ZHCSMR1C october 2019 – september 2021 UCC5870-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Power Supplies
- 7.3.2 Driver Stage
- 7.3.3 Integrated ADC for Front-End Analog (FEA) Signal Processing
- 7.3.4 Fault and Warning Classification
- 7.3.5
Diagnostic Features
- 7.3.5.1 Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO) and Overvoltage Lockout (OVLO)
- 7.3.5.2 CLAMP, OUTH, and OUTL Clamping Circuits
- 7.3.5.3 Active Miller Clamp
- 7.3.5.4 DESAT based Short Circuit Protection (DESAT)
- 7.3.5.5 Shunt Resistor based Overcurrent Protection (OCP) and Short Circuit Protection (SCP)
- 7.3.5.6 Temperature Monitoring and Protection for the Power Transistors
- 7.3.5.7 Active High Voltage Clamping (VCECLP)
- 7.3.5.8 Two-Level Turn-Off
- 7.3.5.9 Soft Turn-Off (STO)
- 7.3.5.10 Thermal Shutdown (TSD) and Temperature Warning (TWN) of Driver IC
- 7.3.5.11 Active Short Circuit Support (ASC)
- 7.3.5.12 Shoot-Through Protection (STP)
- 7.3.5.13 Gate Voltage Monitoring and Status Feedback
- 7.3.5.14 VGTH Monitor
- 7.3.5.15 Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC)
- 7.3.5.16 Configuration Data CRC
- 7.3.5.17 SPI Transfer Write/Read CRC
- 7.3.5.18 TRIM CRC Check
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6 Register Maps
- 8 Applications and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.1.2 Device Addressing
When using the Address-based configuration for SPI communication in the system, all devices must be individually addressed. Upon entering the Configuration 1 state (indicated by nFLT* high, assuming no fault during startup), all devices are addressable 0x1 through 0xE (14 unique addresses), with 0xF being a broadcast address to which all devices respond. Addressing is done in the Configuration 1 state. In this state, the IN+ input is pulled high while the WR_CA command is sent with the defined address. The written address is stored in the GDADDRESS[GD_ADDR] bits (GDADDRESS). Once all devices are addressed, send the CFG_IN command with the broadcast device address (0xF) to lock in the device address and move to configuring the devices (Configuration 2 state). The timing diagram for the addressing is shown in Timing diagram for addressing when using the Address-based SPI Communication Scheme..
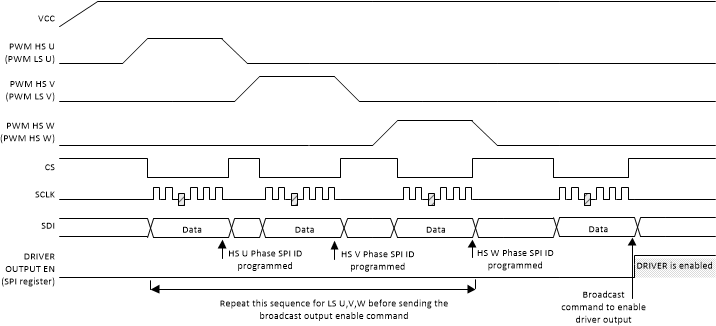 Figure 8-1 Timing diagram for addressing when using the Address-based SPI Communication Scheme.
Figure 8-1 Timing diagram for addressing when using the Address-based SPI Communication Scheme.