ZHCSE43 July 2015 SN65HVD63
PRODUCTION DATA.
12 Layout
12.1 Layout Guidelines
Best practices for high-speed PCB design should be observed because the coax interface to the SN65HVD63 device operates at RF. The RF signaling traces should have a controlled characteristic impedance that is well-matched to the coaxial line. A continuous reference plane should be used to avoid impedance discontinuities. Power and ground distribution should be done through planes rather than traces to decrease series resistance and increase the effective decoupling capacitance on the power rails.
12.2 Layout Example
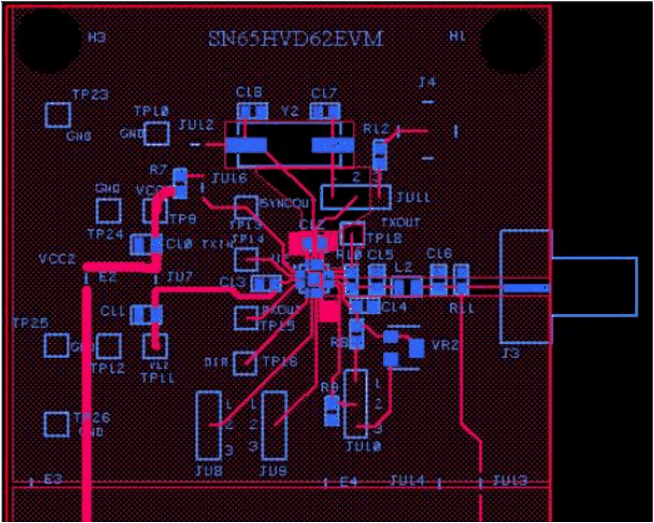 Figure 27. SN65HVD63 Layout
Figure 27. SN65HVD63 Layout