ZHCSLS8 August 2020 DRV5825P
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Typical Characteristics
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3 Feature Description
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Programming and Control
- 8.6 Register Maps
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
8.5.2.6.2 Exclusive or (XOR) Checksum
The XOR checksum is a simpler checksum scheme. It performs sequential XOR of each register byte write with the previous 8-bit checksum register value. XOR supports only Book 0x8C, and excludes page switching and all registers in Page 0x00 of Book 0x8C. XOR checksum is read from location register 0x7D on page 0x00 of book 0x8C (B_140, Page_0, Reg_125). The XOR Checksum can be reset by writing 0x00 to the same register location where it is read.
PurePathTM Console tools supports CRC and XOR check sum value calculation based on register writting scritps.
Example: Update EQ parameters.
- Use PPC3 to calculate the EQ parametes
and save to .cfg file.
w 58 00 00
w 58 7f aa
w 58 00 24
w 58 18 08 25 39 ce f0 bc db 13 07 26 4d 48 0f 43 24 ed f8 b4 78 ea #EQ parameters
- Use PPC3 to calculate CRC and XOR
Checksum results (based on .cfg file).
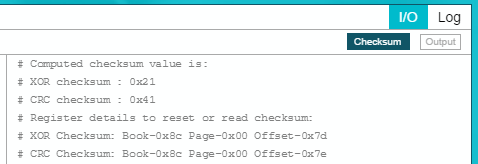
- Update EQ parameters with CRC/XOR
Checksum.
w 58 00 00
w 58 7f 8c
w 58 00 00
w 58 7e 00 #Reset CRC start value to 0x00
w 58 7d 00 #Reset XOR start value to 0x00
w 58 00 00
w 58 7f aa
w 58 00 24
w 58 18 08 25 39 ce f0 bc db 13 07 26 4d 48 0f 43 24 ed f8 b4 78 ea #EQ parameters update
w 58 00 00
w 58 7f 8c
w 58 00 00
r 58 7d 01 #Check if the XOR checksum readback data is 0x21
r 58 7e 01 #Check if the CRC checksum readback data is 0x41