ZHCSIE4A June 2018 – July 2018 TMS320F28035-EP
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1器件概述
- 2修订历史记录
- 3Terminal Configuration and Functions
-
4Specifications
- 4.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 4.2 ESD Ratings
- 4.3 Power-On Hours (POH) Limits
- 4.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 4.5 Power Consumption Summary
- 4.6 Electrical Characteristics
- 4.7 Thermal Resistance Characteristics
- 4.8 Thermal Design Considerations
- 4.9 Emulator Connection Without Signal Buffering for the MCU
- 4.10 Parameter Information
- 4.11 Test Load Circuit
- 4.12 Power Sequencing
- 4.13 Clock Specifications
- 4.14 Flash Timing
-
5Detailed Description
- 5.1
Overview
- 5.1.1 CPU
- 5.1.2 Control Law Accelerator (CLA)
- 5.1.3 Memory Bus (Harvard Bus Architecture)
- 5.1.4 Peripheral Bus
- 5.1.5 Real-Time JTAG and Analysis
- 5.1.6 Flash
- 5.1.7 M0, M1 SARAMs
- 5.1.8 L0 SARAM, and L1, L2, and L3 DPSARAMs
- 5.1.9 Boot ROM
- 5.1.10 Security
- 5.1.11 Peripheral Interrupt Expansion (PIE) Block
- 5.1.12 External Interrupts (XINT1–XINT3)
- 5.1.13 Internal Zero Pin Oscillators, Oscillator, and PLL
- 5.1.14 Watchdog
- 5.1.15 Peripheral Clocking
- 5.1.16 Low-power Modes
- 5.1.17 Peripheral Frames 0, 1, 2, 3 (PFn)
- 5.1.18 General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO) Multiplexer
- 5.1.19 32-Bit CPU-Timers (0, 1, 2)
- 5.1.20 Control Peripherals
- 5.1.21 Serial Port Peripherals
- 5.2 Memory Maps
- 5.3 Register Maps
- 5.4 Device Emulation Registers
- 5.5 VREG/BOR/POR
- 5.6 System Control
- 5.7 Low-Power Modes Block
- 5.8 Interrupts
- 5.9
Peripherals
- 5.9.1 Control Law Accelerator (CLA) Overview
- 5.9.2 Analog Block
- 5.9.3 Detailed Descriptions
- 5.9.4 Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) Module
- 5.9.5 Serial Communications Interface (SCI) Module
- 5.9.6 Local Interconnect Network (LIN)
- 5.9.7 Enhanced Controller Area Network (eCAN) Module
- 5.9.8 Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C)
- 5.9.9 Enhanced PWM Modules (ePWM1/2/3/4/5/6/7)
- 5.9.10 High-Resolution PWM (HRPWM)
- 5.9.11 Enhanced Capture Module (eCAP1)
- 5.9.12 High-Resolution Capture (HRCAP) Module
- 5.9.13 Enhanced Quadrature Encoder Pulse (eQEP)
- 5.9.14 JTAG Port
- 5.9.15 General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO) MUX
- 5.1
Overview
- 6Applications, Implementation, and Layout
- 7器件和文档支持
- 8机械、封装和可订购信息
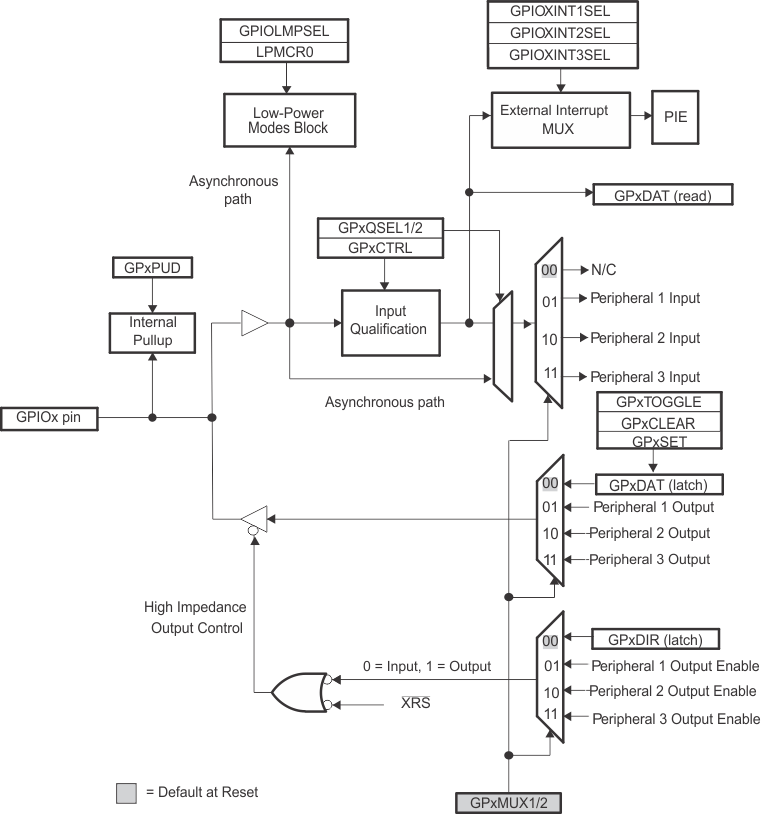
5.9.15 General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO) MUX
The GPIO MUX can multiplex up to three independent peripheral signals on a single GPIO pin in addition to providing individual pin bit-banging I/O capability.
