 14.8.1.2.425 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY45 Register
- 14.8.1.2.426 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY46 Register
- 14.8.1.2.427 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY47 Register
- 14.8.1.2.428 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY48 Register
- 14.8.1.2.429 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY49 Register
- 14.8.1.2.430 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY50 Register
- 14.8.1.2.431 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY51 Register
- 14.8.1.2.432 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY52 Register
- 14.8.1.2.433 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY53 Register
- 14.8.1.2.434 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY54 Register
- 14.8.1.2.435 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY55 Register
- 14.8.1.2.436 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY56 Register
- 14.8.1.2.437 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY57 Register
- 14.8.1.2.438 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY58 Register
- 14.8.1.2.439 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY59 Register
- 14.8.1.2.440 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY60 Register
- 14.8.1.2.441 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY61 Register
- 14.8.1.2.442 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY62 Register
- 14.8.1.2.443 ROM_TABLE_0_1_ROM_MANUAL_ENTRY63 Register
- 14.8.1.2.444 ROM_TABLE_0_1_PERIPHID0 Register
- 14.8.1.2.445 ROM_TABLE_0_1_PERIPHID1 Register
- 14.8.1.2.446 ROM_TABLE_0_1_PERIPHID2 Register
- 14.8.1.2.447 ROM_TABLE_0_1_PERIPHID3 Register
- 14.8.1.2.448 ROM_TABLE_0_1_PERIPHID4 Register
- 14.8.1.2.449 ROM_TABLE_0_1_COMPID0 Register
- 14.8.1.2.450 ROM_TABLE_0_1_COMPID1 Register
- 14.8.1.2.451 ROM_TABLE_0_1_COMPID2 Register
- 14.8.1.2.452 ROM_TABLE_0_1_COMPID3 Register
- 14.8.1.2.453 CFGAP_CFG_1_JTAGID_REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.454 CFGAP_CFG_1_USERID_REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.455 CFGAP_CFG_1_VERSION_REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.456 CFGAP_CFG_1_APID_REGISTER Register
- 14.8.1.2.457 APBAP_CFG_1_CSWREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.458 APBAP_CFG_1_DRWREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.459 APBAP_CFG_1_BD0REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.460 APBAP_CFG_1_BD1REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.461 APBAP_CFG_1_BD2REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.462 APBAP_CFG_1_BD3REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.463 APBAP_CFG_1_ROM_REGISTER Register
- 14.8.1.2.464 APBAP_CFG_1_ID_REGISTER Register
