ZHCSOF9B april 2022 – june 2023 TPS25981
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO and UVP)
- 8.3.2 Overvoltage Lockout (OVLO)
- 8.3.3 Inrush Current, Overcurrent, and Short-Circuit Protection
- 8.3.4 Analog Load Current Monitor
- 8.3.5 Overtemperature Protection (OTP)
- 8.3.6 Fault Response and Indication (FLT)
- 8.3.7 Power Good Indication (PG)
- 8.3.8 Quick Output Discharge (QOD)
- 8.3.9 Reverse Current Blocking FET Driver
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
9.1.2 Parallel Operation
Applications which need higher steady current can use two TPS25981xx devices connected in parallel as shown in Figure 9-10 below. In this configuration, the first device turns on initially to provide the inrush current limiting. The second device is held in an OFF state by driving its EN/UVLO pin low using the PG signal of the first device. After the inrush sequence is complete, the first device asserts its PG pin high and turns on the second device. The second device asserts its PG signal to indicate when it has turned on fully, thereby indicating to the system that the parallel combination is ready to deliver the full steady-state current.
Once in steady-state, both devices share current nearly equally. There can be a slight skew in the currents depending on the part-to-part variation in the RON as well as the PCB trace resistance mismatch.
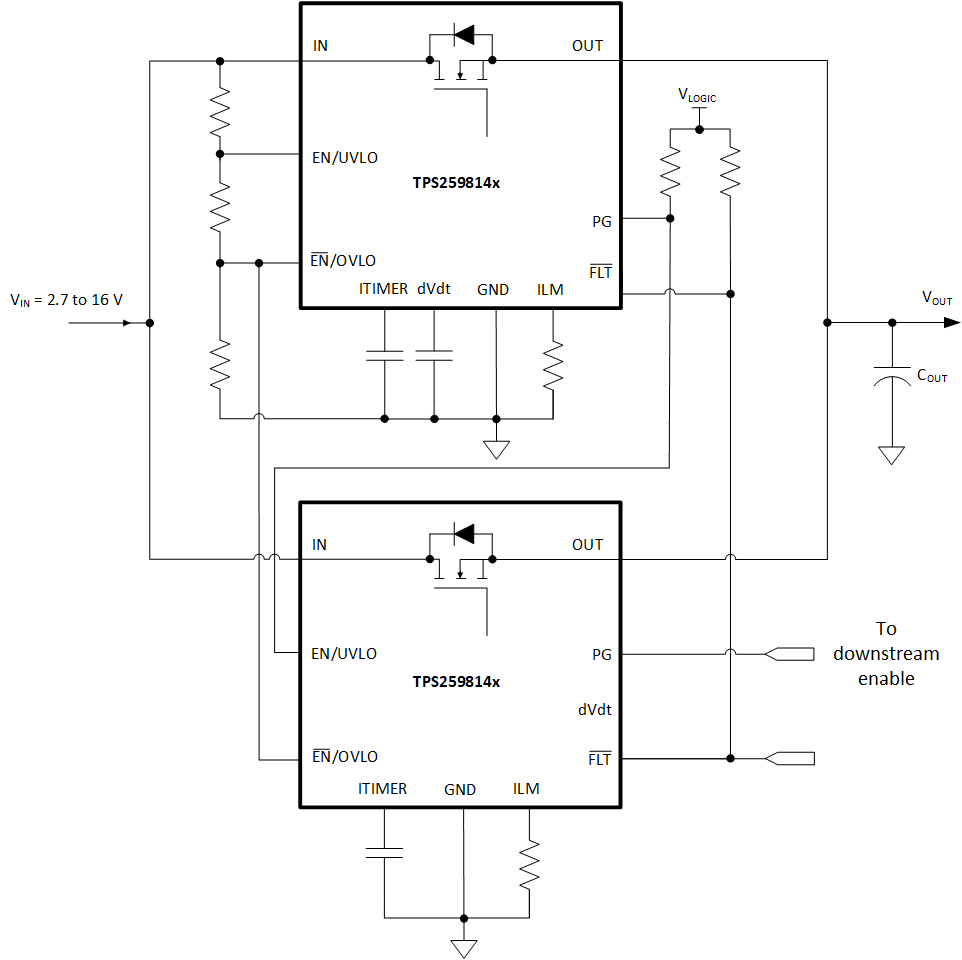 Figure 9-2 Two TPS259814x Devices Connected in Parallel for Higher Steady-State Current Capability
Figure 9-2 Two TPS259814x Devices Connected in Parallel for Higher Steady-State Current CapabilityThe waveforms below illustrate the behavior of the parallel configuration during start-up as well as during steady-state.
