ZHCSQQ4C November 2011 – June 2022 TPA2015D1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3 Feature Description
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
9.4.2 Battery Tracking SpeakerGuard™ Operation
| Phase 1 | Battery discharging normally; supply voltage is above inflection point; audio output remains below limiter level. |
| The limiter level remains constant because the supply voltage is greater than the inflection point. Amplifier gain is constant at fixed-gain as set by the GAIN pin. The audio output remains at a constant loudness. The boost converter allows the audio output to swing above the battery supply voltage. Battery supply current increases as supply voltage decreases. | |
| Phase 2 | Battery continues to discharge normally; supply voltage decreases below inflection point; limiter level decreases below audio output. |
| The limiter level decreases as the battery supply voltage continues to decrease. SpeakerGuard™ lowers amplifier gain, reducing the audio output below the new limiter level. The supply current decreases due to reduced output power. | |
| Phase 3 | Battery supply voltage is constant; audio output remains below limiter level. |
| The audio output, limiter level, and supply current remain constant as well. | |
| Phase 4 | Phone plugged in and battery re-charges; supply voltage increases. |
| The limiter level increases as the supply voltage increases. SpeakerGuard™ increases amplifier gain slowly, increasing audio output. Because the TPA2015D1 supply current is proportional to the PVOUT-to-VBAT ratio, the supply current decreases as battery supply voltage increases. | |
| Phase 5 | Battery supply voltage is constant; audio output is below limiter level. |
| SpeakerGuard™ continues to increase amplifier gain to the fixed-gain as set by the GAIN pin. The audio output signal increases (slowly due to release time) to original value. | |
| Phase 6 | Battery supply voltage is constant; audio output remains below limiter level. |
| Amplifier gain equal to fixed-gain as set by the GAIN pin. Audio output signal does not change. Supply current remains constant. |
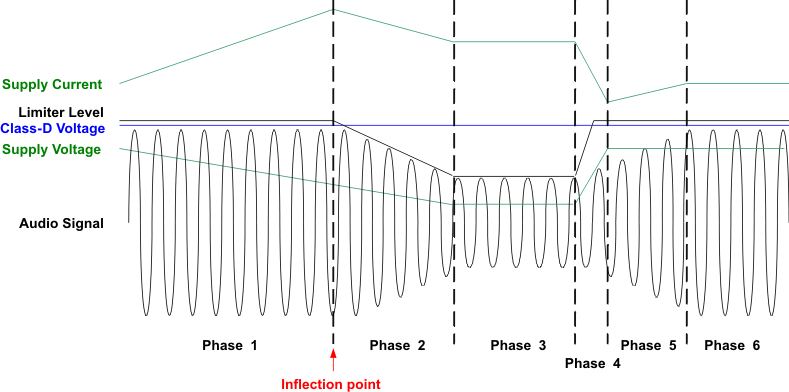 Figure 9-7 Relationship Between Supply Voltage, Current, Limiter Level, and Output Audio Signal
Figure 9-7 Relationship Between Supply Voltage, Current, Limiter Level, and Output Audio Signal