SPRUJ64 September 2022
- Abstract
- Trademarks
- 1Key Features
- 2AM64x SKEVM Overview
- 3Functional Block Diagram
-
4System Description
- 4.1 Clocking
- 4.2 Reset
- 4.3 Power Requirements
- 4.4 Configuration
- 4.5 JTAG
- 4.6 Test Automation
- 4.7 UART Interface
- 4.8 Memory Interfaces
- 4.9 Ethernet Interface
- 4.10 USB 3.0 Interface
- 4.11 PRU Connector
- 4.12 User Expansion Connector
- 4.13 MCU Connector
- 4.14 Interrupt
- 4.15 I2C Interface
- 4.16 IO Expander (GPIOs)
- 5Known Issues and Modifications
- 6Revision History
4.15 I2C Interface
There are three I2C interfaces used in SK EVM board.
- SoC_I2C0 Interface: SoC I2C [0] is connected to Board ID EEPROM, PMIC, PRU Header, and User Expansion Header. I2C0 interface is used by the software to identify the EVM through the Board ID memory device AT24C512C-MAHM-T 512Kb serial EEPROM configured to respond to addresses 0x51. I2C0 interface on the SKEVM is also used by the software to configure and control the PMIC device. I2C0 is also connected to the User expansion Header and PRU Header.
- SOC I2C (1) Interface: SoC I2C [1] is connected to 8-Bit LED driver, 8-Bit GPIO expander, Temperature Sensors, and Test Automation Header.
- SOC I2C (2) Interface: Connected I2C [2] from SoC to the User Expansion Header.
Figure 4-21 depicts the I2C tree.
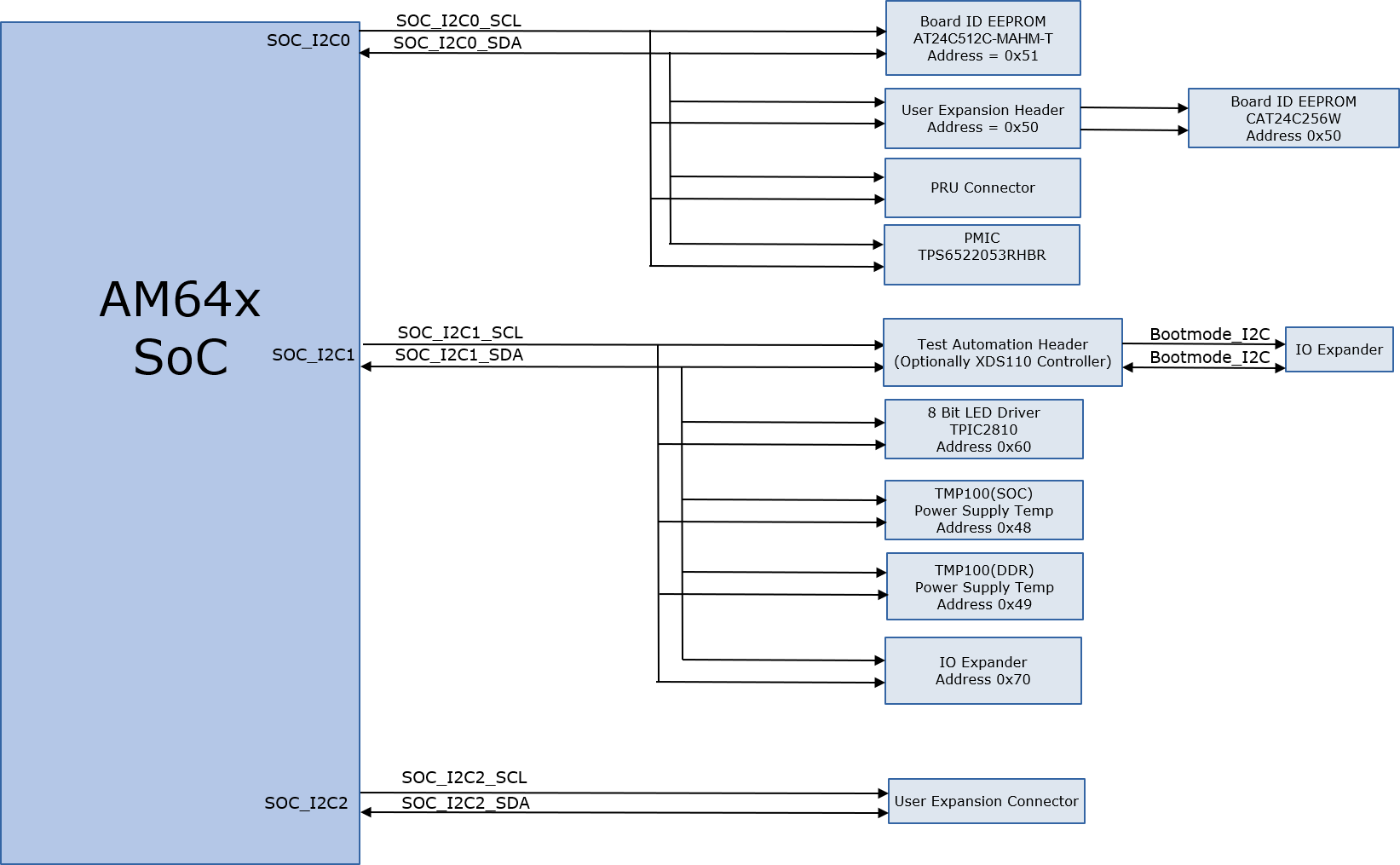 Figure 4-21 I2C Interface
Figure 4-21 I2C Interface