SPRS377F September 2008 – June 2014 TMS320C6745 , TMS320C6747
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1TMS320C6745, TMS320C6747 Fixed- and Floating-Point Digital Signal Processor
- 2Revision History
-
3Device Overview
- 3.1 Device Characteristics
- 3.2 Device Compatibility
- 3.3 DSP Subsystem
- 3.4 Memory Map Summary
- 3.5 Pin Assignments
- 3.6
Terminal Functions
- 3.6.1 Device Reset and JTAG
- 3.6.2 High-Frequency Oscillator and PLL
- 3.6.3 Real-Time Clock and 32-kHz Oscillator
- 3.6.4 External Memory Interface A (ASYNC, SDRAM)
- 3.6.5 External Memory Interface B (only SDRAM)
- 3.6.6 Serial Peripheral Interface Modules (SPI0, SPI1)
- 3.6.7 Enhanced Capture/Auxiliary PWM Modules (eCAP0, eCAP1, eCAP2)
- 3.6.8 Enhanced Pulse Width Modulators (eHRPWM0, eHRPWM1, eHRPWM2)
- 3.6.9 Enhanced Quadrature Encoder Pulse Module (eQEP)
- 3.6.10 Boot
- 3.6.11 Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitters (UART0, UART1, UART2)
- 3.6.12 Inter-Integrated Circuit Modules (I2C0, I2C1)
- 3.6.13 Timers
- 3.6.14 Universal Host-Port Interface (UHPI)
- 3.6.15 Multichannel Audio Serial Ports (McASP0, McASP1, McASP2)
- 3.6.16 Universal Serial Bus Modules (USB0, USB1)
- 3.6.17 Ethernet Media Access Controller (EMAC)
- 3.6.18 Multimedia Card/Secure Digital (MMC/SD)
- 3.6.19 Liquid Crystal Display Controller (LCD)
- 3.6.20 General Purpose Input Output (GPIO)
- 3.6.21 Reserved and No Connect
- 3.6.22 Supply and Ground
- 3.6.23 Unused USB0 (USB2.0) and USB1 (USB1.1) Pin Configurations
- 4Device Configuration
-
5Device Operating Conditions
- 5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings Over Operating Case Temperature Range (Unless Otherwise Noted)
- 5.2 Handling Ratings
- 5.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 5.4 Notes on Recommended Power-On Hours (POH)
- 5.5 Electrical Characteristics Over Recommended Ranges of Supply Voltage and Operating Case Temperature (Unless Otherwise Noted)
-
6Peripheral Information and Electrical Specifications
- 6.1 Parameter Information
- 6.2 Recommended Clock and Control Signal Transition Behavior
- 6.3 Power Supplies
- 6.4 Reset
- 6.5 Crystal Oscillator or External Clock Input
- 6.6 Clock PLLs
- 6.7 Interrupts
- 6.8 General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO)
- 6.9 EDMA
- 6.10 External Memory Interface A (EMIFA)
- 6.11 External Memory Interface B (EMIFB)
- 6.12 Memory Protection Units
- 6.13 MMC / SD / SDIO (MMCSD)
- 6.14 Ethernet Media Access Controller (EMAC)
- 6.15 Management Data Input/Output (MDIO)
- 6.16 Multichannel Audio Serial Ports (McASP0, McASP1, and McASP2)
- 6.17
Serial Peripheral Interface Ports (SPI0, SPI1)
- 6.17.1 SPI Peripheral Registers Description(s)
- 6.17.2
SPI Electrical Data/Timing
- 6.17.2.1
Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) Timing
- Table 6-54 General Timing Requirements for SPI0 Master Modes
- Table 6-55 General Timing Requirements for SPI0 Slave Modes
- Table 6-56 Additional SPI0 Master Timings, 4-Pin Enable Option
- Table 6-57 Additional SPI0 Master Timings, 4-Pin Chip Select Option
- Table 6-58 Additional SPI0 Master Timings, 5-Pin Option
- Table 6-59 Additional SPI0 Slave Timings, 4-Pin Enable Option
- Table 6-60 Additional SPI0 Slave Timings, 4-Pin Chip Select Option
- Table 6-61 Additional SPI0 Slave Timings, 5-Pin Option
- Table 6-62 General Timing Requirements for SPI1 Master Modes
- Table 6-63 General Timing Requirements for SPI1 Slave Modes
- Table 6-64 Additional SPI1 Master Timings, 4-Pin Enable Option
- Table 6-65 Additional SPI1 Master Timings, 4-Pin Chip Select Option
- Table 6-66 Additional SPI1 Master Timings, 5-Pin Option
- Table 6-67 Additional SPI1 Slave Timings, 4-Pin Enable Option
- Table 6-68 Additional SPI1 Slave Timings, 4-Pin Chip Select Option
- Table 6-69 Additional SPI1 Slave Timings, 5-Pin Option
- 6.17.2.1
Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) Timing
- 6.18 Enhanced Capture (eCAP) Peripheral
- 6.19 Enhanced Quadrature Encoder (eQEP) Peripheral
- 6.20 Enhanced High-Resolution Pulse-Width Modulator (eHRPWM)
- 6.21 LCD Controller
- 6.22 Timers
- 6.23 Inter-Integrated Circuit Serial Ports (I2C0, I2C1)
- 6.24 Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (UART)
- 6.25 USB1 Host Controller Registers (USB1.1 OHCI)
- 6.26 USB0 OTG (USB2.0 OTG)
- 6.27 Host-Port Interface (UHPI)
- 6.28 Power and Sleep Controller (PSC)
- 6.29 Programmable Real-Time Unit Subsystem (PRUSS)
- 6.30 Emulation Logic
- 6.31 IEEE 1149.1 JTAG
- 6.32 Real Time Clock (RTC)
- 7Device and Documentation Support
- 8Mechanical Packaging and Orderable Information
3.3.1 C674x DSP CPU Description
The C674x Central Processing Unit (CPU) consists of eight functional units, two register files, and two data paths as shown in Figure 3-2. The two general-purpose register files (A and B) each contain 32 32-bit registers for a total of 64 registers. The general-purpose registers can be used for data or can be data address pointers. The data types supported include packed 8-bit data, packed 16-bit data, 32-bit data, 40-bit data, and 64-bit data. Values larger than 32 bits, such as 40-bit-long or 64-bit-long values are stored in register pairs, with the 32 LSBs of data placed in an even register and the remaining 8 or 32 MSBs in the next upper register (which is always an odd-numbered register).
