SLUAAJ7 June 2022 UCC256402 , UCC256403 , UCC256404
- Abstract
- Trademarks
- 1UCC25640x Selection Guide
- 2UCC25640x Features Brief Overview
- 3UCC25640x Power Up Guidelines and Debugging Notes
- 4References
2.6.2 BMTL/BMTH Ratio Programming
 Figure 2-27 Internal Diagram and Typical
Circuit of BW Pin of UCC25640X
Figure 2-27 Internal Diagram and Typical
Circuit of BW Pin of UCC25640XEquation 8. 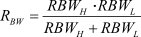
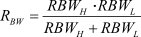
- BW pin is multiplex for BMTL/BMTH ratio programming and Over voltage protection (OVP). This pin sources a fixed current of 54 uA before soft start to determine the BW voltage and it is internally compared with a series of voltage levels to determine the BMTL/BMTH ratio. It would take 2 ms to determine this BW pin voltage.
- In case if the capacitor is connected the BW pin to eliminate the high frequency noise, its value should be such that time constant of RBW and CBW much less than 2 ms of the proper programming.
- Based on the BW pin equivalent resistance (RBW value as given in Equation 8), the ratio of BMTL and BMTH is determined as shown in the Table 2-1
Table 2-1 BMTL/BMTH value
| Option | RBW | BMTL/BMTH |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | > 24.7 k | 0.95 |
| 2 | 17.1 k – 19.9 k | 1 |
| 3 | 12.5 k – 13.6 k | 0.9 |
| 4 | 9.02 k – 9.81 k | 0.8 |
| 5 | 6.48 k – 6.85 k | 0.6 (No Vssinit) |
| 6 | 4.45 k – 4.73 k | 0.6 |
| 7 | 2.42 k – 3.04 k | 0.4 (Burst disabled) |
| 8 | Shorted | 0.6 |