- 14.8.1.2.465 AXIAP_CFG_1_CSWREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.466 AXIAP_CFG_1_DRWREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.467 AXIAP_CFG_1_BD0REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.468 AXIAP_CFG_1_BD1REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.469 AXIAP_CFG_1_BD2REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.470 AXIAP_CFG_1_BD3REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.471 AXIAP_CFG_1_MBT_REGISTER Register
- 14.8.1.2.472 AXIAP_CFG_1_ROM_HI_REGISTER Register
- 14.8.1.2.473 AXIAP_CFG_1_CFG_REGISTER Register
- 14.8.1.2.474 AXIAP_CFG_1_ROM_LO_REGISTER Register
- 14.8.1.2.475 AXIAP_CFG_1_ID_REGISTER Register
- 14.8.1.2.476 PWRAP_CFG_1_ID_REGISTER Register
- 14.8.1.2.477 PVIEW_CFG_1_PVIEW_STATE0 Register
- 14.8.1.2.478 PVIEW_CFG_1_PVIEW_CAPABILITY Register
- 14.8.1.2.479 PVIEW_CFG_1_ID_REGISTER Register
- 14.8.1.2.480 JTAGAP_CFG_1_CSW Register
- 14.8.1.2.481 JTAGAP_CFG_1_PSEL_REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.482 JTAGAP_CFG_1_PSTA_REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.483 JTAGAP_CFG_1_BYTEFIFO1 Register
- 14.8.1.2.484 JTAGAP_CFG_1_BYTEFIFO2 Register
- 14.8.1.2.485 JTAGAP_CFG_1_BYTEFIFO3 Register
- 14.8.1.2.486 JTAGAP_CFG_1_BYTEFIFO4 Register
- 14.8.1.2.487 JTAGAP_CFG_1_ID_REGISTER Register
- 14.8.1.2.488 SECAP_CFG_1_TXDATA Register
- 14.8.1.2.489 SECAP_CFG_1_TXCTRL Register
- 14.8.1.2.490 SECAP_CFG_1_RXDATA Register
- 14.8.1.2.491 SECAP_CFG_1_RXCTRL Register
- 14.8.1.2.492 CORTEX0_CFG_1_CSWREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.493 CORTEX0_CFG_1_DRWREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.494 CORTEX0_CFG_1_BD0REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.495 CORTEX0_CFG_1_BD1REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.496 CORTEX0_CFG_1_BD2REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.497 CORTEX0_CFG_1_BD3REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.498 CORTEX0_CFG_1_ROM_REGISTER Register
- 14.8.1.2.499 CORTEX0_CFG_1_ID_REGISTER Register
- 14.8.1.2.500 CORTEX1_CFG_1_CSWREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.501 CORTEX1_CFG_1_DRWREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.502 CORTEX1_CFG_1_BD0REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.503 CORTEX1_CFG_1_BD1REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.504 CORTEX1_CFG_1_BD2REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.505 CORTEX1_CFG_1_BD3REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.506 CORTEX1_CFG_1_ROM_REGISTER Register
- 14.8.1.2.507 CORTEX1_CFG_1_ID_REGISTER Register
