SLUAAJ7 June 2022 UCC256402 , UCC256403 , UCC256404
- Abstract
- Trademarks
- 1UCC25640x Selection Guide
- 2UCC25640x Features Brief Overview
- 3UCC25640x Power Up Guidelines and Debugging Notes
- 4References
2.3.1 FBreplica Generation
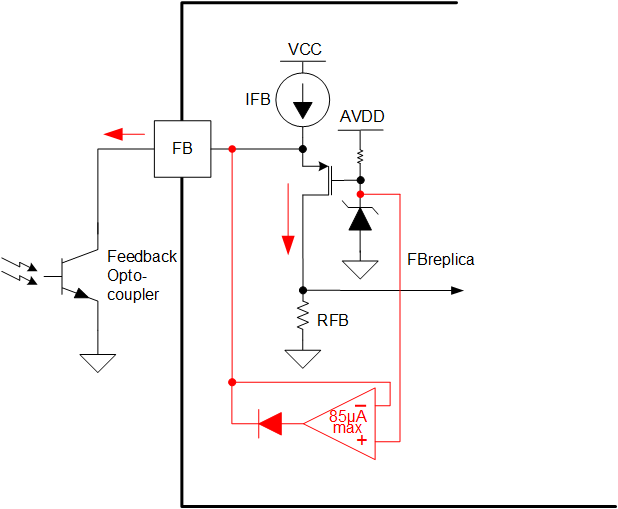 Figure 2-12 FBreplica Generation
Figure 2-12 FBreplica Generation- FB pin is supplied with an IFB current source
- The optocoupler collector voltage maintained at approximate constant voltage (~5.6 V) when FB sourcing current is less than IFB. Due to this, no extra pole introduced due to the optocoupler parasitic capacitor
- The FB clamp circuit is to provide extra 82uA current to the FB pin when needed to prevent FB voltage drop and to maintain good transient performance
- The Optocoupler current is reflected as the FBreplica in the IC for control purpose
- Voltage at the RFB is given by FBreplica = (IFB-Ioptocoupler) *RFB where RFB typical value is 100 kohm and IFB typical values are 82 uA (for 402, 404 devices) and 164 uA (403, 403A devices).
- If the current through optocoupler is zero during the heavy output load, FB pin voltage will be clamped to internal whereas FBreplica is clamped to 6 V.