The device supports 45 GPIO pins. The GPIO control and data registers are mapped to Peripheral Frame 1 to enable 32-bit operations on the registers (along with 16-bit operations). Table 5-60 shows the GPIO register mapping.
Table 5-60 GPIO Registers
| NAME | ADDRESS | SIZE (x16) | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPIO CONTROL REGISTERS (EALLOW PROTECTED) | |||
| GPACTRL | 0x6F80 | 2 | GPIO A Control Register (GPIO0 to 31) |
| GPAQSEL1 | 0x6F82 | 2 | GPIO A Qualifier Select 1 Register (GPIO0 to 15) |
| GPAQSEL2 | 0x6F84 | 2 | GPIO A Qualifier Select 2 Register (GPIO16 to 31) |
| GPAMUX1 | 0x6F86 | 2 | GPIO A MUX 1 Register (GPIO0 to 15) |
| GPAMUX2 | 0x6F88 | 2 | GPIO A MUX 2 Register (GPIO16 to 31) |
| GPADIR | 0x6F8A | 2 | GPIO A Direction Register (GPIO0 to 31) |
| GPAPUD | 0x6F8C | 2 | GPIO A Pullup Disable Register (GPIO0 to 31) |
| GPBCTRL | 0x6F90 | 2 | GPIO B Control Register (GPIO32 to 44) |
| GPBQSEL1 | 0x6F92 | 2 | GPIO B Qualifier Select 1 Register (GPIO32 to 44) |
| GPBMUX1 | 0x6F96 | 2 | GPIO B MUX 1 Register (GPIO32 to 44) |
| GPBDIR | 0x6F9A | 2 | GPIO B Direction Register (GPIO32 to 44) |
| GPBPUD | 0x6F9C | 2 | GPIO B Pullup Disable Register (GPIO32 to 44) |
| AIOMUX1 | 0x6FB6 | 2 | Analog, I/O mux 1 register (AIO0 to AIO15) |
| AIODIR | 0x6FBA | 2 | Analog, I/O Direction Register (AIO0 to AIO15) |
| GPIO DATA REGISTERS (NOT EALLOW PROTECTED) | |||
| GPADAT | 0x6FC0 | 2 | GPIO A Data Register (GPIO0 to 31) |
| GPASET | 0x6FC2 | 2 | GPIO A Data Set Register (GPIO0 to 31) |
| GPACLEAR | 0x6FC4 | 2 | GPIO A Data Clear Register (GPIO0 to 31) |
| GPATOGGLE | 0x6FC6 | 2 | GPIO A Data Toggle Register (GPIO0 to 31) |
| GPBDAT | 0x6FC8 | 2 | GPIO B Data Register (GPIO32 to 44) |
| GPBSET | 0x6FCA | 2 | GPIO B Data Set Register (GPIO32 to 44) |
| GPBCLEAR | 0x6FCC | 2 | GPIO B Data Clear Register (GPIO32 to 44) |
| GPBTOGGLE | 0x6FCE | 2 | GPIO B Data Toggle Register (GPIO32 to 44) |
| AIODAT | 0x6FD8 | 2 | Analog I/O Data Register (AIO0 to AIO15) |
| AIOSET | 0x6FDA | 2 | Analog I/O Data Set Register (AIO0 to AIO15) |
| AIOCLEAR | 0x6FDC | 2 | Analog I/O Data Clear Register (AIO0 to AIO15) |
| AIOTOGGLE | 0x6FDE | 2 | Analog I/O Data Toggle Register (AIO0 to AIO15) |
| GPIO INTERRUPT AND LOW-POWER MODES SELECT REGISTERS (EALLOW PROTECTED) | |||
| GPIOXINT1SEL | 0x6FE0 | 1 | XINT1 GPIO Input Select Register (GPIO0 to 31) |
| GPIOXINT2SEL | 0x6FE1 | 1 | XINT2 GPIO Input Select Register (GPIO0 to 31) |
| GPIOXINT3SEL | 0x6FE2 | 1 | XINT3 GPIO Input Select Register (GPIO0 to 31) |
| GPIOLPMSEL | 0x6FE8 | 2 | LPM GPIO Select Register (GPIO0 to 31) |
NOTE
There is a two-SYSCLKOUT cycle delay from when the write to the GPxMUXn/AIOMUXn and GPxQSELn registers occurs to when the action is valid.
