SLAA870 February 2019 AFE7422 , AFE7444
-
Evaluating the frequency hopping capability of the AFE74xx
- Trademarks
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Phase Coherency vs Phase Continuity
- 3 AFE74xx Architecture
- 4 Frequency Hopping Methods
- 5 NCO Frequency Resolution Versus Hop Time
- 6 Fast Frequency Hopping With the Load and Switch
- 7 Register Addresses
- 8 References
4.2.1.1.2 Test Results
Figure 17 shows that the time required to switch from TXNCO0 (100 MHz) to TXNCO1 (10 MHz) is approximately 658 ns from the issuance of the command through the SPI clock of approximately 40 MHz
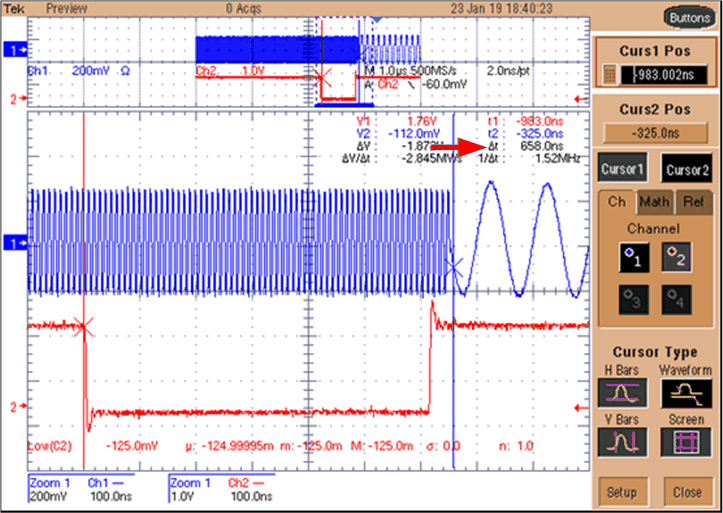 Figure 17. Hop Time When Switching From One NCO to Another is Approximately 658 ns
Figure 17. Hop Time When Switching From One NCO to Another is Approximately 658 ns