ZHCSN33C November 2017 – December 2024 DLP550JE
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
5 Specifications
- 5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 5.2 Storage Conditions
- 5.3 ESD Ratings
- 5.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 5.5 Thermal Information
- 5.6 Electrical Characteristics
- 5.7 Timing Requirements
- 5.8 Window Characteristics
- 5.9 System Mounting Interface Loads
- 5.10 Micromirror Array Physical Characteristics
- 5.11 Micromirror Array Optical Characteristics
- 5.12 Chipset Component Usage Specification
- 6 Detailed Description
- 7 Application and Implementation
- 8 Power Supply Recommendations
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Revision History
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
5.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
Over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted). The functional performance of the device specified in this data sheet is achieved when operating the device within the limits defined by this table. No level of performance is implied when operating the device above or below these limits.
| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VOLTAGE SUPPLY | |||||
| VCC | Supply voltage for LVCMOS core logic(1) | 3.0 | 3.3 | 3.6 | V |
| VCCI | Supply voltage for LVDS interface(1) | 3.0 | 3.3 | 3.6 | V |
| VOFFSET | Mirror Electrode and HVCMOS voltage(1)(2) | 3.0 | 3.3 | 3.6 | V |
| VMBRST | Micromirror clocking pulse voltages(1) | –27 | 26.5 | V | |
| |VCCI–VCC| | Supply voltage delta (absolute value)(3) | 0.3 | V | ||
| LVCMOS INTERFACE | |||||
| VIH | High level input voltage | 1.7 | 2.5 | VCC + 0.3 | V |
| VIL | Low level input voltage | –0.3 | 0.7 | V | |
| IOH | High level output current at VOH = 2.4V | –20 | mA | ||
| IOL | Low level output current at VOL = 0.4V | 15 | mA | ||
| tPWRDNZ | PWRDNZ pulse width4 | 10 | ns | ||
| SCP INTERFACE | |||||
| fSCPCLK | SCP clock frequency(5) | 50 | 500 | kHz | |
| tSCP_PD | Propagation delay, clock to Q, from rising-edge of SCPCLK to valid SCPDO(6) | 0 | 900 | ns | |
| tSCP_DS | SCPDI clock setup time (before SCPCLK falling-edge)(6) | 800 | ns | ||
| tSCP_DH | SCPDI hold time (after SCPCLK falling-edge)(5) | 900 | |||
| tSCP_NEG_ENZ | Time between falling-edge of SCPENZ and the first rising-edge of SCPCLK | 1 | us | ||
| tSCP_POS_ENZ | Time between falling-edge of SCPCLK and the rising-edge of SCPENZ | 1 | us | ||
| tSCP_PW_ENZ | SCPENZ inactive pulse width (high level) | 1 | 1/fSCPCLK | ||
| tr_SCP | Rise time for SCP signals | 200 | ns | ||
| tf_SCP | Fall time for SCP signals | 200 | ns | ||
| LVDS INTERFACE | |||||
| fCLOCK | Clock frequency for LVDS interface (all channels), DCLK(7) | 320 | 330 | MHz | |
| |VID| | Input differential voltage (absolute difference)(8) | 100 | 400 | 600 | mV |
| VCM | Common mode voltage(8) | 1200 | mV | ||
| VLVDS | LVDS voltage(8) | 0 | 2000 | mV | |
| tr | Rise time (20% to 80%) | 100 | 400 | ps | |
| tr | Fall time (80% to 20%) | 100 | 400 | ps | |
| tLVDS_RSTZ | Time required for LVDS receivers to recover from PWRDNZ | 10 | ns | ||
| ZIN | Internal differential termination resistance | 95 | 105 | Ω | |
| ENVIRONMENTAL | |||||
| TARRAY | Array temperature, long-term operational(9) (10)(11) | 10 | 40 to 70(12) | °C | |
| Array temperature, short-term operational 500 hr max(10)(13) | 0 | 10 | °C | ||
| TWINDOW | Window temperature – operational(14) | 85 | °C | ||
| T|DELTA | | Absolute temperature delta between any point on the window edge and the ceramic test point TP1(15) | 26 | °C | ||
| TDP-AVG | Average dew point temperature (non-condensing)(16) | 28 | °C | ||
| TDP-ELR | Elevated dew point temperature range (non-condensing)(17) | 28 | 36 | °C | |
| CTELR | Cumulative time in elevated dew point temperature range | 24 | Months | ||
| SOLID STATE ILLUMINATION | |||||
| ILLUV | Illumination power at wavelengths < 410nm(9)(19) | 10 | mW/cm2 | ||
| ILLVIS | Illumination power at wavelengths ≥ 410nm and ≤ 800nm (18)(19) | 23.7 | W/cm2 | ||
| ILLIR | Illumination power at wavelengths > 800nm(19) | 10 | mW/cm2 | ||
| ILLBLU | Illumination power at wavelengths ≥ 410nm and ≤ 475nm(18)(19) | 7.5 | W/cm2 | ||
| ILLBLU1 | Illumination power at wavelengths ≥ 410nm and ≤ 440nm(18)(19) | 1.3 | W/cm2 | ||
| LAMP ILLUMINATION | |||||
| ILLUV | Illumination power at wavelengths < 395nm(9)(19) | 2.0 | mW/cm2 | ||
| ILLVIS | Illumination power at wavelengths ≥ 395nm and ≤ 800nm(18)(19) | 23.7 | W/cm2 | ||
| ILLIR | Illumination power at wavelengths > 800nm(19) | 10 | mW/cm2 | ||
(1) All voltages are referenced to common ground VSS. VBIAS, VCC, VOFFSET, and VRESET power supplies are all required for proper DMD operation. VSS must also be connected.