- 14.8.1.2.508 CORTEX2_CFG_1_CSWREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.509 CORTEX2_CFG_1_DRWREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.510 CORTEX2_CFG_1_BD0REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.511 CORTEX2_CFG_1_BD1REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.512 CORTEX2_CFG_1_BD2REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.513 CORTEX2_CFG_1_BD3REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.514 CORTEX2_CFG_1_ROM_REGISTER Register
- 14.8.1.2.515 CORTEX2_CFG_1_ID_REGISTER Register
- 14.8.1.2.516 CORTEX3_CFG_1_CSWREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.517 CORTEX3_CFG_1_DRWREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.518 CORTEX3_CFG_1_BD0REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.519 CORTEX3_CFG_1_BD1REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.520 CORTEX3_CFG_1_BD2REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.521 CORTEX3_CFG_1_BD3REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.522 CORTEX3_CFG_1_ROM_REGISTER Register
- 14.8.1.2.523 CORTEX3_CFG_1_ID_REGISTER Register
- 14.8.1.2.524 CORTEX4_CFG_1_CSWREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.525 CORTEX4_CFG_1_DRWREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.526 CORTEX4_CFG_1_BD0REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.527 CORTEX4_CFG_1_BD1REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.528 CORTEX4_CFG_1_BD2REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.529 CORTEX4_CFG_1_BD3REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.530 CORTEX4_CFG_1_ROM_REGISTER Register
- 14.8.1.2.531 CORTEX4_CFG_1_ID_REGISTER Register
- 14.8.1.2.532 CORTEX5_CFG_1_CSWREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.533 CORTEX5_CFG_1_DRWREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.534 CORTEX5_CFG_1_BD0REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.535 CORTEX5_CFG_1_BD1REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.536 CORTEX5_CFG_1_BD2REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.537 CORTEX5_CFG_1_BD3REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.538 CORTEX5_CFG_1_ROM_REGISTER Register
- 14.8.1.2.539 CORTEX5_CFG_1_ID_REGISTER Register
- 14.8.1.2.540 CORTEX6_CFG_1_CSWREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.541 CORTEX6_CFG_1_DRWREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.542 CORTEX6_CFG_1_BD0REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.543 CORTEX6_CFG_1_BD1REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.544 CORTEX6_CFG_1_BD2REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.545 CORTEX6_CFG_1_BD3REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.546 CORTEX6_CFG_1_ROM_REGISTER Register
- 14.8.1.2.547 CORTEX6_CFG_1_ID_REGISTER Register
