ZHCSAF0E September 2012 – January 2018
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用范围
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 说明 (续)
- 6 Device Comparisons
- 7 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 8 Specifications
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagrams
- 9.3 Operational Flow Chart
- 9.4 Feature Description
- 9.5 Device Functional Modes
- 9.6 Programming
- 9.7 Register Description
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14机械、封装和可订购信息
10.1.2 Charge Current Sensing Resistor Selection Guidelines
Both the termination current range and charge current range depend on the sensing resistor (RSNS). The termination current step (IOTERM_STEP) can be calculated using Equation 11:
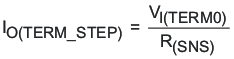
Table 11 shows the termination current settings for three sensing resistors.
Table 11. Termination Current Settings for 55-mΩ, 68-mΩ, 100-mΩ Sense Resistors
| BIT | VI(TERM) (mV) | I(TERM) (mA) R(SNS) = 55mΩ | I(TERM) (mA) R(SNS) = 68mΩ | I(TERM) (mA) R(SNS) = 100mΩ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VI(TERM2) | 13.6 | 247 | 200 | 136 |
| VI(TERM1) | 6.8 | 124 | 100 | 68 |
| VI(TERM0) | 3.4 | 62 | 50 | 34 |
| Offset | 3.4 | 62 | 50 | 34 |
For example, with a 68-mΩ sense resistor, V(ITERM2) = 1, V(ITERM1) = 0, and V(ITERM0) = 1, ITERM = [ (13.6 mV x 1) + (6.8 mV x 0) + (3.4 mV x 1) + 3.4 mV ] / 68 mΩ = 200 mA + 0 + 50 mA + 50 mA = 300 mA.
The charge current step (IO(CHARGE_STEP)) is calculated using Equation 12:
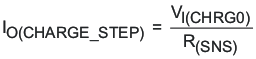
Table 12 shows the charge current settings for three sensing resistors.
Table 12. Charge Current Settings for 55-mΩ, 68-mΩ and 100-mΩ Sense Resistors
| BIT | VI(REG) (mV) | IO(CHARGE) (mA) R(SNS) = 55mΩ | IO(CHARGE) (mA) R(SNS) = 68mΩ | IO(CHARGE) (mA) R(SNS) = 100mΩ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VI(CHRG3) | 27.2 | 495 | 400 | 272 |
| VI(CHRG2) | 13.6 | 247 | 200 | 136 |
| VI(CHRG1) | 6.8 | 124 | 100 | 68 |
| VI(CHRG0) | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Offset | 37.4 | 680 | 550 | 374 |
For example, with a 68-mΩ sense resistor, V(CHRG3) = 1, V(CHRG2) = 1, V(ICHRG1) = 1, ICHRG = [ (27.2 mV x 1) + (13.6 mV x 1) + (6.8 mV x 1) + 37.4 mV ] / 68 mΩ = 400 mA + 200 + 100 + 550 mA = 1250 mA.