SPRUIM6A October 2018 – November 2020
- 1Introduction
- 2AM65x IDK Overview
-
3Common Processor Board
- 3.1 Key Features
- 3.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 3.3
Overview of Common Processor Board
- 3.3.1 Clocking
- 3.3.2 Reset
- 3.3.3 Power Requirements
- 3.3.4 Configuration
- 3.3.5 Memory Interfaces
- 3.3.6 Ethernet Interface
- 3.3.7 LCD Display Interface
- 3.3.8 USB 2.0 Interface
- 3.3.9 CSI-2 Interface
- 3.3.10 Application Card Interface
- 3.3.11 SERDES Interface
- 3.3.12 GPMC/DSS Interface
- 3.3.13 I2C Interface
- 3.3.14 SPI Interface
- 3.3.15 Timer and Interrupt
- 3.3.16 Fan Connector
- 4IDK Application Card
- 5x2 Lane PCIe Personality Card
-
6Known Issues
- 6.1 Determining the Revision and Date Code for the EVM
- 6.2 Known Issues for the A, E4, and E3 Revision
- 6.3 Known Issues for the E4 & E3 Revision
- 6.4
Known Issues for the E3 Revision
- 6.4.1 Resonance Observed on the SoC Side of Some Filters Associated with VDDA_1V8
- 6.4.2 Additional LDO Power Supply Needed for VDDA_1P8_SERDES0
- 6.4.3 Length of the RESET Signal to the PCIE Connectors on the SERDES Daughter Card
- 6.4.4 The PORz_OUT and MCU_PORz_OUT Signals Go High During Power Sequencing
- 6.4.5 Orientation of the Current Monitoring Shunt Resistors
- 6.4.6 SD Card IO Supply Capacitance
- 6.4.7 PHY Resistor Strapping Changed to Disable EEE Mode
- 6.4.8 The I2C Address for the I2C Boot Memory changed to 0x52
- 7Configuring the PRG0 and PRG1 Ethernet Interface to MII
- 8Revision History
3.3.4.1 Boot Modes
The boot mode for the SoC is defined by a bank of switches SW2, SW3, and SW4. Switch set to “ON” corresponds to logic “HIGH”, while “OFF” corresponds to logic “LOW”. The following boot modes are supported:
- No boot
- OSPI
- MMC1 - SDCard
- MMC 0- eMMC installed
- PCIE - PCIE as an endpoint
- CPSW - Ethernet slave boot
- USB - boot using host mode with bulk storage. USB2.0 mass storage device using FAT16/32 (such as a thumb drive)
- USB - device boot DFU
- UART
- I2C EEPROM
The BOOTMODE pins provide the means to select the boot mode before the device is powered up. They are divided into the following categories.
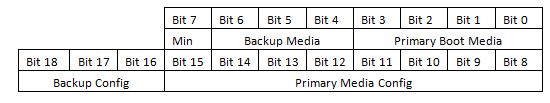 Figure 3-8 BOOTMODE Bits
Figure 3-8 BOOTMODE BitsBOOTMODE[3:0] – This provides the primary boot mode configuration to select the requested boot mode after POR; that is, the peripheral/memory to boot from.
| SW3.4 | SW3.3 | SW3.2 | SW3.1 | Primary Boot Device Selected |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| off | off | off | off | Sleep (No boot – debug mode) |
| off | off | off | on | OSPI |
| off | off | on | off | QSPI |
| off | off | on | on | Hyperflash |
| off | on | off | off | SPI (on QSPI/OSPI port 0 in legacy SPI mode) |
| off | on | off | on | I2C |
| off | on | on | off | MMC/SD card, eMMC boot from UDA or file system |
| off | on | on | on | Ethernet |
| on | off | off | off | USB |
| on | off | off | on | PCIe |
| on | off | on | off | UART |
| on | off | on | on | Reserved |
| on | on | off | off | GPMC XIP |
| on | on | off | on | eMMC boot from boot partition (with auto-fall back to file system) |
| on | on | on | off | Reserved (acts as no boot) |
| on | on | on | on | Reserved (acts as no boot) |
BOOTMODE[6:4] – Select the backup boot mode; that is, the peripheral/memory to boot from, if the primary boot device failed.
| SW3.7 | SW3.6 | SW3.5 | Backup Boot Device Selected |
|---|---|---|---|
| off | off | off | None (No backup mode) |
| off | off | on | USB |
| off | on | off | UART |
| off | on | on | Ethernet |
| on | off | off | MMC/SD |
| on | off | on | SPI on OSPI/OSPI port 0 in legacy SPI mode) |
| on | on | off | Hyper flash |
| on | on | on | I2C |
BOOTMODE07 – This is the minimum (MIN) configuration pin. The min pin is provided as a way to use minimal pin strapping to configure boot. When the min pin value is 1, all configuration fields are based on pre-defined default values. In this case, no boot mode pins beyond the min pin need to be driven because their values are ignored.
