TIDUE59A May 2018 – September 2020
- Description
- Resources
- Features
- Applications
- 1System Description
-
2System Overview
- 2.1 Block Diagram
- 2.2 Design Considerations
- 2.3 Highlighted Products
- 2.4 System Design Theory
- 3Hardware, Software, Testing Requirements, and Test Results
- 4Design Files
- 5Software Files
- 6Related Documentation
- 7Terminology
- 8About the Author
- 9Revision History
3.2.3.3 DRV8837
To accurately measure the power consumption of the DRV8837 on the DRV8837EVM, several hardware modifications are required, in addition to the modifications described in Section 3.1.1. The complete list of hardware modifications required to accurately measure the power consumption of the DRV8837 follows (see Figure 3-13):
- Remove R3 and R4 (0-Ω resistors) from the back of the DRV8837EVM.
- Remove the LP2985 LDO voltage regulator (REG1) from the back of the DRV8837EVM.
- Remove the R1 pull down of the DIR pin on the front of the DRV8837EVM.
- Remove the MSP430G2131 MCU (U1) from the front of the DRV8837EVM.
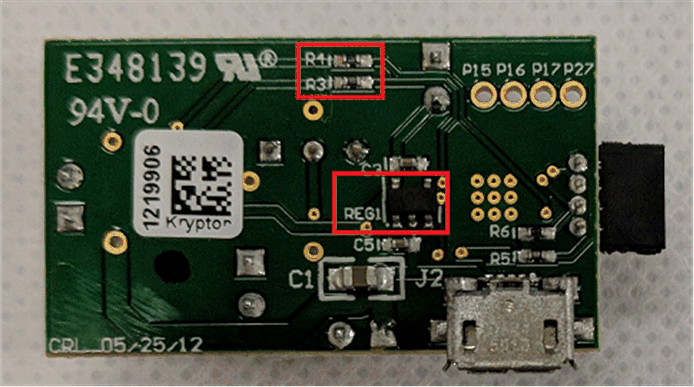 Figure 3-13 Back of DRV8837EVM With Components To Remove Highlighted
Figure 3-13 Back of DRV8837EVM With Components To Remove HighlightedWhen the modifications are complete, the following connections must be made to the DRV8837EVM to perform the power measurement (see Figure 3-14).
- Connect the IN1 and IN2 test points to P16 and P17 of the CC3220 LaunchPad headers, respectively.
- Connect the top of JP2 (nSleep) to P18 of the CC3220 LaunchPad headers.
- Connect the bottom of JP2 (VCC of DRV8837) to one of the 3V3 pins on the CC3220 LaunchPad.
- Apply power across J1 (VM and GND).
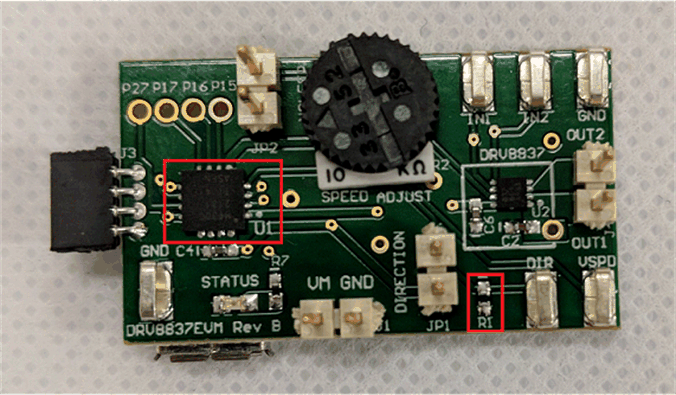 Figure 3-14 Front of DRV8837EVM With Highlighted Components To Remove
Figure 3-14 Front of DRV8837EVM With Highlighted Components To RemoveWhen testing the TIDC-01005, a 5-V input was used to power the DRV8837.