ZHCSIS3D September 2018 – June 2025 DP83869HM
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Device Comparison
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 WoL (Wake-on-LAN) Packet Detection
- 7.3.2 Start of Frame Detect for IEEE 1588 Time Stamp
- 7.3.3 Clock Output
- 7.3.4 Loopback Mode
- 7.3.5 BIST Configuration
- 7.3.6 Interrupt
- 7.3.7 Power-Saving Modes
- 7.3.8 Mirror Mode
- 7.3.9 Speed Optimization
- 7.3.10 Cable Diagnostics
- 7.3.11 Fast Link Drop
- 7.3.12 Jumbo Frames
- 7.4
Device Functional Modes
- 7.4.1 Copper Ethernet
- 7.4.2 Fiber Ethernet
- 7.4.3 Serial GMII (SGMII)
- 7.4.4 Reduced GMII (RGMII)
- 7.4.5 Media Independent Interface (MII)
- 7.4.6 Bridge Modes
- 7.4.7 Media Convertor Mode
- 7.4.8 Register Configuration for Operational Modes
- 7.4.9 Serial Management Interface
- 7.4.10
Auto-Negotiation
- 7.4.10.1 Speed and Duplex Selection - Priority Resolution
- 7.4.10.2 Leader and Follower Resolution
- 7.4.10.3 Pause and Asymmetrical Pause Resolution
- 7.4.10.4 Next Page Support
- 7.4.10.5 Parallel Detection
- 7.4.10.6 Restart Auto-Negotiation
- 7.4.10.7 Enabling Auto-Negotiation Through Software
- 7.4.10.8 Auto-Negotiation Complete Time
- 7.4.10.9 Auto-MDIX Resolution
- 7.5
Programming
- 7.5.1
Strap Configuration
- 7.5.1.1 Straps for PHY Address
- 7.5.1.2 Strap for DP83869HM Functional Mode Selection
- 7.5.1.3 LED Default Configuration Based on Device Mode
- 7.5.1.4 Straps for RGMII/SGMII to Copper
- 7.5.1.5 Straps for RGMII to 1000Base-X
- 7.5.1.6 Straps for RGMII to 100Base-FX
- 7.5.1.7 Straps for Bridge Mode (SGMII-RGMII)
- 7.5.1.8 Straps for 100M Media Convertor
- 7.5.1.9 Straps for 1000M Media Convertor
- 7.5.2 LED Configuration
- 7.5.3 Reset Operation
- 7.5.1
Strap Configuration
- 7.6 Register Maps
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2 Typical Applications
- 8.3 Power Supply Recommendations
- 8.4 Layout
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Revision History
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
7.3.2.1 SFD Latency Variation and Determinism
Time stamping packet transmission and reception using the RX_CTRL and TX_CTRL signals of RGMII is not accurate enough for latency sensitive protocols. SFD pulses offers system designers a method to improve the accuracy of packet time stamping. The SFD pulse, while varying less than RGMII signals inherently, still exhibits latency variation due to the defined architecture of 1000BASE-T. This section provides a method to determine when an SFD latency variation has occurred and how to compensate for the variation in system software to improve timestamp accuracy.
In the following section the terms baseline latency and SFD variation are used. Baseline latency is the time measured between the TX_SFD pulse to the RX_SFD pulse of a connected link partner, assuming an Ethernet cable with all 4 pairs perfectly matched in propagation time. In the scenario where all 4 pairs being perfectly matched, a 1000BASE-T PHY do not have to align the 4 received symbols on the wire and do not introduce extra latency due to alignment.
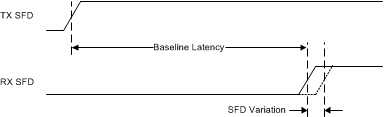 Figure 7-3 Baseline Latency and SFD Variation in Latency Measurement
Figure 7-3 Baseline Latency and SFD Variation in Latency MeasurementSFD variation is additional time added to the baseline latency before the RX_SFD pulse when the PHY must introduce latency to align the 4 symbols from the Ethernet cable. Variation can occur when a new link is established either by cable connection, auto-negotiation restart, PHY reset, or other external system effects. During a single, uninterrupted link, the SFD variation remains constant.
The DP83869HM can limit and report the variation applied to the SFD pulse while in the 1000Mb operating mode. Before a link is established in 1000Mb mode, the Sync FIFO Control Register (register address E9h) must be set to value 0xDF22. The below SFD variation compensation method can only be applied after the Sync FIFO Control Register has been initialized and a new link has been established. Setting the Sync FIFO Control register value and then performing a software restart by setting the SW_RESTART bit[14] in the Control Register (register address 1Fh) if a link is already present is acceptable.