SWRU553A September 2019 – February 2020 AWR1243 , AWR2243
-
AWRx Cascaded Radar RF Evaluation Module (MMWCAS-RF-EVM)
- Trademarks
- 1 Getting Started
- 2 Hardware Description
- 3 Design Files and Software Tools
- 4 PCB Dimensions and Mounting Information
- 5 PCB Storage and Handling Recommendations
- 6 References
- 7 Regulatory Information
- Revision History
2.6.2.1 RX Antenna Element Performance
Simulated RX antenna performance from RX Array A is shown below. Three different RX antenna were excerpted to show the overall performance across the array. These excerpted antenna are labeled RX1, RX4 and RX8 shown. This selection is meant to highlight behavior of the RX antenna near the edge of the RX antenna rrays and near the center of the arrays. Due to coupling between antenna, the performance near the edge of the array changes from the performance near the center of the array.
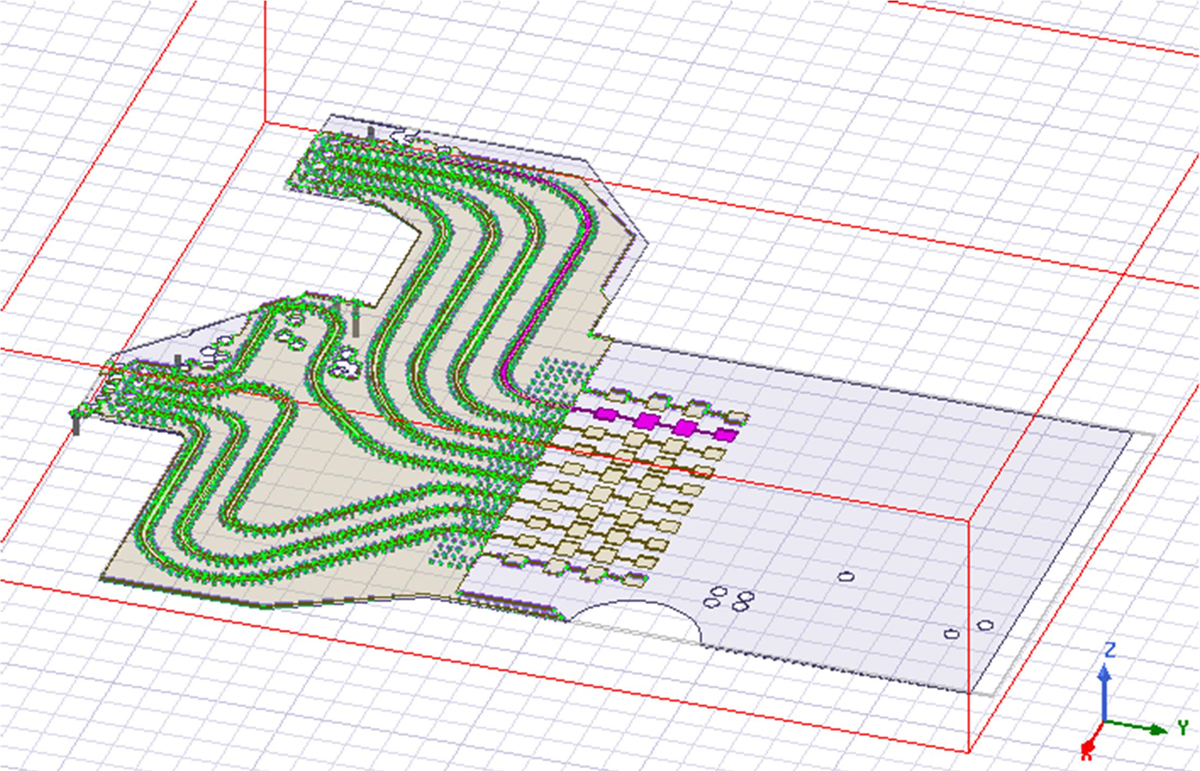 Figure 17. RX Array A Execerpt for Simulation (RX1 at the "top" of the image, RX8 at the "bottom" of the image. RX1 highlighted in purple.)