- 14.8.1.2.548 CORTEX7_CFG_1_CSWREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.549 CORTEX7_CFG_1_DRWREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.550 CORTEX7_CFG_1_BD0REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.551 CORTEX7_CFG_1_BD1REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.552 CORTEX7_CFG_1_BD2REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.553 CORTEX7_CFG_1_BD3REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.554 CORTEX7_CFG_1_ROM_REGISTER Register
- 14.8.1.2.555 CORTEX7_CFG_1_ID_REGISTER Register
- 14.8.1.2.556 CORTEX8_CFG_1_CSWREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.557 CORTEX8_CFG_1_DRWREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.558 CORTEX8_CFG_1_BD0REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.559 CORTEX8_CFG_1_BD1REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.560 CORTEX8_CFG_1_BD2REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.561 CORTEX8_CFG_1_BD3REG Register
- 14.8.1.2.562 CORTEX8_CFG_1_ROM_REGISTER Register
- 14.8.1.2.563 CORTEX8_CFG_1_ID_REGISTER Register
- 14.8.1.2.564 ROM_TABLE_1_1_ROM_ENTRY0 Register
- 14.8.1.2.565 ROM_TABLE_1_1_ROM_ENTRY1 Register
- 14.8.1.2.566 ROM_TABLE_1_1_ROM_ENTRY2 Register
- 14.8.1.2.567 ROM_TABLE_1_1_ROM_ENTRY3 Register
- 14.8.1.2.568 ROM_TABLE_1_1_ROM_ENTRY4 Register
- 14.8.1.2.569 ROM_TABLE_1_1_ROM_ENTRY5 Register
- 14.8.1.2.570 ROM_TABLE_1_1_COMPUTE_CLUSTER0 Register
- 14.8.1.2.571 ROM_TABLE_1_1_COMPUTE_CLUSTER1 Register
- 14.8.1.2.572 ROM_TABLE_1_1_COMPUTE_CLUSTER2 Register
- 14.8.1.2.573 ROM_TABLE_1_1_DEBUG_CELL0 Register
- 14.8.1.2.574 ROM_TABLE_1_1_DEBUG_CELL1 Register
- 14.8.1.2.575 ROM_TABLE_1_1_DEBUG_CELL2 Register
- 14.8.1.2.576 ROM_TABLE_1_1_DEBUG_CELL3 Register
- 14.8.1.2.577 ROM_TABLE_1_1_DEBUG_CELL4 Register
- 14.8.1.2.578 ROM_TABLE_1_1_DEBUG_CELL5 Register
- 14.8.1.2.579 ROM_TABLE_1_1_DEBUG_CELL6 Register
- 14.8.1.2.580 ROM_TABLE_1_1_DEBUG_CELL7 Register
- 14.8.1.2.581 ROM_TABLE_1_1_DEBUG_CELL8 Register
- 14.8.1.2.582 ROM_TABLE_1_1_DEBUG_CELL9 Register
- 14.8.1.2.583 ROM_TABLE_1_1_DEBUG_CELL10 Register
- 14.8.1.2.584 ROM_TABLE_1_1_DEBUG_CELL11 Register
- 14.8.1.2.585 ROM_TABLE_1_1_EXTCSCOMP0 Register
- 14.8.1.2.586 ROM_TABLE_1_1_EXTCSCOMP1 Register
- 14.8.1.2.587 ROM_TABLE_1_1_EXTCSCOMP2 Register
- 14.8.1.2.588 ROM_TABLE_1_1_EXTCSCOMP3 Register
- 14.8.1.2.589 ROM_TABLE_1_1_EXTCSCOMP4 Register
- 14.8.1.2.590 ROM_TABLE_1_1_EXTCSCOMP5 Register
- 14.8.1.2.591 ROM_TABLE_1_1_EXTCSCOMP6 Register
- 14.8.1.2.592 ROM_TABLE_1_1_EXTCSCOMP7 Register
- 14.8.1.2.593 ROM_TABLE_1_1_EXTCSCOMP8 Register
- 14.8.1.2.594 ROM_TABLE_1_1_EXTCSCOMP9 Register
- 14.8.1.2.595 ROM_TABLE_1_1_EXTCSCOMP10 Register
- 14.8.1.2.596 ROM_TABLE_1_1_EXTCSCOMP11 Register
- 14.8.1.2.597 CSCTI_CTICONTROL Register
- 14.8.1.2.598 CSCTI_CTIINTACK Register
- 14.8.1.2.599 CSCTI_CTIAPPSET Register
- 14.8.1.2.600 CSCTI_CTIAPPCLR Register
- 14.8.1.2.601 CSCTI_CTIAPPPULSE Register