(2) VOFFSET supply transients must fall within specified max voltages.
(3) To prevent excess current, the supply voltage delta |VCCI – VCC| must be less than the specified limit. See Section 8.
(4) PWRDNZ input pin resets the SCP and disables the LVDS receivers. PWRDNZ input pin overrides SCPENZ input pin and tristates the SCPDO output pin.
(5) The SCP clock is a gated clock. Duty cycle shall be 50% ± 10%. SCP parameter is related to the frequency of DCLK.
(6) See Figure 5-2.
(9) Simultaneous exposure of the DMD to the maximum Section 5.4 for temperature and UV illumination reduces device lifetime.
(10) The array temperature cannot be measured directly and must be computed analytically from the temperature measured at test point 1 (TP1) shown in Figure 6-1 and the package thermal resistance using the calculation in Section 6.4.
(11) Long-term is defined as the usable life of the device.
(12) Per Figure 5-1, the maximum operational array temperature should be derated based on the micromirror landed duty cycle that the DMD experiences in the end application. See Section 6.6 for a definition of micromirror landed duty cycle.
(13) Short-term is defined as cumulative time over the usable life of the device.
(14) The locations of thermal test points TP2, TP3, TP4, and TP5 in Figure 6-1 are intended to measure the highest window edge temperature. For most applications, the locations shown are representative of the highest window edge temperature. If a particular application causes additional points on the window edge to be at a higher temperature, test points should be added to those locations.
(15) Temperature delta is the highest difference between the ceramic test point 1 (TP1) and anywhere on the window edge as shown in Figure 6-1. The window test points TP2, TP3, TP4, and TP5 shown in Figure 6-1 are intended to result in the worst-case delta temperature. If a particular application causes another point on the window edge to result in a larger delta in temperature, that point should be used.
(16) The average over time (including storage and operating) that the device is not in the "elevated dew point temperature range."
(17) Exposure to dew point temperatures in the elevated range during storage and operation should be limited to less than a total cumulative time of CTELR.
(18) The maximum allowable optical power incident on the DMD is limited by the maximum optical power density for each wavelength range specified and the micromirror array temperature (TARRAY).
(19) To calculate see Section 6.5.
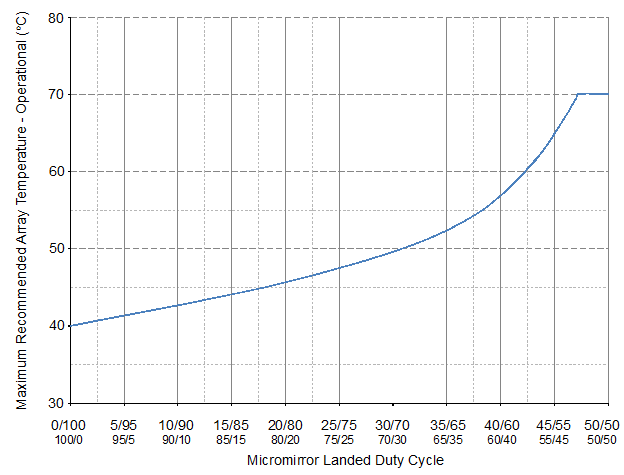 Figure 5-1 Maximum Recommended DMD Temperature—Derating Curve
Figure 5-1 Maximum Recommended DMD Temperature—Derating Curve