ZHCSJS9 May 2019 TLA2528
ADVANCE INFORMATION for pre-production products; subject to change without notice.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6
TLA2528 Registers
- 7.6.1 SYSTEM_STATUS Register (Address = 0x0) [reset = 0x80]
- 7.6.2 GENERAL_CFG Register (Address = 0x1) [reset = 0x0]
- 7.6.3 DATA_CFG Register (Address = 0x2) [reset = 0x0]
- 7.6.4 OSR_CFG Register (Address = 0x3) [reset = 0x0]
- 7.6.5 OPMODE_CFG Register (Address = 0x4) [reset = 0x0]
- 7.6.6 PIN_CFG Register (Address = 0x5) [reset = 0x0]
- 7.6.7 GPIO_CFG Register (Address = 0x7) [reset = 0x0]
- 7.6.8 GPO_DRIVE_CFG Register (Address = 0x9) [reset = 0x0]
- 7.6.9 GPO_OUTPUT_VALUE Register (Address = 0xB) [reset = 0x0]
- 7.6.10 GPI_VALUE_LSB Register (Address = 0xD) [reset = 0x0]
- 7.6.11 SEQUENCE_CFG Register (Address = 0x10) [reset = 0x0]
- 7.6.12 CHANNEL_SEL Register (Address = 0x11) [reset = 0x0]
- 7.6.13 AUTO_SEQ_CHSEL Register (Address = 0x12) [reset = 0x0]
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11器件和文档支持
- 12机械、封装和可订购信息
7.3.1 Multiplexer and ADC
The eight channels of the multiplexer can be independently configured as ADC inputs or general-purpose inputs/outputs (GPIOs). Figure 2 shows that each input pin has electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection diodes to AVDD and GND. On power-up or after device reset, all eight multiplexer channels are configured as analog inputs.
Figure 2 shows an equivalent circuit for pins configured as analog inputs. The ADC sampling switch is represented by an ideal switch (SW) in series with the resistor, RSW (typically 150 Ω), and the sampling capacitor, CSH (typically 12 pF).
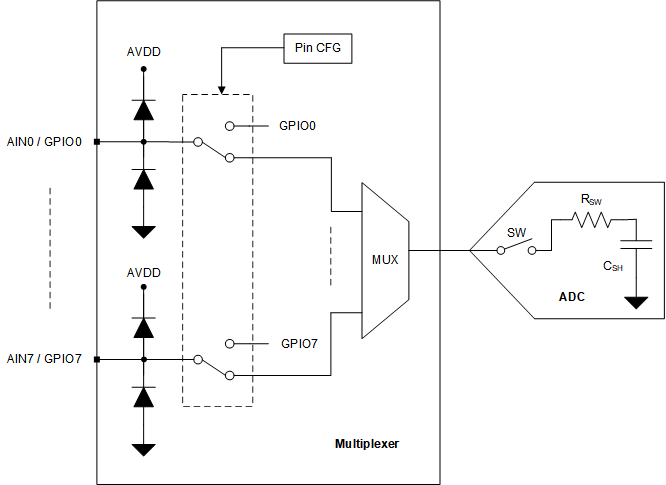 Figure 2. Analog Inputs, GPIOs, and ADC Connections
Figure 2. Analog Inputs, GPIOs, and ADC Connections During acquisition, the SW switch is closed to allow the signal on the selected analog input channel to charge the internal sampling capacitor. During conversion, the SW switch is opened to disconnect the analog input channel from the sampling capacitor.
The multiplexer channels can be configured as GPIOs in the PIN_CFG register. The direction of a GPIO (either as an input or an output) can be set in the GPIO_CFG register. The logic level on the channels configured as digital inputs can be read from the GPI_VALUE register. The digital outputs can be accessed by writing to the GPO_OUTPUT_VALUE register. The digital outputs can be configured as either open-drain or push-pull in the GPO_DRIVE_CFG register.