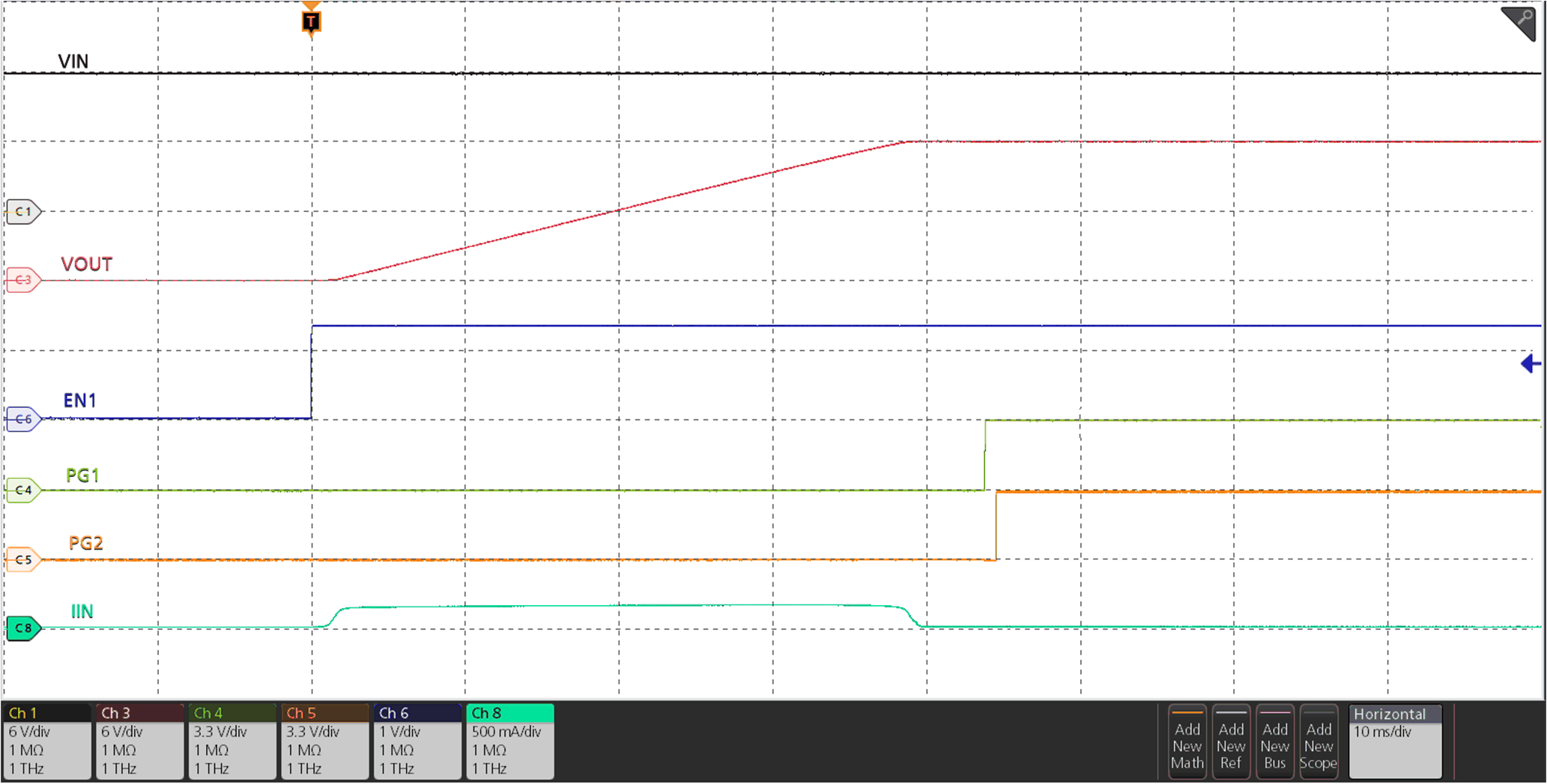 Figure 9-3 Parallel Devices Sequencing During Start-Up
Figure 9-3 Parallel Devices Sequencing During Start-Up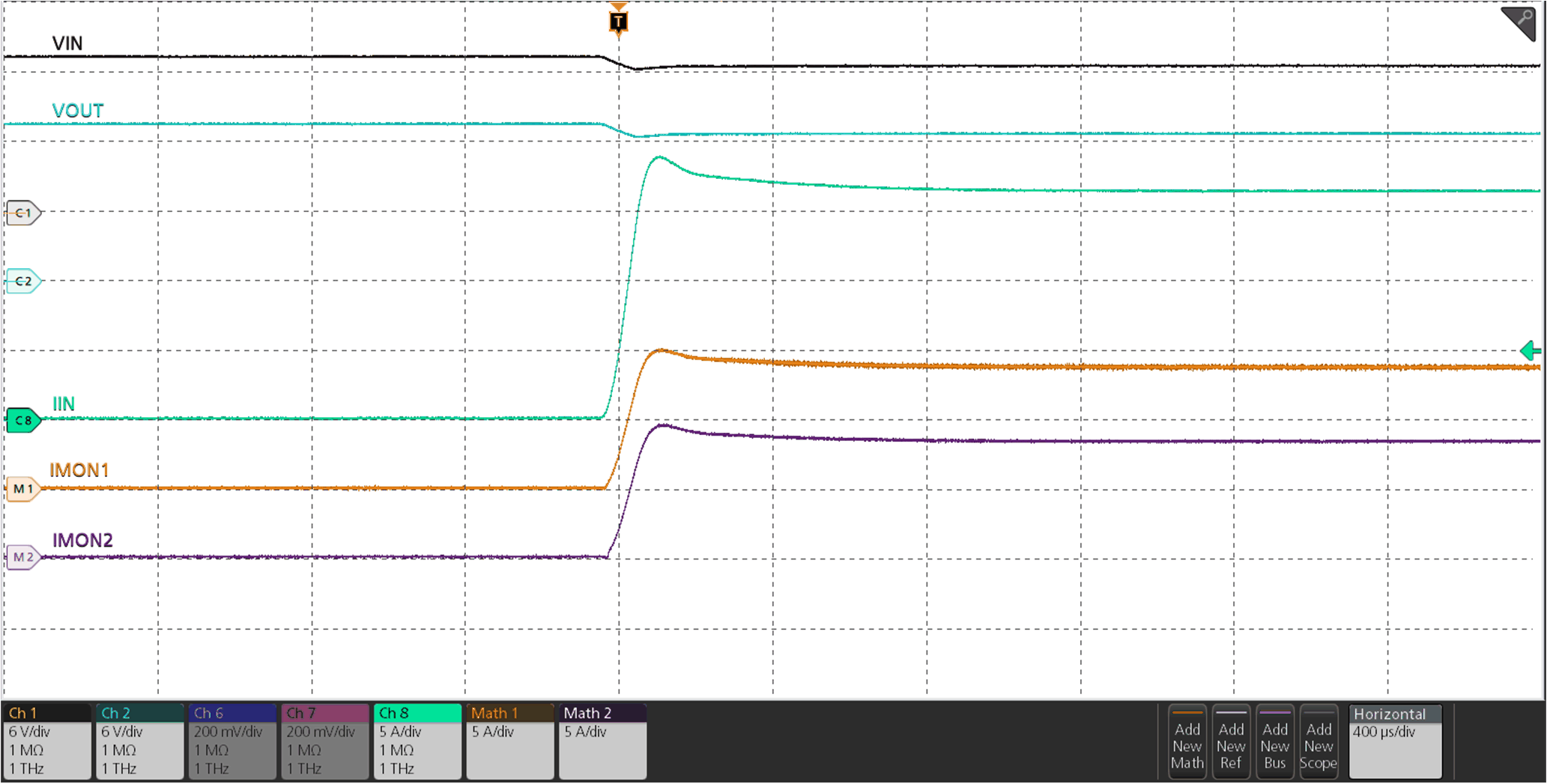 Figure 9-4 Parallel