ZHCSNC8A February 2021 – March 2021 TPS541620
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Fixed-Frequency, Internally Compensated Advanced-Current-Mode Control
- 7.3.2 Enable and UVLO
- 7.3.3 Internal LDO
- 7.3.4 Pre-biased Output Start-up
- 7.3.5 Current Sharing
- 7.3.6 Frequency Selection and Minimum On-Time and Off-Time
- 7.3.7 Ramp Compensation Selection
- 7.3.8 Soft Start
- 7.3.9 Remote Sense Function
- 7.3.10 Adjustable Output Voltage
- 7.3.11 Power Good
- 7.3.12 Overcurrent Protection
- 7.3.13 Overvoltage and Undervoltage Protection
- 7.3.14 Overtemperature Protection
- 7.3.15 Frequency Synchronization
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application - Dual Independent Outputs
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Switching Frequency
- 8.2.2.2 Output Inductor Selection
- 8.2.2.3 Output Capacitor
- 8.2.2.4 Input Capacitor
- 8.2.2.5 Output Voltage Resistors Selection
- 8.2.2.6 Adjustable Undervoltage Lockout
- 8.2.2.7 Bootstrap Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.8 BP5 Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.9 PGOOD Pullup Resistor
- 8.2.2.10 Current Limit
- 8.2.2.11 Soft-Start Time Selection
- 8.2.2.12 MODE1 and MODE2 Pins
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 8.2.4
Typical Application - 2-Phase Operation
- 8.2.4.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.4.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.4.2.1 Switching Frequency
- 8.2.4.2.2 Output Inductor Selection
- 8.2.4.2.3 Output Capacitor
- 8.2.4.2.4 Input Capacitor
- 8.2.4.2.5 Output Voltage Resistors Selection
- 8.2.4.2.6 Adjustable Undervoltage Lockout
- 8.2.4.2.7 Bootstrap Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.4.2.8 BP5 Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.4.2.9 PGOOD Pullup Resistor
- 8.2.4.2.10 Current Limit
- 8.2.4.2.11 Soft-Start Time Selection
- 8.2.4.2.12 MODE1 Pin
- 8.2.4.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
7.3.15 Frequency Synchronization
The TPS541620 device can synchronize to an external clock, which must fall in the ±20% range of the internal frequency setting. For a standalone device, the external clock must be applied to the SYNC pin. A sudden change in synchronization clock frequency causes an associated control loop response. This change results in an overshoot or undershoot on the output voltage. When external sync is lost, the IC switches to its internal preset switching frequency.
When the device is synchronized to an external clock signal, if the external clock signal is missing, the device switches back to 75% of the preset free running frequency for approximately eight cycles. After that, the device runs at its free running frequency.
The following occurs in dual-phase configuration with external clock:
- Both the outputs of the device are tied together.
- Switching frequency is set by the clock received at the SYNC pin of the device.
- Clock phase shift is set by MODE1 pin of the device. See Current Sharing for more details.
- GOSNS functions as the GND remote sense input.
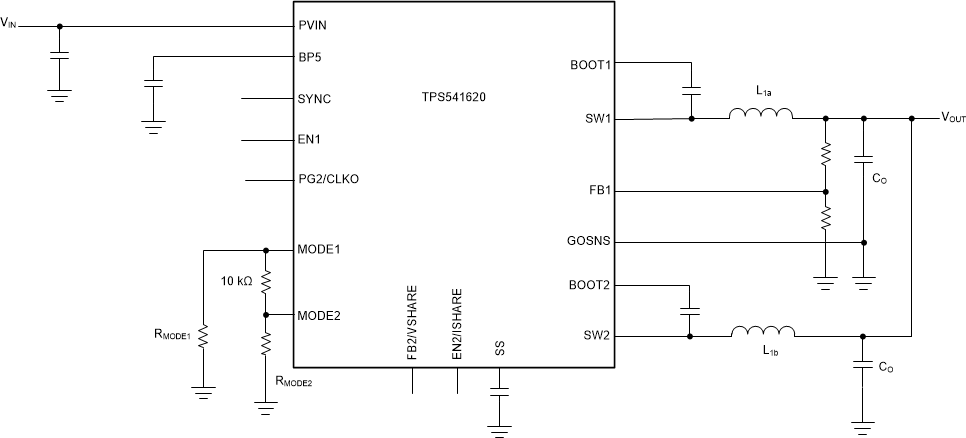 Figure 7-3 Dual-phase Configuration with External
Clock
Figure 7-3 Dual-phase Configuration with External
Clock