Figure 17. RX Array A Execerpt for Simulation (RX1 at the "top" of the image, RX8 at the "bottom" of the image. RX1 highlighted in purple.) 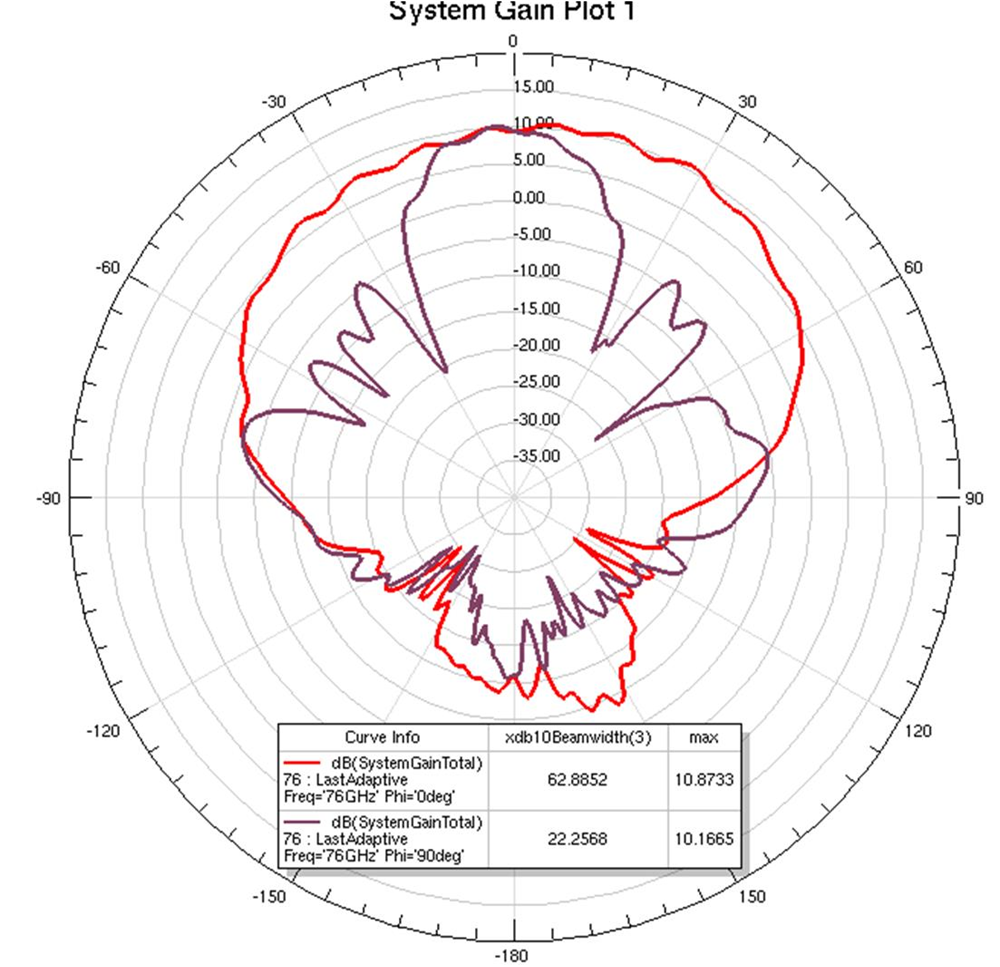 Figure 18. RX Array A, RX1, 76 GHz Operation (Maximum E-plane (Phi = 90) and H-plane (Phi = 0) slices shown. 3dB beamwidths shown.)
