ZHCSRW0C February 2023 – November 2025 AM68 , AM68A
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 器件比较
-
5 端子配置和功能
- 5.1 引脚图
- 5.2 引脚属性
- 5.3
信号说明
- 13
- 5.3.1 ADC
- 5.3.2 DDRSS
- 5.3.3 GPIO
- 5.3.4 I2C
- 5.3.5 I3C
- 5.3.6 MCAN
- 5.3.7 MCSPI
- 5.3.8 UART
- 5.3.9 MDIO
- 5.3.10 CPSW2G
- 5.3.11 ECAP
- 5.3.12 EQEP
- 5.3.13 EPWM
- 5.3.14 USB
- 5.3.15 显示端口
- 5.3.16 HyperLink
- 5.3.17 PCIE
- 5.3.18 SERDES
- 5.3.19 DSI
- 5.3.20 CSI
- 5.3.21 MCASP
- 5.3.22 DMTIMER
- 5.3.23 CPTS
- 5.3.24 DSS
- 5.3.25 GPMC
- 5.3.26 MMC
- 5.3.27 OSPI
- 5.3.28 Hyperbus
- 5.3.29 仿真和调试
- 5.3.30 系统和其他
- 5.3.31 电源
- 5.4 未使用引脚的连接
-
6 规格
- 6.1 绝对最大额定值
- 6.2 ESD 等级
- 6.3 建议运行条件
- 6.4 通电时间 (POH) 限制
- 6.5 运行性能点
- 6.6 电气特性
- 6.7 一次性可编程 (OTP) 电子保险丝的 VPP 规格
- 6.8 热阻特性
- 6.9 温度传感器特性
- 6.10
时序和开关特性
- 6.10.1 时序参数和信息
- 6.10.2 电源时序控制
- 6.10.3 系统时序
- 6.10.4 时钟规格
- 6.10.5
外设
- 6.10.5.1 ATL
- 6.10.5.2 CPSW2G
- 6.10.5.3 CSI-2
- 6.10.5.4 DDRSS
- 6.10.5.5 DSS
- 6.10.5.6 eCAP
- 6.10.5.7 EPWM
- 6.10.5.8 eQEP
- 6.10.5.9 GPIO
- 6.10.5.10 GPMC
- 6.10.5.11 HyperBus
- 6.10.5.12 I2C
