SPRUHW1A June 2014 – October 2021 TMS320F28052-Q1 , TMS320F28052M , TMS320F28052M-Q1 , TMS320F28054-Q1 , TMS320F28054M , TMS320F28054M-Q1
- 1Read This First
- 1 F2805xM InstaSPIN-MOTION Enabled MCUs
- 2InstaSPIN-MOTION Key Capabilities and Benefits
- 3InstaSPIN-MOTION Block Diagrams
- 4Application Examples
- 5Evaluating InstaSPIN-MOTION Performance
- 6Microcontroller Resources
2.1 Overview
InstaSPIN-MOTION replaces inefficient, older design techniques with a solution that maximizes system performance and minimizes design effort. By embedding the motor expertise on the chip, InstaSPIN-MOTION enables users to focus on optimizing their application rather than struggling with motion control.
InstaSPIN-MOTION provides the following core capabilities:
- The FAST unified observer, which exploits the similarities between all motors that use magnetic flux for energy transduction. The FAST estimator measures rotor flux (magnitude, angle, and speed) as well as shaft torque in a sensorless FOC system.
- Motor parameter identification, used to tune the FAST observer and initialize the innermost current (torque) PI controllers for Iq and Id control of the FOC system.
- SpinTAC, a comprehensive motion control suite (see Figure 3-1) from LineStream Technologies, simplifies tuning and ensures optimal performance across dynamic speed and position ranges.
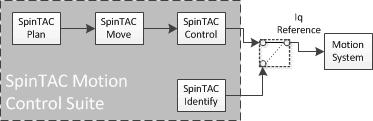 Figure 2-1 SpinTAC
Motion Control Suite Components
Figure 2-1 SpinTAC
Motion Control Suite Components