Figure 18. RX Array A, RX1, 76 GHz Operation (Maximum E-plane (Phi = 90) and H-plane (Phi = 0) slices shown. 3dB beamwidths shown.) 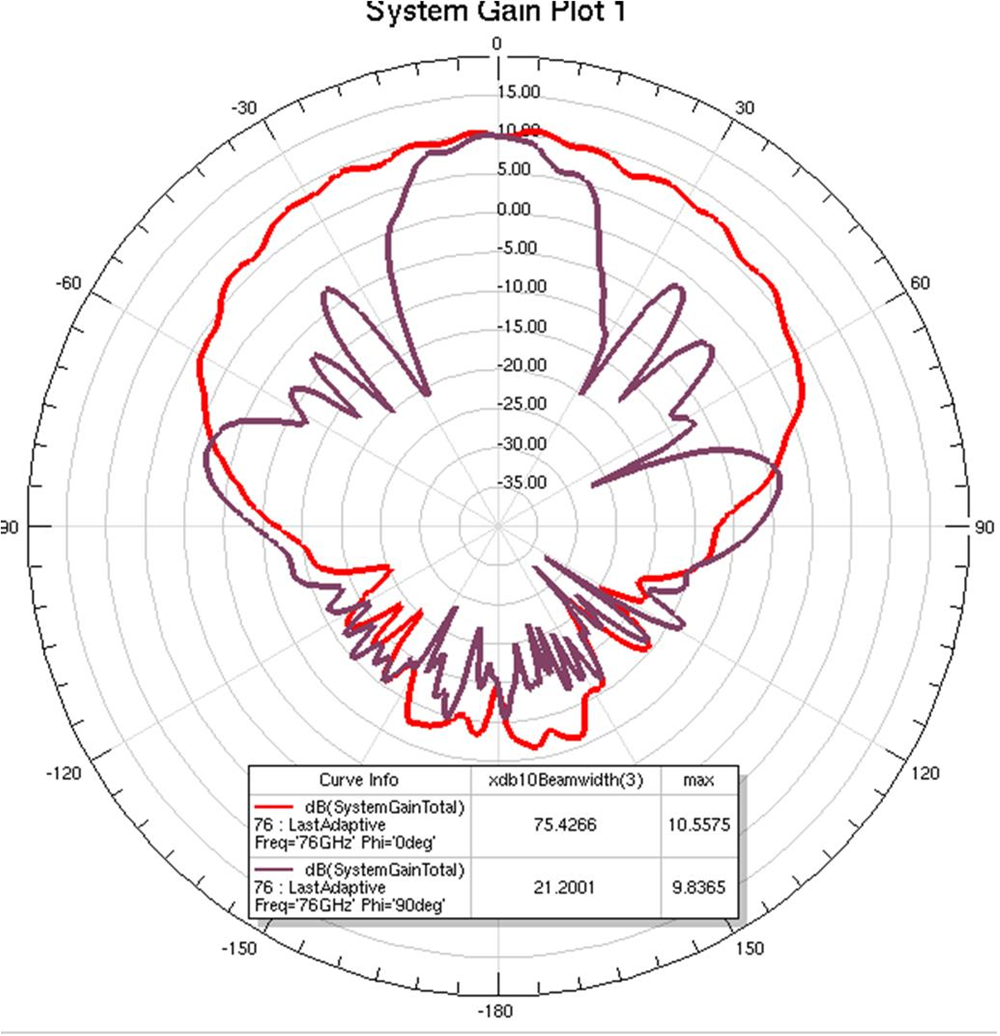 Figure 19. RX Array A, RX4, 76 GHz Operation (Maximum E-plane (Phi = 90) and H-plane (Phi = 0) slices shown. 3dB beamwidths shown.)
Figure 19. RX Array A, RX4, 76 GHz Operation (Maximum E-plane (Phi = 90) and H-plane (Phi = 0) slices shown. 