- 6.10.5.13 I3C
- 6.10.5.14 MCAN
- 6.10.5.15 MCASP
- 6.10.5.16 MCSPI
- 6.10.5.17 MMCSD
- 6.10.5.18 CPTS
- 6.10.5.19 OSPI
- 6.10.5.20 PCIE
- 6.10.5.21 计时器
- 6.10.5.22 UART
- 6.10.5.23 USB
- 6.10.6 仿真和调试
- 7 详细说明
- 8 应用、实施和布局
- 9 器件和文档支持
- 10修订历史记录
- 11机械、封装和可订购信息
6.10.2.5 隔离式 MCU 域和 Main 域下电时序 - 选项 1
图 6-7 介绍了选项 1 的器件下电时序。
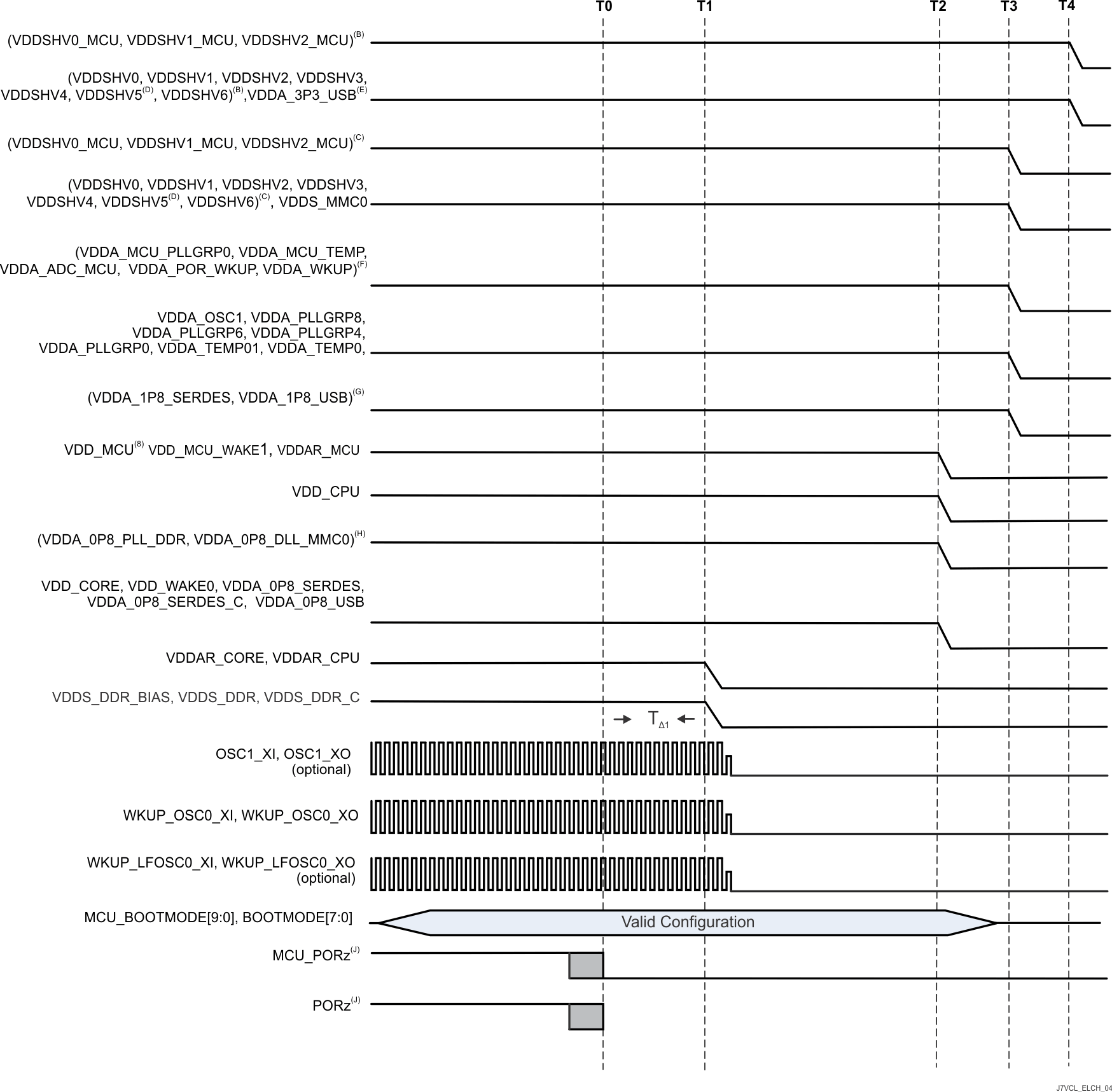
A. 时间戳标记:
- T0 - MCU_PORz 和 PORz 置为低电平有效,用于将所有处理器资源置于安全状态。(0ms)
- T1 - 主 DDR、SRAM 内核和 SRAM CPU 电源域开始斜降。(0.5ms)
- T2 - 所有内核电压开始电源斜降。(2.5ms)
- T3 – 所有 1.8V 电压开始电源斜降。(3.0ms)
- T4 – 所有 3.3V 电压开始电源斜降。(3.5ms)
B. 任何 MCU 或 Main 双电压 IO 域(VDDSHVn_MCU 或 VDDSHVn)由 3.3V 电压供电以支持 3.3V 数字接口。
C. 任何 MCU 或 Main 双电压 IO 电源(VDDSHVn_MCU 或 VDDSHVn)由 1.8V 电压供电以支持 1.8V 数字接口。使用 eMMC 存储器时,由于 PDN 设计将电源与 VDD_MMC0 组合在一起,因此 Main 1.8V 电源的斜降电压可能与 T1 相一致。
D. VDDSHV5 支持 SD 存储卡的 MMC1 信号。需要使用双电压 (3.3V/1.8V) 电源轨以实现合规的高速 SD 卡运行。如果需要实现合规的高速 SD 卡运行,则需要独立的双电压 (3.3V/1.8V) 电源和电源轨。从 3.3V/1.8V 斜降的开始时间与所示的其他 3.3V 域相同。如果不需要 SD 卡或可以接受具有固定 3.3V 工作电压的标准数据速率,则可以将域与数字 IO 3.3V 电源轨分组在一起。如果 SD 卡能够在固定 1.8V 的电压下运行,则可以将域与数字 IO 1.8V 电源轨分组在一起。
