SLVAF10 March 2021 TPS1H000-Q1 , TPS1H100-Q1 , TPS1H200A-Q1 , TPS1HA08-Q1 , TPS1HB08-Q1 , TPS1HB16-Q1 , TPS1HB35-Q1 , TPS1HB50-Q1 , TPS2H000-Q1 , TPS2H160-Q1 , TPS2HB16-Q1 , TPS2HB35-Q1 , TPS2HB50-Q1 , TPS4H000-Q1 , TPS4H160-Q1
3.3.2 Impact of Finite Slew Rate on Resistive Load Power
In earlier sections of this report, it was shown that as PWM frequency increases the effects of PWD on load power increases causing significant divergence from the calculated ideal power.
A high side switch's finite slew rate introduces additional challenges that deviates true load power from an ideal case. Unlike PWD, which can either increase or decrease delivered load power, finite slew-rate always results in reduced load power compared to an ideal high side switch as the rise times reduce the time when the full input voltage is present across the load. As frequency increases, the rise and fall times account for more and more of the output ON pulse.
Figure 3-8 defines timing parameters used for analysis.
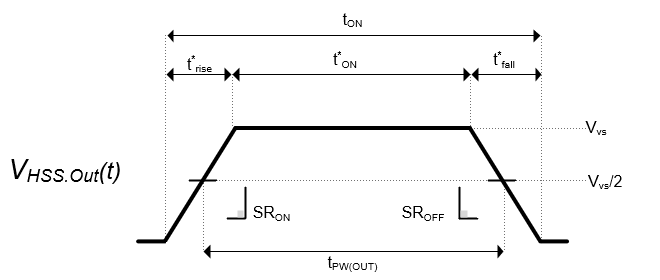 Figure 3-8 Timing Definition for Resistor
Power Analysis
Figure 3-8 Timing Definition for Resistor
Power Analysis- t'ON is the total duration where output is at final voltage
- tpw(OUT) is the output pulse width
- trise,fall are rise and fall times calculated from device slew rate, such that





 , where
Vvs is the supply voltage. This can be further
simplified to:
, where
Vvs is the supply voltage. This can be further
simplified to: