ZHCSK66C January 2014 – August 2019 ADS1283
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3 Feature Description
- 8.4
Device Functional Modes
- 8.4.1 Synchronization (SYNC PIN and SYNC Command)
- 8.4.2 Reset (RESET Pin and Reset Command)
- 8.4.3 Power-Down (PWDN Pin and STANDBY Command)
- 8.4.4 Power-On Sequence
- 8.4.5 DVDD Power Supply
- 8.4.6 Serial Interface
- 8.4.7 Data Format
- 8.4.8 Reading Data
- 8.4.9 One-Shot Operation
- 8.4.10 Offset and Full-Scale Calibration Registers
- 8.4.11 Calibration Commands (OFSCAL and GANCAL)
- 8.4.12 User Calibration
- 8.5
Programming
- 8.5.1
Commands
- 8.5.1.1 SDATAC Requirements
- 8.5.1.2 WAKEUP: Wake-Up From Standby Mode
- 8.5.1.3 STANDBY: Standby Mode
- 8.5.1.4 SYNC: Synchronize the Analog-to-Digital Conversion
- 8.5.1.5 RESET: Reset the Device
- 8.5.1.6 RDATAC: Read Data Continuous
- 8.5.1.7 SDATAC: Stop Read Data Continuous
- 8.5.1.8 RDATA: Read Data by Command
- 8.5.1.9 RREG: Read Register Data
- 8.5.1.10 WREG: Write to Register
- 8.5.1.11 OFSCAL: Offset Calibration
- 8.5.1.12 GANCAL: Gain Calibration
- 8.5.1
Commands
- 8.6
Register Maps
- 8.6.1
Register Descriptions
- 8.6.1.1 ID_CFG: ID_Configuration Register (address = 00h) [reset =x0h]
- 8.6.1.2 CONFIG0: Configuration Register 0 (address = 01h) [reset = 52h]
- 8.6.1.3 CONFIG1: Configuration Register 1 (address = 02h) [reset = 08h]
- 8.6.1.4 HPF0 and HPF1 Registers
- 8.6.1.5 OFC0, OFC1, OFC2 Registers
- 8.6.1.6 FSC0, FSC1, FSC2 Registers
- 8.6.1
Register Descriptions
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10器件和文档支持
- 11机械、封装和可订购信息
7.1 Noise Performance
The ADS1283 offers outstanding signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). The SNR depends on the ADC data rate and the PGA gain selected. As the bandwidth is reduced by decreasing the data rate, the SNR improves correspondingly. Similarly, as gain is increased, the input-referred noise decreases. The PGA noise is independent of gain; therefore, as the gain increases, the input range correspondingly decreases, resulting in decreased SNR.
The ADS1283 provides a chop feature that reduces the PGA 1/f noise. See the Programmable Gain Amplifier (PGA) section for more information about chopping. Table 1 summarizes the SNR and input noise voltage with the CHOP bit enabled. Disabling the CHOP bit results in increased low-frequency noise, particularly evident with high PGA gains and lower sample rates. Table 2 summarizes SNR and input noise voltage with CHOP disabled.
Table 1. Signal-to-Noise Ratio (dB) and Input Noise (µV), CHOP Bit Enabled
| DATA RATE (SPS) | PGA (SNR, dB)(1) | PGA (Input-Referred Noise, µV RMS) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 16 | 32 | 64 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 16 | 32 | 64 | |
| 250 | 130 | 129 | 129 | 127 | 125 | 119 | 114 | 0.59 | 0.30 | 0.16 | 0.10 | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.06 |
| 500 | 127 | 126 | 126 | 124 | 122 | 116 | 111 | 0.84 | 0.43 | 0.23 | 0.14 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.08 |
| 1000 | 124 | 123 | 123 | 121 | 119 | 113 | 108 | 1.19 | 0.60 | 0.32 | 0.20 | 0.13 | 0.12 | 0.11 |
| 2000 | 121 | 120 | 120 | 118 | 116 | 110 | 105 | 1.68 | 0.86 | 0.46 | 0.28 | 0.18 | 0.17 | 0.16 |
| 4000 | 117 | 117 | 117 | 115 | 113 | 107 | 102 | 2.40 | 1.22 | 0.66 | 0.40 | 0.26 | 0.25 | 0.23 |
Table 2. Signal-to-Noise Ratio (dB) and Input Noise (µV), CHOP Bit Disabled
| DATA RATE (SPS) | PGA (SNR, dB)(1) | PGA (Input-Referred Noise, µV RMS) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 16 | 32 | 64 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 16 | 32 | 64 | |
| 250 | 129 | 128 | 125 | 120 | 116 | 110 | 104 | 0.63 | 0.37 | 0.26 | 0.21 | 0.18 | 0.17 | 0.18 |
| 500 | 126 | 125 | 123 | 119 | 114 | 108 | 103 | 0.87 | 0.47 | 0.31 | 0.25 | 0.21 | 0.21 | 0.20 |
| 1000 | 123 | 123 | 121 | 117 | 114 | 108 | 102 | 1.20 | 0.65 | 0.39 | 0.30 | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.22 |
| 2000 | 120 | 120 | 119 | 116 | 112 | 107 | 101 | 1.69 | 0.91 | 0.51 | 0.37 | 0.26 | 0.25 | 0.25 |
| 4000 | 117 | 117 | 116 | 114 | 111 | 105 | 99 | 2.41 | 1.24 | 0.70 | 0.46 | 0.33 | 0.31 | 0.30 |
Input-referred noise is related to SNR by Equation 1:
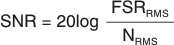
where
- FSRRMS = Full-scale range RMS = VREF / (2 × √2 × PGA)
- NRMS = Noise (RMS, input-referred)