- 14.8.1.2.602 CSCTI_CTIINEN0 Register
- 14.8.1.2.603 CSCTI_CTIINEN1 Register
- 14.8.1.2.604 CSCTI_CTIINEN2 Register
- 14.8.1.2.605 CSCTI_CTIINEN3 Register
- 14.8.1.2.606 CSCTI_CTIINEN4 Register
- 14.8.1.2.607 CSCTI_CTIINEN5 Register
- 14.8.1.2.608 CSCTI_CTIINEN6 Register
- 14.8.1.2.609 CSCTI_CTIINEN7 Register
- 14.8.1.2.610 CSCTI_CTIOUTEN0 Register
- 14.8.1.2.611 CSCTI_CTIOUTEN1 Register
- 14.8.1.2.612 CSCTI_CTIOUTEN2 Register
- 14.8.1.2.613 CSCTI_CTIOUTEN3 Register
- 14.8.1.2.614 CSCTI_CTIOUTEN4 Register
- 14.8.1.2.615 CSCTI_CTIOUTEN5 Register
- 14.8.1.2.616 CSCTI_CTIOUTEN6 Register
- 14.8.1.2.617 CSCTI_CTIOUTEN7 Register
- 14.8.1.2.618 CSCTI_CTITRIGINSTATUS Register
- 14.8.1.2.619 CSCTI_CTITRIGOUTSTATUS Register
- 14.8.1.2.620 CSCTI_CTICHINSTATUS Register
- 14.8.1.2.621 CSCTI_CTICHOUTSTATUS Register
- 14.8.1.2.622 CSCTI_CTIGATE Register
- 14.8.1.2.623 CSCTI_ASICCTL Register
- 14.8.1.2.624 CSCTI_ITCHINACK Register
- 14.8.1.2.625 CSCTI_ITTRIGINACK Register
- 14.8.1.2.626 CSCTI_ITCHOUT Register
- 14.8.1.2.627 CSCTI_ITTRIGOUT Register
- 14.8.1.2.628 CSCTI_ITCHOUTACK Register
- 14.8.1.2.629 CSCTI_ITTRIGOUTACK Register
- 14.8.1.2.630 CSCTI_ITCHIN Register
- 14.8.1.2.631 CSCTI_ITTRIGIN Register
- 14.8.1.2.632 CSCTI_ITCTRL Register
- 14.8.1.2.633 CSCTI_CLAIMSET Register
- 14.8.1.2.634 CSCTI_CLAIMCLR Register
- 14.8.1.2.635 CSCTI_LOCKACCESS Register
- 14.8.1.2.636 CSCTI_LOCKSTATUS Register
- 14.8.1.2.637 CSCTI_AUTHSTATUS Register
- 14.8.1.2.638 CSCTI_DEVID Register
- 14.8.1.2.639 CSCTI_DEVTYPE Register
- 14.8.1.2.640 CSCTI_PERIPHID4 Register
- 14.8.1.2.641 CSCTI_PERIPHID0 Register
- 14.8.1.2.642 CSCTI_PERIPHID1 Register
- 14.8.1.2.643 CSCTI_PERIPHID2 Register
- 14.8.1.2.644 CSCTI_PERIPHID3 Register
- 14.8.1.2.645 CSCTI_COMPONID0 Register
- 14.8.1.2.646 CSCTI_COMPONID1 Register
- 14.8.1.2.647 CSCTI_COMPONID2 Register
- 14.8.1.2.648 CSCTI_COMPONID3 Register
- 14.8.1.2.649 DRM_CFG_1_PERIPH_ID Register
- 14.8.1.2.650 DRM_CFG_1_VERSION Register
- 14.8.1.2.651 DRM_CFG_1_CAPABILITY Register
- 14.8.1.2.652 DRM_CFG_1_TRACE_CTRL Register
- 14.8.1.2.653 DRM_CFG_1_VBUSM_CTRL Register
- 14.8.1.2.654 DRM_CFG_1_DAP_TIMEOUT Register
- 14.8.1.2.655 DRM_CFG_1_CONFIG Register
- 14.8.1.2.656 DRM_CFG_1_EMUTRIGEN Register
- 14.8.1.2.657 DRM_CFG_1_BINVALLO Register
- 14.8.1.2.658 DRM_CFG_1_BINVALHI Register
- 14.8.1.2.659 DRM_CFG_1_SUSPEND_REG0 Register
- 14.8.1.2.660 DRM_CFG_1_SUSPEND_REG1 Register
- 14.8.1.2.661 DRM_CFG_1_SUSPEND_REG2 Register
- 14.8.1.2.662 DRM_CFG_1_SUSPEND_REG3 Register
- 14.8.1.2.663 DRM_CFG_1_SUSPEND_REG4 Register
- 14.8.1.2.664 DRM_CFG_1_SUSPEND_REG5 Register
- 14.8.1.2.665 DRM_CFG_1_SUSPEND_REG6 Register
- 14.8.1.2.666 DRM_CFG_1_SUSPEND_REG7 Register
- 14.8.1.2.667 DRM_CFG_1_SUSPEND_REG8 Register
- 14.8.1.2.668 DRM_CFG_1_SUSPEND_REG9 Register