Devices Load Current During Steady-State
Figure 9-4 Parallel Devices Load Current During Steady-State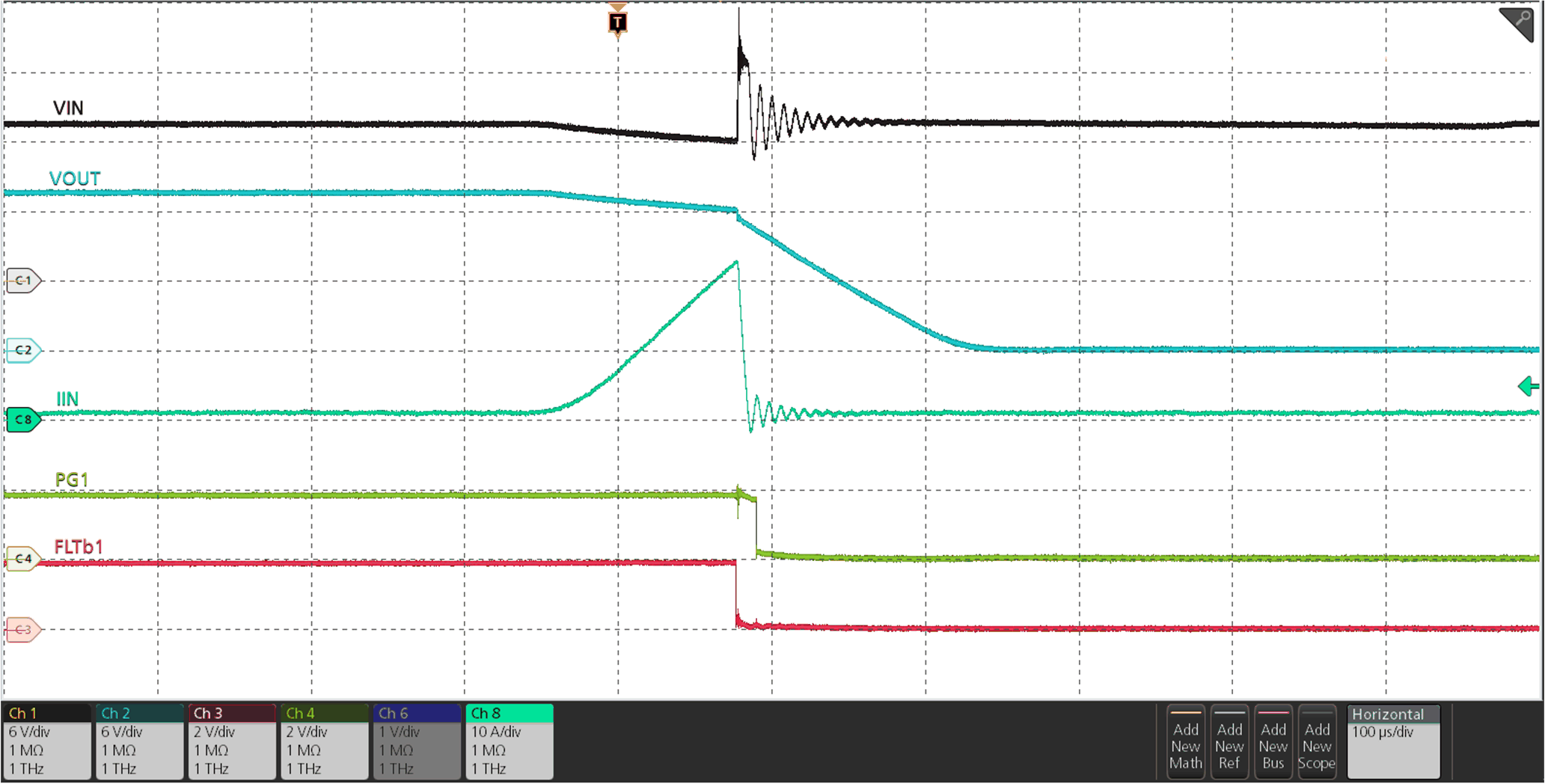 Figure 9-5 Parallel Devices Overcurrent Response
Figure 9-5 Parallel Devices Overcurrent ResponseAnother way to increase current handling capability of the eFuse in steady-state is by connecting a TPS25981xx eFuse in parallel with a TPS22811x load switch as shown in Figure 9-6.
