SLUSFR7 August 2025 BQ24810
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
-
6 Detailed Description
- 6.1 Overview
- 6.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 6.3
Feature Description
- 6.3.1 Device Power Up
- 6.3.2 System Power Selection
- 6.3.3 Current and Power Monitor
- 6.3.4 Processor Hot Indication for CPU Throttling
- 6.3.5 Input Current Dynamic Power Management
- 6.3.6 Two-Level Adapter Current Limit (Peak Power Mode)
- 6.3.7 EMI Switching Frequency Adjust
- 6.3.8 Device Protections Features
- 6.4 Device Functional Modes
- 6.5 Programming
- 6.6
Register Maps
- 6.6.1 Battery-Charger Commands
- 6.6.2 Setting Charger Options
- 6.6.3 ChargeOption1 Register
- 6.6.4 ChargeOption2 Register
- 6.6.5 ChargeOption3 Register
- 6.6.6 ChargeOption4 Register
- 6.6.7 ProchotOption0 Register
- 6.6.8 ProchotOption1 Register
- 6.6.9 ProchotStatus Register
- 6.6.10 Charge Current Register
- 6.6.11 Charge Voltage Register
- 6.6.12 Discharge Current Register
- 6.6.13 Minimum System Voltage Register
- 6.6.14 Input Current Register
- 6.6.15 Register Exceptions
-
7 Application and Implementation
- 7.1 Application Information
- 7.2
Typical Applications
- 7.2.1
Typical System Schematic
- 7.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 7.2.1.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 7.2.1.2.1 Adapter Current Sense Filter
- 7.2.1.2.2 Negative Output Voltage Protection
- 7.2.1.2.3 Reverse Input Voltage Protection
- 7.2.1.2.4 Reduce Battery Quiescent Current
- 7.2.1.2.5 CIN Capacitance
- 7.2.1.2.6 L1 Inductor Selection
- 7.2.1.2.7 CBATT Capacitance
- 7.2.1.2.8 Buck Charging Internal Compensation
- 7.2.1.2.9 CSYS Capacitance
- 7.2.1.2.10 Battery Only Boost Internal Compensation
- 7.2.1.2.11 Power MOSFETs Selection
- 7.2.1.2.12 Input Filter Design
- 7.2.1.3 Application Curves
- 7.2.2 Migration from Previous Devices (Does Not Support Battery Only Boost)
- 7.2.1
Typical System Schematic
- 7.3 Power Supply Recommendations
- 7.4 Layout
- 8 Device and Documentation Support
- 9 Revision History
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
7.4.2.3 Layout Consideration for Short Circuit Protection
The BQ24810 has a unique short circuit protection feature. Its cycle-by-cycle current monitoring feature is achieved through monitoring the voltage drop across RDS(on) of the MOSFETs after a certain amount of blanking time. For a MOSFET short or inductor short circuit, the over current condition is sensed by two comparators, and two counters are triggered. After seven occurrences of a short circuit event, the charger will be latched off. To reset the charger from latch-off status, remove and then reconnect the adapter. Figure 7-25 shows the BQ24810 short circuit protection block diagram.
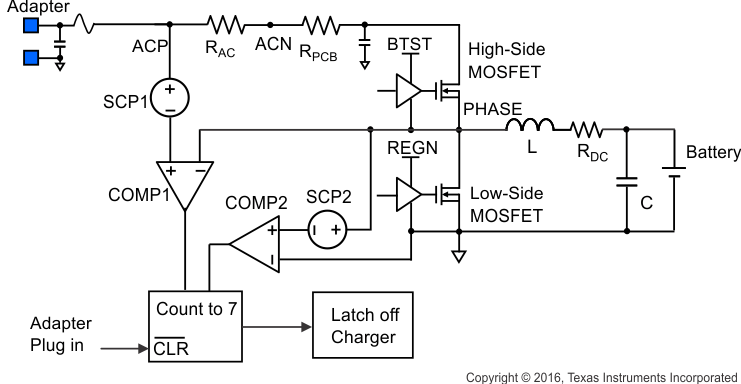 Figure 7-25 Block Diagram of BQ24810
Short Circuit Protection
Figure 7-25 Block Diagram of BQ24810
Short Circuit ProtectionIn normal operation, the low side MOSFET current is from source to drain which generates a negative voltage drop when it turns on, as a result the over current comparator can not be triggered. When the high side switch short circuit or inductor short circuit happens, the large current of low side MOSFET is from drain to source and can trigger low side switch over current comparator. The BQ24810 senses the low side switch voltage drop through the PHASE pin and GND pin.
