ZHCS155C March 2011 – November 2023 TPS40170
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
-
6 Detailed Description
- 6.1 Overview
- 6.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 6.3
Feature Description
- 6.3.1 LDO Linear Regulators and Enable
- 6.3.2 Input Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO)
- 6.3.3 Oscillator and Voltage Feed-Forward
- 6.3.4 Overcurrent Protection and Short-Circuit Protection (OCP and SCP)
- 6.3.5 Soft-Start and Fault-Logic
- 6.3.6 Overtemperature Fault
- 6.3.7 Tracking
- 6.3.8 Adaptive Drivers
- 6.3.9 Start-Up into Pre-Biased Output
- 6.3.10 Power Good (PGOOD)
- 6.3.11 PGND and AGND
- 6.4 Device Functional Modes
-
7 Application and Implementation
- 7.1 Application Information
- 7.2
Typical Application
- 7.2.1 Design Requirements
- 7.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 7.2.2.1 Custom Design with WEBENCH® Tools
- 7.2.2.2 List of Materials
- 7.2.2.3 Select a Switching Frequency
- 7.2.2.4 Inductor Selection (L1)
- 7.2.2.5 Output Capacitor Selection (C9)
- 7.2.2.6 Peak Current Rating of Inductor
- 7.2.2.7 Input Capacitor Selection (C1, C6)
- 7.2.2.8 MOSFET Switch Selection (Q1, Q2)
- 7.2.2.9 Timing Resistor (R7)
- 7.2.2.10 UVLO Programming Resistors (R2, R6)
- 7.2.2.11 Boot-Strap Capacitor (C7)
- 7.2.2.12 VIN Bypass Capacitor (C18)
- 7.2.2.13 VBP Bypass Capacitor (C19)
- 7.2.2.14 VDD Bypass Capacitor (C16)
- 7.2.2.15 SS Timing Capacitor (C15)
- 7.2.2.16 ILIM Resistor (R9, C17)
- 7.2.2.17 SCP Multiplier Selection (R5)
- 7.2.2.18 Feedback Divider (R10, R11)
- 7.2.2.19 Compensation: (R4, R13, C13, C14, C21)
- 7.2.3 Application Curves
- 7.3 Power Supply Recommendations
- 7.4 Layout
- 8 Device and Documentation Support
- 9 Revision History
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
6.3.5.1 Soft Start During Overcurrent Fault
The soft-start block also has a role to controls the fault-logic timing. If an overcurrent fault (OC_FAULT) is declared, the soft-start capacitor is discharged internally through the device by a small current ISS(sink) (1.05 µA, typ.). After the SS pin capacitor is discharged to below VSS(flt,low) (300 mV, typ.), the soft-start capacitor begins charging again. If the fault is persistent, a fault is declared which is determined by the overcurrent protection state machine. If the soft-start capacitor is below VSS(flt,high) (2.5 V, typ.), then the soft-start capacitor continues to charge until it reaches VSS(flt,high) before a discharge cycle is initiated. This ensures that the re-start time-interval is always constant. Figure 6-7 shows the restart timing.
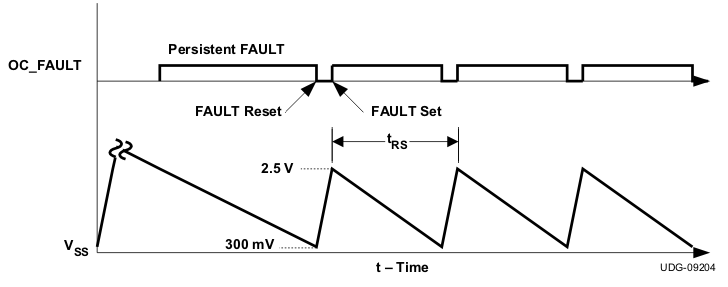 Figure 6-7 Overcurrent Fault Restart Timing
Figure 6-7 Overcurrent Fault Restart TimingFor the feedback to be regulated to the SS_EAMP voltage, the TRK pin must be pulled up high directly or through a resistor to VDD.