ZHCSBT2G November 2012 – October 2017 66AK2H06 , 66AK2H12 , 66AK2H14
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 器件概述
- 2 修订历史记录
- 3 Device Comparison
- 4 Terminal Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
- 6 C66x CorePac
- 7 ARM CorePac
-
8 Memory, Interrupts, and EDMA for 66AK2Hxx
- 8.1 Memory Map Summary for 66AK2Hxx
- 8.2 Memory Protection Unit (MPU) for 66AK2Hxx
- 8.3 Interrupts for 66AK2Hxx
- 8.4 Enhanced Direct Memory Access (EDMA3) Controller for 66AK2Hxx
- 9 System Interconnect
-
10Device Boot and Configuration
- 10.1
Device Boot
- 10.1.1 Boot Sequence
- 10.1.2
Boot Modes Supported
- 10.1.2.1 Boot Device Field
- 10.1.2.2 Device Configuration Field
- 10.1.2.3 Serial Rapid I/O Boot Device Configuration
- 10.1.2.4 Ethernet (SGMII) Boot Device Configuration
- 10.1.2.5
Boot Parameter Table
- 10.1.2.5.1 EMIF16 Boot Parameter Table
- 10.1.2.5.2 SRIO Boot Parameter Table
- 10.1.2.5.3 Ethernet Boot Parameter Table
- 10.1.2.5.4 PCIe Boot Parameter Table
- 10.1.2.5.5 I2C Boot Parameter Table
- 10.1.2.5.6 SPI Boot Parameter Table
- 10.1.2.5.7 HyperLink Boot Parameter Table
- 10.1.2.5.8 UART Boot Parameter Table
- 10.1.2.5.9 NAND Boot Parameter Table
- 10.1.2.5.10 DDR3 Configuration Table
- 10.1.2.6 Second-Level Bootloaders
- 10.1.3 SoC Security
- 10.1.4 System PLL Settings
- 10.2
Device Configuration
- 10.2.1 Device Configuration at Device Reset
- 10.2.2 Peripheral Selection After Device Reset
- 10.2.3
Device State Control Registers
- 10.2.3.1 Device Status (DEVSTAT) Register
- 10.2.3.2 Device Configuration Register
- 10.2.3.3 JTAG ID (JTAGID) Register Description
- 10.2.3.4 Kicker Mechanism (KICK0 and KICK1) Register
- 10.2.3.5 DSP Boot Address Register (DSP_BOOT_ADDRn)
- 10.2.3.6 LRESETNMI PIN Status (LRSTNMIPINSTAT) Register
- 10.2.3.7 LRESETNMI PIN Status Clear (LRSTNMIPINSTAT_CLR) Register
- 10.2.3.8 Reset Status (RESET_STAT) Register
- 10.2.3.9 Reset Status Clear (RESET_STAT_CLR) Register
- 10.2.3.10 Boot Complete (BOOTCOMPLETE) Register
- 10.2.3.11 Power State Control (PWRSTATECTL) Register
- 10.2.3.12 NMI Event Generation to C66x CorePac (NMIGRx) Register
- 10.2.3.13 IPC Generation (IPCGRx) Registers
- 10.2.3.14 IPC Acknowledgment (IPCARx) Registers
- 10.2.3.15 IPC Generation Host (IPCGRH) Register
- 10.2.3.16 IPC Acknowledgment Host (IPCARH) Register
- 10.2.3.17 Timer Input Selection Register (TINPSEL)
- 10.2.3.18 Timer Output Selection Register (TOUTPSEL)
- 10.2.3.19 Reset Mux (RSTMUXx) Register
- 10.2.3.20 Device Speed (DEVSPEED) Register
- 10.2.3.21 ARM Endian Configuration Register 0 (ARMENDIAN_CFGr_0), r=0..7
- 10.2.3.22 ARM Endian Configuration Register 1 (ARMENDIAN_CFGr_1), r=0..7
- 10.2.3.23 ARM Endian Configuration Register 2 (ARMENDIAN_CFGr_2), r=0..7
- 10.2.3.24 Chip Miscellaneous Control (CHIP_MISC_CTL0) Register
- 10.2.3.25 Chip Miscellaneous Control (CHIP_MISC_CTL1) Register
- 10.2.3.26 System Endian Status Register (SYSENDSTAT)
- 10.2.3.27 SYNECLK_PINCTL Register
- 10.2.3.28
USB PHY Control (USB_PHY_CTLx) Registers
- Table 10-57 USB_PHY_CTL0 Register Field Descriptions
- Table 10-58 USB_PHY_CTL1 Register Field Descriptions