The high-side FET short is detected by monitoring the voltage drop between ACP and PHASE. As a result, it not only monitors the high side switch voltage drop, but also the adapter sensing resistor voltage drop and PCB trace voltage drop from ACN pin of RAC to charger high side switch drain. Usually, there is a long trance between input sensing resistor and charger converting input, a careful layout will minimize the trace effect.
To prevent unintentional charger shut down in normal operation, MOSFET RDS(on) selection and PCB layout is very important. Figure 7-26 shows a improvement PCB layout example and its equivalent circuit. In this layout, the system current path and charger input current path is not separated, as a result, the system current causes voltage drop in the PCB copper and is sensed by the IC. The worst layout is when a system current pull point is after charger input; as a result all system current voltage drops are counted into over current protection comparator. The worst case for IC is when the total system current and charger input current sum equals the DPM current. When the system pulls more current, the charger IC tries to regulate the RAC current as a constant current by reducing the charging current.
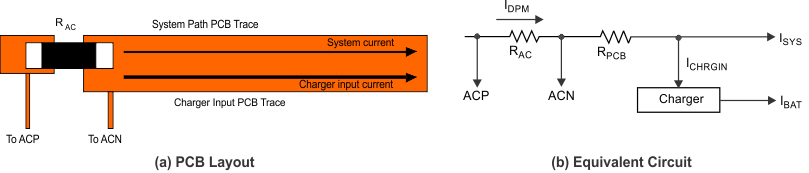 Figure 7-26 PCB Layout Example
Figure 7-26 PCB Layout ExampleFigure 7-27 shows the optimized PCB layout example. The system current path and charge input current path is separated, as a result the IC only senses charger input current caused PCB voltage drop and minimized the possibility of unintentional charger shut down in normal operation. This also makes PCB layout easier for high system current application.
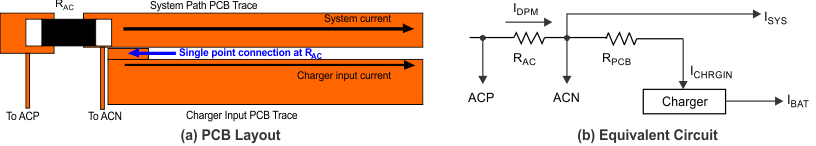 Figure 7-27 Optimized PCB Layout Example
Figure 7-27 Optimized PCB Layout ExampleThe total voltage drop sensed by IC can be express as the following equation.
where the RAC is the AC adapter current sensing resistance, IDPM is the DPM current set point, RPCB is the PCB trace equivalent resistance, ICHRGIN is the charger input current, k is the PCB factor, RDS(on) is the high side MOSFET turn on resistance and IPEAK is the peak current of inductor. Here the PCB factor k equals 0 means the best layout shown in Figure 7-27 where the PCB trace only goes through charger input current while k equals 1 means the worst layout shown in Figure 7-26 where the PCB trace goes through all the DPM current. The total voltage drop must below the high side short circuit protection threshold to prevent unintentional charger shut down in normal operation.
The low side MOSFET short circuit voltage drop threshold can be adjusted via SMBus command. ChargeOption() bit[7] disables LSFET protection when set to 0 and enables the protectoin with a threshold of 250 mV when set to 1. The high side MOSFET short circuit voltage drop threshold can be adjusted via SMBus command. ChargeOption() bit[8] disables HSFET protection when set to 0 and enables the protection with a threshold of 750 mV when set to 1. For a fixed PCB layout, host should set proper short circuit protection threshold level to prevent unintentional charger shut down in normal operation.