ZHCS614G October 2011 – September 2022 TPS40422
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 说明(续)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 PMBus Interface Protocol General Description
- 8.3.2 Voltage Reference
- 8.3.3 Output Voltage
- 8.3.4 Voltage Feed Forward
- 8.3.5 Current Sensing
- 8.3.6 Overcurrent Protection
- 8.3.7 Current Sharing
- 8.3.8 Linear Regulators
- 8.3.9 BP Switch-over
- 8.3.10 Switching Frequency Setting
- 8.3.11 Switching Node and BOOT Voltage
- 8.3.12 Reading the Output Current
- 8.3.13 Soft-Start Time
- 8.3.14 Turn-On/Turn-Off Delay and Sequencing
- 8.3.15 Pre-Biased Output Start-Up
- 8.3.16 Undervoltage Lockout
- 8.3.17 Overvoltage and Undervoltage Fault Protection
- 8.3.18 Power Good
- 8.3.19 Overtemperature Fault Protection
- 8.3.20 Thermal Shutdown
- 8.3.21 Programmable Fault Responses
- 8.3.22 User Data
- 8.3.23 Adjustable Anti-Cross Conduction Delay
- 8.3.24 Connection of Unused Pins
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Programming
- 8.6
Register Maps
- 8.6.1
Supported Commands
- 8.6.1.1 PAGE (00h)
- 8.6.1.2 OPERATION (01h)
- 8.6.1.3 ON_OFF_CONFIG (02h)
- 8.6.1.4 CLEAR_FAULTS (03h)
- 8.6.1.5 WRITE_PROTECT (10h)
- 8.6.1.6 STORE_USER_ALL (15h)
- 8.6.1.7 RESTORE_USER_ALL (16h)
- 8.6.1.8 CAPABILITY (19h)
- 8.6.1.9 VOUT_MODE (20h)
- 8.6.1.10 VIN_ON (35h)
- 8.6.1.11 VIN_OFF (36h)
- 8.6.1.12 IOUT_CAL_GAIN (38h)
- 8.6.1.13 IOUT_CAL_OFFSET (39h)
- 8.6.1.14 IOUT_OC_FAULT_LIMIT (46h)
- 8.6.1.15 IOUT_OC_FAULT_RESPONSE (47h)
- 8.6.1.16 IOUT_OC_WARN_LIMIT (4Ah)
- 8.6.1.17 OT_FAULT_LIMIT (4Fh)
- 8.6.1.18 OT_WARN_LIMIT (51h)
- 8.6.1.19 TON_RISE (61h)
- 8.6.1.20 STATUS_BYTE (78h)
- 8.6.1.21 STATUS_WORD (79h)
- 8.6.1.22 STATUS_VOUT (7Ah)
- 8.6.1.23 STATUS_IOUT (7Bh)
- 8.6.1.24 STATUS_TEMPERATURE (7Dh)
- 8.6.1.25 STATUS_CML (7Eh)
- 8.6.1.26 STATUS_MFR_SPECIFIC (80h)
- 8.6.1.27 READ_VOUT (8Bh)
- 8.6.1.28 READ_IOUT (8Ch)
- 8.6.1.29 READ_TEMPERATURE_2 (8Eh)
- 8.6.1.30 PMBUS_REVISION (98h)
- 8.6.1.31 MFR_SPECIFIC_00 (D0h)
- 8.6.1.32 VREF_TRIM (MFR_SPECIFIC_04) (D4h)
- 8.6.1.33 STEP_VREF_MARGIN_HIGH (MFR_SPECIFIC_05) (D5h)
- 8.6.1.34 STEP_VREF_MARGIN_LOW (MFR_SPECIFIC_06) (D6h)
- 8.6.1.35 PCT_VOUT_FAULT_PG_LIMIT (MFR_SPECIFIC_07) (D7h)
- 8.6.1.36 126
- 8.6.1.37 SEQUENCE_TON_TOFF_DELAY (MFR_SPECIFIC_08) (D8h)
- 8.6.1.38 128
- 8.6.1.39 OPTIONS (MFR_SPECIFIC_21) (E5h)
- 8.6.1.40 DEVICE_CODE (MFR_SPECIFIC_44) (FCh)
- 8.6.1
Supported Commands
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Application
- 9.2.1
Dual-Output Converter
- 9.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 9.2.1.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.1.2.1 Custom Design with WEBENCH® Tools
- 9.2.1.2.2 Step 1: Inductor Selection
- 9.2.1.2.3 Step 2: Output Capacitor Selection
- 9.2.1.2.4 Step 3: Input Capacitance Selection
- 9.2.1.2.5 Step 4: MOSFET Selection
- 9.2.1.2.6 Step 5: Snubber Circuit Design
- 9.2.1.2.7 Step 6: Soft-Start Time
- 9.2.1.2.8
Step 7: Peripheral Component Design
- 9.2.1.2.8.1 RT (Pin 1) Switching Frequency Setting
- 9.2.1.2.8.2 FB1 (Pin 2) and FB2 (Pin 8) Output Voltage Setting
- 9.2.1.2.8.3 Compensation Network Using COMP1 (Pin 3) , COMP2 (Pin 7), FB1 (Pin 2) FB2 DIFFO1 (Pin 8) (Pin 39)
