SPRUJ51 june 2023
- 1
- 1Abstract
- 2EVM Revisions and Assembly Variants
- Trademarks
-
3System Description
- 3.1 Key Features
- 3.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 3.3 AM62x-Low Power SK EVM Interface Mapping
- 3.4 Power ON OFF Procedures
- 3.5
Peripheral and Major Component Description
- 3.5.1 Clocking
- 3.5.2 Reset
- 3.5.3 OLDI Display Interface
- 3.5.4 CSI Interface
- 3.5.5 Audio Codec Interface
- 3.5.6 HDMI Display Interface
- 3.5.7 JTAG Interface
- 3.5.8 Test Automation Header
- 3.5.9 UART Interface
- 3.5.10 USB Interface
- 3.5.11 Memory Interfaces
- 3.5.12 Ethernet Interface
- 3.5.13 GPIO Port Expander
- 3.5.14 GPIO Mapping
- 3.5.15 Power
- 3.5.16 AM62x-Low Power SK EVM User Setup and Configuration
- 3.5.17 Expansion Headers
- 3.5.18 Push Buttons
- 3.5.19 I2C Address Mapping
- 4Known Issues and Modifications
- 5Revision History
- 6IMPORTANT NOTICE AND DISCLAIMER
3.5.1 Clocking
The clocking architectue of the AM62x Low-Power SK EVM is shown below.
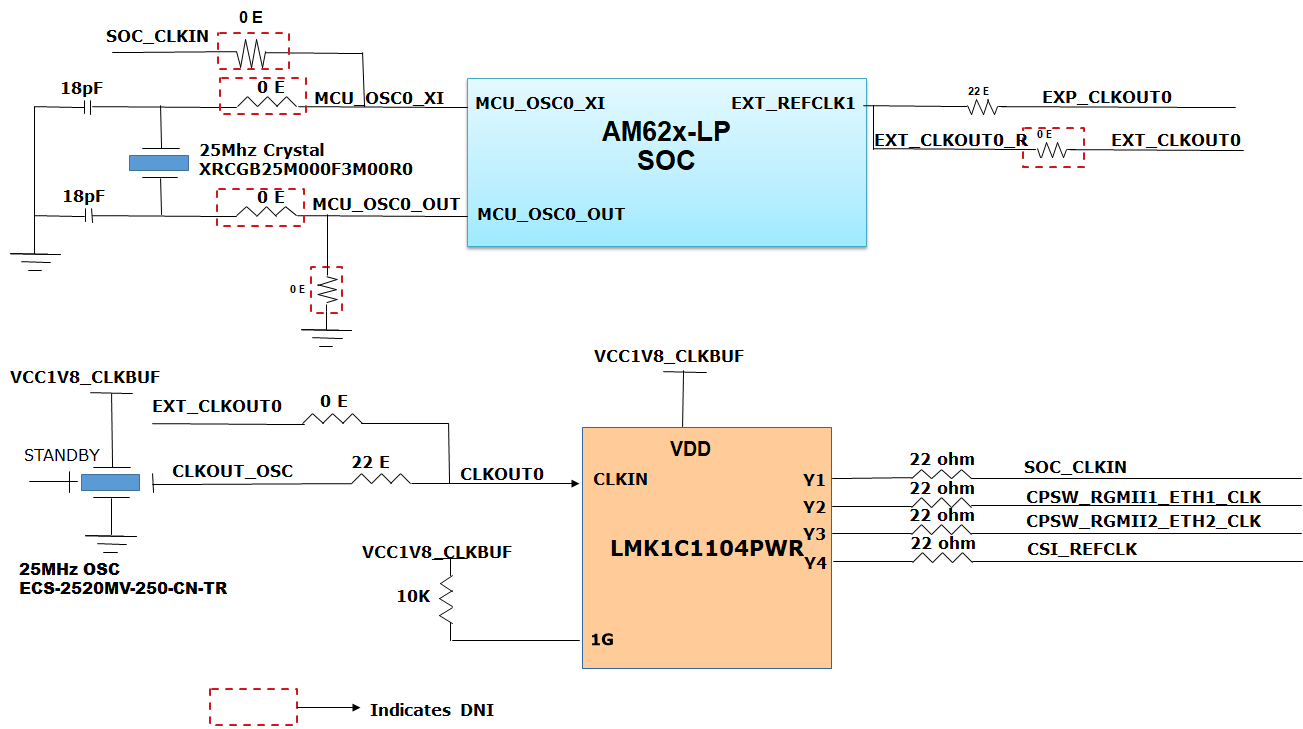 Figure 3-6 Clock architecture
Figure 3-6 Clock architectureA clock generator of part number LMK1C1104PWR is used to drive the 25MHz clock to the SOC and two Ethernet PHYs. LMK1C1104PWR is a 1:4 LVCMOS clock buffer, which takes the 25MHz crystal/LVCMOS referenceinput and provides four 25MHz LVCMOS clock outputs. The source for the clock buffer shall be either the CLKOUT0 pin from the SOC or a 25MHz oscillator, the selection is made using a set of resistors. By default, an oscillator is used as input to the clock buffer on the AM62x Low Power SK EVM . Output Y2 and Y3 of the clock buffer are used as reference clock inputs for two Gigabit Ethernet PHYs. Output Y4 of the clock buffer are used as reference clock inputs for CSI Camera inetrace.
