ZHCSAF0E September 2012 – January 2018
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用范围
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 说明 (续)
- 6 Device Comparisons
- 7 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 8 Specifications
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagrams
- 9.3 Operational Flow Chart
- 9.4 Feature Description
- 9.5 Device Functional Modes
- 9.6 Programming
- 9.7 Register Description
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14机械、封装和可订购信息
10.1.1.2 Detailed Design Procedure
Systems Design Specifications:
- VBUS = 5 V
- VBAT = 4.2 V (1-Cell)
- I(charge) = 1.25 A
- Inductor ripple current = 30% of fast charge current
- Determine the inductor value (LOUT) for the specified charge current ripple:
- Determine the output capacitor value (COUT) using 40 kHz as the resonant frequency:
- Determine the sense resistor using the following equation:
- Measured efficiency and total power loss with different inductors are shown in Figure 24. SW node and inductor current waveform are shown in Figure 34.
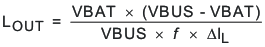 , the worst case is when battery voltage is as close as to half of the input voltage.
, the worst case is when battery voltage is as close as to half of the input voltage.
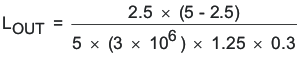
LOUT = 1.11 μH
Select the output inductor to standard 1 μH. Calculate the total ripple current with using the 1-μH inductor:
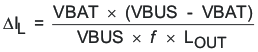
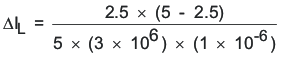
ΔIL = 0.42 A
Calculate the maximum output current:
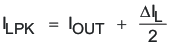
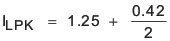
ILPK = 1.46 A
Select 2.5mm by 2mm 1-μH 1.5-A surface mount multi-layer inductor. The suggested inductor part numbers are shown as following.
Table 10. Inductor Part Numbers(1)
| PART NUMBER | INDUCTANCE | SIZE | MANUFACTURER |
|---|---|---|---|
| LQM2HPN1R0MJ0 | 1 μH | 2.5 x 2.0 mm | Murata |
| MIPS2520D1R0 | 1 μH | 2.5 x 2.0 mm | FDK |
| MDT2520-CN1R0M | 1 μH | 2.5 x 2.0 mm | TOKO |
| CP1008 | 1 μH | 2.5 x 2.0 mm | Inter-Technical |
spacer
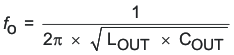
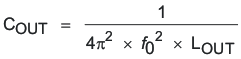
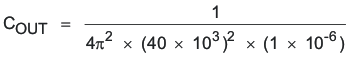
COUT = 15.8 μF
Select two 0603 X5R 6.3V 10-μF ceramic capacitors in parallel i.e., Murata GRM188R60J106M.
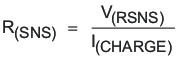
The maximum sense voltage across the sense resistor is 85 mV. In order to get a better current regulation accuracy, V(RSNS) should equal 85mV, and calculate the value for the sense resistor.
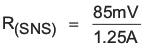
R(SNS) = 68 mΩ
This is a standard value. If it is not a standard value, then choose the next close value and calculate the real charge current. Calculate the power dissipation on the sense resistor:
P(RSNS) = I(CHARGE)2 × R(SNS)
P(RSNS) = 1.252 × 0.068
P(RSNS) = 0.106 W
Select 0402 0.125-W 68-mΩ 2% sense resistor, i.e. Panasonic ERJ2BWGR068.
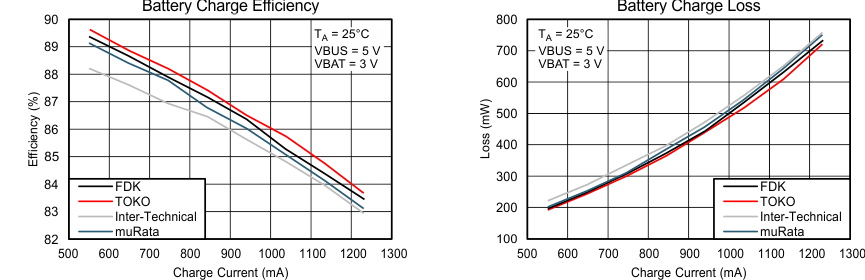 Figure 24. Measured Efficiency and Power Loss
Figure 24. Measured Efficiency and Power Loss