ZHCSGZ7E March 2017 – May 2021 CC3220MOD , CC3220MODA
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 功能方框图
- 5 Revision History
- 6 Device Comparison
- 7 Terminal Configuration and Functions
-
8 Specifications
- 8.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 8.2 ESD Ratings
- 8.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 8.4 Current Consumption (CC3220MODS and CC3220MODAS)
- 8.5 Current Consumption (CC3220MODSF and CC3220MODASF)
- 8.6 TX Power and IBAT Versus TX Power Level Settings
- 8.7 Brownout and Blackout Conditions
- 8.8 Electrical Characteristics
- 8.9 CC3220MODAx Antenna Characteristics
- 8.10 WLAN Receiver Characteristics
- 8.11 WLAN Transmitter Characteristics
- 8.12 Reset Requirement
- 8.13 Thermal Resistance Characteristics for MOB and MON Packages
- 8.14
Timing and Switching Characteristics
- 8.14.1 Power-Up Sequencing
- 8.14.2 Power-Down Sequencing
- 8.14.3 Device Reset
- 8.14.4 Wake Up From Hibernate Timing
- 8.14.5 Peripherals Timing
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Arm® Cortex®-M4 处理器内核子系统
- 9.3 Wi-Fi® Network Processor Subsystem
- 9.4 Security
- 9.5 Power-Management Subsystem
- 9.6 Low-Power Operating Mode
- 9.7 Memory
- 9.8 Restoring Factory Default Configuration
- 9.9 Boot Modes
- 9.10 Device Certification and Qualification
- 9.11 Module Markings
- 9.12 End Product Labeling
- 9.13 Manual Information to the End User
- 10Applications, Implementation, and Layout
- 11Environmental Requirements and Specifications
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
请参考 PDF 数据表获取器件具体的封装图。
机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
- MON|63
散热焊盘机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
8.7 Brownout and Blackout Conditions
The module enters a brownout condition whenever the input voltage dips below VBROWNOUT (see Figure 8-4 and Figure 8-5). This condition must be considered during design of the power supply routing, especially if operating from a battery. High-current operations, such as a TX packet or any external activity (not necessarily related directly to networking) can cause a drop in the supply voltage, potentially triggering a brownout. The resistance includes the internal resistance of the battery, contact resistance of the battery holder (four contacts for a 2× AA battery), and the wiring and PCB routing resistance.
When the module is in HIBERNATE state, brownout is not detected. Only blackout is in effect during HIBERNATE state.
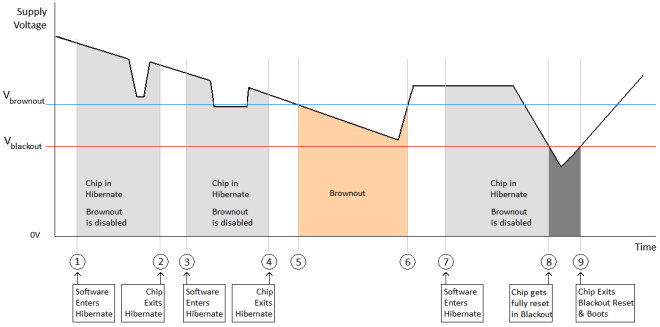 Figure 8-4 Brownout and Blackout Levels (1 of 2)
Figure 8-4 Brownout and Blackout Levels (1 of 2)
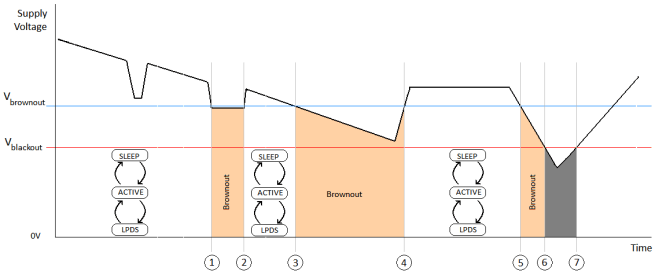 Figure 8-5 Brownout and Blackout Levels (2 of 2)
Figure 8-5 Brownout and Blackout Levels (2 of 2)In the brownout condition, all sections of the device shut down within the module except for the Hibernate block (including the 32-kHz RTC clock), which remains on. The current in this state can reach approximately 400 µA. The blackout condition is equivalent to a hardware reset event in which all states within the module are lost. Vbrownout = 2.1 V and Vblackout = 1.67 V
Table 8-1 lists the brownout and blackout voltage levels.
| CONDITION | VOLTAGE LEVEL | UNIT |
|---|---|---|
| Vbrownout | 2.1 | V |
| Vblackout | 1.67 | V |