ZHCSCU3C January 2014 – September 2019 TCA5013
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 Handling Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics—Power Supply and ESD
- 6.6 Electrical Characteristics—Card VCC
- 6.7 Electrical Characteristics—Card RST
- 6.8 Electrical Characteristics—Card CLK
- 6.9 Electrical Characteristics—Card Interface IO, C4 and C8
- 6.10 Electrical Characteristics—PRES
- 6.11 Electrical Characteristics—IOMC1 and IOMC2
- 6.12 Electrical Characteristics—CLKIN1 and CLKIN2
- 6.13 Electrical Characteristics—A0 and SHDN
- 6.14 Electrical Characteristics—INT
- 6.15 Electrical Characteristics—GPIO
- 6.16 Electrical Characteristics—SDA and SCL
- 6.17 Electrical Characteristics—Fault Condition Detection
- 6.18 I2C Interface Timing Requirements
- 6.19 I2C Interface Timing Characteristics
- 6.20 Synchronous Type 1 Card Activation Timing Characteristics
- 6.21 Synchronous Type 2 Card Activation Timing Characteristics
- 6.22 Card Deactivation Timing Characteristics
- 6.23 Typical Characteristics
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3 Feature Description
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Programming
- 8.6 Register Maps
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12器件和文档支持
- 13机械、封装和可订购信息
8.5.1.1 I2C Read and Write Procedures
Following the successful acknowledgment of the I2C address byte, the bus master shall send one register address byte indicating the address of the register on which the read or write operation needs to be performed. This register address is stored in an internal register and used by the device for subsequent read/write to the device. After the device address is acknowledged by the slave, all register addresses will be acknowledged even if an actual register is not defined for that address
The TCA5013 supports an auto increment feature by which multiple bytes can be written to consecutive registers without requiring the master to send the device address and register address for each data byte. Auto increment is enabled by setting the MSB of the register address to a 1 (see Figure 23). If auto increment is used to write the entire register map, the gaps in the register address map need to be written with dummy bytes. If auto increment is used to read the entire register map then data read from gaps in the register map will be 8’hFF
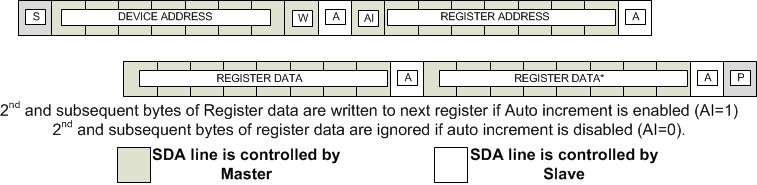 Figure 23. I2C Write Procedure
Figure 23. I2C Write Procedure  Figure 24. I2C Read Procedure
Figure 24. I2C Read Procedure  Figure 25. I2C Read Procedure with Repeated Start
Figure 25. I2C Read Procedure with Repeated Start