E. VDDA_3P3_USB 是用于 USB 2.0 差分接口信号传输的 3.3V 模拟域。建议使用低噪声模拟电源来提供最佳信号完整性,以确保 USB 数据眼罩合规性。从 3.3V 斜降的开始时间与所示的其他 3.3V 域相同。如果不需要 USB 接口或可以容忍数据位错误,则可以直接或通过电源滤波器将域与 3.3V 数字 IO 电源轨分组在一起。
F. VDDA_1P8_<clk/pll/ana> 是 1.8V 模拟域,支持需要使用低噪声电源以实现最佳性能的时钟振荡器、PLL 和模拟电路。不建议将数字 VDDSHVn_MCU 和 VDDSHVn IO 域组合在一起,因为高频开关噪声会对时钟、PLL 和 DLL 信号的抖动性能产生负面影响。应避免组合模拟 VDDA_1p8_<phy> 域,但如果分组在一起,则需要进行直列式铁氧体磁珠电源滤波。
G. VDDA_1P8_<phy> 是 1.8V 模拟域,支持多个串行 PHY 接口。建议使用低噪声模拟电源来提最佳信号完整性、接口性能和规格符合性。如果不需要这些接口中的任何一个,可以容忍数据位错误或不合规运行,则可以直接或通过直列式电源滤波器将域与数字 IO 1.8V 电源轨分组在一起。
H. VDDA_0P8_<dll/pll> 是 0.8V 模拟域,支持需要使用低噪声电源以实现最佳性能的 PLL 和 DLL 电路。不建议将这些域与任何其他 0.8V 域组合在一起,因为高频开关噪声会对 PLL 和 DLL 信号的抖动性能产生负面影响。
I. MCU_PORz 和 PORz 必须置为低电平有效(至少 TΔ1 = 200μs),以确保 SoC 资源在任何电压开始斜降之前进入安全状态。
图 6-7 隔离式 MCU 域和 Main 域,初级下电时序 - 选项 1隔离式 MCU 域和 Main 域下电时序 - 选项 2
图 6-8 介绍了选项 2 的器件下电时序。
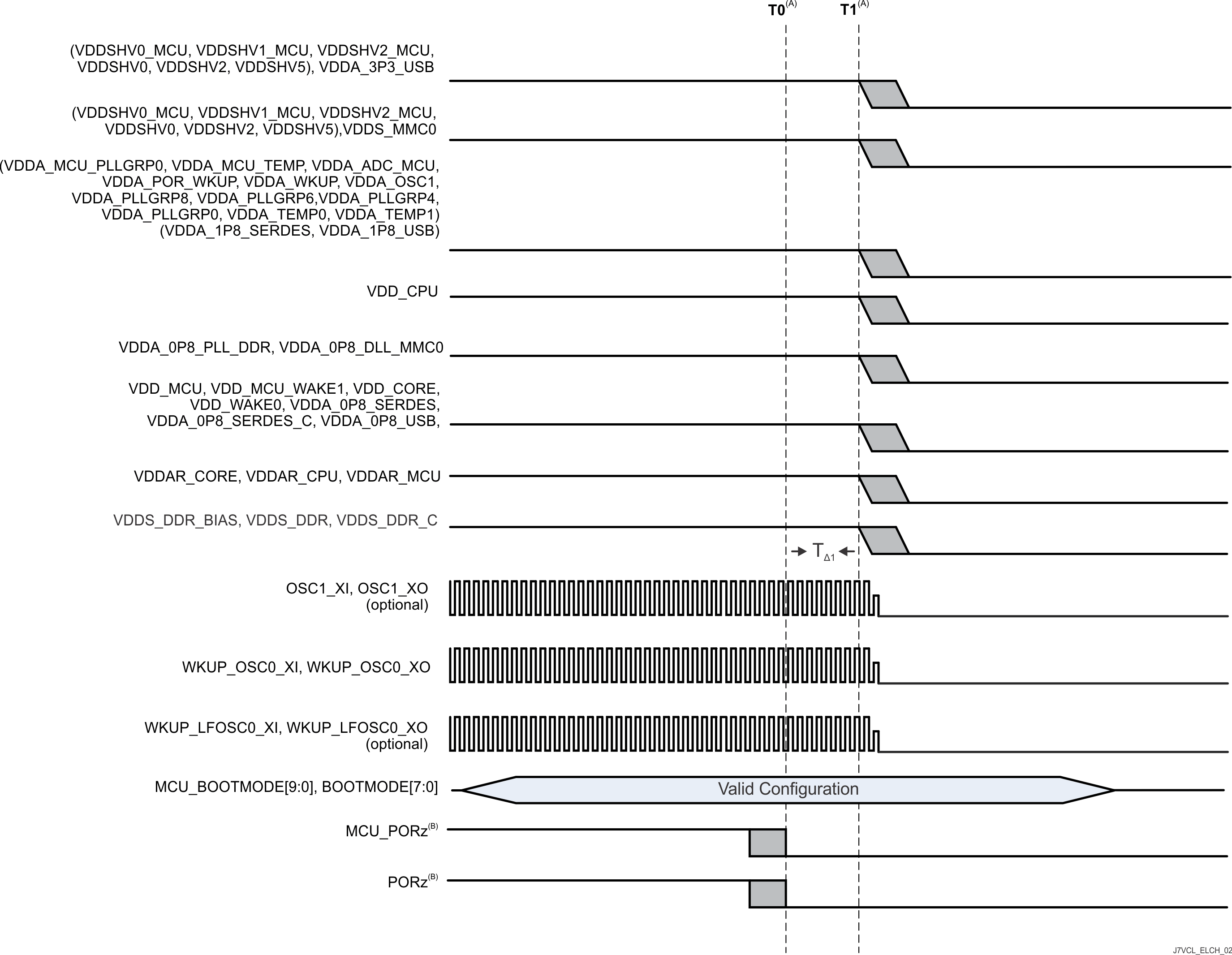
A. 时间戳标记:
- T0 - MCU_PORz 和 PORz 置为低电平有效,用于将所有处理器资源置于安全状态。(0ms)
- T1 – 所有电源开始斜降。(0.2ms)
B. MCU_PORz 和 PORz 必须置为低电平有效(至少 TΔ1 = 200μs),以确保 SoC 资源在任何电压开始斜降之前进入安全状态。
图 6-8 隔离式 MCU 域和 Main 域,初级下电时序 - 选项 2