The eight functional units (.M1, .L1, .D1, .S1, .M2, .L2, .D2, and .S2) are each capable of executing one instruction every clock cycle. The .M functional units perform all multiply operations. The .S and .L units perform a general set of arithmetic, logical, and branch functions. The .D units primarily load data from memory to the register file and store results from the register file into memory.
The C674x CPU combines the performance of the C64x+ core with the floating-point capabilities of the C67x+ core.
Each C674x .M unit can perform one of the following each clock cycle: one 32 x 32 bit multiply, one 16 x 32 bit multiply, two 16 x 16 bit multiplies, two 16 x 32 bit multiplies, two 16 x 16 bit multiplies with add/subtract capabilities, four 8 x 8 bit multiplies, four 8 x 8 bit multiplies with add operations, and four 16 x 16 multiplies with add/subtract capabilities (including a complex multiply). There is also support for Galois field multiplication for 8-bit and 32-bit data. Many communications algorithms such as FFTs and modems require complex multiplication. The complex multiply (CMPY) instruction takes four 16-bit inputs and produces a 32-bit real and a 32-bit imaginary output. There are also complex multiplies with rounding capability that produces one 32-bit packed output that contain 16-bit real and 16-bit imaginary values. The 32 x 32 bit multiply instructions provide the extended precision necessary for high-precision algorithms on a variety of signed and unsigned 32-bit data types.
The .L Unit (or Arithmetic Logic Unit) now incorporates the ability to do parallel add/subtract operations on a pair of common inputs. Versions of this instruction exist to work on 32-bit data or on pairs of 16-bit data performing dual 16-bit add and subtracts in parallel. There are also saturated forms of these instructions.
The C674x core enhances the .S unit in several ways. On the previous cores, dual 16-bit MIN2 and MAX2 comparisons were only available on the .L units. On the C674x core they are also available on the .S unit which increases the performance of algorithms that do searching and sorting. Finally, to increase data packing and unpacking throughput, the .S unit allows sustained high performance for the quad 8-bit/16-bit and dual 16-bit instructions. Unpack instructions prepare 8-bit data for parallel 16-bit operations. Pack instructions return parallel results to output precision including saturation support.
Other new features include:
- SPLOOP - A small instruction buffer in the CPU that aids in creation of software pipelining loops where multiple iterations of a loop are executed in parallel. The SPLOOP buffer reduces the code size associated with software pipelining. Furthermore, loops in the SPLOOP buffer are fully interruptible.
- Compact Instructions - The native instruction size for the C6000™ devices is 32 bits. Many common instructions such as MPY, AND, OR, ADD, and SUB can be expressed as 16 bits if the C674x compiler can restrict the code to use certain registers in the register file. This compression is performed by the code generation tools.
- Instruction Set Enhancement - As noted above, there are new instructions such as 32-bit multiplications, complex multiplications, packing, sorting, bit manipulation, and 32-bit Galois field multiplication.
- Exceptions Handling - Intended to aid the programmer in isolating bugs. The C674x CPU is able to detect and respond to exceptions, both from internally detected sources (such as illegal op-codes) and from system events (such as a watchdog time expiration).
- Privilege - Defines user and supervisor modes of operation, allowing the operating system to give a basic level of protection to sensitive resources. Local memory is divided into multiple pages, each with read, write, and execute permissions.
- Time-Stamp Counter - Primarily targeted for Real-Time Operating System (RTOS) robustness, a free-running time-stamp counter is implemented in the CPU which is not sensitive to system stalls.
For more details on the C674x CPU and its enhancements over the C64x architecture, see the following documents:
- TMS320C64x/C64x+ DSP CPU and Instruction Set Reference Guide (SPRU732)
- TMS320C64x Technical Overview (SPRU395)
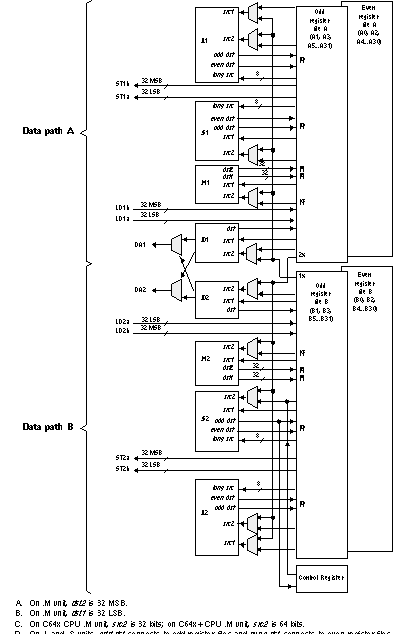 Figure 3-2 TMS320C674x CPU (DSP Core) Data Paths
Figure 3-2 TMS320C674x CPU (DSP Core) Data Paths