ZHCSEF7G December 2014 – February 2019 TPS659037
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 器件概述
- 2 修订历史记录
- 3 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
4 Specifications
- 4.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 4.2 ESD Ratings
- 4.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 4.4 Thermal Information
- 4.5 Electrical Characteristics: Latch Up Rating
- 4.6 Electrical Characteristics: LDO Regulator
- 4.7 Electrical Characteristics: Dual-Phase (SMPS12 and SMPS45) and Triple-Phase (SMPS123 and SMPS457) Regulators
- 4.8 Electrical Characteristics: Stand-Alone Regulators (SMPS3, SMPS6, SMPS7, SMPS8, and SMPS9)
- 4.9 Electrical Characteristics: Reference Generator (Bandgap)
- 4.10 Electrical Characteristics: 16-MHz Crystal Oscillator, 32-kHz RC Oscillator, and Output Buffers
- 4.11 Electrical Characteristics: DC-DC Clock Sync
- 4.12 Electrical Characteristics: 12-Bit Sigma-Delta ADC
- 4.13 Electrical Characteristics: Thermal Monitoring and Shutdown
- 4.14 Electrical Characteristics: System Control Threshold
- 4.15 Electrical Characteristics: Current Consumption
- 4.16 Electrical Characteristics: Digital Input Signal Parameters
- 4.17 Electrical Characteristics: Digital Output Signal Parameters
- 4.18 Electrical Characteristics: I/O Pullup and Pulldown
- 4.19 I2C Interface Timing Requirements
- 4.20 SPI Timing Requirements
- 4.21 Typical Characteristics
-
5 Detailed Description
- 5.1 Overview
- 5.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 5.3
Feature Description
- 5.3.1 Power Management
- 5.3.2
Power Resources (Step-Down and Step-Up SMPS Regulators, LDOs)
- 5.3.2.1
Step-Down Regulators
- 5.3.2.1.1 Sync Clock Functionality
- 5.3.2.1.2 Output Voltage and Mode Selection
- 5.3.2.1.3 Current Monitoring and Short Circuit Detection
- 5.3.2.1.4 POWERGOOD
- 5.3.2.1.5 DVS-Capable Regulators
- 5.3.2.1.6 Non DVS-Capable Regulators
- 5.3.2.1.7 Step-Down Converters SMPS12 and SMPS123
- 5.3.2.1.8 Step-Down Converter SMPS45 and SMPS457
- 5.3.2.1.9 Step-Down Converters SMPS3, SMPS6, SMPS7, SMPS8, and SMPS9
- 5.3.2.2 LDOs – Low Dropout Regulators
- 5.3.2.1
Step-Down Regulators
- 5.3.3 Long-Press Key Detection
- 5.3.4 RTC
- 5.3.5 GPADC – 12-Bit Sigma-Delta ADC
- 5.3.6 General-Purpose I/Os (GPIO Pins)
- 5.3.7 Thermal Monitoring
- 5.3.8 Interrupts
- 5.3.9 Control Interfaces
- 5.3.10 Device Identification
- 5.4 Device Functional Modes
-
6 Application and Implementation
- 6.1 Application Information
- 6.2
Typical Application
- 6.2.1 Design Requirements
- 6.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
- 6.2.3 Application Curves
- 7 Power Supply Recommendations
- 8 Layout
- 9 器件和文档支持
- 10机械、封装和可订购信息
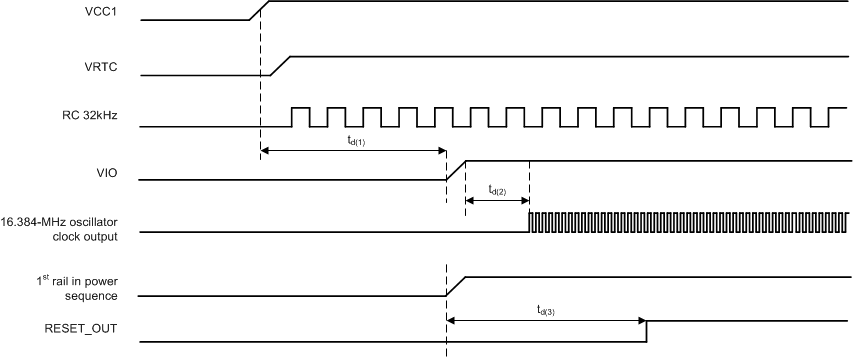
5.4.4 Startup Timing and RESET_OUT Generation
The total start-up time of the TPS659037 device from the first supply insertion until the release of reset to the processor is defined by the boot time of internal resources as well as the OTP defined boot sequence.
Following figure shows the power up sequence timing and the generation of the RESET_OUT signal.
The td(1) time is the delay between VCC1 crossing the POR threshold and VIO (first rail in the power sequence) rising up. The td(1) time must be at least 6 ms. If the time from VCC to VIO is less than 6 ms, the VIO buffers are supplied while the OTP is still being initialized, which could cause glitches on any VIO output buffer. Supplying VIO at least 6 ms after supplying VCC makes sure that the OTP is initialized and the output buffers are held low when VIO is supplied. The VIO_IN pin may be supplied before or after the first rail in the power sequence is enabled, as long as it is at least 6 ms after VCC.
The td(2) time is the internal 16.384-MHz crystal oscillator start-up time, or the external 32-kHz clock input availability delay time.
The td(3) time is the delay between the power up sequence start and RESET_OUT release. RESET_OUT is released when the power up sequence is complete and one of the following:
- The 16.384-MHz clock is stabilized if the 16.384-MHz crystal is present and the oscillator is enable.
- The external 32-kHz clock is stabilized and the 16.384-MHz oscillator is bypassed.
- The GATE_RESET_OUT_OTP bit is used to allow the TPS659037 device to power up without the presence of the 16.384-MHz crystal nor the external 32-kHz clock input.
The duration of the power-up sequence depends on OTP programming; average value is about 10 ms.