ZHCSME3 November 2020 TPS27SA08
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Summary Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3
Feature Description
- 9.3.1 Protection Mechanisms
- 9.3.2 Diagnostic Mechanisms
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
9.3.1.5 Reverse supply
In the reverse supply condition, the switch will automatically be enabled (regardless of EN status) to prevent power dissipation inside the MOSFET body diode. In many applications (for example, resistive load), the full load current may be present during reverse supply. In order to activate the automatic switch on feature, the SEL2 pin must have a path to module ground. This may be path 1 as shown below, or, if the SEL2 pin is unused, the path may be through RPROT to module ground.
Protection features (for example, thermal shutdown) are not available during reverse supply. Care must be taken to ensure that excessive power is not dissipated in the switch during the reverse supply condition.
There are two options for blocking reverse current in the system. Option 1 is to place a blocking device (FET or diode) in series with the supply. This will block all current paths. Option 2 is to place a blocking diode in series with the GND node of the high-side switch. This method will protect the controller portion of the switch (path 2), but it will not prevent current from flowing through the load (path 3). The diode used for Option 2 may be shared amongst multiple high-side switches.
Path 1 shown in #SLVSDM42222 is blocked inside of the device.
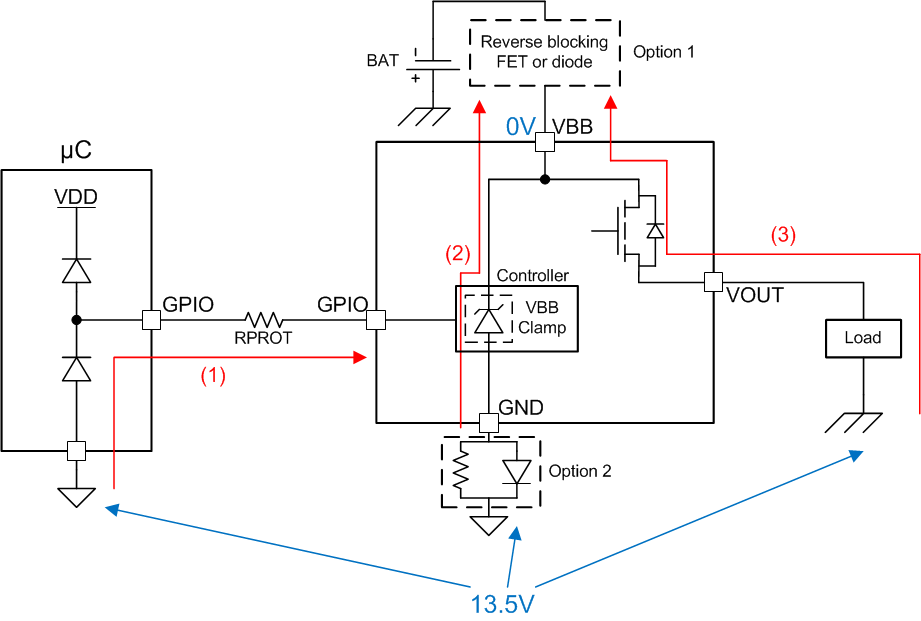 Figure 9-3 Current Path During Reverse supply
Figure 9-3 Current Path During Reverse supply