- 14.8.1.2.669 DRM_CFG_1_SUSPEND_REG10 Register
- 14.8.1.2.670 DRM_CFG_1_SUSPEND_REG11 Register
- 14.8.1.2.671 DRM_CFG_1_SUSPEND_REG12 Register
- 14.8.1.2.672 DRM_CFG_1_SUSPEND_REG13 Register
- 14.8.1.2.673 DRM_CFG_1_SUSPEND_REG14 Register
- 14.8.1.2.674 DRM_CFG_1_SUSPEND_REG15 Register
- 14.8.1.2.675 DRM_CFG_1_SUSPEND_REG16 Register
- 14.8.1.2.676 DRM_CFG_1_SUSPEND_REG17 Register
- 14.8.1.2.677 DRM_CFG_1_SUSPEND_REG18 Register
- 14.8.1.2.678 DRM_CFG_1_SUSPEND_REG19 Register
- 14.8.1.2.679 DRM_CFG_1_SUSPEND_REG20 Register
- 14.8.1.2.680 DRM_CFG_1_SUSPEND_REG21 Register
- 14.8.1.2.681 DRM_CFG_1_SUSPEND_REG22 Register
- 14.8.1.2.682 DRM_CFG_1_SUSPEND_REG23 Register
- 14.8.1.2.683 DRM_CFG_1_SUSPEND_REG24 Register
- 14.8.1.2.684 DRM_CFG_1_SUSPEND_REG25 Register
- 14.8.1.2.685 DRM_CFG_1_SUSPEND_REG26 Register
- 14.8.1.2.686 DRM_CFG_1_SUSPEND_REG27 Register
- 14.8.1.2.687 DRM_CFG_1_SUSPEND_REG28 Register
- 14.8.1.2.688 DRM_CFG_1_SUSPEND_REG29 Register
- 14.8.1.2.689 DRM_CFG_1_SUSPEND_REG30 Register
- 14.8.1.2.690 DRM_CFG_1_SUSPEND_REG31 Register
- 14.8.1.2.691 CSTPIU_CFG_1_SUPPORTSIZE Register
- 14.8.1.2.692 CSTPIU_CFG_1_CURPORTSIZE Register
- 14.8.1.2.693 CSTPIU_CFG_1_TRIGMODEREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.694 CSTPIU_CFG_1_TRIGCTRREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.695 CSTPIU_CFG_1_TRIGMPYREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.696 CSTPIU_CFG_1_SUPTESTPAT Register
- 14.8.1.2.697 CSTPIU_CFG_1_CURTESTPAT Register
- 14.8.1.2.698 CSTPIU_CFG_1_TESTPATCNT Register
- 14.8.1.2.699 CSTPIU_CFG_1_FORMFLUSHSTAT Register
- 14.8.1.2.700 CSTPIU_CFG_1_FORMFLUSHCTL Register
- 14.8.1.2.701 CSTPIU_CFG_1_FORMSYNCCTR Register
- 14.8.1.2.702 CSTPIU_CFG_1_EXTCTLIN Register
- 14.8.1.2.703 CSTPIU_CFG_1_EXTCTLOUT Register
- 14.8.1.2.704 CSTPIU_CFG_1_ITTRFLINACK Register
- 14.8.1.2.705 CSTPIU_CFG_1_ITTRFLIN Register
- 14.8.1.2.706 CSTPIU_CFG_1_ITATBDATA0 Register
- 14.8.1.2.707 CSTPIU_CFG_1_ITATBCTR2 Register
- 14.8.1.2.708 CSTPIU_CFG_1_ITATBCTR1 Register
- 14.8.1.2.709 CSTPIU_CFG_1_ITATBCTR0 Register
- 14.8.1.2.710 CSTPIU_CFG_1_INTCTRL Register
- 14.8.1.2.711 CSTPIU_CFG_1_CTSET Register
- 14.8.1.2.712 CSTPIU_CFG_1_CTCLR Register
- 14.8.1.2.713 CSTPIU_CFG_1_LAREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.714 CSTPIU_CFG_1_LSREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.715 CSTPIU_CFG_1_AUTHST Register
- 14.8.1.2.716 CSTPIU_CFG_1_DEVID Register
- 14.8.1.2.717 CSTPIU_CFG_1_DEVTYPE Register
- 14.8.1.2.718 CSTPIU_CFG_1_PERID4 Register
- 14.8.1.2.719 CSTPIU_CFG_1_PERID0 Register
- 14.8.1.2.720 CSTPIU_CFG_1_PERID1 Register
- 14.8.1.2.721 CSTPIU_CFG_1_PERID2 Register
- 14.8.1.2.722 CSTPIU_CFG_1_PERID3 Register
- 14.8.1.2.723 CSTPIU_CFG_1_COMPID0 Register
- 14.8.1.2.724 CSTPIU_CFG_1_COMPID1 Register
- 14.8.1.2.725 CSTPIU_CFG_1_COMPID2 Register
