SLUSFR7 August 2025 BQ24810
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
-
6 Detailed Description
- 6.1 Overview
- 6.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 6.3
Feature Description
- 6.3.1 Device Power Up
- 6.3.2 System Power Selection
- 6.3.3 Current and Power Monitor
- 6.3.4 Processor Hot Indication for CPU Throttling
- 6.3.5 Input Current Dynamic Power Management
- 6.3.6 Two-Level Adapter Current Limit (Peak Power Mode)
- 6.3.7 EMI Switching Frequency Adjust
- 6.3.8 Device Protections Features
- 6.4 Device Functional Modes
- 6.5 Programming
- 6.6
Register Maps
- 6.6.1 Battery-Charger Commands
- 6.6.2 Setting Charger Options
- 6.6.3 ChargeOption1 Register
- 6.6.4 ChargeOption2 Register
- 6.6.5 ChargeOption3 Register
- 6.6.6 ChargeOption4 Register
- 6.6.7 ProchotOption0 Register
- 6.6.8 ProchotOption1 Register
- 6.6.9 ProchotStatus Register
- 6.6.10 Charge Current Register
- 6.6.11 Charge Voltage Register
- 6.6.12 Discharge Current Register
- 6.6.13 Minimum System Voltage Register
- 6.6.14 Input Current Register
- 6.6.15 Register Exceptions
-
7 Application and Implementation
- 7.1 Application Information
- 7.2
Typical Applications
- 7.2.1
Typical System Schematic
- 7.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 7.2.1.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 7.2.1.2.1 Adapter Current Sense Filter
- 7.2.1.2.2 Negative Output Voltage Protection
- 7.2.1.2.3 Reverse Input Voltage Protection
- 7.2.1.2.4 Reduce Battery Quiescent Current
- 7.2.1.2.5 CIN Capacitance
- 7.2.1.2.6 L1 Inductor Selection
- 7.2.1.2.7 CBATT Capacitance
- 7.2.1.2.8 Buck Charging Internal Compensation
- 7.2.1.2.9 CSYS Capacitance
- 7.2.1.2.10 Battery Only Boost Internal Compensation
- 7.2.1.2.11 Power MOSFETs Selection
- 7.2.1.2.12 Input Filter Design
- 7.2.1.3 Application Curves
- 7.2.2 Migration from Previous Devices (Does Not Support Battery Only Boost)
- 7.2.1
Typical System Schematic
- 7.3 Power Supply Recommendations
- 7.4 Layout
- 8 Device and Documentation Support
- 9 Revision History
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
6.3.4 Processor Hot Indication for CPU Throttling
When CPU is running turbo mode, the peak power may exceed total available power from adapter and battery. The BQ24810 provides the PROCHOT output to signal the CPU that an overload condition has occurred. When adapter or battery discharge current exceeds the allowed threshold or system voltage drops, this indicates an overload condition has occurred. Likewise, adapter or battery removal may result in insufficient power for the CPU. The processor hot function in the BQ24810 monitors these events, and optionally asserts the PROCHOT signal when they occur.
The PROCHOT triggering events are:
- ICRIT: adapter peak current (110% of ILIM2), internal maximum upper limit is 200mV across ACP/ACN voltage.
- INOM: adapter average current (110% of ILIM1)
- IDCHG: battery discharge current
- VBATT: battery voltage on SRP
- ACOK: upon adapter removal (ACOK pin HIGH to LOW)
- BATPRES: upon battery removal ( BATPRES pin LOW to HIGH)
- CMPOUT: Independent comparator output (CMPOUT pin HIGH to LOW)
- Adapter insertion while battery only boost is active (triggers ICRIT event if enabled.)
The threshold of ICRIT, IDCHG or VBATT, and the deglitch time of ICRIT, INOM, IDCHG or CMPOUT are programmable through SMBus. Each triggering event can be individually enabled in REG0x3D[6:0]. The ICRIT threshold is 110% of the ILIM2 value as set in REG0x3C[14:11]. When ILIM2 is set to a low value, and particularly when the ICRIT deglitch is set to one of the faster values of 10 or 100 uS, the ICRIT PROCHOTmay trip upon adapter insertion due to inrush current. The exact values which may cause this depend on the amount of capacitance on the system rail and the voltage difference between the adapter and battery. Larger capacitance will lead to larger inrush current, as will larger voltage difference between the adapter and battery. This is most likely to be a concern if the ILIM2 value is set to 512 mA or less.
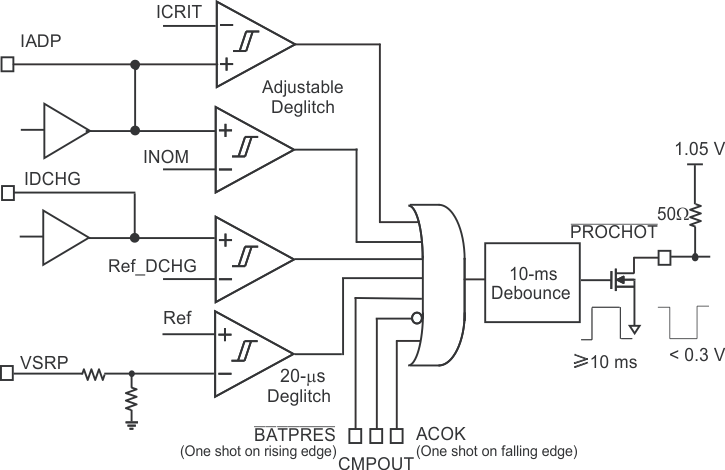 Figure 6-1 PROCHOT Profile
Figure 6-1 PROCHOT ProfileWhen any event in PROCHOT profile is triggered, PROCHOT is asserted low for minimum 10 ms (default REG0x3C[4:3]=10). At the end of the 10 ms, if the PROCHOT event is still active, the pulse gets extended.
If multiple PROCHOT events occur while the PROCHOT signal remains asserted low, all of the triggering events are saved in status register REG0x3A[6:0]. If the PROCHOT signal deasserts and then is reasserted, the status register will be cleared upon the new high to low transition of the PROCHOT signal so that only the newly detected event is read. Whenever the host reads REG0x3A, this will also clear all of the flagged events from that register after they are read.