SWRU596 December 2022
- 1Abstract
- 2Getting Started
- 3Hardware
- 4EVM Mux Block Diagram
- 5PCB Storage and Handling Recommendations:
- 6XWRL6432BOOST Antenna
- 7Software, Development Tools, and Example Code
- 8TI E2E Community
- 9References
6.8 CANFD Connector
The CAN connector provides access to the CAN_FD interfaces (CAN_L and CAN_H signals) from the onboard CAND-FD transceivers. These signals can be directly wired to the CAN bus.
 Figure 6-11 CANFD Connector
Figure 6-11 CANFD ConnectorThe J3 connector shown in Figure 6-11 provides the CAN_L and CAN_H signals from the onboard CAND-FD transceivers (TCAN1042HGVDRQ1). These signals are wired to the CAN bus after muxing with the SPI interface signals; one of the two paths must be selected. CAN signals are selected to PHY by changing the switch S1.5 to off position.
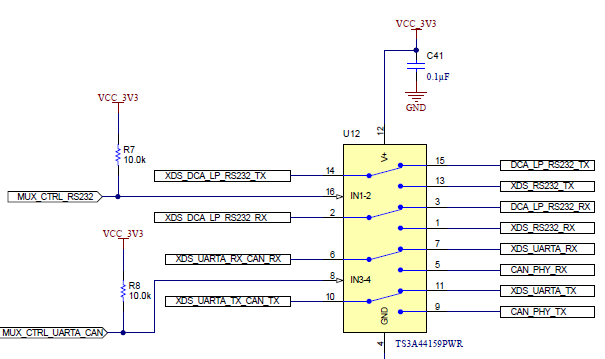 Figure 6-12 Analog Mux for the CAN PHY Switch
Figure 6-12 Analog Mux for the CAN PHY Switch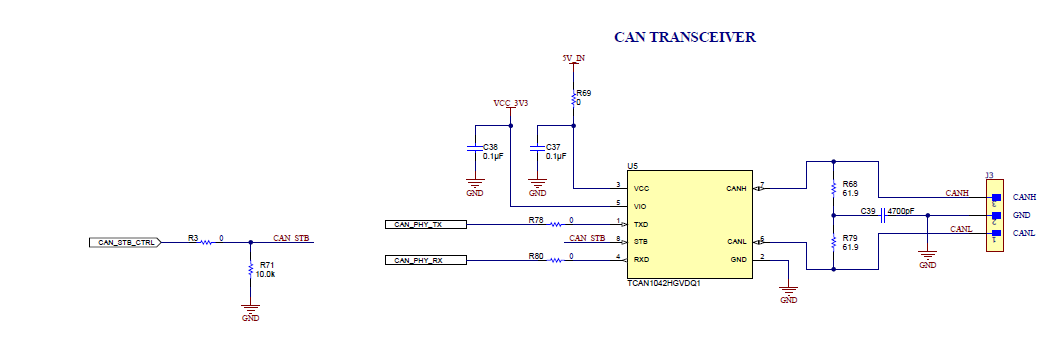 Figure 6-13 CAN FD PHY used in the EVM
Figure 6-13 CAN FD PHY used in the EVM