Table 5-61 GPIOA MUX(1)(2)
| DEFAULT AT RESET
PRIMARY I/O FUNCTION |
PERIPHERAL
SELECTION 1 |
PERIPHERAL
SELECTION 2 |
PERIPHERAL
SELECTION 3 |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPAMUX1 REGISTER BITS | (GPAMUX1 BITS = 00) | (GPAMUX1 BITS = 01) | (GPAMUX1 BITS = 10) | (GPAMUX1 BITS = 11) |
| 1-0 | GPIO0 | EPWM1A (O) | Reserved | Reserved |
| 3-2 | GPIO1 | EPWM1B (O) | Reserved | COMP1OUT (O) |
| 5-4 | GPIO2 | EPWM2A (O) | Reserved | Reserved |
| 7-6 | GPIO3 | EPWM2B (O) | SPISOMIA (I/O) | COMP2OUT (O) |
| 9-8 | GPIO4 | EPWM3A (O) | Reserved | Reserved |
| 11-10 | GPIO5 | EPWM3B (O) | SPISIMOA (I/O) | ECAP1 (I/O) |
| 13-12 | GPIO6 | EPWM4A (O) | EPWMSYNCI (I) | EPWMSYNCO (O) |
| 15-14 | GPIO7 | EPWM4B (O) | SCIRXDA (I) | Reserved |
| 17-16 | GPIO8 | EPWM5A (O) | Reserved | ADCSOCAO (O) |
| 19-18 | GPIO9 | EPWM5B (O) | LINTXA (O) | HRCAP1 (I) |
| 21-20 | GPIO10 | EPWM6A (O) | Reserved | ADCSOCBO (O) |
| 23-22 | GPIO11 | EPWM6B (O) | LINRXA (I) | HRCAP2 (I) |
| 25-24 | GPIO12 | TZ1 (I) | SCITXDA (O) | SPISIMOB (I/O) |
| 27-26 | GPIO13(3) | TZ2 (I) | Reserved | SPISOMIB (I/O) |
| 29-28 | GPIO14(3) | TZ3 (I) | LINTXA (O) | SPICLKB (I/O) |
| 31-30 | GPIO15(3) | TZ1 (I) | LINRXA (I) | SPISTEB (I/O) |
| GPAMUX2 REGISTER BITS | (GPAMUX2 BITS = 00) | (GPAMUX2 BITS = 01) | (GPAMUX2 BITS = 10) | (GPAMUX2 BITS = 11) |
| 1-0 | GPIO16 | SPISIMOA (I/O) | Reserved | TZ2 (I) |
| 3-2 | GPIO17 | SPISOMIA (I/O) | Reserved | TZ3 (I) |
| 5-4 | GPIO18 | SPICLKA (I/O) | LINTXA (O) | XCLKOUT (O) |
| 7-6 | GPIO19/XCLKIN | SPISTEA (I/O) | LINRXA (I) | ECAP1 (I/O) |
| 9-8 | GPIO20 | EQEP1A (I) | Reserved | COMP1OUT (O) |
| 11-10 | GPIO21 | EQEP1B (I) | Reserved | COMP2OUT (O) |
| 13-12 | GPIO22 | EQEP1S (I/O) | Reserved | LINTXA (O) |
| 15-14 | GPIO23 | EQEP1I (I/O) | Reserved | LINRXA (I) |
| 17-16 | GPIO24 | ECAP1 (I/O) | Reserved | SPISIMOB (I/O) |
| 19-18 | GPIO25(3) | Reserved | Reserved | SPISOMIB (I/O) |
| 21-20 | GPIO26(3) | HRCAP1 (I) | Reserved | SPICLKB (I/O) |
| 23-22 | GPIO27(3) | HRCAP2 (I) | Reserved | SPISTEB (I/O) |
| 25-24 | GPIO28 | SCIRXDA (I) | SDAA (I/OD) | TZ2 (I) |
| 27-26 | GPIO29 | SCITXDA (O) | SCLA (I/OD) | TZ3 (I) |
| 29-28 | GPIO30 | CANRXA (I) | Reserved | Reserved |
| 31-30 | GPIO31 | CANTXA (O) | Reserved | Reserved |
Table 5-62 GPIOB MUX(1)
| DEFAULT AT RESET
PRIMARY I/O FUNCTION |
