ZHCSK35C March 2019 – March 2021 TPS92682-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Device Enable
- 7.3.2 Internal Regulator and Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO)
- 7.3.3 Oscillator
- 7.3.4 Spread Spectrum Function
- 7.3.5 Gate Driver
- 7.3.6 Rail-to-Rail Current Sense Amplifier
- 7.3.7 Transconductance Error Amplifier
- 7.3.8 Switch Current Sense
- 7.3.9 Slope Compensation
- 7.3.10 ILED Setting in CC Mode
- 7.3.11 Output Voltage Setting in CV Mode
- 7.3.12 PWM Dimming
- 7.3.13 P-Channel FET Gate Driver Output
- 7.3.14 Soft Start
- 7.3.15 Two-Phase Operation
- 7.3.16 Faults and Diagnostics
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6
TPS92682 Registers
- 7.6.1 EN Register
- 7.6.2 CFG1 Register
- 7.6.3 CFG2 Register
- 7.6.4 SWDIV Register
- 7.6.5 ISLOPE Register
- 7.6.6 FM Register
- 7.6.7 SOFTSTART Register
- 7.6.8 CH1IADJ Register
- 7.6.9 CH2IADJ Register
- 7.6.10 PWMDIV Register
- 7.6.11 CH1PWML Register
- 7.6.12 CH1PWMH Register
- 7.6.13 CH2PWML Register
- 7.6.14 CH2PWMH Register
- 7.6.15 ILIM Register
- 7.6.16 IFT Register
- 7.6.17 MFT Register
- 7.6.18 FLT1 Register (read only)
- 7.6.19 FLT2 Register (read only)
- 7.6.20 FEN1 Register
- 7.6.21 FEN2 Register
- 7.6.22 FLATEN Register
- 7.6.23 OV Register
- 7.6.24 LHCFG Register
- 7.6.25 LHCH1IADJ Register
- 7.6.26 LHCH2IADJ Register
- 7.6.27 LHCH1PWML Register
- 7.6.28 LHCH1PWMH Register
- 7.6.29 LHCH2PWML Register
- 7.6.30 LHCH2PWMH Register
- 7.6.31 LHILIM Register
- 7.6.32 LHIFT Register
- 7.6.33 LHMFT Register
- 7.6.34 LHFEN1 Register
- 7.6.35 LHFEN2 Register
- 7.6.36 LHFLATEN Register
- 7.6.37 LHOV Register
- 7.6.38 CAL Register
- 7.6.39 RESET Register
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information General Design Considerations
- 8.2 Application Information CC Mode
- 8.3 Typical Application CV Mode
- 8.4
Typical Application CC Mode
- 8.4.1 CC Boost Design Requirements
- 8.4.2
CC Boost Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.4.2.1 Calculating Duty Cycle
- 8.4.2.2 Setting Switching Frequency
- 8.4.2.3 Setting Dither Modulation Frequency
- 8.4.2.4 Inductor Selection
- 8.4.2.5 Output Capacitor Selection
- 8.4.2.6 Input Capacitor Selection
- 8.4.2.7 Main N-Channel MOSFET Selection
- 8.4.2.8 Rectifier Diode Selection
- 8.4.2.9 Setting ILED and Selecting RCS
- 8.4.2.10 Setting Switch Current Limit
- 8.4.2.11 Slope Compensation
- 8.4.2.12 Compensator Parameters
- 8.4.2.13 Overvoltage Protection
- 8.4.2.14 Series P-Channel MOSFET Selection
- 8.4.3 CC Buck-Boost Design Requirements
- 8.4.4
CC Buck-Boost Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.4.4.1 Calculating Duty Cycle
- 8.4.4.2 Setting Switching Frequency
- 8.4.4.3 Setting Dither Modulation Frequency
- 8.4.4.4 Inductor Selection
- 8.4.4.5 Output Capacitor Selection
- 8.4.4.6 Input Capacitor Selection
- 8.4.4.7 Main N-Channel MOSFET Selection
- 8.4.4.8 Rectifier Diode Selection
- 8.4.4.9 Setting ILED and Selecting RCS
- 8.4.4.10 Setting Switch Current Limit
- 8.4.4.11 Slope Compensation
