ZHCSKF4C March 2017 – October 2019 LMH1228
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 4-Level Input Pins and Thresholds
- 7.3.2 OUT0_SEL and SDI_OUT2_SEL Control
- 7.3.3 Input Signal Detect
- 7.3.4 Continuous Time Linear Equalizer (CTLE)
- 7.3.5 Clock and Data (CDR) Recovery
- 7.3.6 Internal Eye Opening Monitor (EOM)
- 7.3.7 Output Function Control
- 7.3.8 Output Driver Control
- 7.3.9 Status Indicators and Interrupts
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Register Maps
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11器件和文档支持
- 12机械、封装和可订购信息
7.4.2.3 SPI Read Transaction Format
A SPI read transaction is 34 bits per device and consists of two 17-bit frames. The first 17-bit read transaction frame shifts in the address to be read, followed by a dummy transaction second frame to shift out 17-bit read data. The R/W bit is 1'b for the read transaction, as shown in Figure 18.
The first 17 bits from the read transaction specifies 1-bit of R/W and 8-bits of address A7-A0 in the first 8 bits. The eight 1’s following the address are ignored. The second dummy transaction acts like a read operation on address 0xFF and needs to be ignored. However, the transaction is necessary to shift out the read data D7-D0 in the last 8 bits of the MISO output. As with the SPI Write, the prime values on MISO during the first 16 clocks are listed as don’t care for this portion of the transaction. The values shifted out on MISO during the last 17 clocks reflect the read address and 8-bit read data for the current transaction.
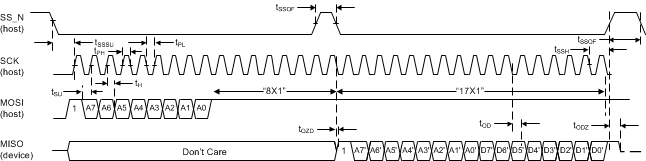 Figure 18. Signal Timing for a SPI Read Transaction
Figure 18. Signal Timing for a SPI Read Transaction