SNVA559C September 2012 – February 2019 LM2574 , LM2575-N , LM2575HV , LM2576 , LM2576HV , LM2577
-
Switching regulator fundamentals
- Trademarks
- 1 Switching Fundamentals
- 2 Switching Converter Topologies
- 3 Application Hints for Switching Regulators
- 4 Application Circuits
- 5 References and Related Products
- Revision History
2.7 Generating Multiple Outputs
Another big advantage of a flyback is the capability of providing multiple outputs (see Figure 10). In such applications, one of the outputs (usually the highest current) is selected to provide PWM feedback to the control loop, which means this output is directly regulated.
The other secondary winding(s) are indirectly regulated, as their pulse widths will follow the regulated winding. The load regulation on the unregulated secondaries is not great (typically 5% to 10%), but is adequate for many applications.
If tighter regulation is needed on the lower current secondaries, an LDO post-regulator is an excellent solution. The secondary voltage is set about 1 V above the desired output voltage, and the LDO provides excellent output regulation with very little loss of efficiency.
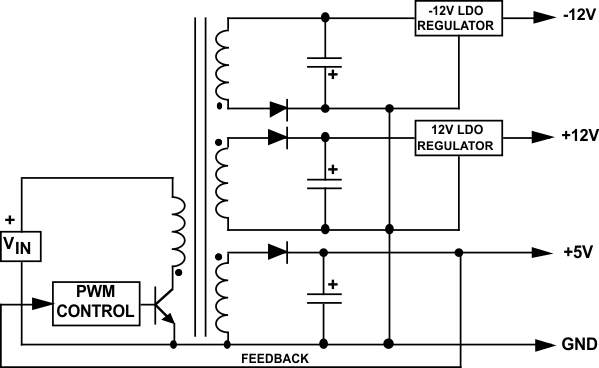 Figure 10. Typical Multiple-Output Flyback
Figure 10. Typical Multiple-Output Flyback