SPRAD28 October 2022 AM2431 , AM2432 , AM2434 , AM2631 , AM2631-Q1 , AM2632 , AM2632-Q1 , AM2634 , AM2634-Q1 , AM263P2-Q1 , AM263P4 , AM263P4-Q1 , AM26C31-EP , AM26C31M , AM26C32-EP , AM26C32C , AM26C32M , AM26LS31M , AM26LS32AM , AM26LS33A-SP , AM26LS33AM , AM26LV31E-EP , AM26LV32E-EP , AM26S10 , AM2732 , AM2732-Q1
- Abstract
- Trademarks
- 1 Building for Debug
- 2 Code Composer Studio Stop-Mode Debugging
- 3 Debug Logging
- 4 Multi-Core Debug
- 5 Debugging Arm Cortex-R5 Exceptions
- 6 Debugging Arm Cortex-M4 Exceptions
- 7 Debugging Memory
- 8 Debugging Boot
- 9 Debugging Real-Time Control Loops
- 10E2E Support Forums
7.6 FreeRTOS ROV
The Runtime Object View (ROV) provides tools that enable developers to quickly visualize the state of embedded applications. ROV reads memory from the target and intelligently displays data.
- ROV does not disturb the run-time behavior of the application on the target (when using a JTAG connection). ROV can read current memory from a running target. ROV also automatically refreshes all of its views whenever the target is stopped–for example when single stepping, when the target hits a breakpoint, or when you halt the target asynchronously.
- ROV adds zero footprint to the target code (when using a JTAG connection).
- ROV provides visual tools that show changes in the target state, memory use, and data structures on the host computer. The tool shows high-level information needed by embedded application developers.
- ROV is provided automatically with the TI-RTOS Kernel component of the Sitara SDK. If you use Code Composer Studio (CCS) you have an access to ROV. Nothing needs to be enabled in the application code.
ROV can be extended to work with any embedded library. The examples on this page use the TI-RTOS Kernel, which includes ROV support for its entities including threads, heap memory, and CPU load.
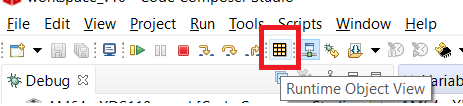
- To launch ROV views, click on the
“ROV” button in the CCS toolbar as shown below:
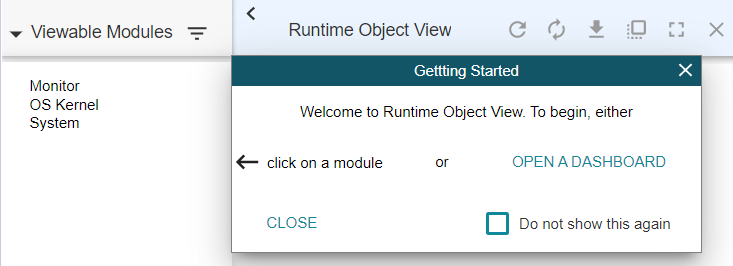
- Click on various “Viewable
Modules”. “OS Kernel” is the one which has useful views:
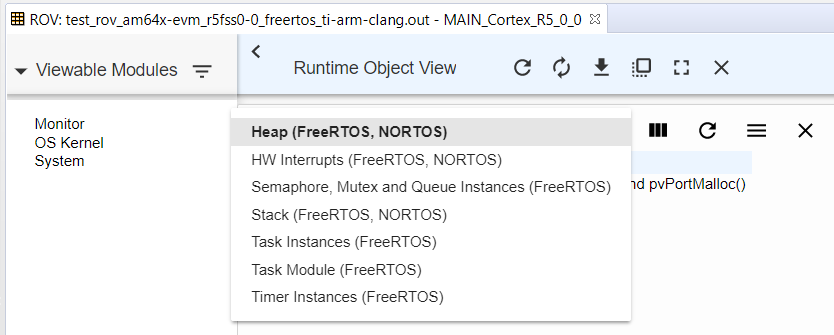
- After clicking on "OS Kernel",
click on the drop down to see all the supported ROV views:
- Shown below is a sample after
"Task Instances" view is selected.
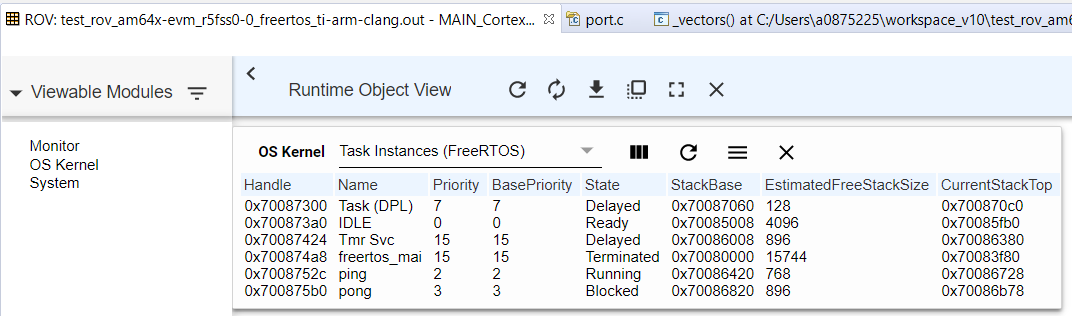
The ROV can be very helpful for debugging stack overflow issues. When an error such as a stack overflow occurs, the corresponding field is highlighted in red. Hover your cursor over a red field to see a brief description of the error.