- 9.2.1.2.8.4 Remote Sensing Using VSNS1 (Pin 37), GSNS1 (Pin 38) , VSNS2 (Pin 15), and GSNS2 (Pin 14)
- 9.2.1.2.8.5 Temperate Sensing Using TSNS1 (Pin36) and TSNS2 (Pin 16)
- 9.2.1.2.8.6 Current Sensing Network Design Using CS1P (Pin 34), CS1N (Pin 35) , CS2P (Pin 18), and CS2N (Pin 17)
- 9.2.1.2.8.7 PMBus Address ADDR1 (Pin 9) , and ADDR0 (Pin 10)
- 9.2.1.2.8.8
Voltage Decoupling Capacitors
- 9.2.1.2.8.8.1 VDD (Pin 31)
- 9.2.1.2.8.8.2 BP3 (Pin 32)
- 9.2.1.2.8.8.3 BNEXT (Pin 24)
- 9.2.1.2.8.8.4 BP6 (Pin 25)
- 9.2.1.2.8.8.5 Power Good PGOOD1 (Pin 33), PGOOD2 (Pin 19)
- 9.2.1.2.8.8.6 Bootstrap Capacitors BOOT1 (Pin 30), and BOOT2 (Pin 20)
- 9.2.1.2.8.8.7 High-Side MOSFET (Gate) Resistor
- 9.2.1.2.8.8.8 Synchronization Setting SYNC (Pin 40)
- 9.2.1.2.8.8.9 BP6 (Pin 25)
- 9.2.1.2.8.8.10 DIFFO (Pin 39)
- 9.2.1.3 Application Curves
- 9.2.1
Dual-Output Converter
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
9.2.1.2.8.3 Compensation Network Using COMP1 (Pin 3) , COMP2 (Pin 7), FB1 (Pin 2) FB2 DIFFO1 (Pin 8) (Pin 39)
The TPS4022 device uses voltage mode control topology in a single phase dual-output configuration. In this example, a Type III compensation network is implemented to compensate for the double pole, close the loop and stabilize the system. TI provides a compensation calculator tool to streamline the compensation design process.
The TPS4022 Loop Compensation Tool (SLUC263) provides the recommended compensation components as a starting point and approximate bode plots. It is always recommended to measure the real system bode plot after the design and adjust the compensation values accordingly. The chosen compensation values are derived from the tool calculation along with the Venable K-factor method and optimization based on the measured data.
- R1 = R2 = 47.5 kΩ
- R3 = 4.75 kΩ
- R4 = 20 kΩ
- C1 = 470 pF
- C2 = 1.2 nF
- C3 = 120 pF
In this design example, the desired crossover frequency chosen is approximately 4 × fDP (20 kHz). Use Equation 32 to calculate the double pole frequency formed by the output inductor and capacitor bank.
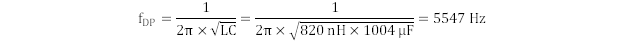
Because the Venable K-factor method was used to derive these compensation values, it is important to ensure that the poles and zeroes are coincident. A way to confirm that the poles and zeroes are coincident is to calculate the poles and zeroes from the gain of the Type-III compensation network.
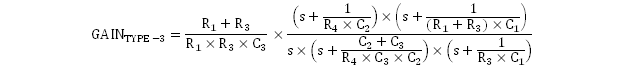
The first and second zeroes should yield approximately equal frequency values of 6480 Hz and 6631 Hz.
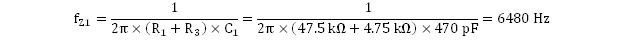
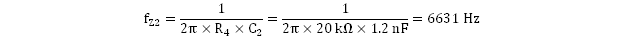
Analogous to the zeroes being coincident, the first and second poles are coincident as well and are shown in Equation 36 and Equation 37.
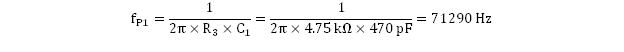
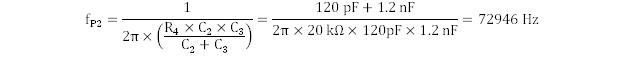
The resulting compensated system Bode plot is shown in Figure 9-4 and the PWR091 EVM user guide (SLVU638). A more comprehensive discussion is presented in Under the Hood of Low-Voltage DC/DC Converters from the 2003 TI Power Supply Seminar (SLUP206).