ZHCSND1A November 2020 – May 2022 DRV8434
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 规格
- 7 详细说明
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
封装选项
机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
散热焊盘机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
- RGE|24
订购信息
9.1 大容量电容
配备合适的局部大容量电容是电机驱动系统设计中的重要因素。使用更多的大容量电容通常是有益的,但缺点在于这会增加成本和物理尺寸。
所需的局部电容数量取决于多种因素,包括:
- 电机系统所需的最高电流
- 电源的电容和拉电流的能力
- 电源和电机系统之间的寄生电感量
- 可接受的电压纹波
- 使用的电机类型(有刷直流、无刷直流、步进电机)
- 电机制动方法
电源和电机驱动系统之间的电感将限制电流可以从电源变化的速率。如果局部大容量电容太小,系统将以电压变化的方式对电机中的电流不足或过剩电流作出响应。当使用足够多的大容量电容时,电机电压保持稳定,可以快速提供大电流。
数据表通常会给出建议值,但需要进行系统级测试来确定大小适中的大容量电容。
大容量电容的额定电压应高于工作电压,以在电机将能量传递给电源时提供裕度。
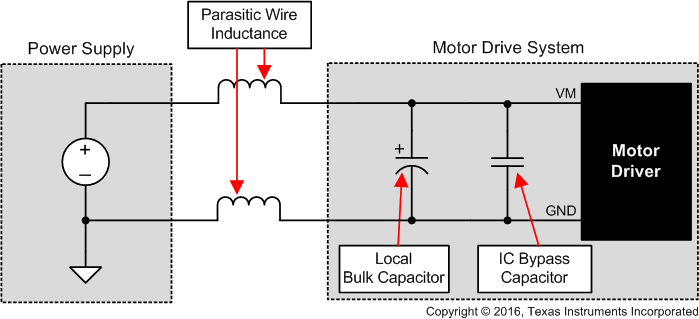 图 9-1 带外部电源的电机驱动系统示例设置
图 9-1 带外部电源的电机驱动系统示例设置