ZHCSHA4B July 2007 – January 2018 DAC8881
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11器件和文档支持
封装选项
机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
- RGE|24
散热焊盘机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
- RGE|24
订购信息
7.3.2 Reference Inputs
The reference high input, VREFH, can be set to any voltage in the range of 1.25 V to AVDD. The reference low input, VREFL, can be set to any voltage in the range of –0.2 V to +0.2 V (to provide a small offset to the output of the DAC8881, if desired). The current into VREFH and out of VREFL depends on the DAC code, and can vary from approximately 0.5mA to 1mA in the gain = 1X mode of operation. The reference high and low inputs appear as varying loads to the external reference circuit. If the external references can source or sink the required current, and if low impedance connections are made to the VREFH and VREFL pins, external reference buffers are not required. Figure 67 shows a simple configuration of the DAC8881 using external references without force/sense reference buffers.
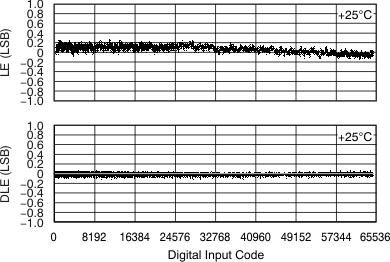
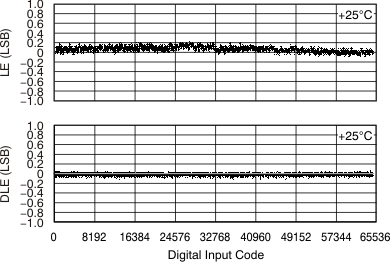
Kelvin sense connections for the reference high and low are included on the DAC8881. When properly used with external reference buffer op amps, these reference Kelvin sense pins ensure that the driven reference high and low voltages remain stable versus varying reference load currents. Figure 69 shows an example of a reference force/sense configuration of the DAC8881 operating from a single analog supply voltage. Both the VREFL and VREFH reference voltages are set to levels of 100 mV from the DAC8881 supply rails, and are derived from a 5-V external reference. Figure 71 and Figure 70 illustrate the effect of not using the reference force/sense buffers to drive the DAC8881 VREFL and VREFH pins. A slight degradation in INL and DNL performance of approximately 0.1 LSB may be seen without the use of the force/sense buffer configuration.
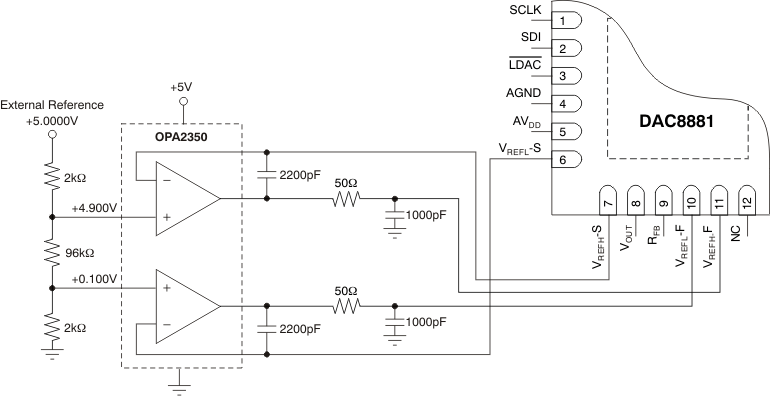 Figure 69. Buffered References (VREFH = +4.900 V and VREFL = 100 mV)
Figure 69. Buffered References (VREFH = +4.900 V and VREFL = 100 mV)