BOOTMODE[15:8] – These pins provide optional settings and are used in conjunction with the primary boot device selected. Refer to the AM65x Multicore ARM Keystone III System-on-Chip (SoC) Technical Reference Manual for more details.
| SW2.6 | SW2.5 | SW2.4 | SW2.3 | SW2.2 | SW2.1 | SW3.10 | SW3.9 | Boot Device |
| Not Used | Sleep | |||||||
| Pin Cmd | Csel | Speed | Adr Wid | OSPI | ||||
| Port | Pin Cmd | Csel | Speed | Adr Wid | QSPI | |||
| Not Used | Csel | Speed | Hyperflash | |||||
| Port | Mode | Csel | Cmd | Adr Width | SPI | |||
| Not Used | Bus Reset | Mode | Spd | Addr | I2C | |||
| Not Used | Port | Interface Config | 1bit | MMC/SD card | ||||
| clkout | iface | spd | dplx | Extern con | Ethernet | |||
| Not Used | Usb3 | Mode | Port | USB | ||||
| Port | Dual | sref | BAR Config PCIe | |||||
| Not Used | UART | |||||||
| Idx | AD mux | Csel Size | Csel | Wid | GPMC XIP | |||
| Not Used | Port | Alt | Bus Width | Speed | ack | eMMC | ||
BOOTMODE[18:16] – These pins provide optional settings and are used in conjunction with the backup boot device devices. Refer to the AM65x Multicore ARM Keystone III System-on-Chip (SoC) Technical Reference Manual for more information on bit details. Switches SW2.[7:9] when on sets 1 and sets 0 if off.
| SW2.9 | SW2.8 | SW2.7 | Boot Device |
|---|---|---|---|
| Not Used | None | ||
| Not Used | Port | USB | |
| Not Used | UART | ||
| clkout | Interface | Ethernet | |
| Not Used | Port | 1 Bit | MMC/SD |
| Port | Adr Width/Cmd | SPI | |
| Speed | Hyperflash | ||
| reset | Mode | Addr | I2C |
MCU_BOOTMODE pins provide ROM code with information for the system clock speed and fail-safe boot device.
| Bit 10 | Bit 9 | Bit 8 | Bit 7 | Bit 6 | Bit 5 | Bit 4 | Bit 3 | Bit 2 | Bit 1 | Bit 0 |
| Reserved | Fail Safe mode | Ref Clock Select | ||||||||
MCU_BOOTMODE[2:0] – Denotes system clock frequency for PLL configuration. By default, these bits are set for 25 MHz.
| Bit 2 | Bit 1 | Bit 0 | PLL REF CLK (MHz) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 19.2 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 20 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 24 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 25 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 26 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 27 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | Reserved |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | No PLL Configuration Done (slow speed backup) |
MCU_BOOTMODE[4:3] – Select the fail-safe boot mode, as shown in Table 3-14.
| SW4.2 | SW4.1 | PLL REF CLK (MHz) |
|---|---|---|
| off | off | No fail-safe boot supported |
| off | on | I2C port 0 |
| on | off | SPI Port 0 |
| on | on | Hyperflash Port 0 |
MCU_BOOTMODE[10:5]- Reserved
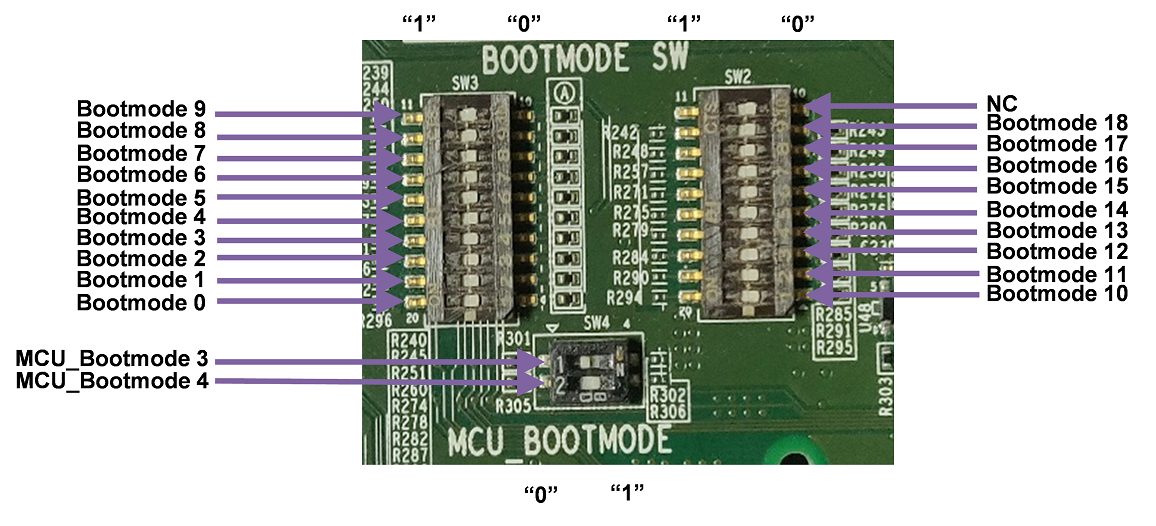 Figure 3-9 BOOT Switches Provided on the Processor Card
Figure 3-9 BOOT Switches Provided on the Processor Card