PERIPHERAL SELECTION 1 | PERIPHERAL SELECTION 2 | PERIPHERAL SELECTION 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPBMUX1 REGISTER BITS | (GPBMUX1 BITS = 00) | (GPBMUX1 BITS = 01) | (GPBMUX1 BITS = 10) | (GPBMUX1 BITS = 11) |
| 1-0 | GPIO32 | SDAA (I/OD) | EPWMSYNCI (I) | ADCSOCAO (O) |
| 3-2 | GPIO33 | SCLA (I/OD) | EPWMSYNCO (O) | ADCSOCBO (O) |
| 5-4 | GPIO34 | COMP2OUT (O) | Reserved | COMP3OUT (O) |
| 7-6 | GPIO35 (TDI) | Reserved | Reserved | Reserved |
| 9-8 | GPIO36 (TMS) | Reserved | Reserved | Reserved |
| 11-10 | GPIO37 (TDO) | Reserved | Reserved | Reserved |
| 13-12 | GPIO38/XCLKIN (TCK) | Reserved | Reserved | Reserved |
| 15-14 | GPIO39(2) | Reserved | Reserved | Reserved |
| 17-16 | GPIO40(2) | EPWM7A (O) | Reserved | Reserved |
| 19-18 | GPIO41(2) | EPWM7B (O) | Reserved | Reserved |
| 21-20 | GPIO42(2) | Reserved | Reserved | COMP1OUT (O) |
| 23-22 | GPIO43(2) | Reserved | Reserved | COMP2OUT (O) |
| 25-24 | GPIO44(2) | Reserved | Reserved | Reserved |
| 27-26 | Reserved | Reserved | Reserved | Reserved |
| 29-28 | Reserved | Reserved | Reserved | Reserved |
| 31-30 | Reserved | Reserved | Reserved | Reserved |
The user can select the type of input qualification for each GPIO pin through the GPxQSEL1/2 registers from four choices:
- Synchronization To SYSCLKOUT Only (GPxQSEL1/2 = 0, 0): This is the default mode of all GPIO pins at reset and it simply synchronizes the input signal to the system clock (SYSCLKOUT).
- Qualification Using Sampling Window (GPxQSEL1/2 = 0, 1 and 1, 0): In this mode the input signal, after synchronization to the system clock (SYSCLKOUT), is qualified by a specified number of cycles before the input is allowed to change.
- The sampling period is specified by the QUALPRD bits in the GPxCTRL register and is configurable in groups of 8 signals. It specifies a multiple of SYSCLKOUT cycles for sampling the input signal. The sampling window is either 3-samples or 6-samples wide and the output is only changed when ALL samples are the same (all 0s or all 1s) as shown in Figure 4-18 (for 6 sample mode).
- No Synchronization (GPxQSEL1/2 = 1,1): This mode is used for peripherals where synchronization is not required (synchronization is performed within the peripheral).
Due to the multilevel multiplexing that is required on the device, there may be cases where a peripheral input signal can be mapped to more then one GPIO pin. Also, when an input signal is not selected, the input signal will default to either a 0 or 1 state, depending on the peripheral.