- 8.4.4.12 Compensator Parameters
- 8.4.4.13 Overvoltage Protection
- 8.4.5 PWM Dimming Consideration
- 8.4.6 Application Curves
- 8.5
Typical Application CV Mode
- 8.5.1 CV Design Requirements
- 8.5.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.5.2.1 Calculating Duty Cycle
- 8.5.2.2 Setting Switching Frequency
- 8.5.2.3 Setting Dither Modulation Frequency
- 8.5.2.4 Inductor Selection
- 8.5.2.5 Output Capacitor Selection
- 8.5.2.6 Input Capacitor Selection
- 8.5.2.7 Main N-Channel MOSFET Selection
- 8.5.2.8 Rectifier Diode Selection
- 8.5.2.9 Programming VOUT
- 8.5.2.10 Setting Switch Current Limit
- 8.5.2.11 Slope Compensation
- 8.5.2.12 Compensator Parameters
- 8.5.2.13 Overvoltage Protection
- 8.5.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
封装选项
机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
散热焊盘机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
订购信息
7.3.8 Switch Current Sense
Figure 7-9 shows the simplified block diagram of the switch current sense circuitry. The ISPx input pin monitors the main MOSFET current to implement peak current mode control. The GATEx output duty cycle is derived by comparing the peak switch current, measured by the RIS resistor, to the internal CHx_COMP voltage threshold. An internal slope signal, CHx_ISLOPE, is added to the measured sense voltage to prevent sub-harmonic oscillations for duty cycles greater than 50%.
An internal leading-edge blanking (LEB) is applied to the switch current sense at the beginning of each switching cycle by shunting the ISPx input to the ISNx (GND connection of the RIS) for the duration of the LEB time. The LEB circuit prevents unwanted duty cycle termination due to MOSFET switching-current spike at the beginning of the new switching cycle. The LEB time can be set to 150 ns or 75 ns (typical) using the CHxLEB bit set in Table 7-5. For additional noise suppression, connect an external low-pass RC filter with resistor values ranging from 100 Ω to 500 Ω and a 1000-pF capacitor across RIS.
Cycle-by-cycle current limit is accomplished by a separate internal comparator. The current limit threshold is set based on the status of internal PWM signal and the CHxILIM setting. The current limit threshold is set to a value programmed in the CHxILIM in Table 7-17 when PWM signal is high. The current limit threshold is set to 700 mV (typical) when PWM signal is low. In CC mode, the transition between the two thresholds in conjunction with the slope compensation and the error amplifier circuit allows for higher inductor current immediately after the PWM transition, to improve LED current transient response in PWM dimming.
The device immediately terminates the GATEx and PDRVx outputs when the sensed voltage at the ISPx input exceeds the current limit threshold. For more detail on the cycle-by-cycle current limit, refer to the Faults and Diagnostics section.
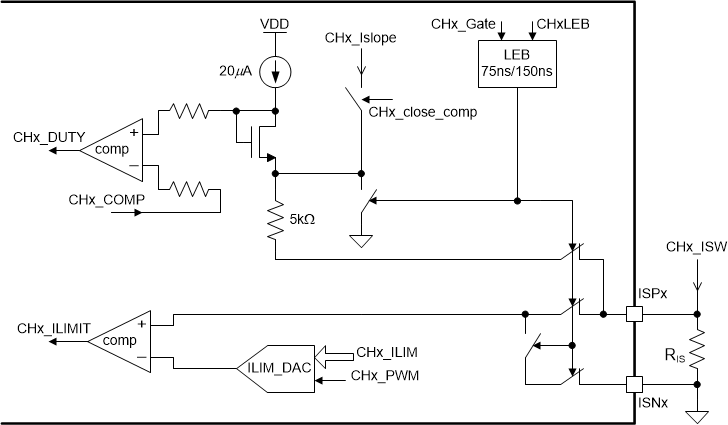 Figure 7-9 Switch Current Sense and Current Limit
Figure 7-9 Switch Current Sense and Current Limit