ZHCS026C December 2010 – February 2016 TPS57060-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特征
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Fixed Frequency PWM Control
- 7.3.2 Slope Compensation Output Current
- 7.3.3 Low Dropout Operation and Bootstrap Voltage (BOOT)
- 7.3.4 Error Amplifier
- 7.3.5 Voltage Reference
- 7.3.6 Adjusting the Output Voltage
- 7.3.7 Enable and Adjusting Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO)
- 7.3.8 Slow Start and Tracking Pin (SS/TR)
- 7.3.9 Overload Recovery Circuit
- 7.3.10 Constant Switching Frequency and Timing Resistor (RT/CLK Pin)
- 7.3.11 Overcurrent Protection and Frequency Shift
- 7.3.12 Selecting the Switching Frequency
- 7.3.13 How to Interface to RT/CLK Pin
- 7.3.14 Power Good (PWRGD Pin)
- 7.3.15 Overvoltage Transient Protection
- 7.3.16 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.3.17 Small Signal Model for Loop Response
- 7.3.18 Simple Small-Signal Model for Peak Current-Mode Control
- 7.3.19 Small Signal Model for Frequency Compensation
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Selecting the Switching Frequency
- 8.2.2.2 Output Inductor Selection (LO)
- 8.2.2.3 Output Capacitor
- 8.2.2.4 Catch Diode
- 8.2.2.5 Input Capacitor
- 8.2.2.6 Slow Start Capacitor
- 8.2.2.7 Bootstrap Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.8 Undervoltage Lockout Set Point
- 8.2.2.9 Output Voltage and Feedback Resistors Selection
- 8.2.2.10 Compensation
- 8.2.2.11 Discontinuous Mode and Eco Mode Boundary
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11器件和文档支持
- 12机械、封装和可订购信息
封装选项
机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
散热焊盘机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
订购信息
8.2.2.5 Input Capacitor
The TPS57060-Q1 requires a high quality ceramic, type X5R or X7R, input decoupling capacitor of at least 3 μF of effective capacitance and in some applications a bulk capacitance. The effective capacitance includes any dc bias effects. The voltage rating of the input capacitor must be greater than the maximum input voltage. The capacitor must also have a ripple current rating greater than the maximum input current ripple of the TPS57060-Q1. The input ripple current can be calculated using Equation 38.
The value of a ceramic capacitor varies significantly over temperature and the amount of dc bias applied to the capacitor. The capacitance variations due to temperature can be minimized by selecting a dielectric material that is stable over temperature. X5R and X7R ceramic dielectrics are usually selected for power regulator capacitors because they have a high capacitance to volume ratio and are fairly stable over temperature. The output capacitor must also be selected with the dc bias taken into account. The capacitance value of a capacitor decreases as the dc bias across a capacitor increases.
For this example design, a ceramic capacitor with at least a 60 V voltage rating is required to support the maximum input voltage. Common standard ceramic capacitor voltage ratings include 4 V, 6.3 V, 10 V, 16 V, 25 V, 50 V or 100 V so a 100-V capacitor should be selected. For this example, two 2.2-μF, 100-V capacitors in parallel have been selected. Table 2 shows a selection of high voltage capacitors. The input capacitance value determines the input ripple voltage of the regulator. The input voltage ripple can be calculated using Equation 39. Using the design example values, Ioutmax = 0.5 A, Cin = 4.4 μF, ƒsw = 500 kHz, yields an input voltage ripple of 57 mV and a RMS input ripple current of 0.223 A.
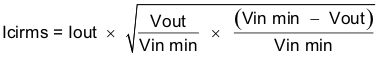
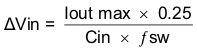
Table 2. Capacitor Types
| VENDOR | VALUE (μF) | EIA Size | VOLTAGE | DIALECTRIC | COMMENTS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Murata | 1 to 2.2 | 1210 | 100 V | X7R | GRM32 series |
| 1 to 4.7 | 50 V | ||||
| 1 | 1206 | 100 V | GRM31 series | ||
| 1 to 2.2 | 50 V | ||||
| Vishay | 1 10 1.8 | 2220 | 50 V | VJ X7R series | |
| 1 to 1.2 | 100 V | ||||
| 1 to 3.9 | 2225 | 50 V | |||
| 1 to 1.8 | 100 V | ||||
| TDK | 1 to 2.2 | 1812 | 100 V | C series C4532 | |
| 1.5 to 6.8 | 50 V | ||||
| 1 to 2.2 | 1210 | 100 V | C series C3225 | ||
| 1 to 3.3 | 50 V | ||||
| AVX | 1 to 4.7 | 1210 | 50 V | X7R dielectric series | |
| 1 | 100 V | ||||
| 1 to 4.7 | 1812 | 50 V | |||
| 1 to 2.2 | 100 V |