ZHCSI22F October 2017 – December 2021 TPS2662
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3
Feature Description
- 9.3.1 Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO)
- 9.3.2 Overvoltage Protection (OVP)
- 9.3.3 Hot Plug-In and Inrush Current Control
- 9.3.4 Reverse Polarity Protection
- 9.3.5 Overload and Short-Circuit Protection
- 9.3.6 Reverse Current Protection
- 9.3.7 FAULT Response
- 9.3.8 IN, OUT, RTN, and GND Pins
- 9.3.9 Thermal Shutdown
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
-
10Application and Implementation
- 10.1 Application Information
- 10.2 Typical Application
- 10.3 System Examples
- 10.4 Do's and Don'ts
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
10.3.1 Field Supply Protection in PLC, DCS I/O Modules
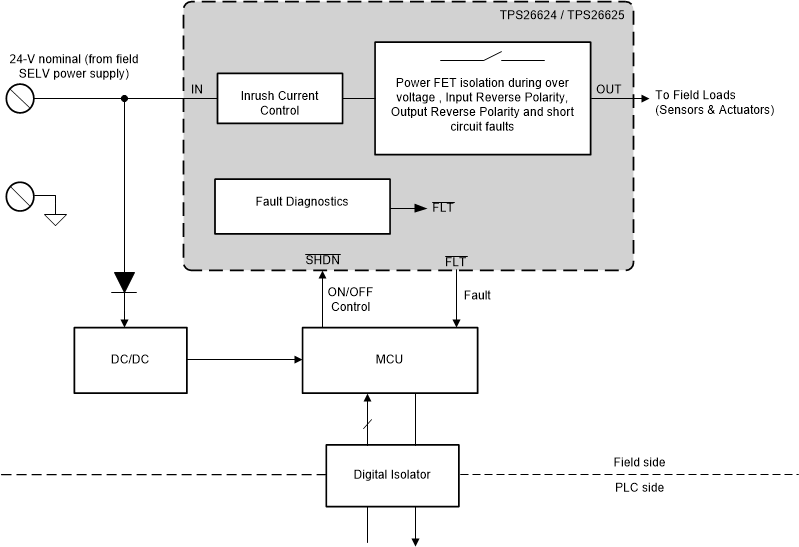 Figure 10-13 Power Delivery Circuit Block Diagram in I/O Modules
Figure 10-13 Power Delivery Circuit Block Diagram in I/O ModulesThe PLC or Distributed Control System (DCS) I/O modules are often connected to an external field power supply to support higher power requirements of the field loads like sensors and actuators. Power-supply faults or miswiring can damage the loads or cause the loads not to operate correctly. The TPS26624 and TPS26625 can be used as a front end protection circuit to protect and provide stable supply to the field loads. Undervoltage, overvoltage, and input and output side reverse polarity protection features of these devices prevent the loads to experience voltages outside the operating range, which can permanently damage the loads.
Field power supply is often connected to multiple I/O modules that can deliver more current than a single I/O module can handle. Overcurrent protection scheme of the TPS2662x family limits the current from the power supply to the module so that the maximum current does not rise above what the board is designed for. Fast short-circuit protection scheme isolates the faulty load from the field supply quickly and prevents the field supply to dip and cause interrupts in the other I/O modules connected to the same field supply. High accurate (±5% at 0.88 A) current limit facilitates more I/O modules to be connected to field supply. Fault indication ( FLT) features facilitate continuous load monitoring.
The TPS26624 and TPS26625 also acts as a smart diode with protection against reverse current during output side miswiring. Reverse current can potentially damage the field power supply and cause the I/O modules to run hot or can cause permanent damage.
If the field power supply is connected in reverse polarity on the input side (which is not unlikely as field power supplies are usually connected with screw terminals), field loads can permanently get damaged due to the reverse voltage. Also, during the installation the field power supply can be miswired on the output side instead of on the input side which can damage the upstream power supply and electronics. The input and output reverse polarity protection feature of the TPS26624 and TPS26625 prevents the reverse voltage to appear at the load side as well as supply side offering complete system protection during field miswiring.