SWRA715 December 2021 CC2642R , CC2652R
- Trademarks
- 1Introduction
- 2Bluetooth Low Energy Introduction
- 3HOGP Introduction
-
4Project Description and
Walkthrough
- 4.1 General Project Discussion
- 4.2 Report Map Discussion
- 4.3 Hid_input struct/union Discussion
- 4.4 Mouse Operation
- 4.5 Keyboard Operation
- 4.6 Consumer Report Operation
- 4.7 Connection Interval
- 4.8 Notification System
- 4.9 PDU Size and Number of PDUs per Connection Event
- 4.10 Notification Payload Discussion
- 4.11 Throughput Discussion
- 4.12 Overall Block Diagrams
- 5Demo Usage
- 6Summary
4.10.2 Keyboard Notification
The keyboard notifications have a payload that is comprised of 8 bytes. Each byte corresponds to a specific piece of HID keyboard input information. Table 4-2 describes what each byte of the keyboard notification payload corresponds to.
| Byte 0 | Byte 1 | Byte 2 | Byte 3 | Byte 4 | Byte 5 | Byte 6 | Byte 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Modifier Key | Reserved | Keypress 1 | Keypress 2 | Keypress 3 | Keypress 4 | Keypress 5 | Keypress 6 |
An example of a keyboard notification payload that is generated by this project is “00 00 50 00 00 00 00 00”, which would be parsed by the HID Host as shown in Figure 4-7.
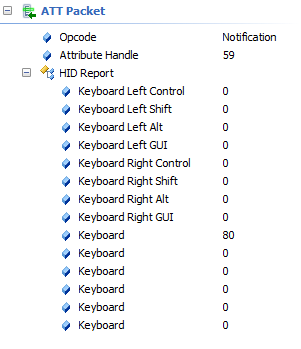 Figure 4-7 Parsed Keyboard Notification
Payload
Figure 4-7 Parsed Keyboard Notification
PayloadFor more details on how the HOGP specification makes use of notification, see Chapter 4 HID Host Requirements and Behaviors and Chapter 5 Connection Establishment in the HOGP specification.