3dB beamwidths shown.) 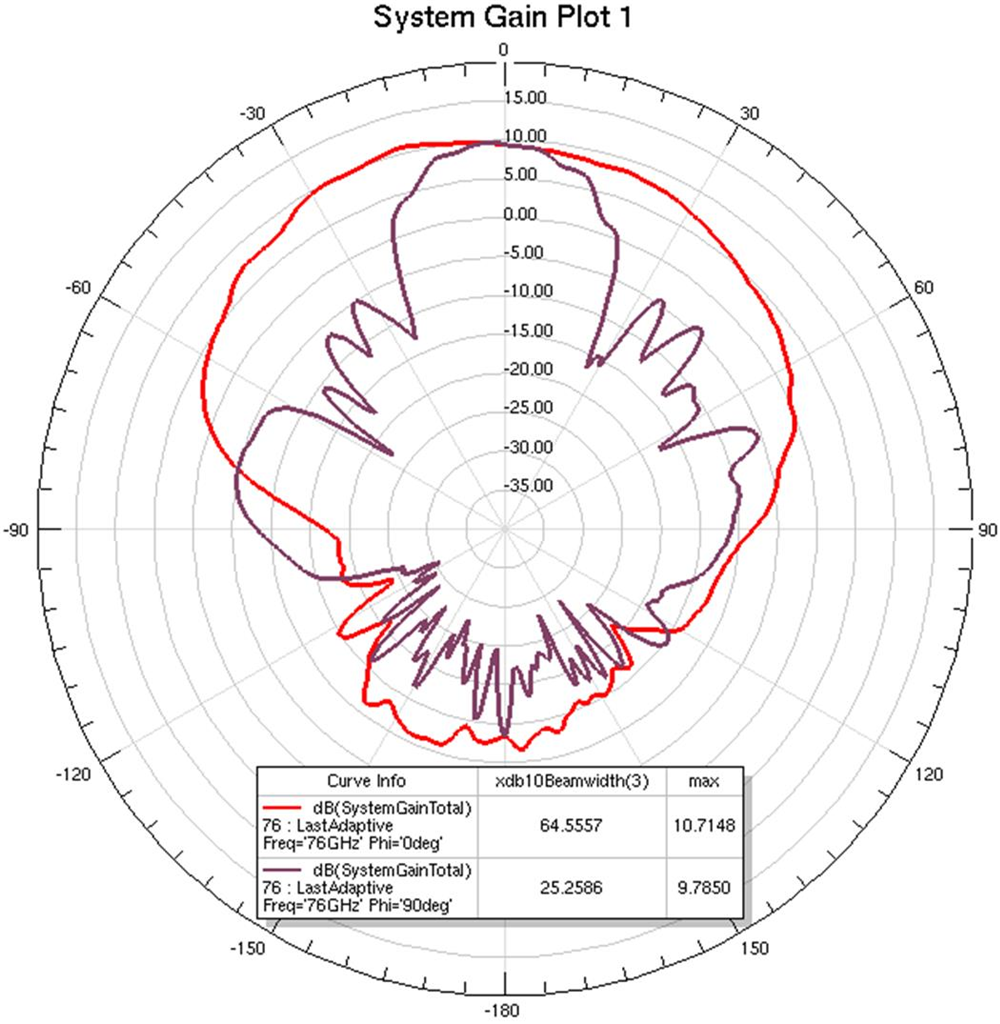 Figure 20. RX Array A, RX8, 76 GHz Operation (Maximum E-plane (Phi = 90) and H-plane (Phi = 0) slices shown. 3dB beamwidths shown.)
Figure 20. RX Array A, RX8, 76 GHz Operation (Maximum E-plane (Phi = 90) and H-plane (Phi = 0) slices shown. 3dB beamwidths shown.) 