SLVAEX3 October 2020 TPS8802 , TPS8804
2.3 Amplifier and LED Settings
Optimally amplifying the photodiode current requires careful selection of the amplifier gains, amplifier speeds, LED current and LED pulse width. The photodiode current can be as low as 1 nA, making the amplified signal highly susceptible to noise.
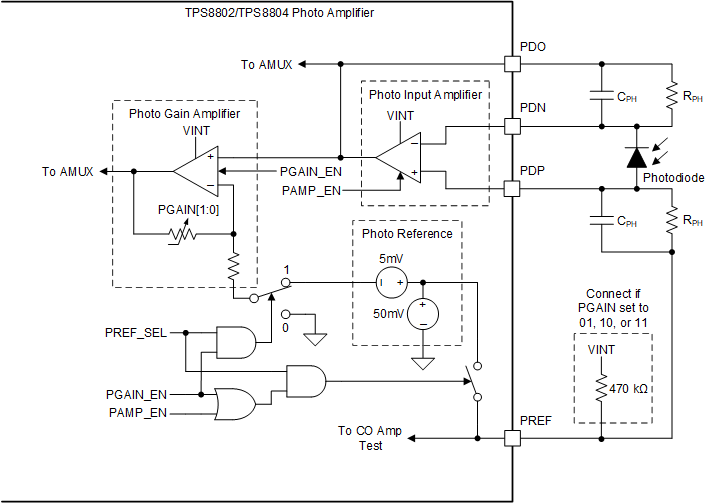 Figure 2-1 TPS880x Photo Amplifier Schematics
Figure 2-1 TPS880x Photo Amplifier Schematics