- Table 10-59 USB_PHY_CTL2 Register Field Descriptions
- Table 10-60 USB_PHY_CTL3 Register Field Descriptions
- Table 10-61 USB_PHY_CTL4 Register Field Descriptions
- Table 10-62 USB_PHY_CTL5 Register Field Descriptions
- 10.1
Device Boot
-
1166AK2Hxx Peripheral Information
- 11.1 Recommended Clock and Control Signal Transition Behavior
- 11.2 Power Supplies
- 11.3 Power Sleep Controller (PSC)
- 11.4 Reset Controller
- 11.5
Main PLL, ARM PLL, DDR3A PLL, DDR3B PLL, PASS PLL and the PLL Controllers
- 11.5.1 Main PLL Controller Device-Specific Information
- 11.5.2
PLL Controller Memory Map
- 11.5.2.1 PLL Secondary Control Register (SECCTL)
- 11.5.2.2 PLL Controller Divider Register (PLLDIV3 and PLLDIV4)
- 11.5.2.3 PLL Controller Clock Align Control Register (ALNCTL)
- 11.5.2.4 PLLDIV Divider Ratio Change Status Register (DCHANGE)
- 11.5.2.5 SYSCLK Status Register (SYSTAT)
- 11.5.2.6 Reset Type Status Register (RSTYPE)
- 11.5.2.7 Reset Control Register (RSTCTRL)
- 11.5.2.8 Reset Configuration Register (RSTCFG)
- 11.5.2.9 Reset Isolation Register (RSISO)
- 11.5.3 Main PLL Control Registers
- 11.5.4 ARM PLL Control Registers
- 11.5.5 Main PLL Controller, ARM, SRIO, HyperLink, PCIe, USB Clock Input Electrical Data and Timing
- 11.6 DDR3A PLL and DDR3B PLL
- 11.7 PASS PLL
- 11.8 External Interrupts
- 11.9 DDR3A and DDR3B Memory Controllers
- 11.10 I2C Peripheral
- 11.11 SPI Peripheral
- 11.12 HyperLink Peripheral
- 11.13 UART Peripheral
- 11.14 PCIe Peripheral
- 11.15 Packet Accelerator
- 11.16 Security Accelerator
- 11.17 Network Coprocessor Gigabit Ethernet (GbE) Switch Subsystem
- 11.18 SGMII and XFI Management Data Input/Output (MDIO)
- 11.19 Ten-Gigabit Ethernet (10GbE) Switch Subsystem
- 11.20 Timers
- 11.21 Serial RapidIO (SRIO) Port
- 11.22 General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO)
- 11.23 Semaphore2
- 11.24 Universal Serial Bus 3.0 (USB 3.0)
- 11.25 EMIF16 Peripheral
- 11.26 Emulation Features and Capability
- 11.27 Debug Port (EMUx)
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
11.2.1.1 Core-Before-IO Power Sequencing
The details of the Core-before-IO power sequencing are defined in Table 11-2. Figure 11-1 shows power sequencing and reset control of the 66AK2Hxx. POR may be removed after the power has been stable for the required 100 µsec. RESETFULL must be held low for a period (see item 9 in Figure 11-1) after the rising edge of POR, but may be held low for longer periods if necessary. The configuration bits shared with the GPIO pins will be latched on the rising edge of RESETFULL and must meet the setup and hold times specified. SYSCLK1 must always be active before POR can be removed.
NOTE
TI recommends a maximum of 80 ms between one power rail being valid and the next power rail in the sequence starting to ramp.
Table 11-2 Core-Before-IO Power Sequencing
| ITEM | SYSTEM STATE |
|---|---|
| 1 | Begin Power Stabilization Phase
|
| 2a |
|
| 2b |
|
| 2c |
|
| 2d |
|
| 3 |
|
| 3a |
|
| 4 |
|
| 5 |
|
| 6 |
|
| 7 |
|
| 8 |
|
| 9 |
|
| 10 |
|
| 11 |
|
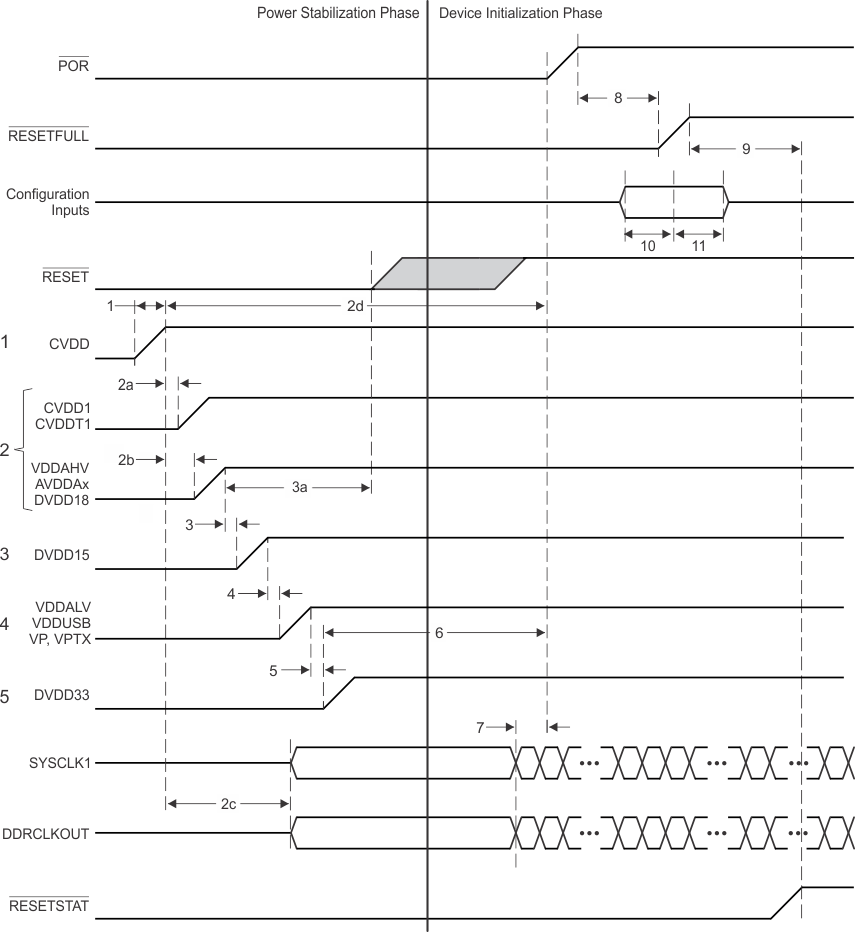 Figure 11-1 Core-Before-IO Power Sequencing
Figure 11-1 Core-Before-IO Power Sequencing