There is one external crystal attached to the AM62x SoC to provide clock to the WKUP domain of the SoC (32.768 KHz).
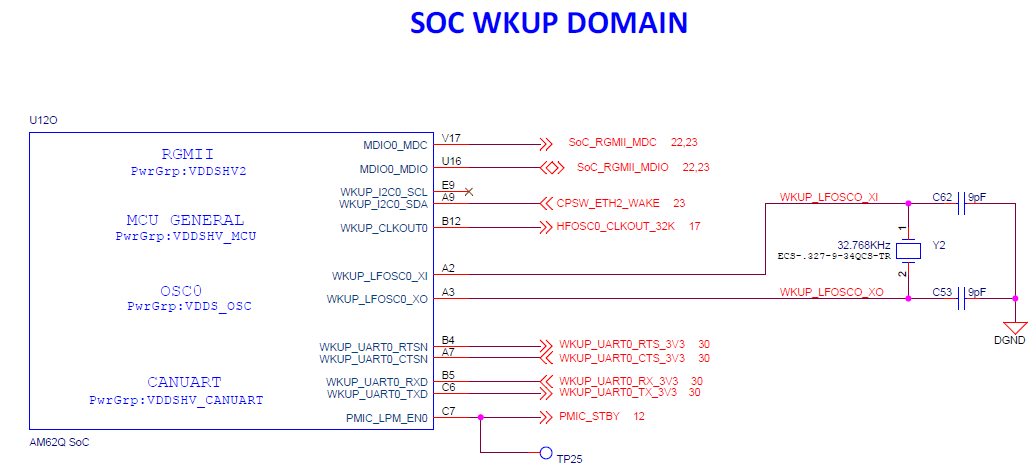 Figure 3-7 SoC Wakeup Domain
Clock
Figure 3-7 SoC Wakeup Domain
ClockClock inputs required for peripherals such as XDS110, FT4232, HDMI transmitter and audio codec are generated locally using separate crystals or oscillators. Crystals or oscillators used to provide the reference clocks to the EVM peripherals are shown in the table below.
| Peripheral | Mfr.Part # | Description | Frequency |
| XDS110 emulator(Y3) | XRCGB16M000FXN01R0 | CRY 16.000MHz 8pF SMD | 16.000MHz |
| FT4232 Bridge(Y4) | 445I23D12M00000 | CRY12.000MHz 18pF SMD | 12.000MHz |
| Audio Codec(U64) | KC3225Z12.2880C1KX00 | OSC12.288MHz CMOS SMD | 12.288MHz |
| HDMITransmitter(U9) | KC3225Z12.2880C1KX00 | OSC12.288MHz CMOS SMD | 12.288MHz |
The clock required by the HDMI transmitter can be provided by either the on board oscillator or the SoC’s AUDIO_EXT_REFCLK1, which can be selected through a resistor mux. SoC’s EXT_REFCLK1 is used to provide clock to the User Expansion Connector on the SK EVM. The 32 KHz clock to the M.2 module is provided by WKUP_CLKOUT0 of AM62x SoC through a voltage translational buffer.