ZHCSEV8D March 2016 – January 2018 ADS131A02 , ADS131A04
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 Electrical Characteristics
- 7.6 Timing Requirements: Asynchronous Interrupt Interface Mode
- 7.7 Switching Characteristics: Asynchronous Interrupt Interface Mode
- 7.8 Timing Requirements: Synchronous Master Interface Mode
- 7.9 Switching Characteristics: Synchronous Master Interface Mode
- 7.10 Timing Requirements: Synchronous Slave Interface Mode
- 7.11 Switching Characteristics: Synchronous Slave Interface Mode
- 7.12 Typical Characteristics
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3 Feature Description
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9.5
Programming
- 9.5.1 Interface Protocol
- 9.5.2 SPI Interface
- 9.5.3
SPI Command Definitions
- 9.5.3.1 NULL: Null Command
- 9.5.3.2 RESET: Reset to POR Values
- 9.5.3.3 STANDBY: Enter Standby Mode
- 9.5.3.4 WAKEUP: Exit STANDBY Mode
- 9.5.3.5 LOCK: Lock ADC Registers
- 9.5.3.6 UNLOCK: Unlock ADC Registers
- 9.5.3.7 RREG: Read a Single Register
- 9.5.3.8 RREGS: Read Multiple Registers
- 9.5.3.9 WREG: Write Single Register
- 9.5.3.10 WREGS: Write Multiple Registers
- 9.6
Register Maps
- 9.6.1
User Register Description
- 9.6.1.1 ID_MSB: ID Control Register MSB (address = 00h) [reset = xxh]
- 9.6.1.2 ID_LSB: ID Control Register LSB (address = 01h) [reset = xxh]
- 9.6.1.3 STAT_1: Status 1 Register (address = 02h) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.1.4 STAT_P: Positive Input Fault Detect Status Register (address = 03h) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.1.5 STAT_N: Negative Input Fault Detect Status Register (address = 04h) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.1.6 STAT_S: SPI Status Register (address = 05h) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.1.7 ERROR_CNT: Error Count Register (address = 06h) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.1.8 STAT_M2: Hardware Mode Pin Status Register (address = 07h) [reset = xxh]
- 9.6.1.9 Reserved Registers (address = 08h to 0Ah) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.1.10 A_SYS_CFG: Analog System Configuration Register (address = 0Bh) [reset = 60h]
- 9.6.1.11 D_SYS_CFG: Digital System Configuration Register (address = 0Ch) [reset = 3Ch]
- 9.6.1.12 CLK1: Clock Configuration 1 Register (address = 0Dh) [reset = 08h]
- 9.6.1.13 CLK2: Clock Configuration 2 Register (address = 0Eh) [reset = 86h]
- 9.6.1.14 ADC_ENA: ADC Channel Enable Register (address = 0Fh) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.1.15 Reserved Register (address = 10h) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.2 ADCx: ADC Channel Digital Gain Configuration Registers (address = 11h to 14h) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.1
User Register Description
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13器件和文档支持
- 14机械、封装和可订购信息
9.5.1.6 Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC)
The CRC word is the last device word in the DIN and DOUT data frame. The CRC device word is optional and is enabled by the CRC_EN control bit in the D_SYS_CFG register. When enabled, a 16-bit CRC data check word is present in the 16 most significant bits of the last device word in the data frame on both DIN and DOUT. Use the CRC to provide detection of single and multiple bit errors during data transmission.
The ADS131A0x implements a standard CRC16-CCITT algorithm using a polynomial of 11021h and an initial remainder of FFFFh.
The CRC on all DIN commands is verified by the device prior to command execution except for the WREGS command; see the WREGS: Write Multiple Registers section. The WREGS command does not check the CRC prior to writing registers but does indicate if an error occurred. If the CRC on DIN is incorrect, F_CHECK in the STAT_1 register is set to 1 and the input command does not execute (for all commands except WREGS). Fill the unused device words on DIN with zeroes, placing the CRC word in the last device word.
The number of input CRC errors is counted and stored in the error count register. The register counts errors up to 255 before rolling over to 0. The counter is cleard by reading the ERROR_CNT register.
The CRC is calculated using specific device words in the data frame determined by the CRC_MODE and FIXED bits in the D_SYS_CFG register. For DIN, when the FIXED bit is 0, all device words are calculated into the CRC. When the FIXED bit is 1 and the CRC_MODE bit is 1, all device words are used for calculating the CRC on DIN. When the FIXED bit is 1 and the CRC_MODE bit is 0, only the command word and device words are used for the CRC calculation on DIN.
For DOUT, when the FIXED bit is 0, all device words in the data frame are included in the CRC calculation. When the FIXED bit is 1 and CRC_MODE is 1, all device words in the data frame are included in the DOUT CRC calculation. When the FIXED bit is 1 and CRC_MODE is 0, only the command, status word, and active device words are included in the DOUT CRC calculation. When hamming codes are enabled, the hamming byte of each word is omitted in the CRC calculation.
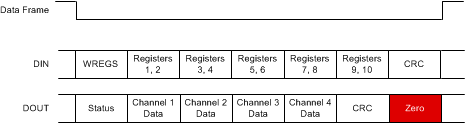
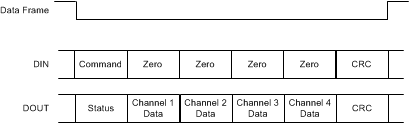
Figure 55 and Figure 56 show which device words are included in the CRC calculation on DIN and DOUT under various CRC settings. In the following examples, the device words that are not checked are highlighted in red.
NOTE:
CRC_MODE = 1.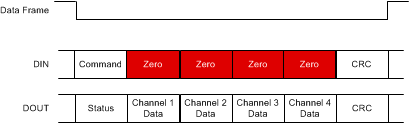
NOTE:
CRC_MODE = 0.The WREGS command causes the data frame to extend until the last register is written (see the WREGS: Write Multiple Registers section for more details), thus requiring the CRC to be placed on DIN after the data frame extension. The ADS131A0x places the CRC word on DOUT at the end of all ADC data. When sending the WREGS command, the device words following the CRC on DOUT are padded with zeroes and are not included in the CRC calculation; see Figure 57. The device words that are not checked are highlighted in red.