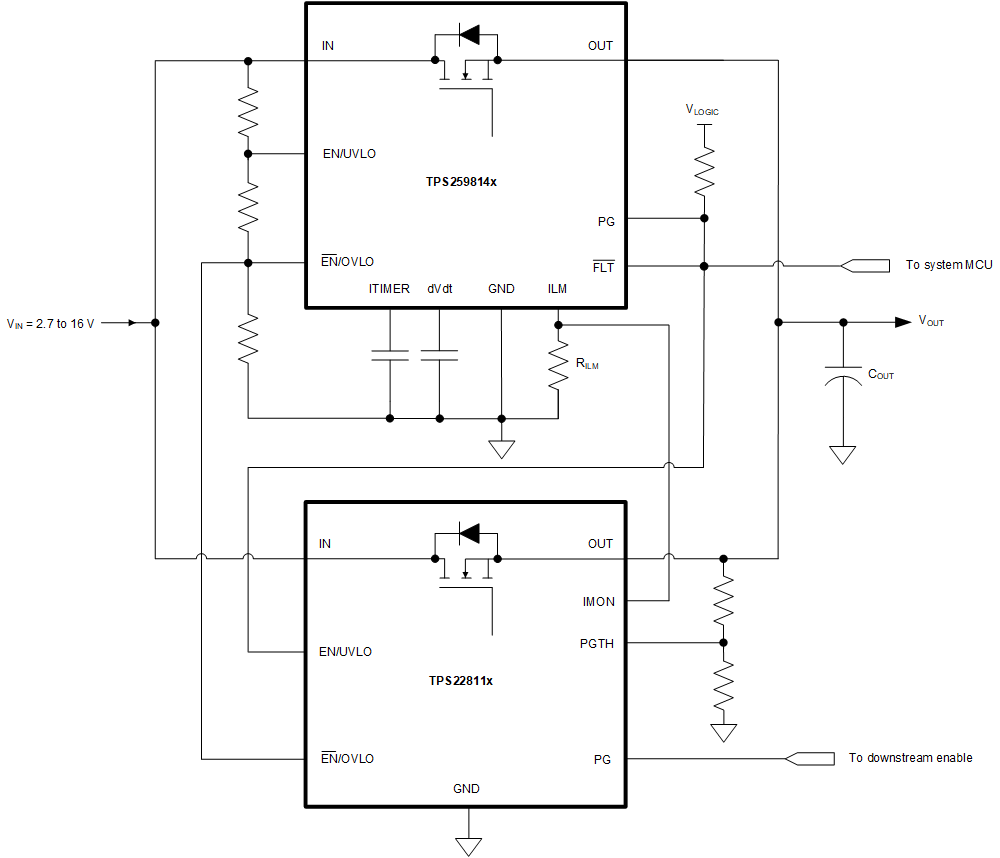 Figure 9-6 TPS259814x and TPS22811x Connected in Parallel for Higher Steady-State Current Capability
Figure 9-6 TPS259814x and TPS22811x Connected in Parallel for Higher Steady-State Current Capability