ZHCS026C December 2010 – February 2016 TPS57060-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特征
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Fixed Frequency PWM Control
- 7.3.2 Slope Compensation Output Current
- 7.3.3 Low Dropout Operation and Bootstrap Voltage (BOOT)
- 7.3.4 Error Amplifier
- 7.3.5 Voltage Reference
- 7.3.6 Adjusting the Output Voltage
- 7.3.7 Enable and Adjusting Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO)
- 7.3.8 Slow Start and Tracking Pin (SS/TR)
- 7.3.9 Overload Recovery Circuit
- 7.3.10 Constant Switching Frequency and Timing Resistor (RT/CLK Pin)
- 7.3.11 Overcurrent Protection and Frequency Shift
- 7.3.12 Selecting the Switching Frequency
- 7.3.13 How to Interface to RT/CLK Pin
- 7.3.14 Power Good (PWRGD Pin)
- 7.3.15 Overvoltage Transient Protection
- 7.3.16 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.3.17 Small Signal Model for Loop Response
- 7.3.18 Simple Small-Signal Model for Peak Current-Mode Control
- 7.3.19 Small Signal Model for Frequency Compensation
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Selecting the Switching Frequency
- 8.2.2.2 Output Inductor Selection (LO)
- 8.2.2.3 Output Capacitor
- 8.2.2.4 Catch Diode
- 8.2.2.5 Input Capacitor
- 8.2.2.6 Slow Start Capacitor
- 8.2.2.7 Bootstrap Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.8 Undervoltage Lockout Set Point
- 8.2.2.9 Output Voltage and Feedback Resistors Selection
- 8.2.2.10 Compensation
- 8.2.2.11 Discontinuous Mode and Eco Mode Boundary
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11器件和文档支持
- 12机械、封装和可订购信息
封装选项
机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
散热焊盘机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
订购信息
10.3 Power Dissipation Estimate
The following formulas show how to estimate the device power dissipation under continuous conduction mode (CCM) operation. These equations should not be used if the device is working in discontinuous conduction mode (DCM).
The power dissipation of the device includes the parameters that follow:
- Conduction loss (Pcon)
- RDS(on) is the on-resistance of the high-side MOSFET (Ω).
- VOUT is the output voltage (V).
- VIN is the input voltage (V).
- Switching loss (Psw)
- fsw is the switching frequency (Hz).
- Io is the output current (A).
- Gate drive loss (Pgd)
- Supply current (Pq)
Equation 49. 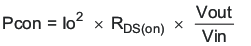
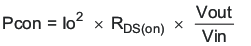
where
Equation 50. 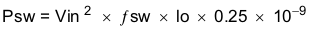
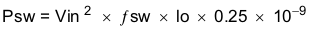
where
Equation 51. 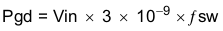
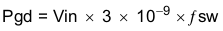
Equation 52. 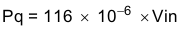
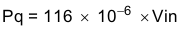
Therefore:
Equation 53. 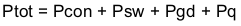
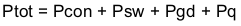
where
- Ptot is the total device power dissipation (W).
For given TA:
Equation 54. 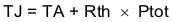
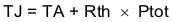
where
- TJ is the junction temperature (°C).
- TA is the ambient temperature (°C).
- Rth is the thermal resistance of the package (°C/W).
For given TJMAX = 150°C:
Equation 55. 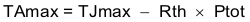
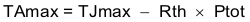
where
- TJmax is maximum junction temperature (°C).
- TAmax is maximum ambient temperature (°C).
Additional power losses occur in the regulator circuit because of the inductor AC and DC losses, the catch diode, and trace resistance which impact the overall efficiency of the regulator.