SLUSAM9E July 2011 – April 2020
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (Continued)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 Electrical Characteristics: Supply Current
- 7.6 Internal Power Control (Startup and Shutdown)
- 7.7 3.3-V Voltage Regulator
- 7.8 Voltage Reference
- 7.9 Cell Voltage Amplifier
- 7.10 Current Sense Amplifier
- 7.11 Overcurrent Comparator
- 7.12 Internal Temperature Measurement
- 7.13 Cell Balancing and Open Cell Detection
- 7.14 I2C Compatible Interface
- 7.15 Typical Characteristics
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3 Feature Description
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Programming
- 8.6 Register Maps
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.5.1.3 Bus Read Command from BQ76925 Device
The Host reads from the registers of the BQ76925 device as shown in Figure 14. This protocol is similar to the write protocol, except that the slave now drives data back to the Host. The BQ76925 device acknowledges each received byte by pulling the SDA line low during the acknowledge period. When the BQ76925 device sends data back to the Host, the Host drives the acknowledge.
The Host may optionally request a CRC byte following the Data byte as shown. The CRC for read commands is always enabled, but not required. If the CRC is not used, then the Host simply NACK’s the Data byte and then generates the Stop condition.
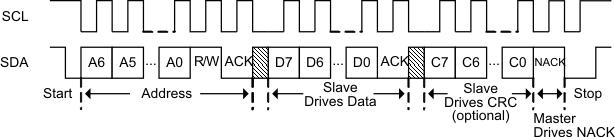 Figure 14. I2C Read Command
Figure 14. I2C Read Command