- 14.8.1.2.726 CSTPIU_CFG_1_COMPID3 Register
- 14.8.1.2.727 CTF_CFG_1_CSTFCTLREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.728 CTF_CFG_1_PRIORCTLREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.729 CTF_CFG_1_ITATBDATA0 Register
- 14.8.1.2.730 CTF_CFG_1_ITATBCTR2 Register
- 14.8.1.2.731 CTF_CFG_1_ITATBCTR1 Register
- 14.8.1.2.732 CTF_CFG_1_ITATBCTR0 Register
- 14.8.1.2.733 CTF_CFG_1_INTCTRL Register
- 14.8.1.2.734 CTF_CFG_1_CTSET Register
- 14.8.1.2.735 CTF_CFG_1_CTCLR Register
- 14.8.1.2.736 CTF_CFG_1_LAREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.737 CTF_CFG_1_LSREG Register
- 14.8.1.2.738 CTF_CFG_1_AUTHST Register
- 14.8.1.2.739 CTF_CFG_1_DEVID Register
- 14.8.1.2.740 CTF_CFG_1_DEVTYPEID Register
- 14.8.1.2.741 CTF_CFG_1_PERID4 Register
- 14.8.1.2.742 CTF_CFG_1_PERID5 Register
- 14.8.1.2.743 CTF_CFG_1_PERID6 Register
- 14.8.1.2.744 CTF_CFG_1_PERID7 Register
- 14.8.1.2.745 CTF_CFG_1_PERID0 Register
- 14.8.1.2.746 CTF_CFG_1_PERID1 Register
- 14.8.1.2.747 CTF_CFG_1_PERID2 Register
- 14.8.1.2.748 CTF_CFG_1_PERID3 Register
- 14.8.1.2.749 CTF_CFG_1_COMPID0 Register
- 14.8.1.2.750 CTF_CFG_1_COMPID1 Register
- 14.8.1.2.751 CTF_CFG_1_COMPID2 Register
- 14.8.1.2.752 CTF_CFG_1_COMPID3 Register
- 14.8.2
PBIST
- 14.8.2.1 PBIST Summaries
- 14.8.2.2
PBIST Registers
- 14.8.2.2.1 PBIST_RF0L Register
- 14.8.2.2.2 PBIST_RF1L Register
- 14.8.2.2.3 PBIST_RF2L Register
- 14.8.2.2.4 PBIST_RF3L Register
- 14.8.2.2.5 PBIST_RF4L Register
- 14.8.2.2.6 PBIST_RF5L Register
- 14.8.2.2.7 PBIST_RF6L Register
- 14.8.2.2.8 PBIST_RF7L Register
- 14.8.2.2.9 PBIST_RF8L Register
- 14.8.2.2.10 PBIST_RF9L Register
- 14.8.2.2.11 PBIST_RF10L Register
- 14.8.2.2.12 PBIST_RF11L Register
- 14.8.2.2.13 PBIST_RF12L Register
- 14.8.2.2.14 PBIST_RF13L Register
- 14.8.2.2.15 PBIST_RF14L Register
- 14.8.2.2.16 PBIST_RF15L Register
- 14.8.2.2.17 PBIST_RF0U Register
- 14.8.2.2.18 PBIST_RF1U Register
- 14.8.2.2.19 PBIST_RF2U Register
- 14.8.2.2.20 PBIST_RF3U Register
- 14.8.2.2.21 PBIST_RF4U Register
- 14.8.2.2.22 PBIST_RF5U Register
- 14.8.2.2.23 PBIST_RF6U Register
- 14.8.2.2.24 PBIST_RF7U Register
- 14.8.2.2.25 PBIST_RF8U Register
- 14.8.2.2.26 PBIST_RF9U Register
- 14.8.2.2.27 PBIST_RF10U Register
- 14.8.2.2.28 PBIST_RF11U Register
- 14.8.2.2.29 PBIST_RF12U Register
- 14.8.2.2.30 PBIST_RF13U Register
- 14.8.2.2.31 PBIST_RF14U Register
- 14.8.2.2.32 PBIST_RF15U Register
- 14.8.2.2.33 PBIST_A0 Register
- 14.8.2.2.34 PBIST_A1 Register
- 14.8.2.2.35 PBIST_A2 Register
- 14.8.2.2.36 PBIST_A3 Register
- 14.8.2.2.37 PBIST_L0 Register
- 14.8.2.2.38 PBIST_L1 Register
- 14.8.2.2.39 PBIST_L2 Register
- 14.8.2.2.40 PBIST_L3 Register
- 14.8.2.2.41 PBIST_D Register
- 14.8.2.2.42 PBIST_E Register
- 14.8.2.2.43 PBIST_CA0 Register
- 14.8.2.2.44 PBIST_CA1 Register