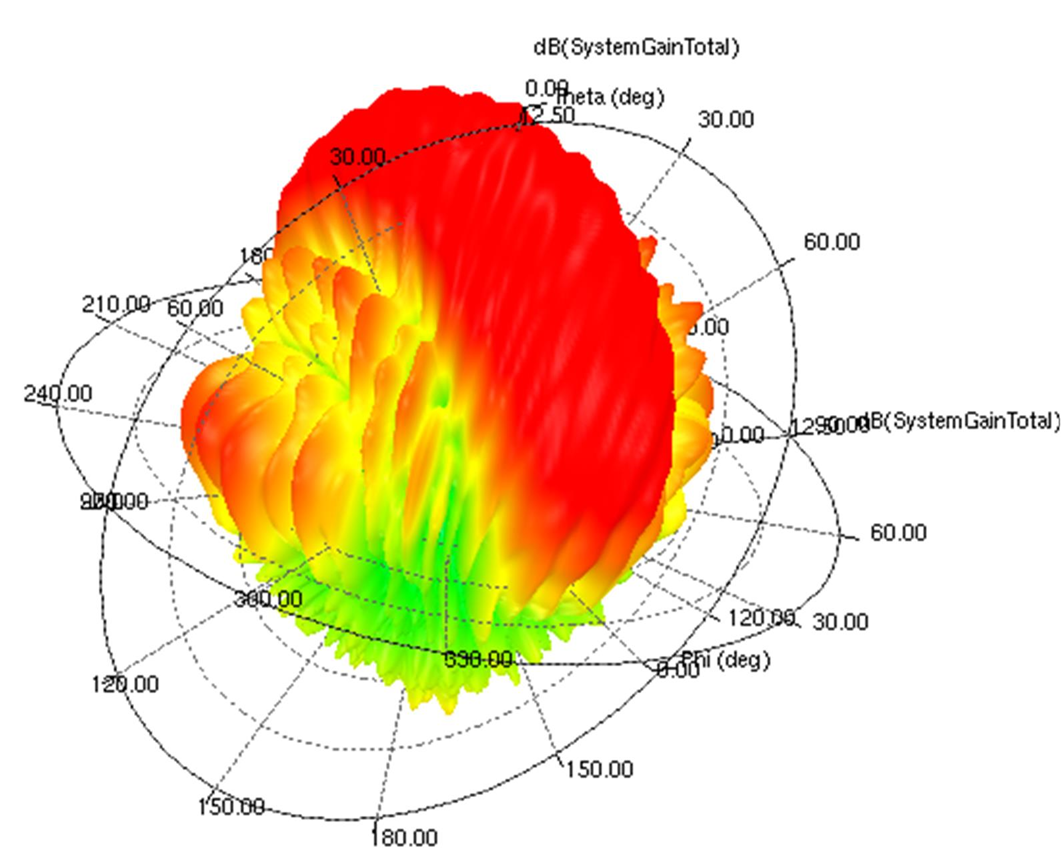 Figure 21. RX Array A, RX4, 76 GHz Operation (3D Antenna Gain Pattern)
Figure 21. RX Array A, RX4, 76 GHz Operation (3D Antenna Gain Pattern) 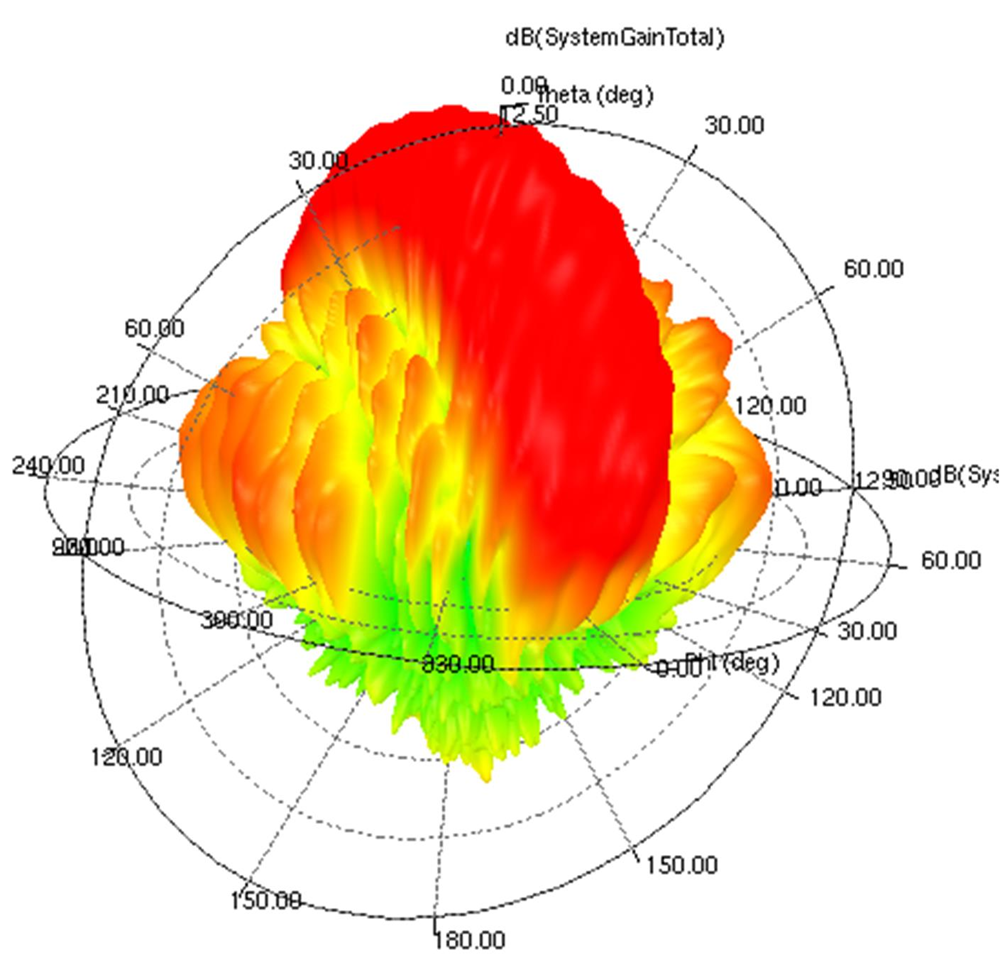 Figure 22. RX Array A, RX4, 78.5 GHz Operation (3D Antenna Gain Pattern)
Figure 22. RX Array A, RX4, 78.5 GHz Operation (3D Antenna Gain Pattern)