TIDUEX1A December 2020 – March 2021
3.2.2.2.5 Register Tab
The Register Map page, shown in Figure 3-13, allows low-level access to all I2C registers of the TMP117 devices and provides access to the registers raw data of the TMP117, performing read and writes commands. Clicking the question mark to the right of the Register Name brings up an extraction short version from the data sheet describing that register. Clicking on a specific Register Name populates the Field View to on the right side of the screen. The Field View describes each bit field within that register. Changes to the configuration page are mirrored here, and vice versa.
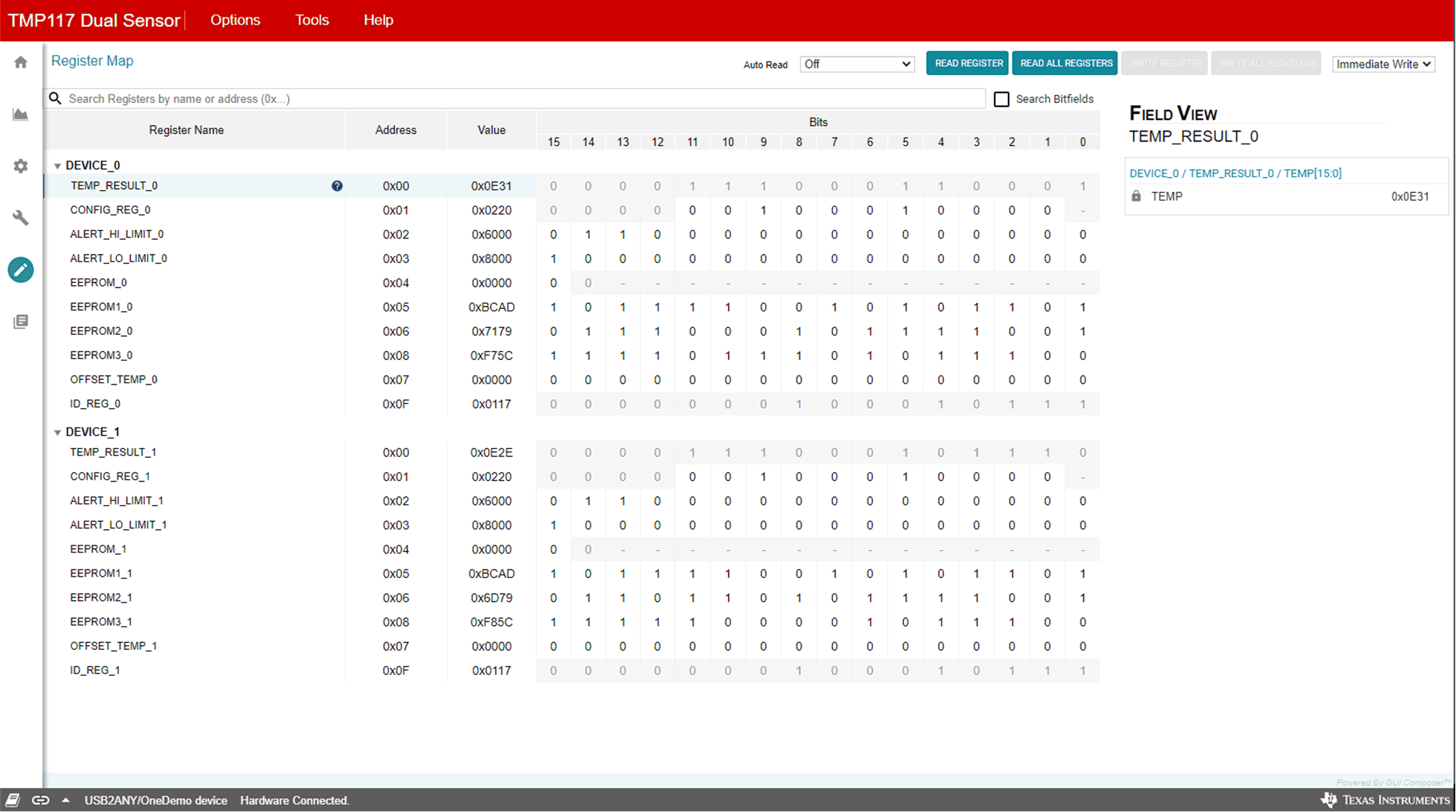 Figure 3-13 Register Tab
Figure 3-13 Register Tab- Read Registers performs one single read for the selected register.
- Read All Registers performs a read for all registers contents.
- Auto Read sets the desired time frame fetching each data.