- 14.8.2.2.45 PBIST_CA2 Register
- 14.8.2.2.46 PBIST_CA3 Register
- 14.8.2.2.47 PBIST_CL0 Register
- 14.8.2.2.48 PBIST_CL1 Register
- 14.8.2.2.49 PBIST_CL2 Register
- 14.8.2.2.50 PBIST_CL3 Register
- 14.8.2.2.51 PBIST_I0 Register
- 14.8.2.2.52 PBIST_I1 Register
- 14.8.2.2.53 PBIST_I2 Register
- 14.8.2.2.54 PBIST_I3 Register
- 14.8.2.2.55 PBIST_RAMT Register
- 14.8.2.2.56 PBIST_DLR Register
- 14.8.2.2.57 PBIST_CMS Register
- 14.8.2.2.58 PBIST_STR Register
- 14.8.2.2.59 PBIST_SCR Register
- 14.8.2.2.60 PBIST_CSR Register
- 14.8.2.2.61 PBIST_FDLY Register
- 14.8.2.2.62 PBIST_PACT Register
- 14.8.2.2.63 PBIST_PID Register
- 14.8.2.2.64 PBIST_OVER Register
- 14.8.2.2.65 PBIST_FSRF Register
- 14.8.2.2.66 PBIST_FSRC Register
- 14.8.2.2.67 PBIST_FSRA Register
- 14.8.2.2.68 PBIST_FSRDL0 Register
- 14.8.2.2.69 PBIST_FSRDL1 Register
- 14.8.2.2.70 PBIST_MARGIN_MODE Register
- 14.8.2.2.71 PBIST_WRENZ Register
- 14.8.2.2.72 PBIST_PAGE_PGS Register
- 14.8.2.2.73 PBIST_ROM Register
- 14.8.2.2.74 PBIST_ALGO Register
- 14.8.2.2.75 PBIST_RINFO Register
- 14.8.1
DEBUGSS_WRAP
- 14.1
System Interconnect Registers
- 15Revision History
12.1.4.3.1 MLBSS Block Diagram
Figure 12-47 shows the MLBSS block diagram. It includes the following functional blocks:
- MediaLB core – Implements the physical and link layer requirements of either a 3-pin or the 6-pin interface. Serial-to-parallel/parallel-to-serial are also implemented along with MediaLB frame synchronization.
- Routing fabric block – Manages the flow of data between the MediaLB core and the DMA block, implementing bus arbiter and muxing logic to the channel table RAM and the data buffer RAM.
- Channel table RAM (CTR) – Used for storing channel descriptors for managing accesses to dynamic buffers in the data buffer RAM.
- Data buffer RAM (DBR) – Provides dynamic circular buffering between the transmit and receive devices.
- Memory interface – Implements a bridge between the configuration TeraNet_CFG slave interface and the channel table RAM or data buffer RAM interfaces.
- DMA – Implements a bus bridge between the DMA master and the routing fabric block.
- Registers – Used for configuration.
- Interrupt logic.
- RAT – The MLBSS natively supports 32-bit addressing. As the SoC has 40-bit address bus a RAT module is put on the MLBSS master interface to translate the 32-bit addresses into 40-bit system addresses. For information about the RAT module functionality, see Region-based Address Translation (RAT) Module.
- ECC Aggregator – Performs single error correction and double error detection over the DBR. For information about the ECC aggregator functionality, see ECC Aggregator.
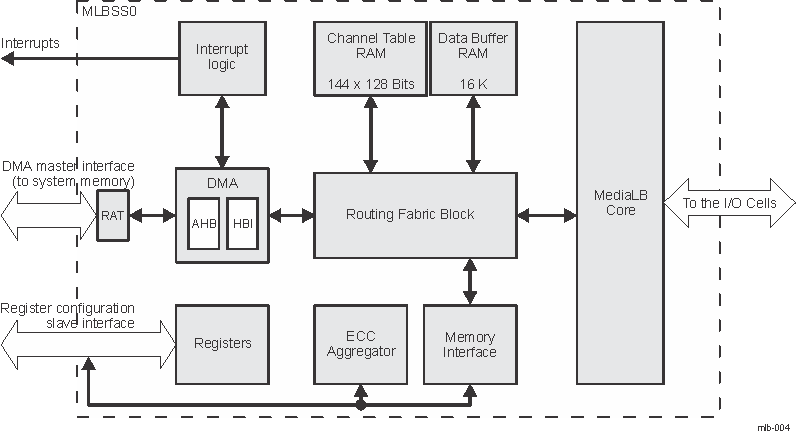
AHB - Advanced High-performance Bus
HBI - Host Bus Interface
Figure 12-47 MLBSS Structural Overview